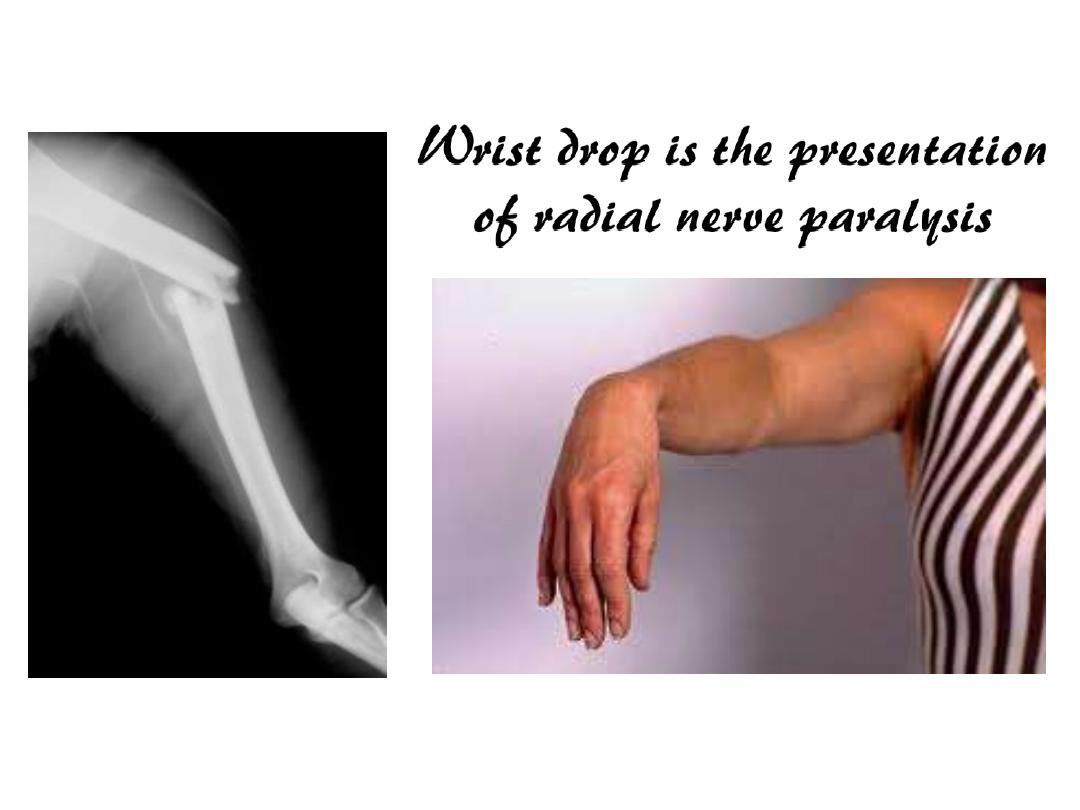
The forearm
(Extensor compartment)
Dorsum of the hand

OBJECTIVES
…
To list muscles of the posterior compartment of the
forearm
To describe the course of the posterior interosseous
artery
To follow the radial nerve & its branches
To describe dorsum of the hand
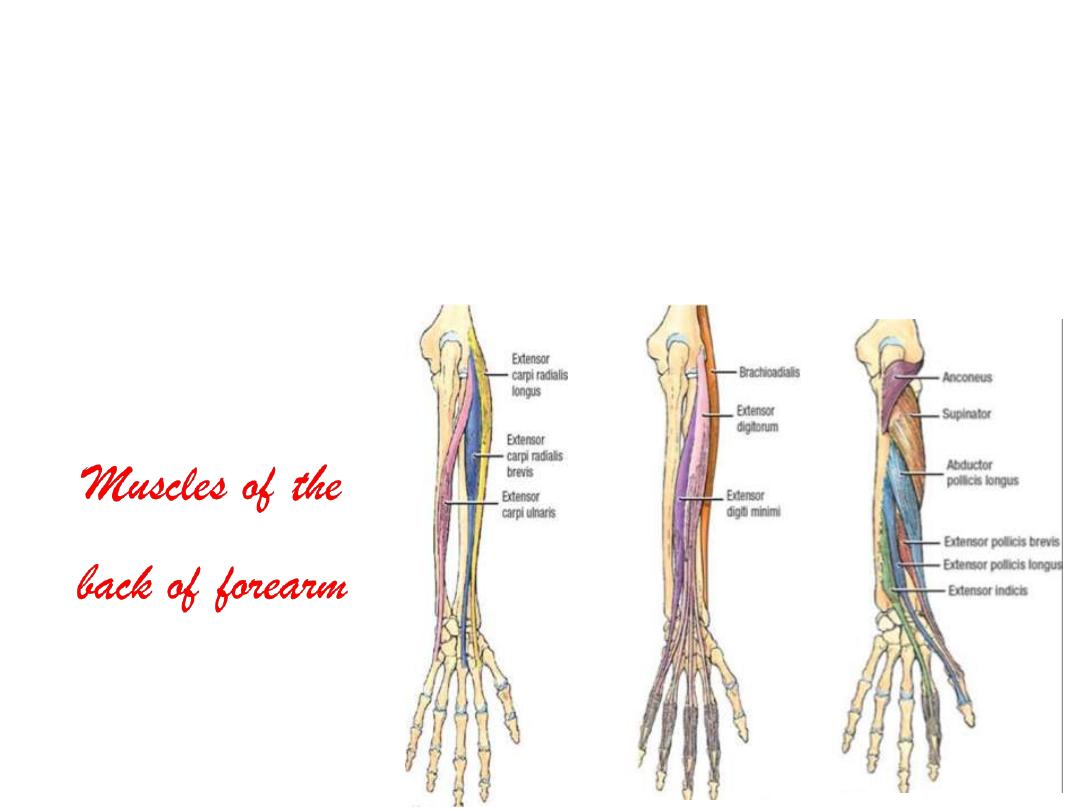
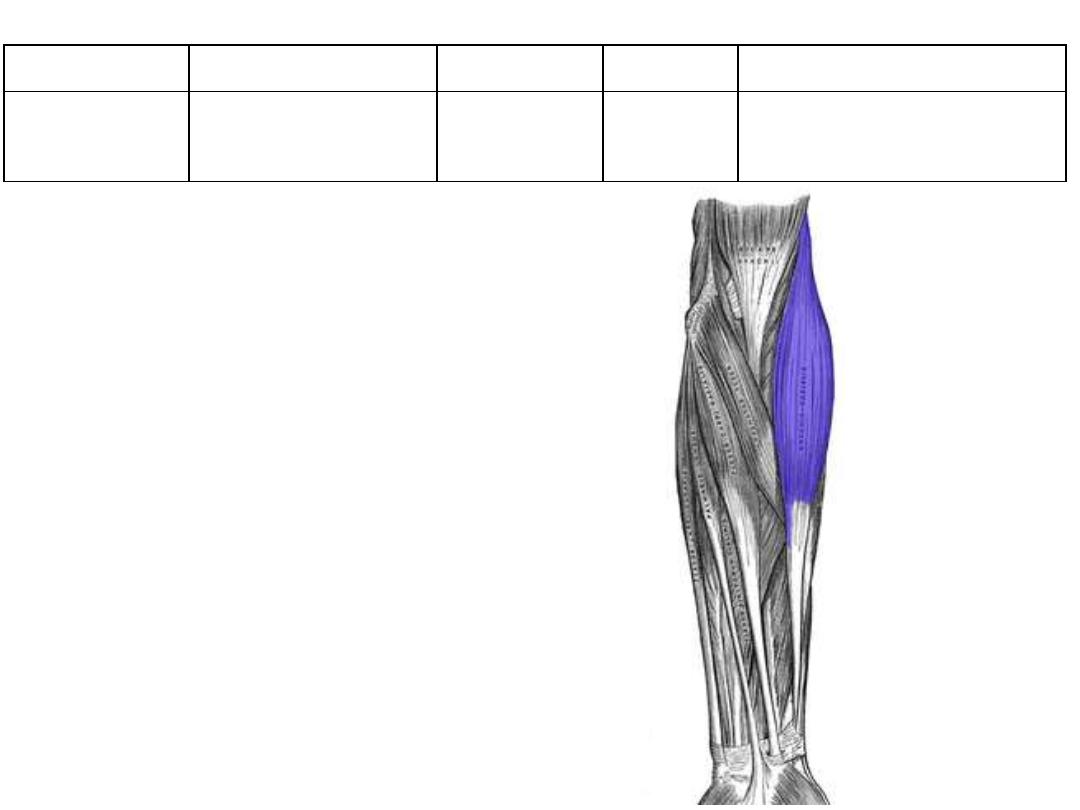
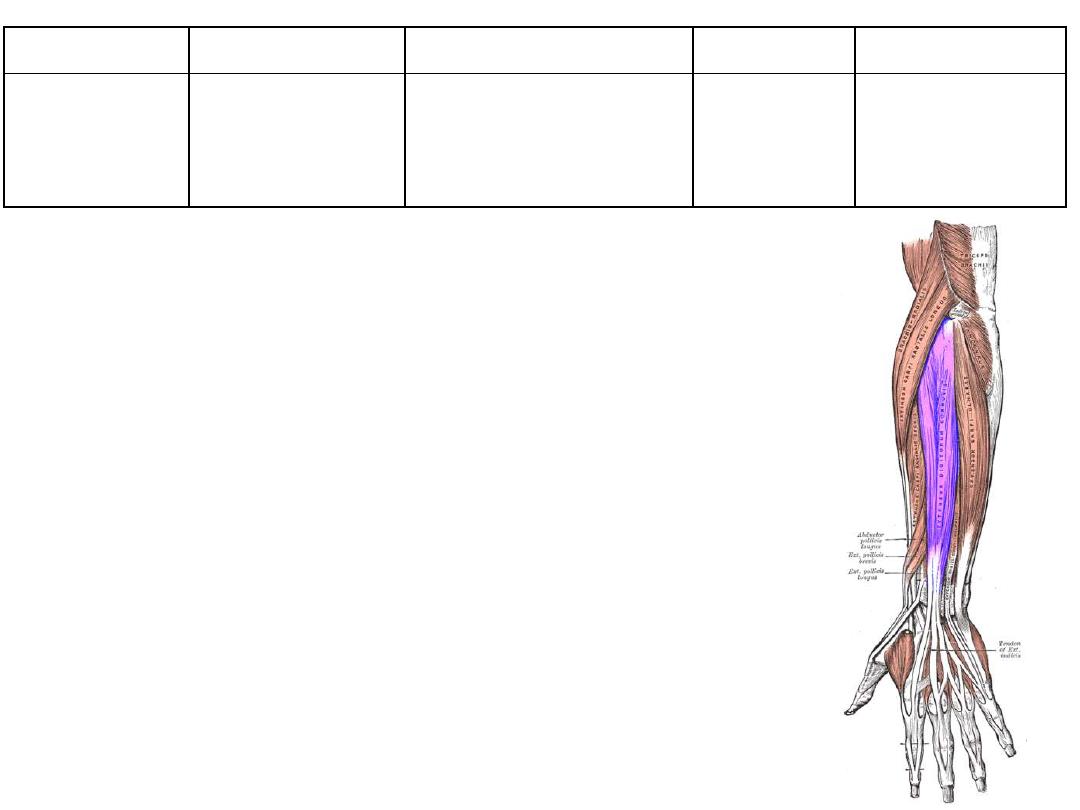
1. Brachioradialis
2. Extensor carpiradialis longus
3. Extensor carpiradialis brevis
4. Extensor digitorum
5. Extensor digiti minimi
6. Extensor carpiulnaris
7. Anconeus
8. Supinator
9. Abd. Pollicis longus
10. Extensor pollicis brevis
