
The palm

OBJECTIVES
…
To Describe the carpal tunnel & surrounding
structures
To define the layers of the palm
To study the muscles of the hand & their action
& nerve supply
To identify palmar arterial arches
To list the nerves which supply the hand
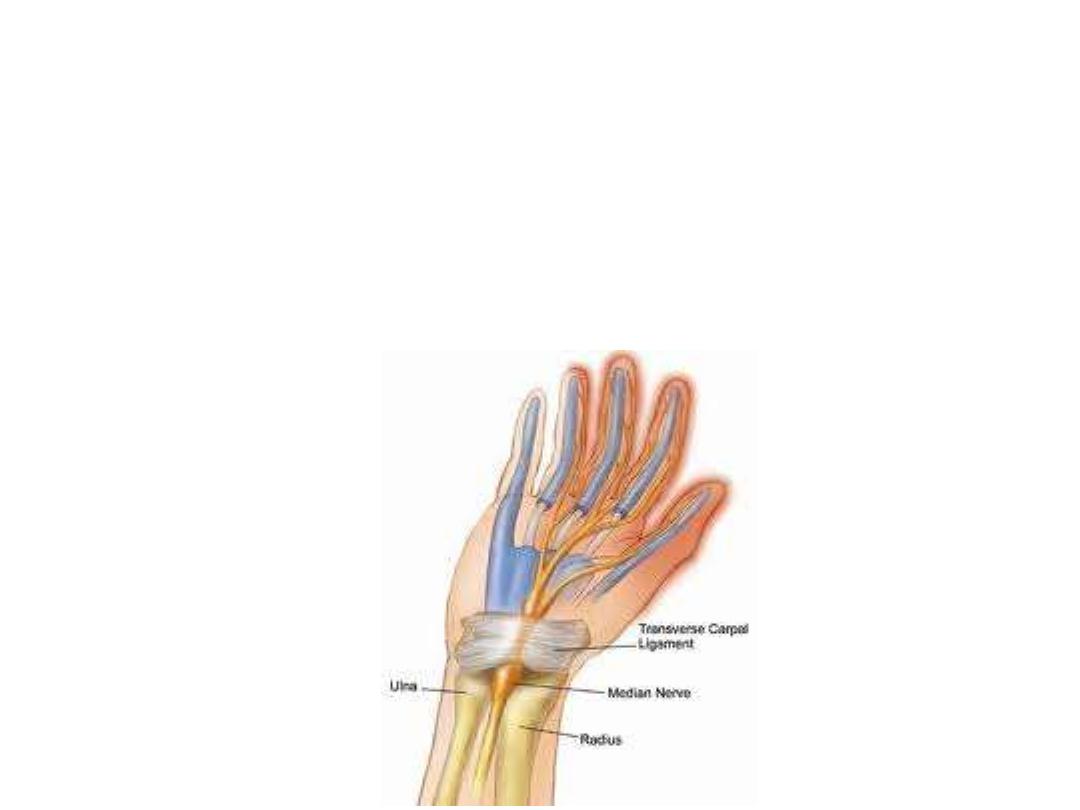
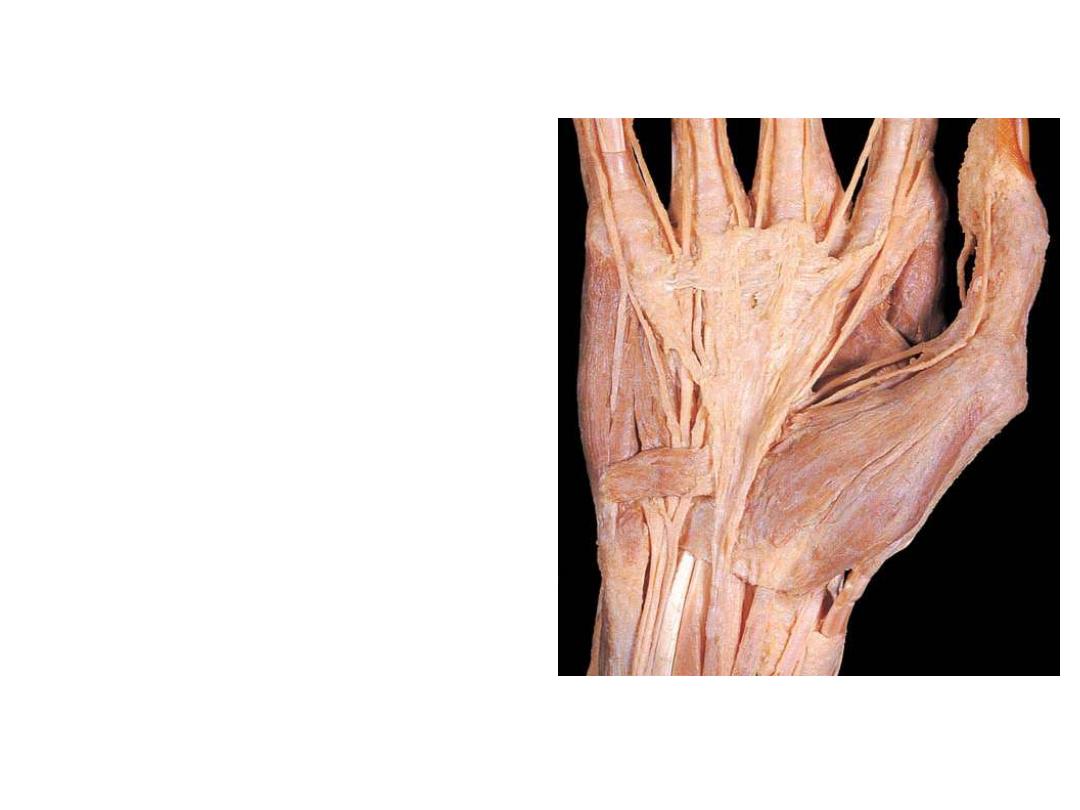
Carpal tunnel and structures at the wrist:
Flexor retinaculum:
- Is a thick connective tissue ligament that bridges the space between the
medial and lateral sides of carpus & converts the carpal arch into the carpal
tunnel.
-FR is attached medially to the pisiform and the hook of the hamate & laterally
to the tubercles of the scaphoid and trapezium
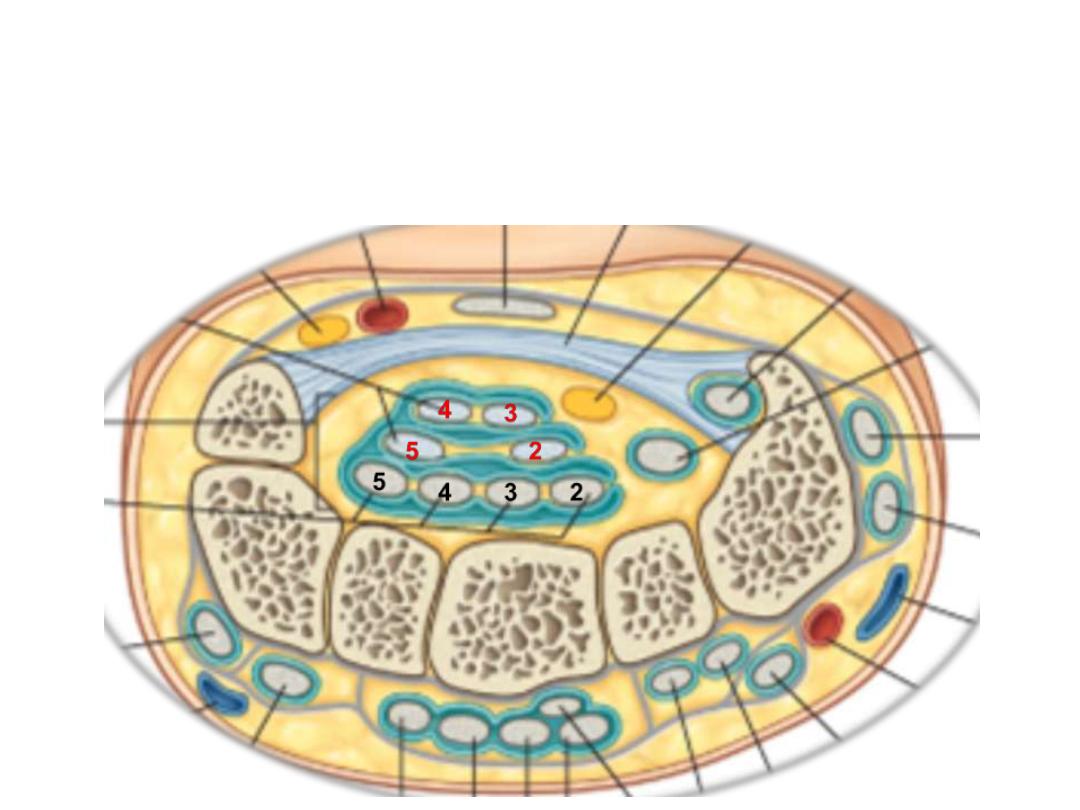
Structures passing in relation to FR:
-Tendons of FDS, FDP, FPL & median nerve pass through this tunnel
-FR holds the tendons & prevents bowing
-The median nerve is anterior to the tendons in the carpal tunnel.