11. Extensor pollicis longus
12. Extensor indicis
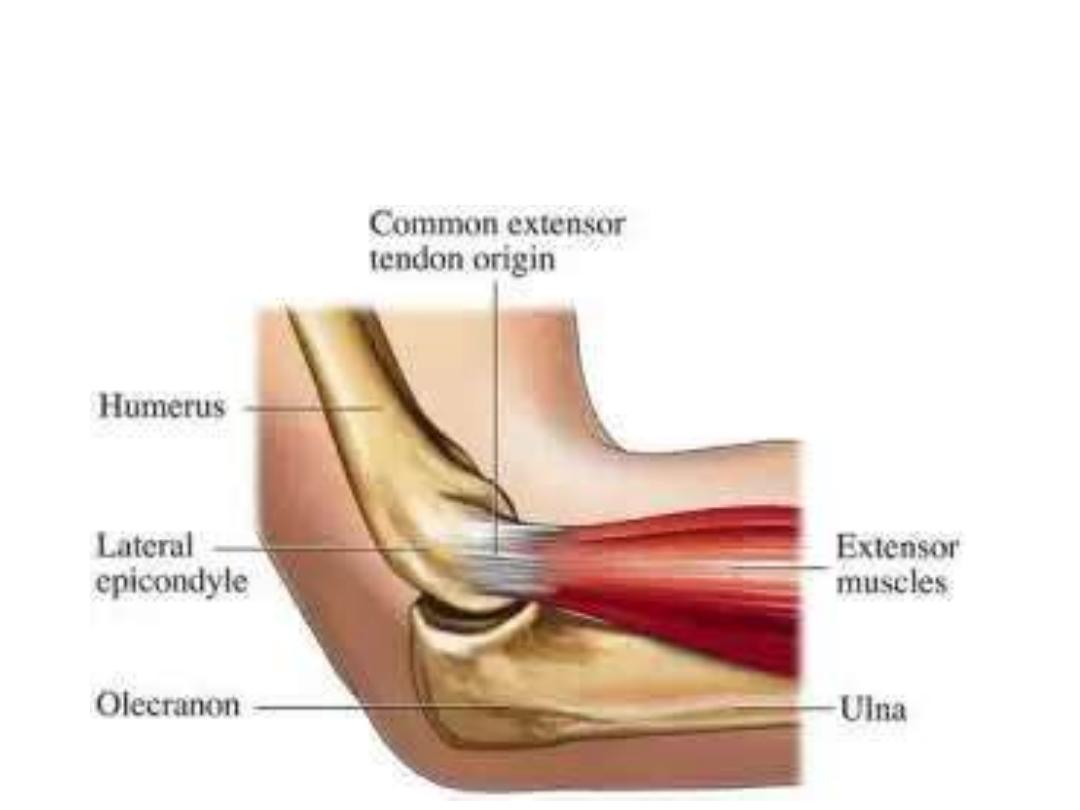
The common extensor tendon:
• The front of the lateral condyle of humerus
• Gives attachment to most of the muscles of the back of forearm
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Innervation
Function
Brachioradialis
Lateral
supracondylar ridge
Radial styloid Radial n
• Flexes the elbow
• Position in the midprone
• Although a posterior muscle,
its main bulk is seen from
the front
• Although supplied by radial
nerve, it is elbow flexor!
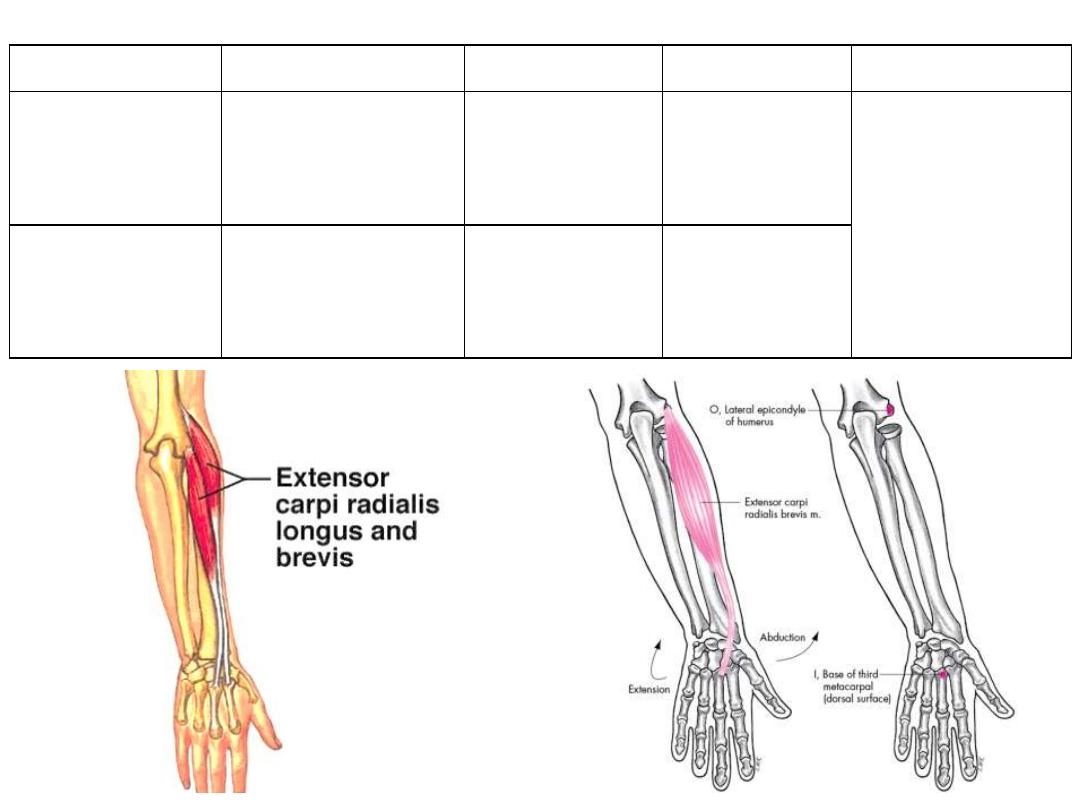
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Innervation
Function