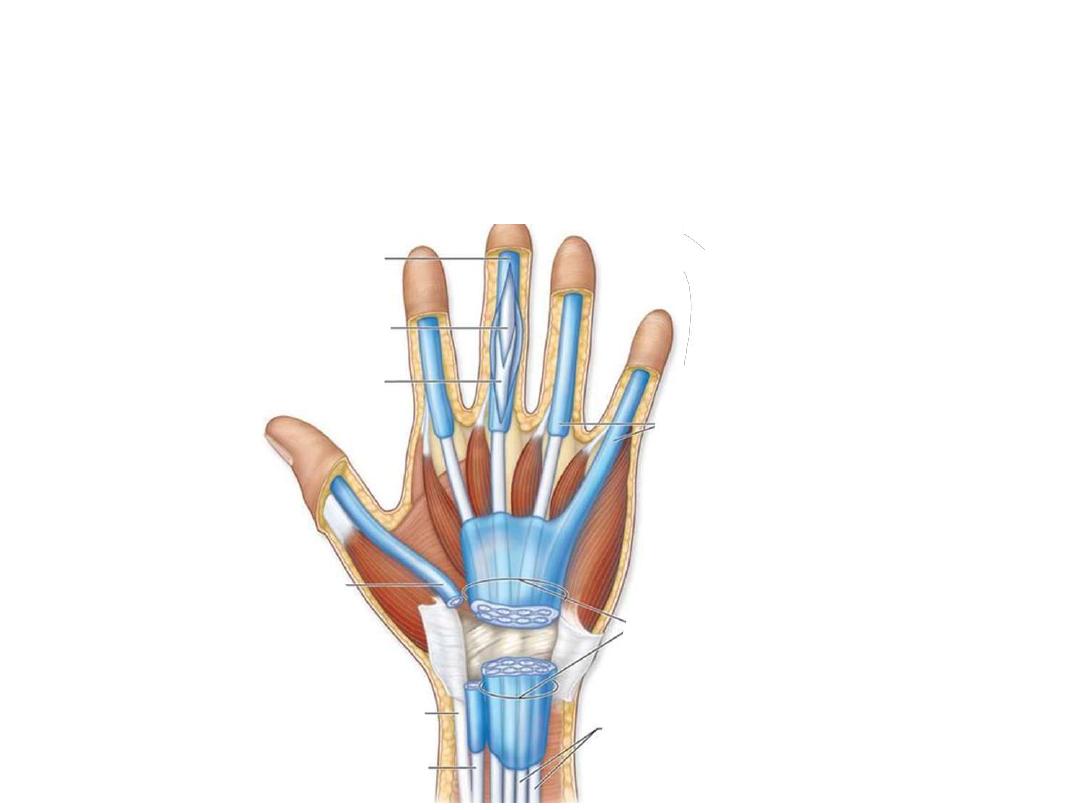
-Free movement of the tendons in the carpal tunnel is facilitated by
synovial
sheaths
, which surround the tendons.
-All the tendons of the FDS & FDP are surrounded by a single synovial sheath
-A separate sheath surrounds the tendon of the FPL
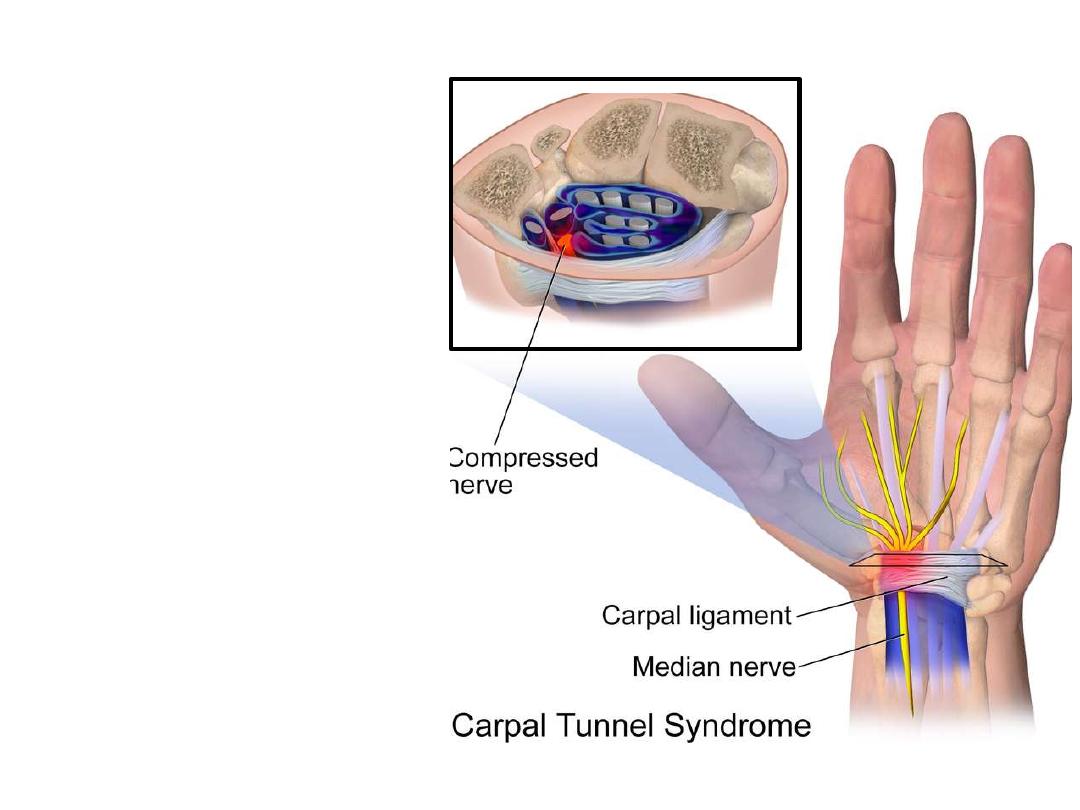
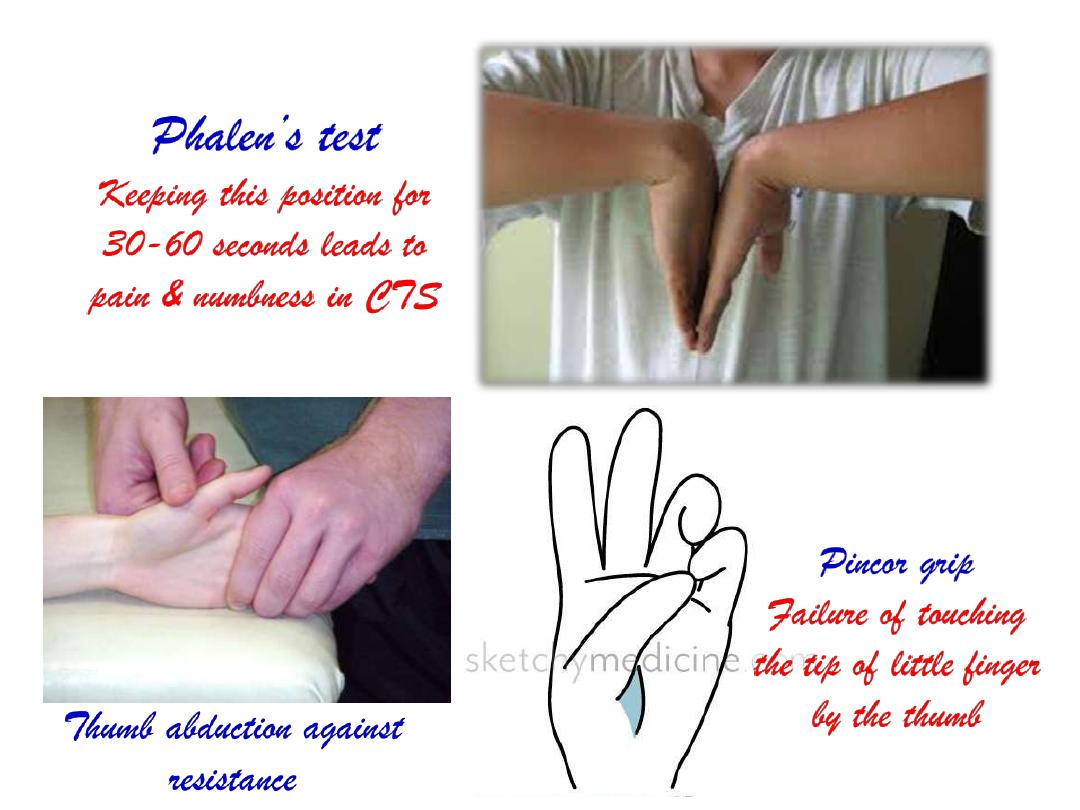
The Carpal tunnel syndrome:
-Compression of the median
nerve as it travels through the
wrist at the carpal tunnel.
- The main symptoms are pain
& numbness in the lateral 3
½
fingers.
- Weak
grip
strength
may
occur and after a long period
of time the muscles at the base
of the thumb may waste away
-Sensation of thenar skin is
maintained?