Extensor carpi
radialis longus
Lateral
supracondylar ridge
Base of 2
nd
metacarpal
posteriorly
Radial n
• Wrist extensor
• Wrist abductor
Extensor carpi
radialis brevis
Common extensor
tendon
Base of 3
rd
metacarpal
posteriorly
Deep branch of
radial n
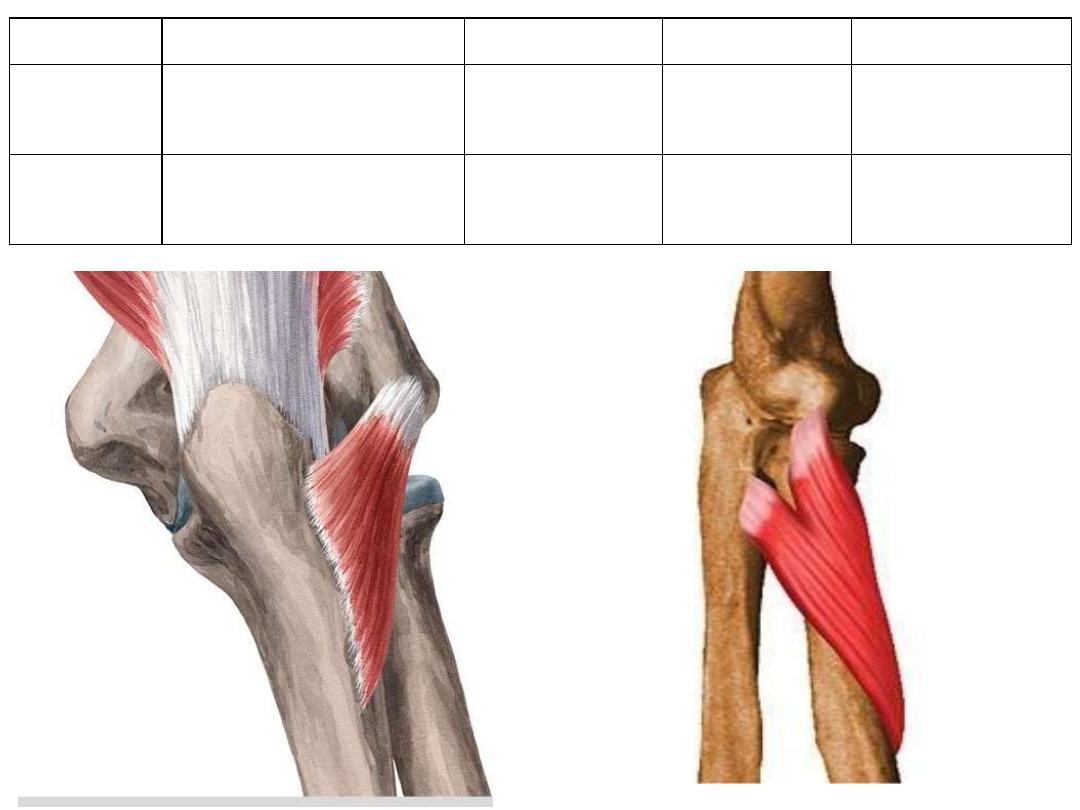
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Innervation
Function
Anconeus
Common extensor origin
Lateral surface
of olecranon
Radial n
Elbow extensor
Supinator
• CEO
• Supinator crest of ulna
Neck & oblique
line of radius
Deep branch of
radial n
Supinator
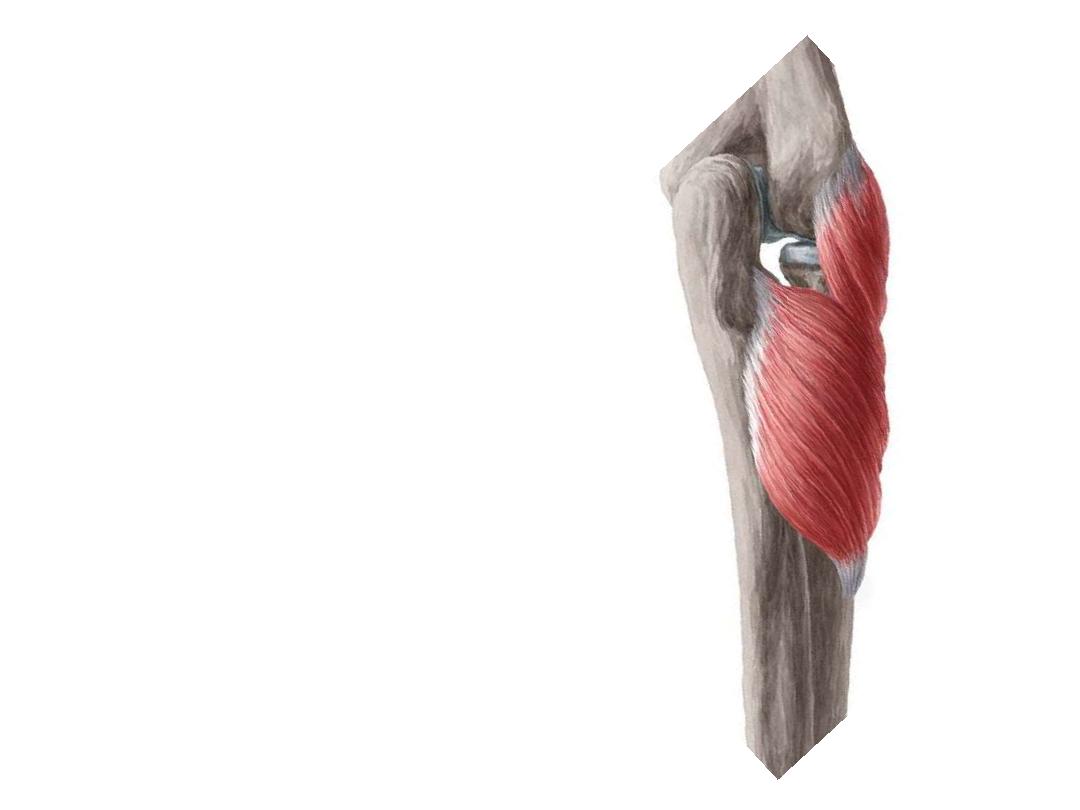
Supinator:
Supinator has 2 heads (superficial & deep)
the radial n passes between them
The superficial head surround the upper
part of the radius & is inserted into the
lateral
edge
of
the
radial
tuberosity
approaching the insertion of the pronator
teres
The deep head forms a sling-like fasciculus,
which encircles the neck of the radius
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Innervation
Function
Extensor
digitorum
Common extensor
tendon
Middle & distal
phalanges of medial 4
fingers (Ex. Expansion)
Posterior
interosseous
n
• Extends digits
• Extends wrist
• The extensor digitorum communis extends the
phalanges, then the wrist, and finally the elbow
• It tends to separate the fingers as it extends them.