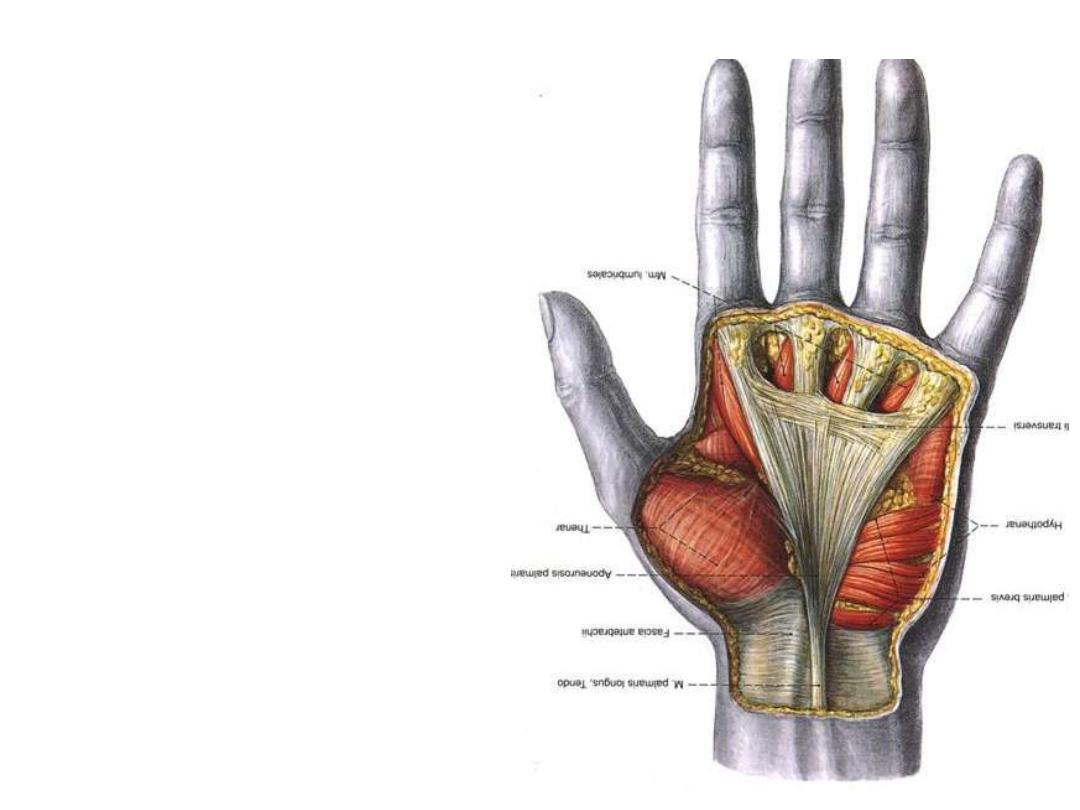
Palmar aponeurosis:
-A triangular-shaped condensation of
deep fascia that covers the palm and
is anchored to the skin
-The
apex
of
the
triangle
is
continuous with the palmaris longus
tendon, fibers radiate to extensions
at the base of the digits
-The four longitudinal digital bands
are attach distally to the bases of the
proximal phalanges and become
continuous with the fibrous digital
sheaths
Functions of palmar aponeurosis:
1- Anchoring skin, eases the grip
2- Protection of deeper structures
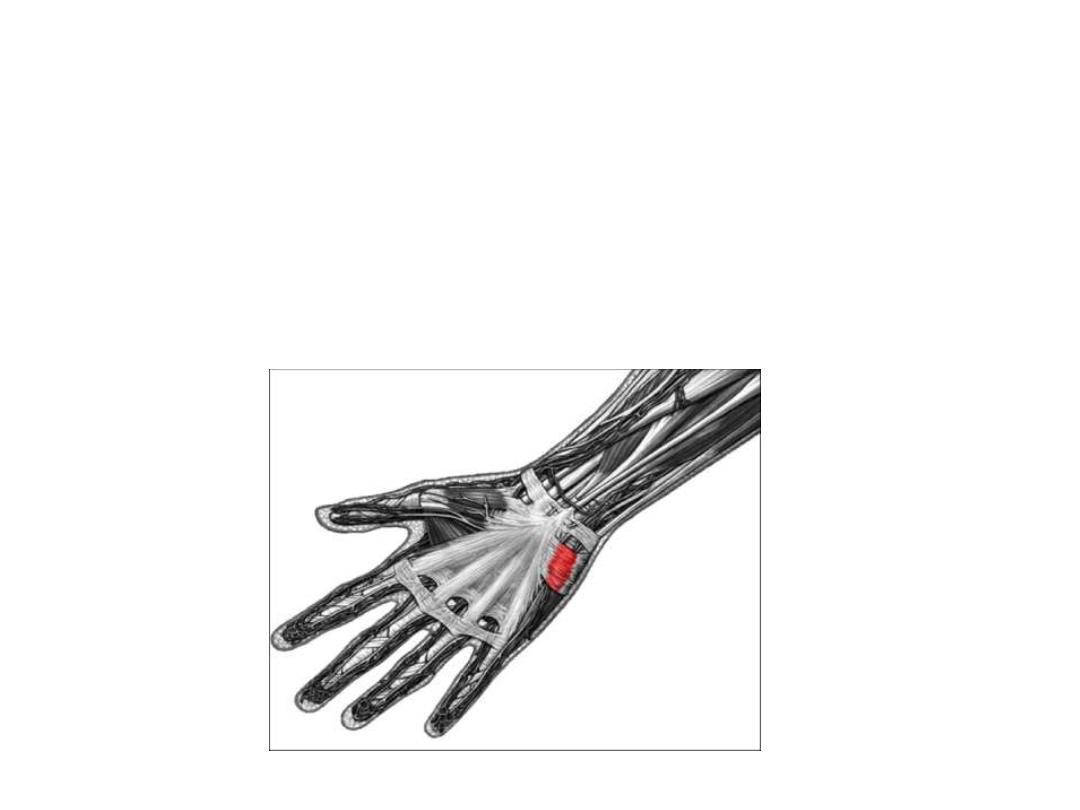
Palmaris brevis:
Origin; palmar aponeurosis
Insertion; skin on the medial margin of the hand.
Innervation; superficial branch of the ulnar nerve.
Action; Deepens the hollow of the palm
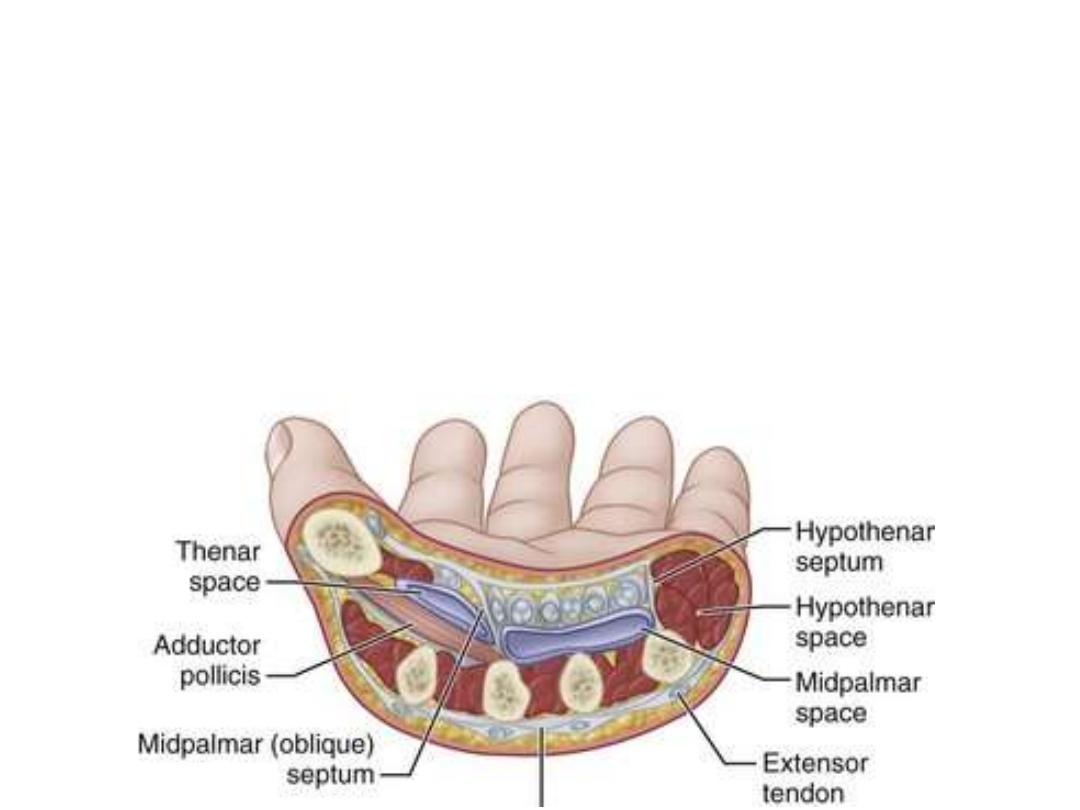
Palmar fascial spaces:
• A medial fibrous septum extends deeply from the medial border of the PA to the 5th
metacarpal
• Lateral fibrous septum extends similarly to the 3rd metacarpal.
• These septa divide the palm into 3 fascial compartments:
1- Thenar space
containig thenar muscles
2- Hypothenar space
containing hypothenar muscles
3- Midpalmar space
located underneath the PA containing the flexor tendons, the
lumbricals with the digital vessels and nerves.