• The muscle acts principally on the proximal
phalanges
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Innervation
Function
Extensor digiti
minimi
Common extensor
tendon
Extensor
expansion of the
little finger
Posterior
interosseous n
Extends finger 5
especially at MCPJ
Extensor carpi
ulnaris
Base of
metacarpal 5
• Wrist extensor
• Wrist adductor
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Innervation
Function
Abductor pollicis
longus
Posterior
surface of R&U
Base of metacarpal
thumb
Posterior
interosseous n
• Thumb abductor
• Thumb extensor
Extensor pollicis
brevis
Posterior
surface of R
Proximal phalanx
thumb
Thumb extensor at
MCPJ
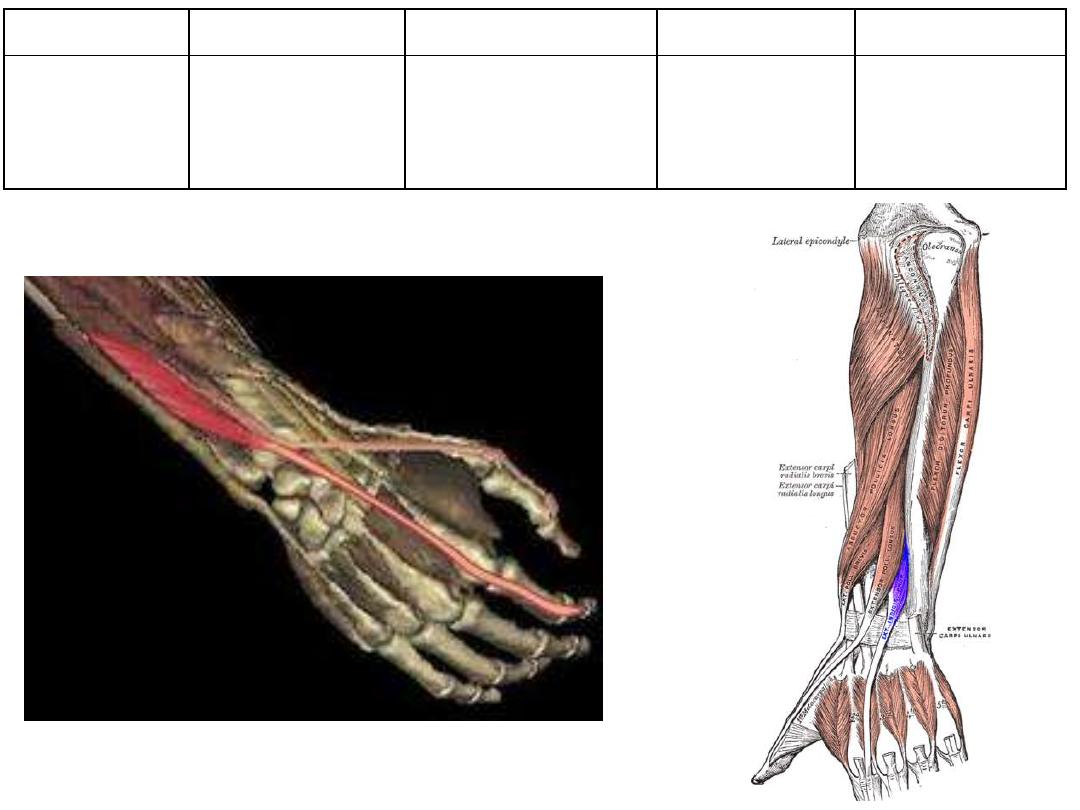
Extensor pollicis
longus
Posterior
surface of U
Distal phalanx
thumb
Extensor of distal
phalanx thumb
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Innervation
Function
Extensor
indicis
Back of ulna
(lower 1/3)
Ulnar side of
extensor expansion
Posterior
interosseous n
• Extends index
• Extends wrist
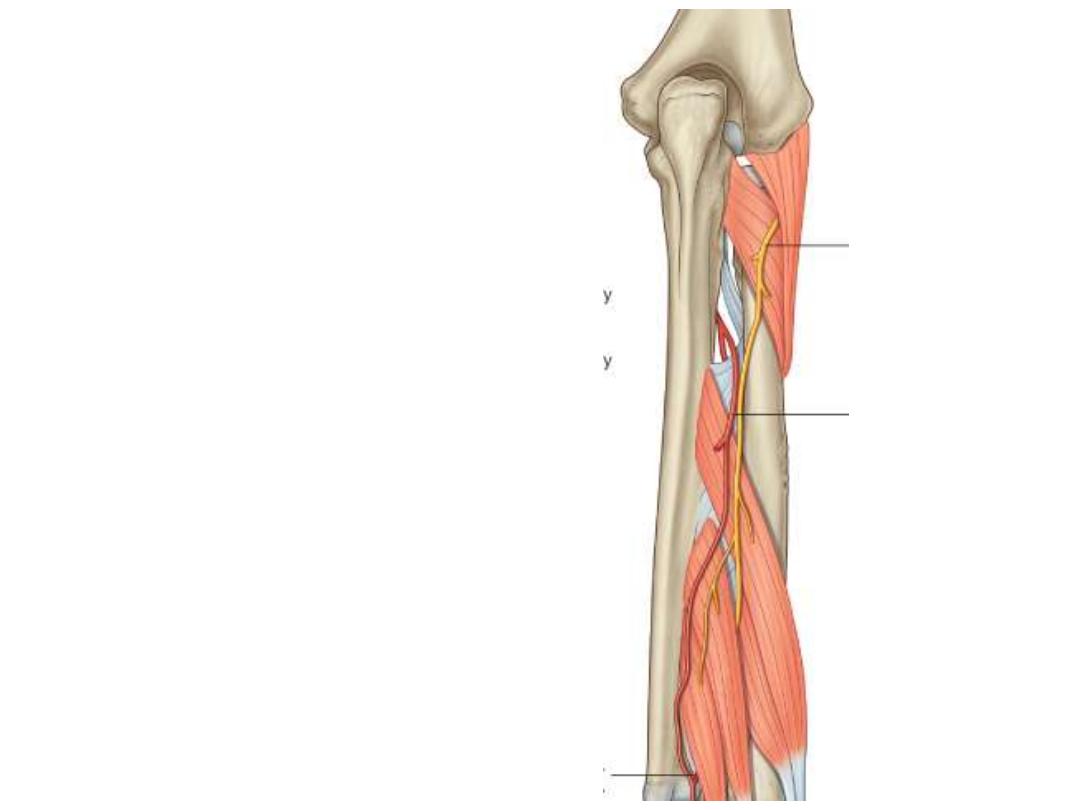
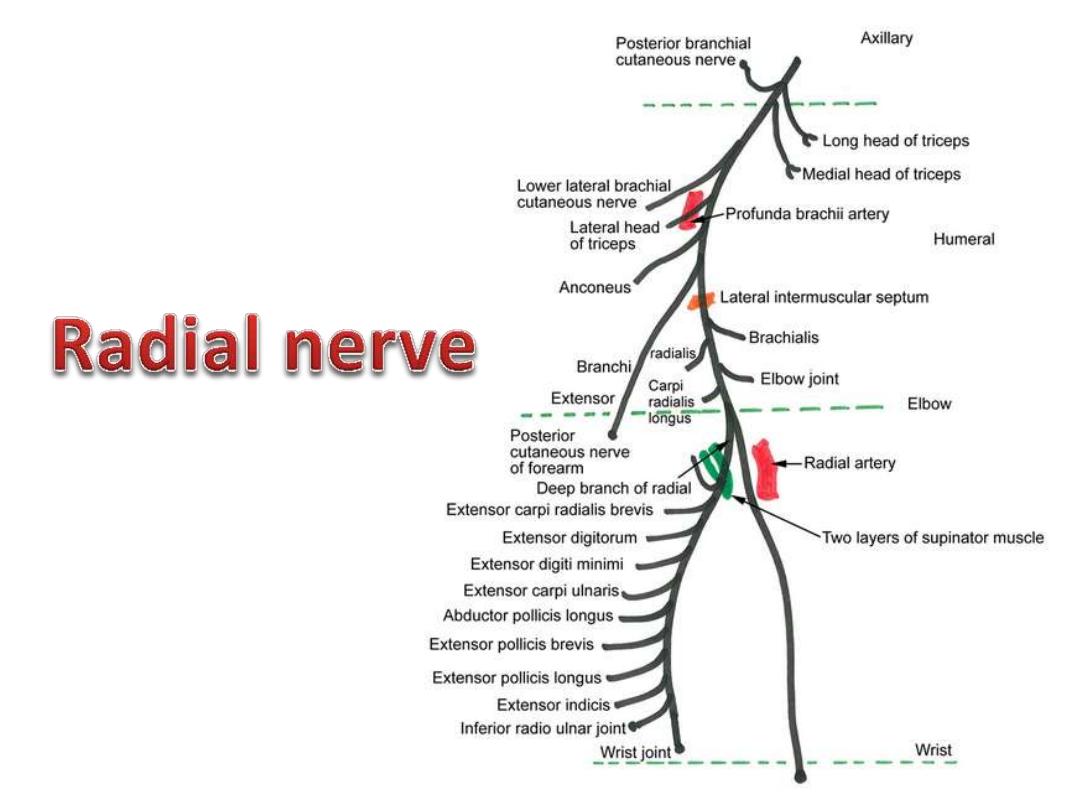
Radial nerve in the forearm:
Divides deep to brachioradialis
into superficial & deep branches:
Deep branch:
- Winds around the lateral side of
the radius between the two
heads of supinator
- Prolonged downward between
the superficial and deep layers
of muscles
- Provides motor function to the
muscles
in
the
posterior
compartment of the forearm
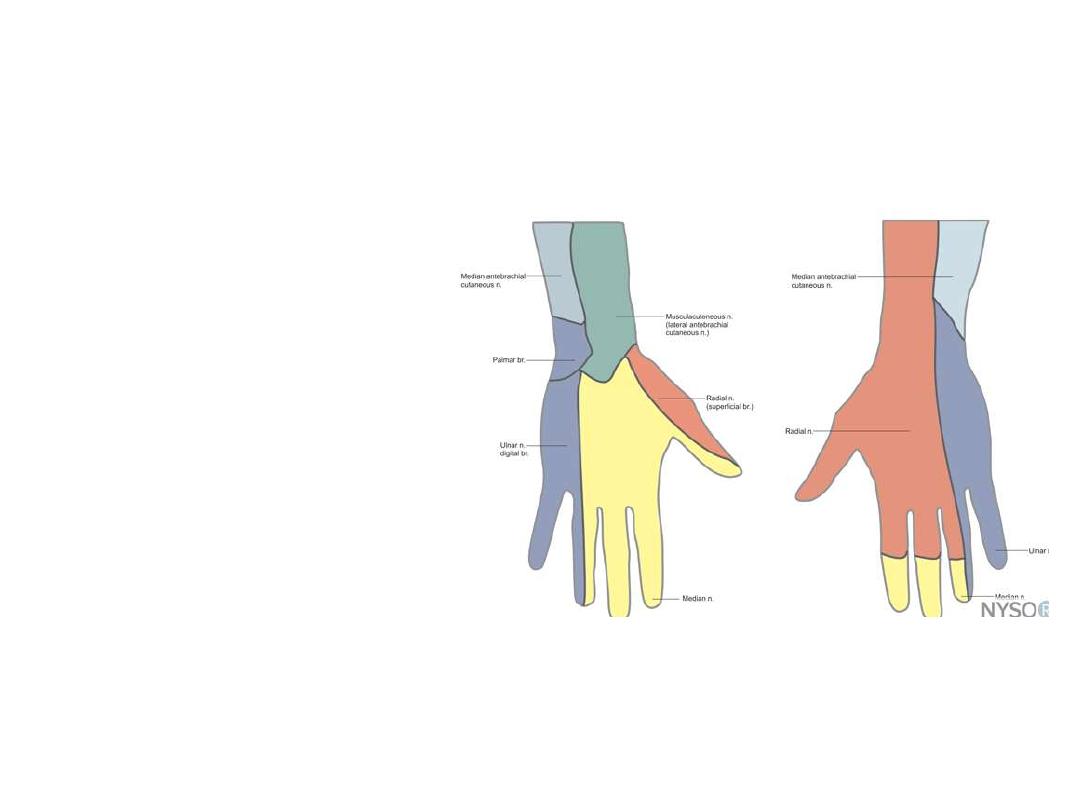
Superficial branch:
- Completely sensory
- Passes along the radial side of
the forearm
- Lies lateral to the radial artery