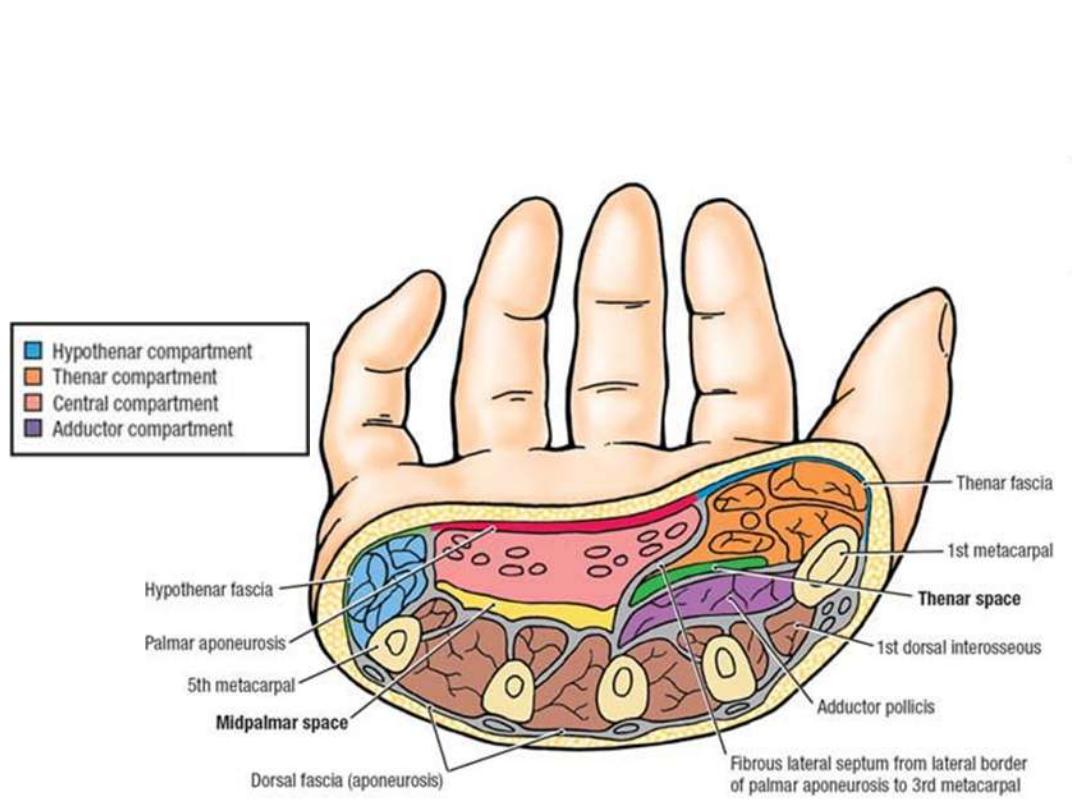
• Most fascial compartments end at the MP joints where they become
continuous with lumbrical canals
• The midpalmar space is continuous with the anterior compartment of the
forearm via the carpal tunnel
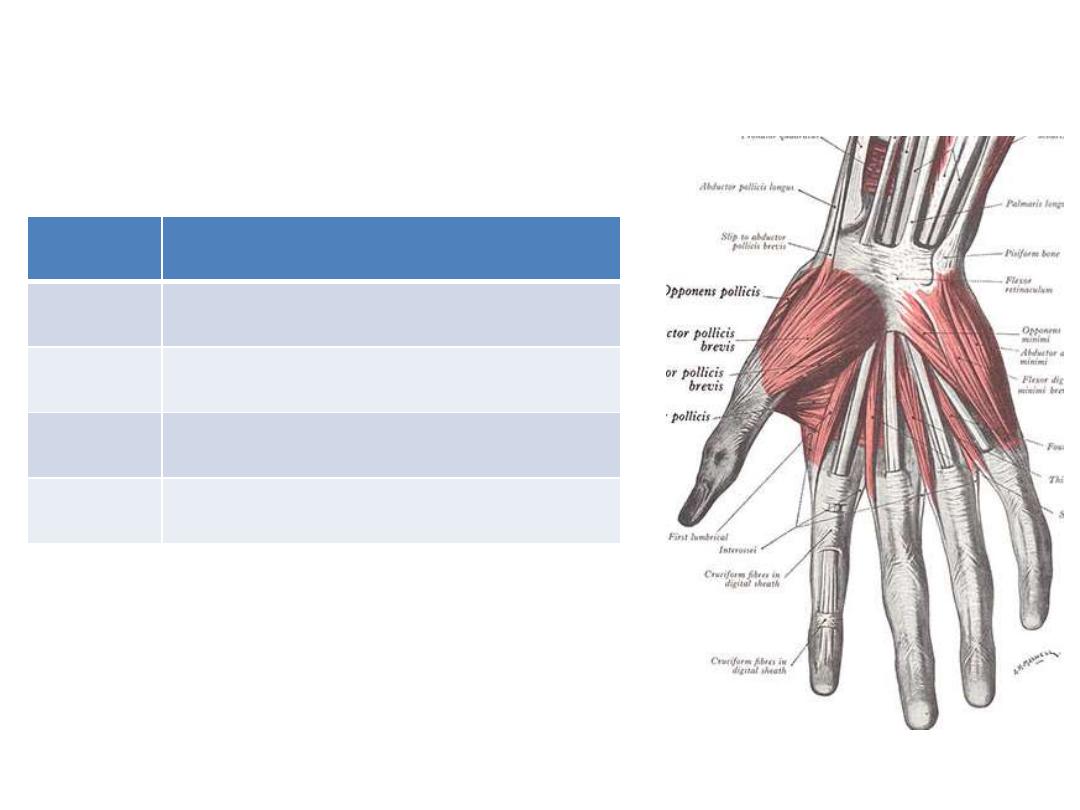
Hand muscles:
-Intrinsic muscles execute precision
movements ('precision grip') with the
fingers and thumb.
-All intrinsic muscles of the hand are
innervated by the deep branch of the
ulnar nerve except for the three thenar
and two lateral lumbrical muscles,
innervated by the median nerve.
-Spinal cord segment T1 with a
contribution
from
C8
are
the
segments responsible for their supply
Layers… !!
Contents
Layer
Thenar & hypothenar muscles
I
Long flexors & lumbricals
II
Adductor pollicis
III
Interossei
IV
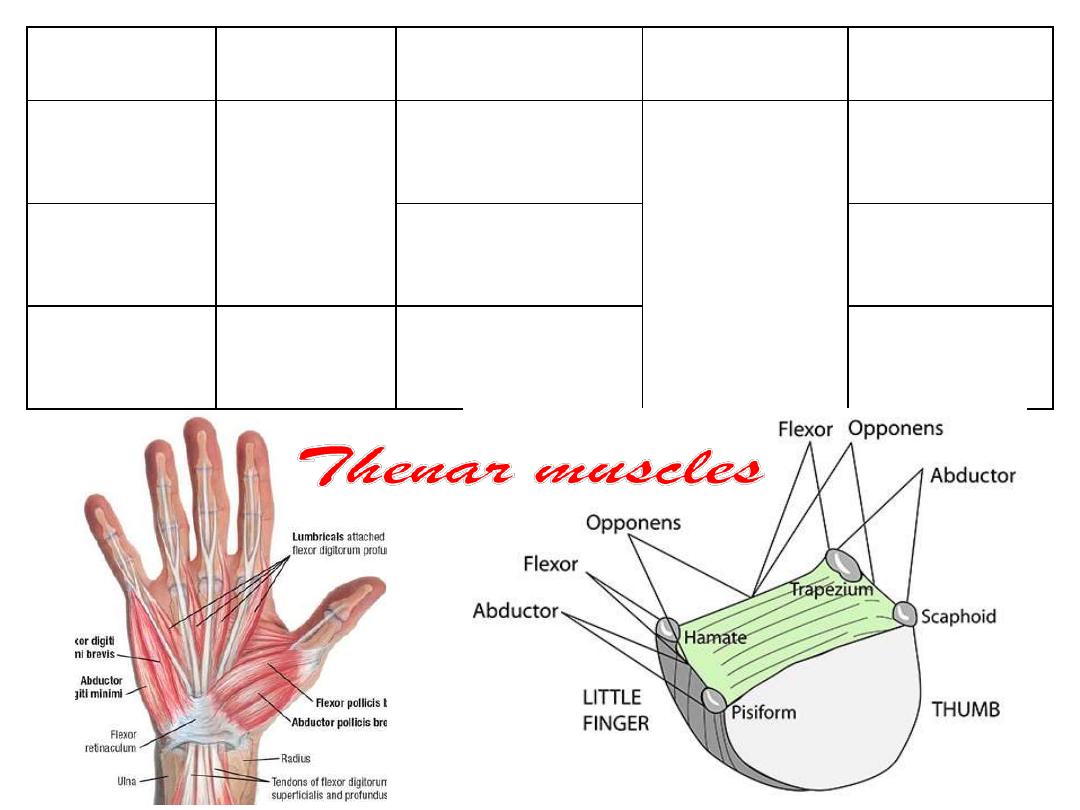
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Nerve
Action
Opponens
pollicis
Trapezium
FR
1
st
metacarpal
Recurrent
branch of
median n.
Medially
rotates thumb
Flexor pollicis
brevis
Proximal phalanx
Flexes the
thumb at MPJ
Abductor
pollicis brevis
Scaphoid
FR
Extensor hood
Abducts the
thumb at MPJ
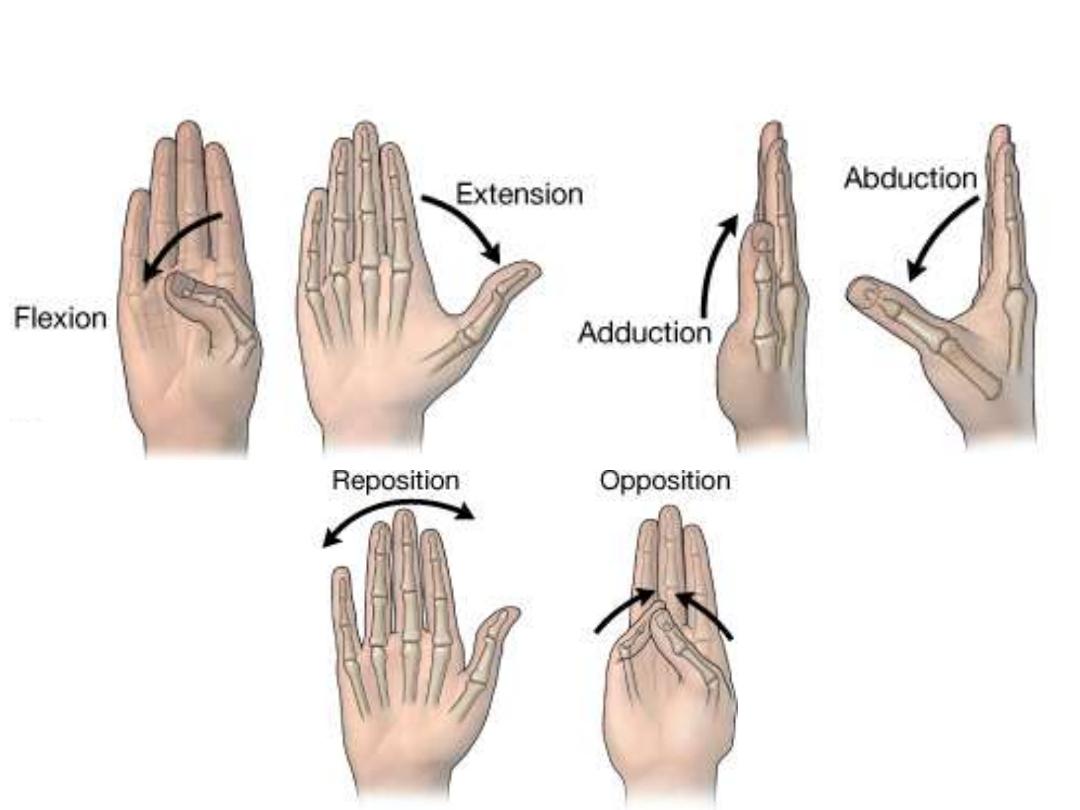
Thumb movements
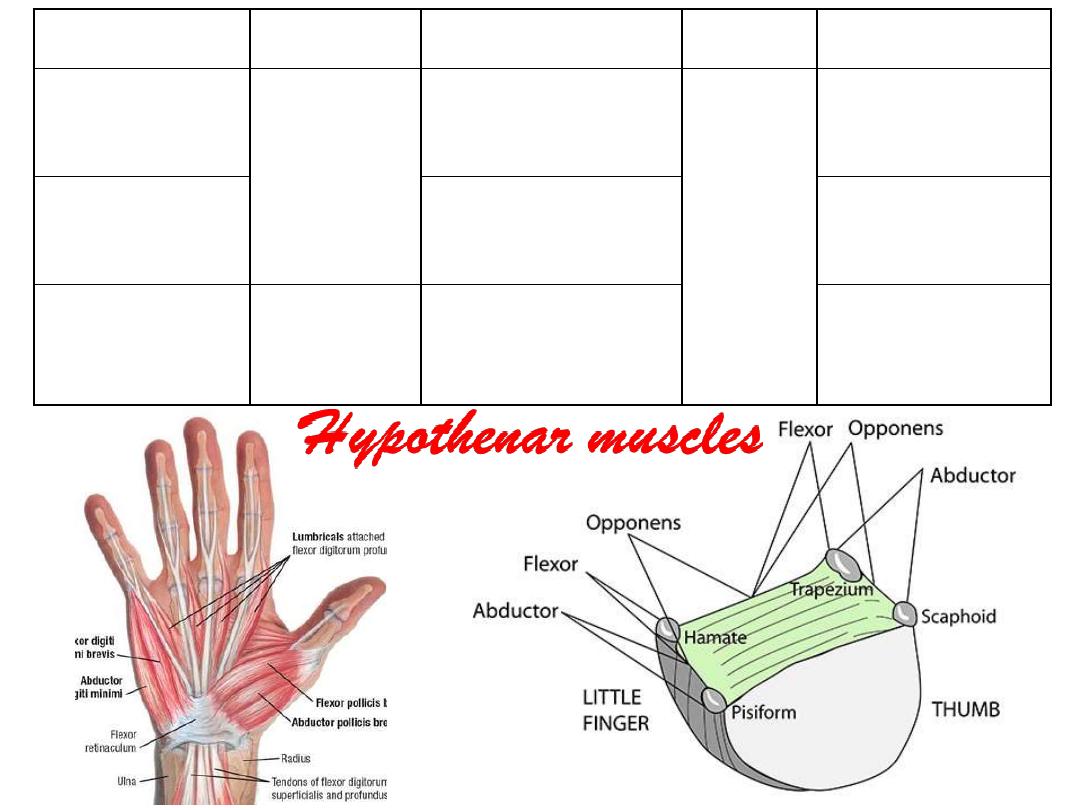
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Nerve
Action
Opponens
digiti minimi
Hamate
FR
Medial aspect of
metacarpal V
Deep
branch
of ulnar
n.
Laterally rotates
metacarpal V
Flexor digiti
minimi brevis
Medial side of
proximal phalanx
Flexes LF at
MPJ
Abductor digiti
minimi
Pisiform
FR
Lateral side of
proximal phalanx
Abducts LF at
MPJ
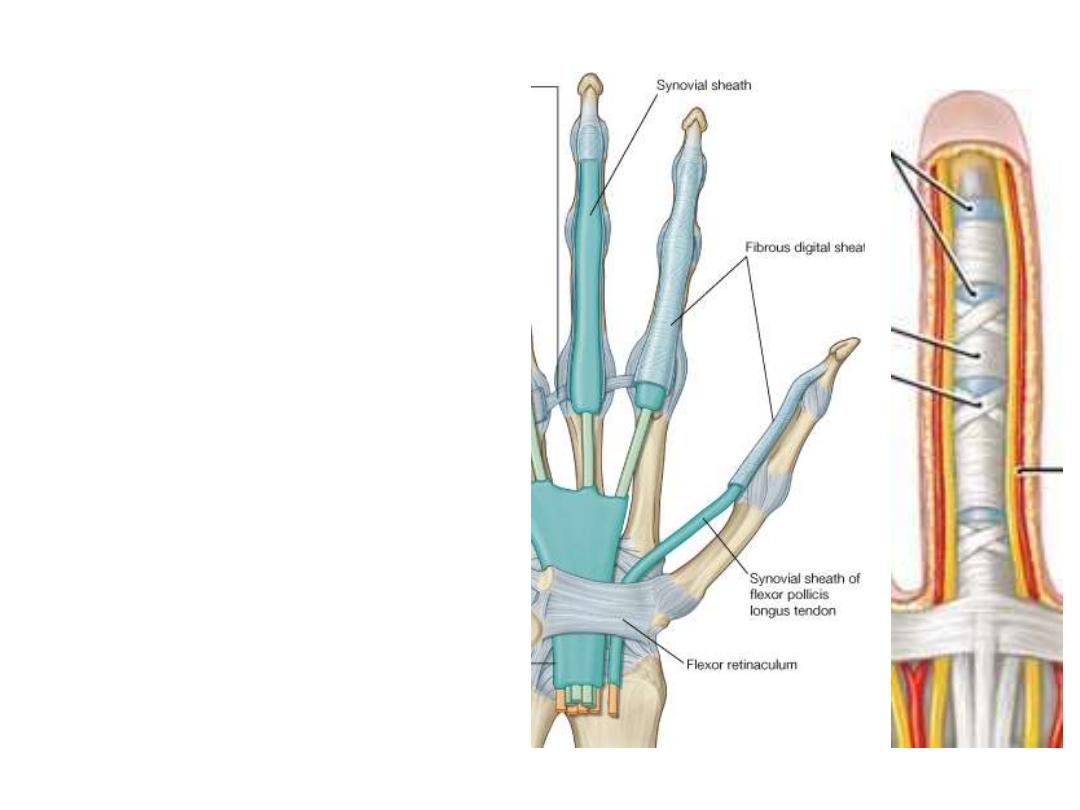
Fibrous digital sheaths:
-These are ligamentous tunnels that
enclose long flexor tendons as they
enter the receptive fingers
-They begin anterior to the MCPJ &
extend to the distal phalanges
-Formed by fibrous arches attached
posteriorly to the phalanges
-Prevent the tendons from bowing
when the digits are flexed.
-Within each tunnel, the tendons are
surrounded by a synovial sheath
-Fibrous sheaths are weak at the site
of IPJ
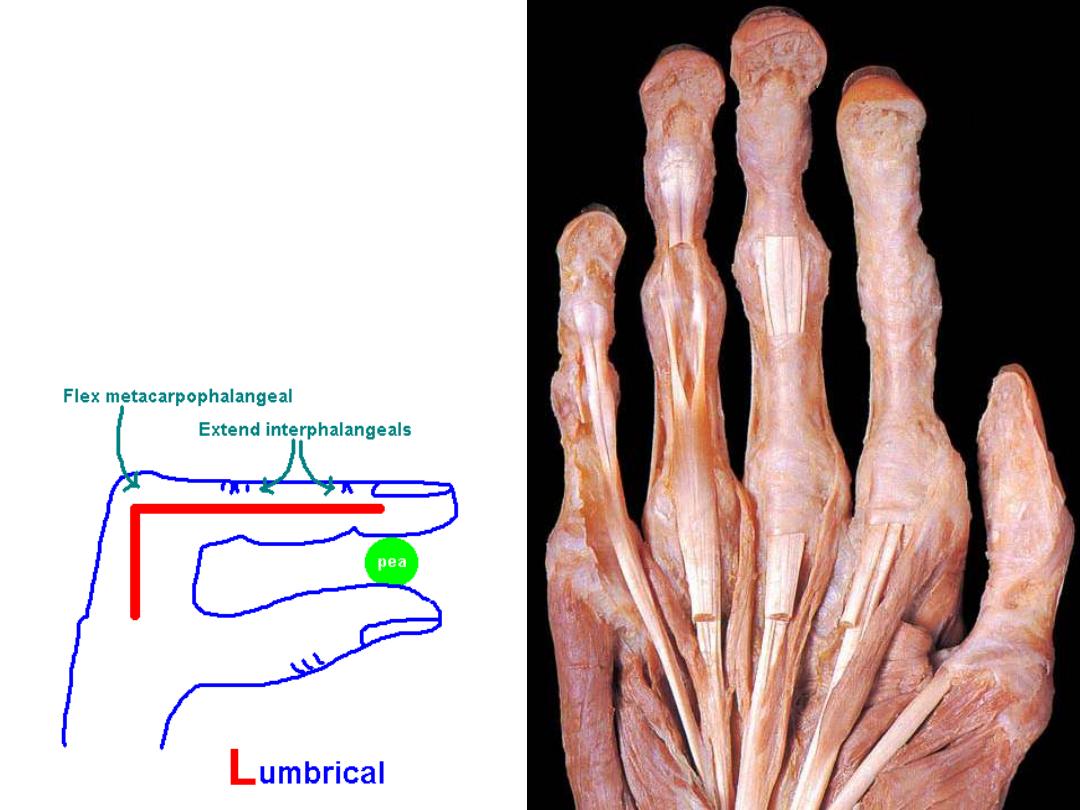
The lumbricals (4 muscles):
Origin;
Lateral aspect of tendons of FDP
Insertion;
Extensor hoods of medial 4
fingers
Nerve;
like mother tendons
Action:
-Flexion MPJ (direct action)
-Extension IPJ (via the extensor hoods)
1
2
3
4
Adductor pollicis:
Origin;
Oblique
head;
capitate
&
metacarpals 2 & 3 (base)
Straight head; metacarpal 3 (shaft)
Insertion
; Proximal phalanx thumb
(medial aspect)
Nerve
; deep branch ulnar n.