deep to brachioradialis
- Becomes superficial in the lower
1/3 of the forearm in the roof of
the snuff box
- Supplies the skin of the lateral
2/3 of the dorsum of hand & 3
1/2
fingers
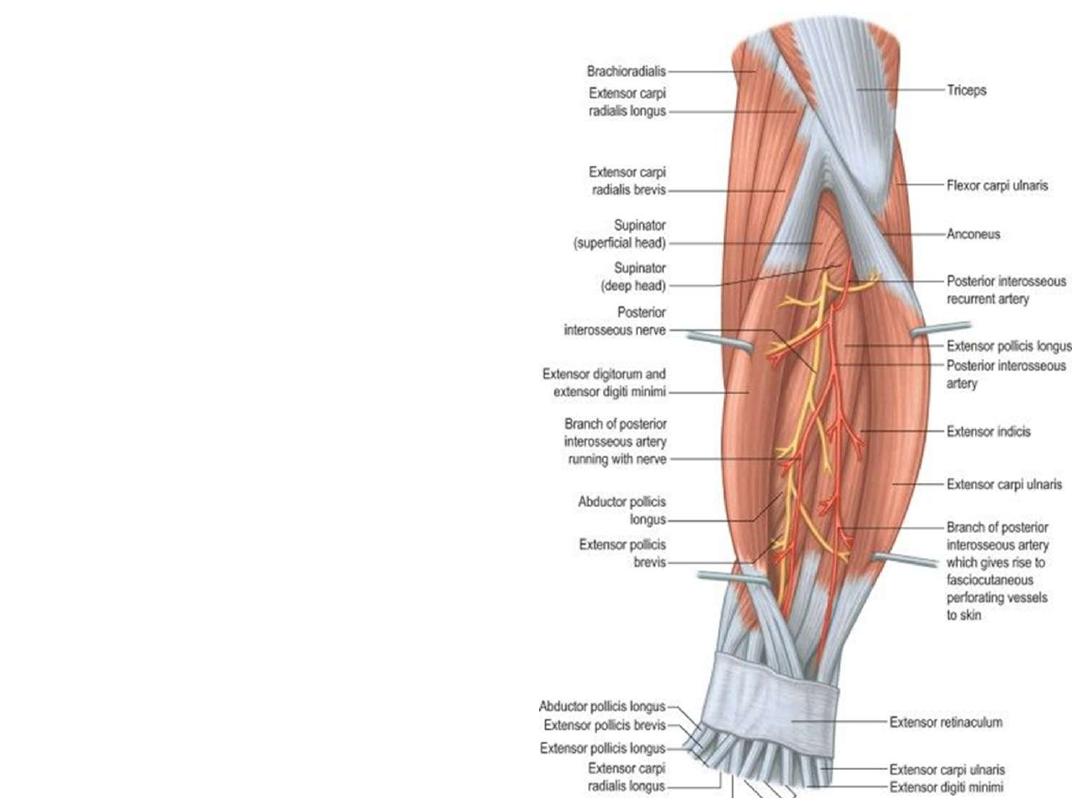
Posterior interosseous artery:
• Passes backward above the upper
border
of
the
interosseous
membrane
• Runs down the back of the forearm
between the superficial and deep
layers of muscles, to both of which
it distributes branches.
• At the lower part of the forearm it
anastomoses with the termination
of the volar interosseous artery
• Gives the interosseous recurrent
artery to elbow anastomosis

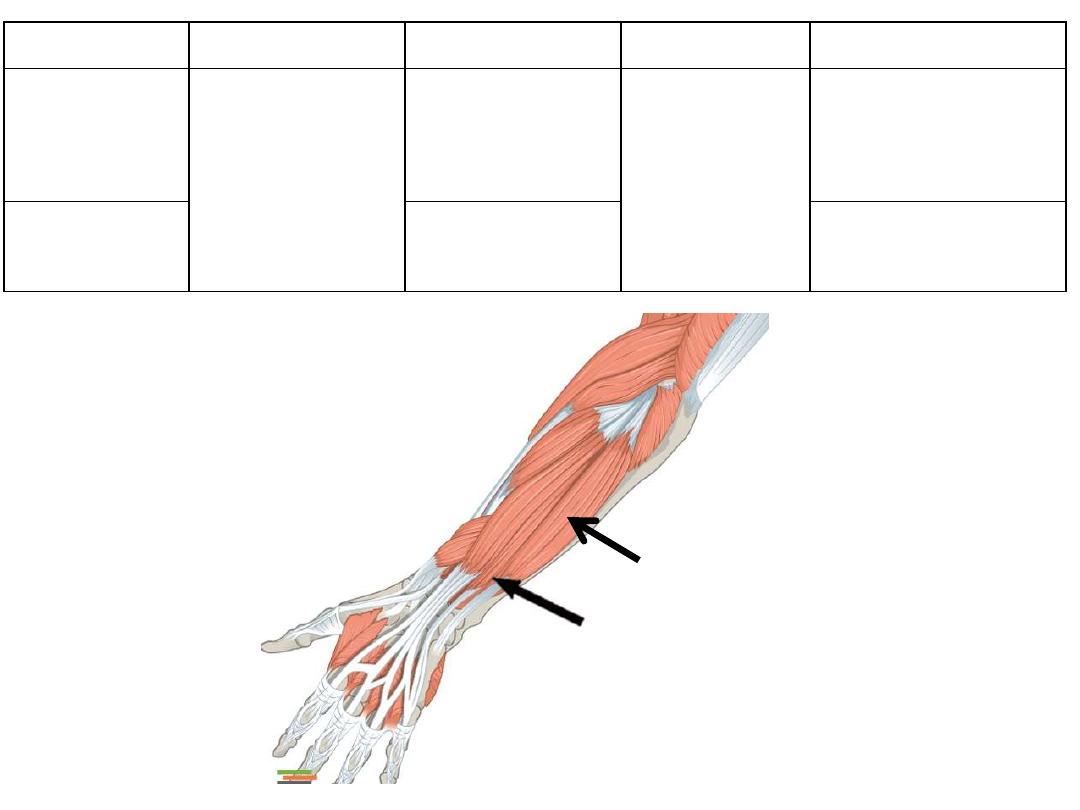
Anatomical snuffbox:
• A triangular depressed area on the
radial side of carpus
• Boundaries:
o Medial: EPL
o Lateral: EPB & AbPL