Action
: thumb adduction
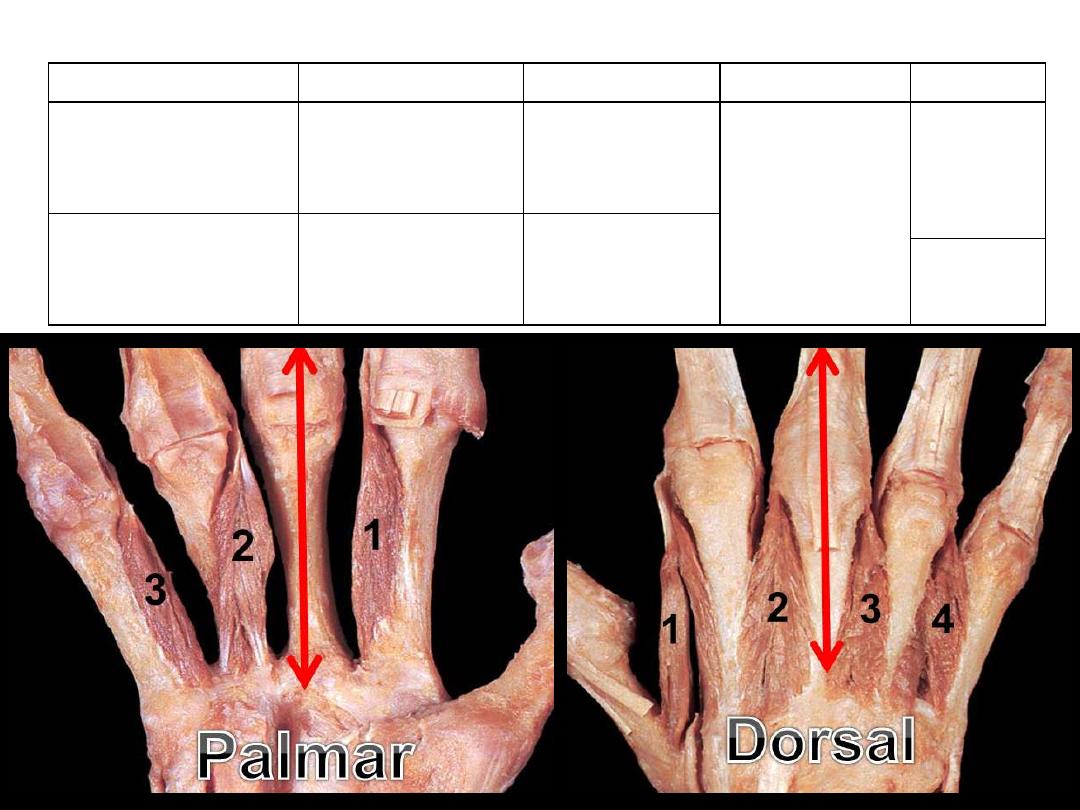
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Nerve
Action
Dorsal interossei
(4)
Adjacent sides
of metacarpals
(2 heads)
Extensor hood
2,3 & 4
Deep branch
of ulnar nerve
DAB
Palmar interossei
(3)
Sides of
metacarpals
(single head)
Extensor
hoods 2,4 & 5
PAD
The interossei:
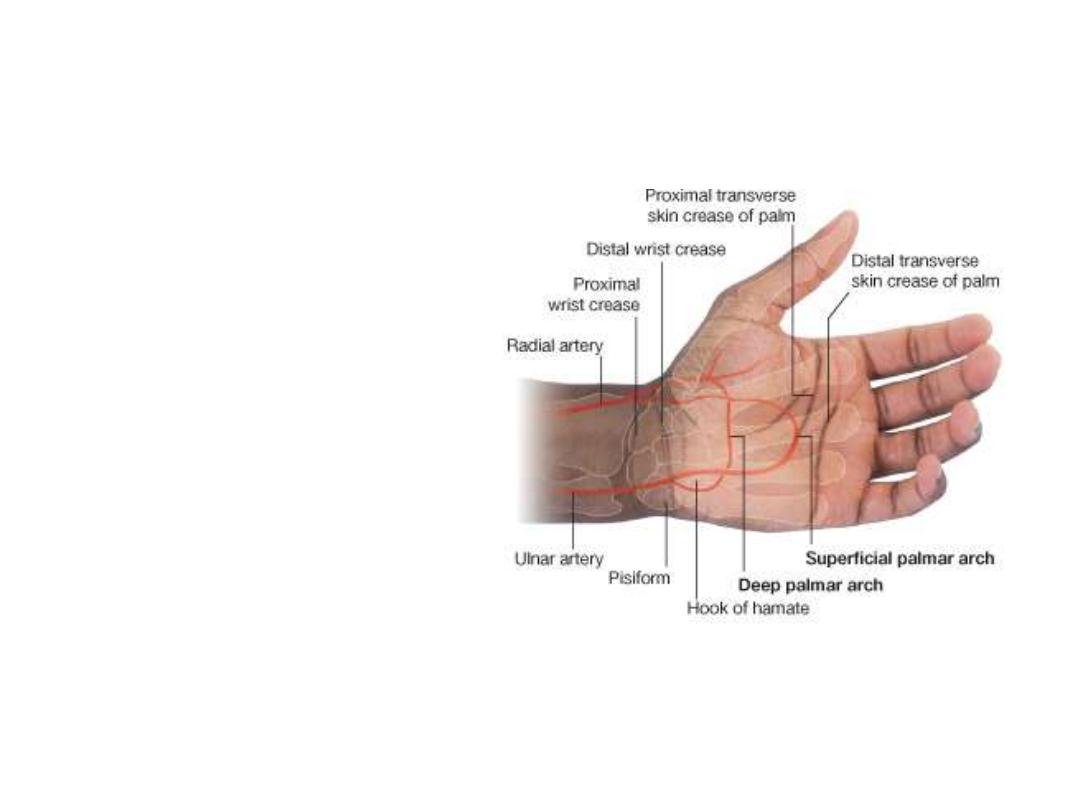
Arteries of the hand:
• Superficial (mainly ulnar) &
deep (mainly radial) palmar
arches form at the proximal
& distal borders of a
stretched thumb
• From these arches blood is
distributed to the fingers &
dorsum of the hand
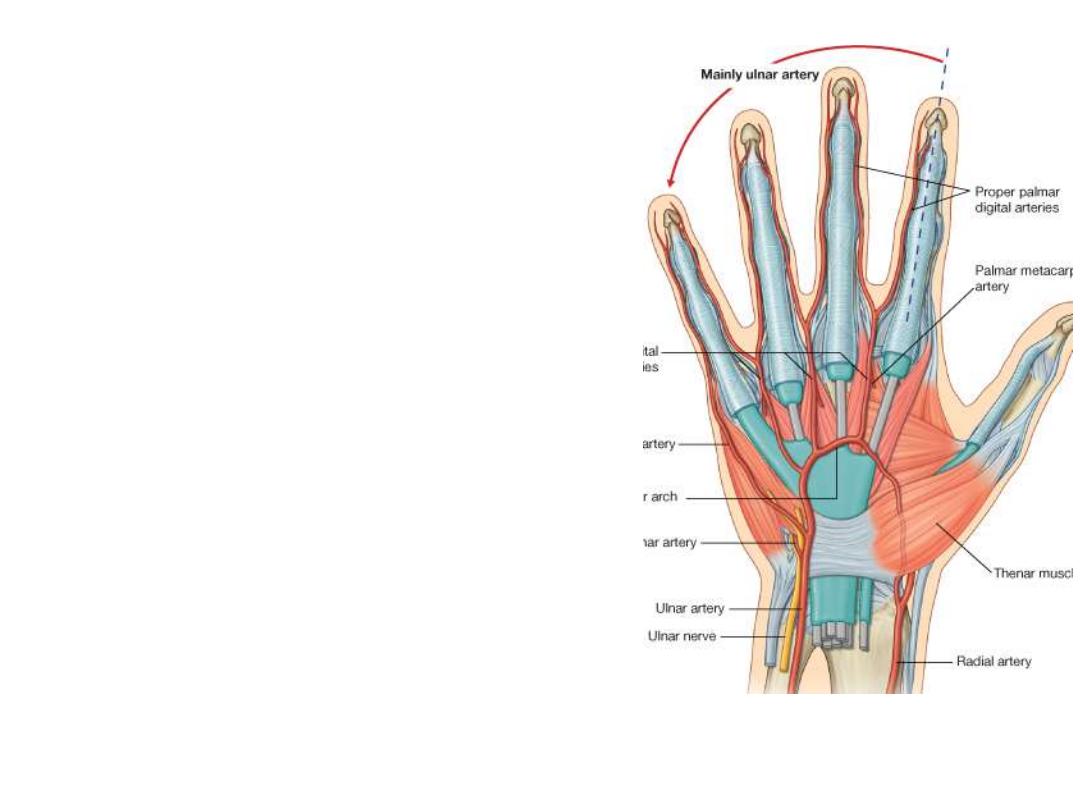
Superficial palmar arch:
Formation:
Ulnar a. + palmar branch of radial a.
Location:
Superficial to long flexor tendons
Branches:
1-
1
palmar digital branch to the little finger
2-
3
common palmar digital branches to the medial
three webs, each of the three will divide into
2
proper
palmar digital branches to adjacent fingers
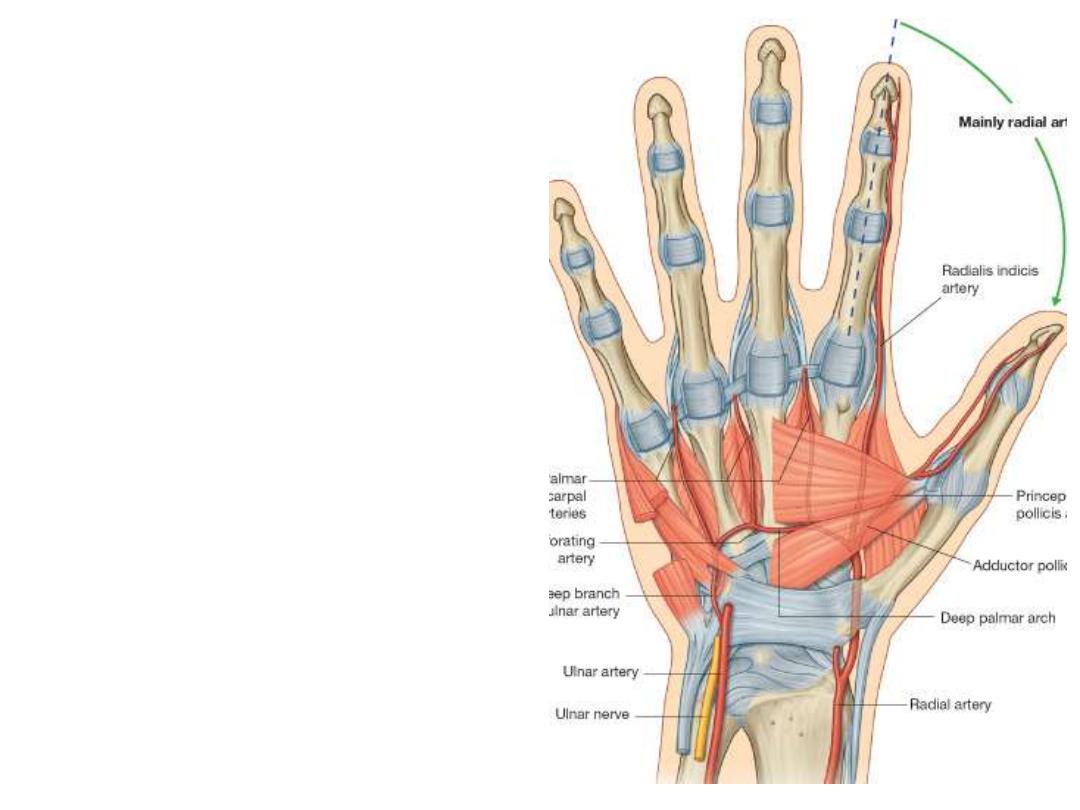
Radial artery in the hand:
- After passing in the floor of the
snuffbox, radial artery enters the
palm between the 2 heads of the
1
st
dorsal interosseous muscle
- It
gives
2
branches
before
continuing
on
the
adductor
pollicis muscle as the deep
palmar arch with the deep branch
of ulnar artery
- Branches:
1- Radialis indicis: radial border of
index
2- Princeps pollicis: to the thumb
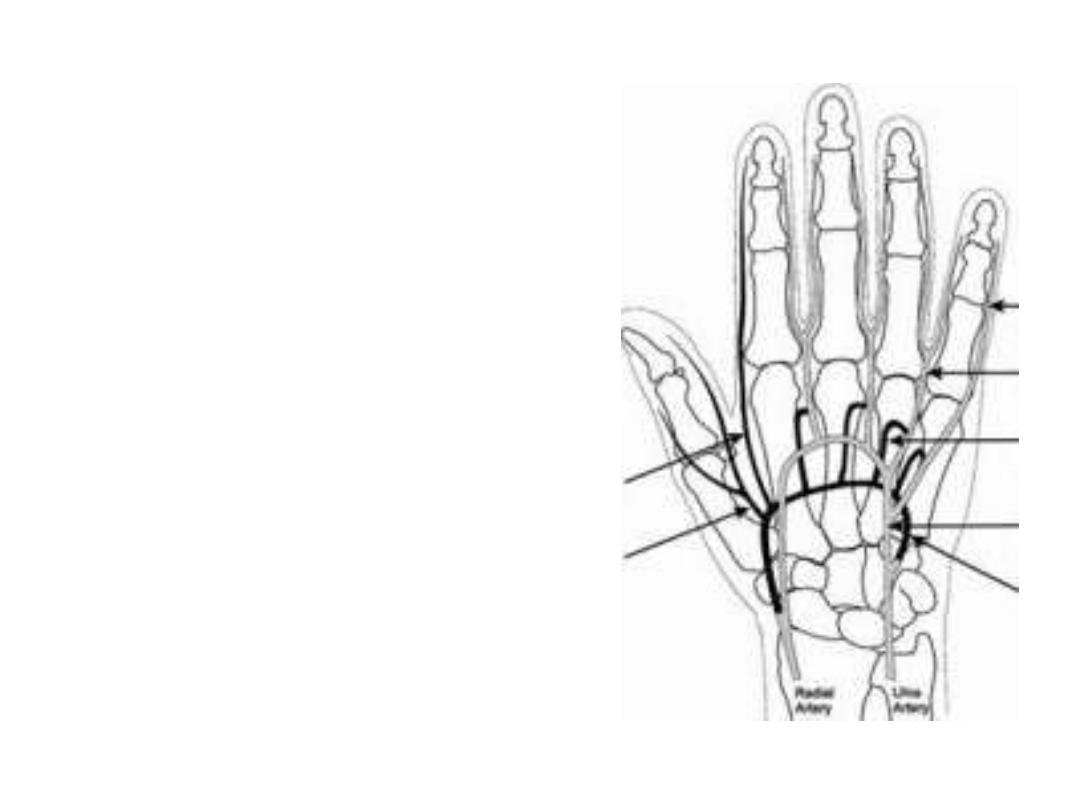
Deep palmar arch:
Formation:
Radial a. + deep branch of ulnar a.
Location:
Deep to long flexor tendons
Branches:
1-
3
palmar metacarpal branches
which join the three common palmar
digital branches of the superficial arch
2- Perforating branches anastomose
with dorsal metacarpal arteries
3-
Ascending
branches
to
the
anastomosis around the wrist
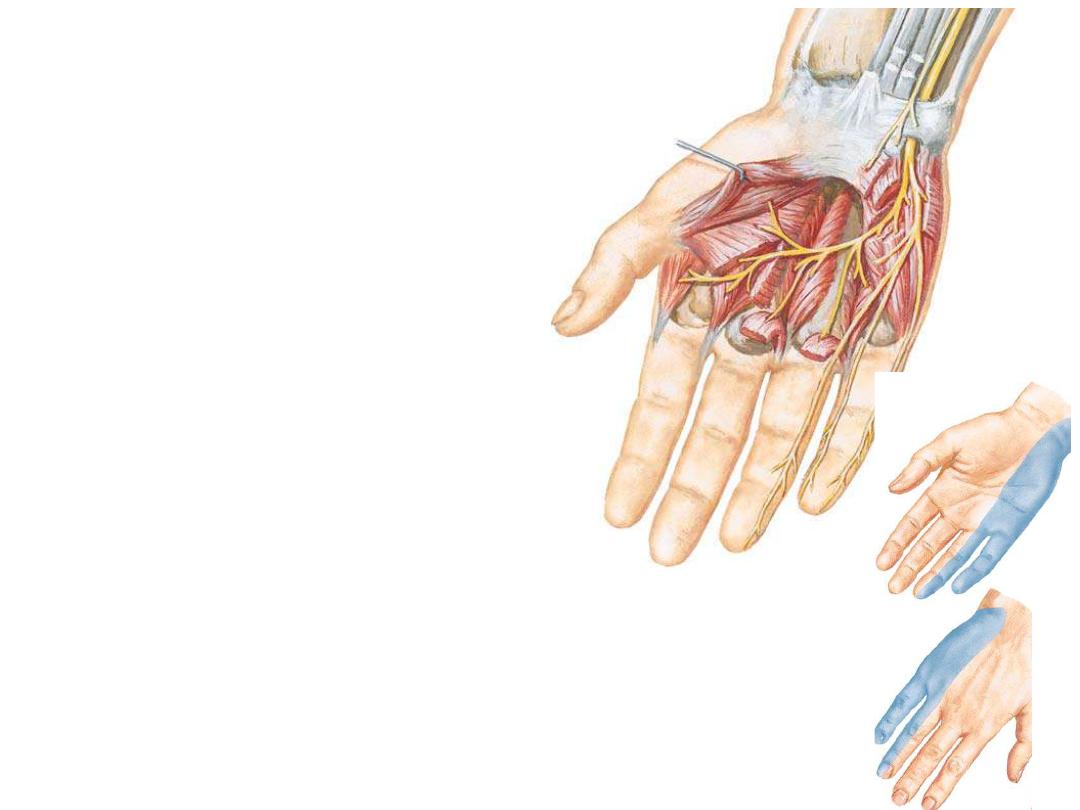
Nerves of the hand:
Ulnar nerve:
-Before reaching the hand it gives a
dorsal cutaneous branch to the medial
skin of the dorsum & medial 1 &
½
fingers
-Enters the hand lateral to the pisiform
& divides into:
1- Superficial branch;
for palmaris
brevis & skin of medial 1
1/2
fingers
(palmar aspect)
2-
Deep
branch;
passes
in
the
concavity
of
deep
arterial
arch,
supplies hand muscles except the
thenar & lumbricals 1 & 2
Median nerve:
After leaving the carpal tunnel, median nerve enters the hand & gives:
1- The recurrent branch;
given near the distal margin of the flexor retinaculum,
it curves around the margin of the retinaculum enters the thenar muscles
2- Three palmar digital nerves;
for the palmar aspect of lateral 31/2 fingers +
dorsal skin of nailbed
* Palmar branch of median nerve which supplies the skin covering the thenar
muscles is given before the nerve enters the CT so it is not affected by CTS
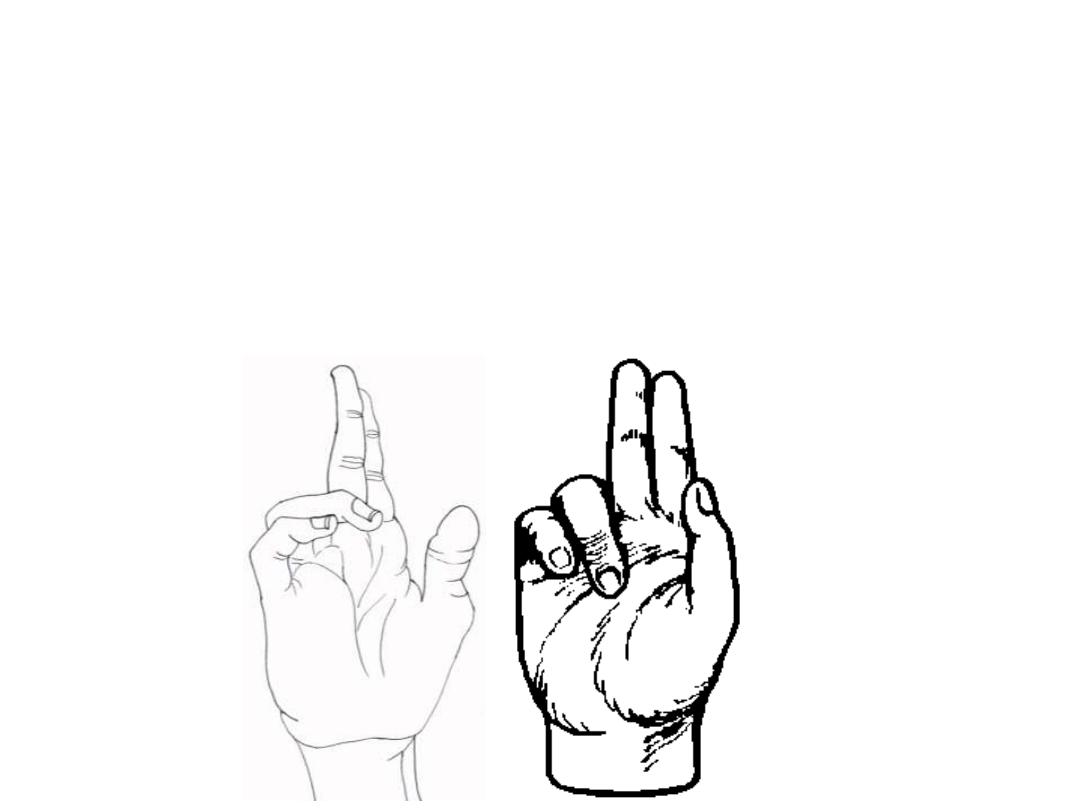

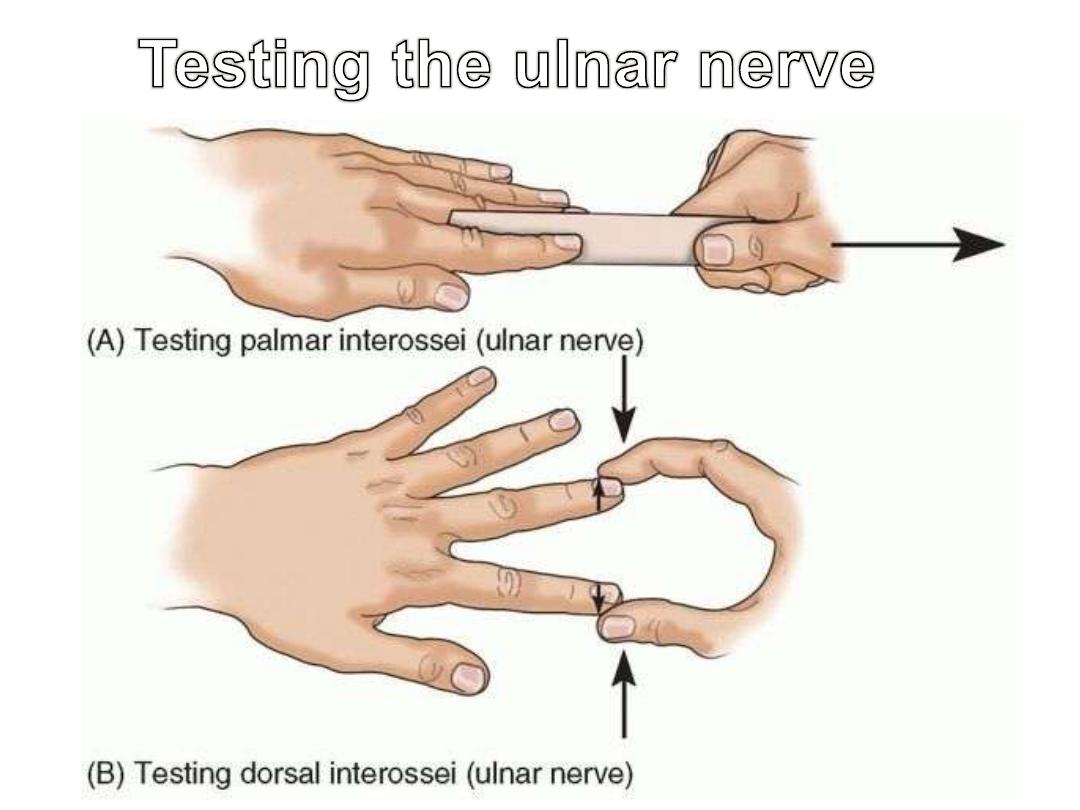
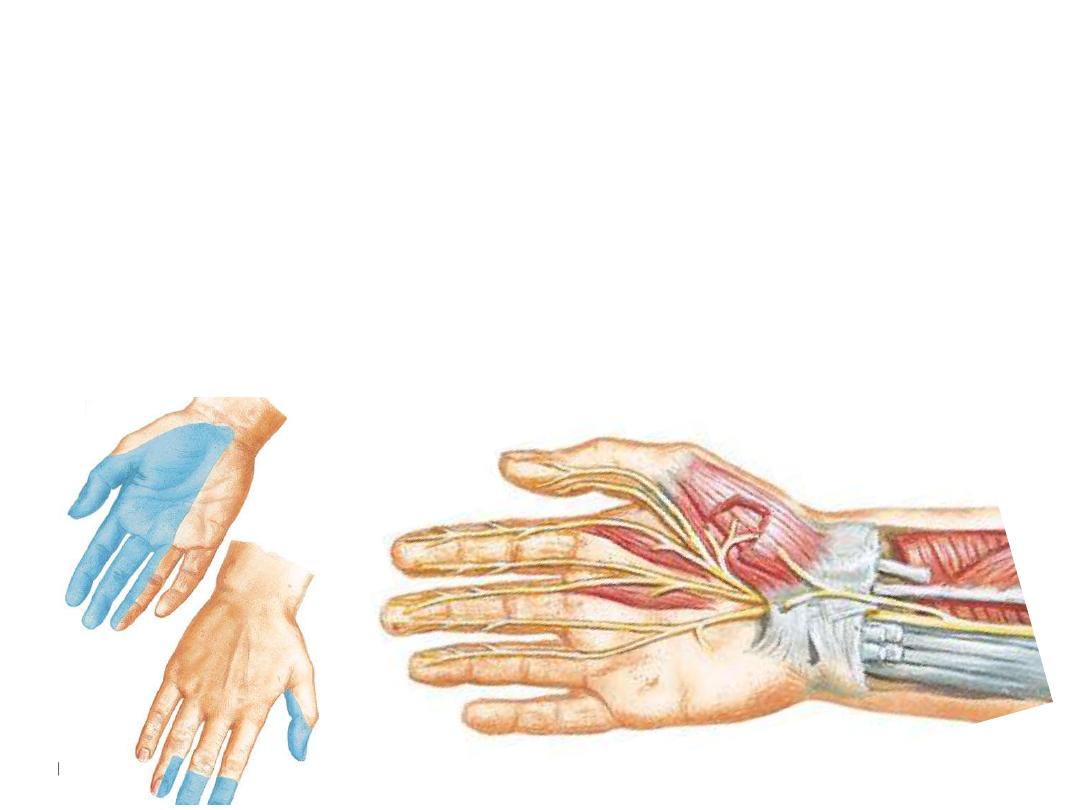
Claw hand (Ulnar nerve paralysis)
-
Paralysed lumbricals 4 & 5
-
Loss of flexion of MCPJ & extension of IPJ
-
Extension of MCPJ & flexion of IPJ
Benediction hand (Median nerve paralysis)
-
Paralysed long flexors except tendons 4 & 5 of FDP
-
Flexion of fingers 4 & 5 & failure of flexion in fingers 2 & 3
-
This happens only when the patient is asked to flex his fingers
Claw
Benediction