o Proximal: Radial styloid
• Floor:
scaphoid & trapezium
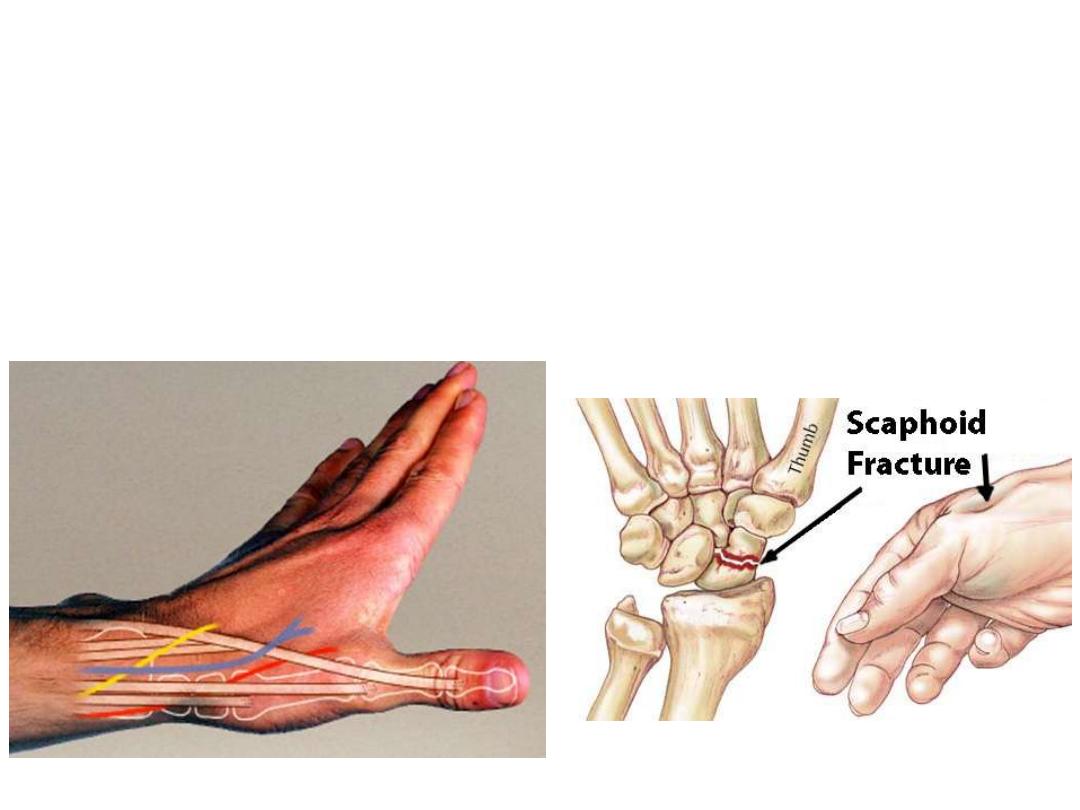
• Structures in the roof:
o Beginning of cephalic vein
o Superficial radial nerve
• Structures in the floor:
Radial artery
• Clinical significance:
It is the site where maximum tenderness is felt in scaphoid fractures
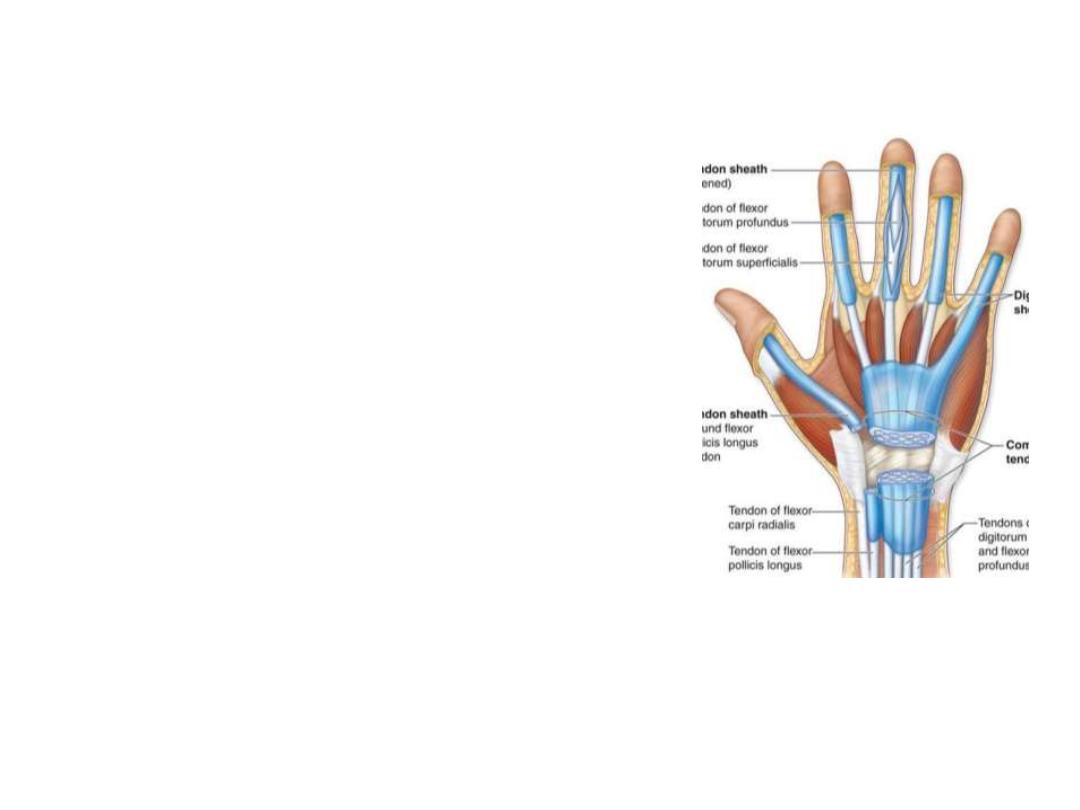
The synovial sheath:
A lubricating membrane which covers a
tendon & prevents friction
The tendon invaginates the synovial sheath
from one side so that the tendon is suspended
from the membrane by the mesotendon,
through which the blood vessels reach the
tendon
The synovial sheath is found where the tendon
passes
under
ligaments
and
through
osseofibrous tunnels; their function is to
reduce friction between the tendon and their
surrounding structure.
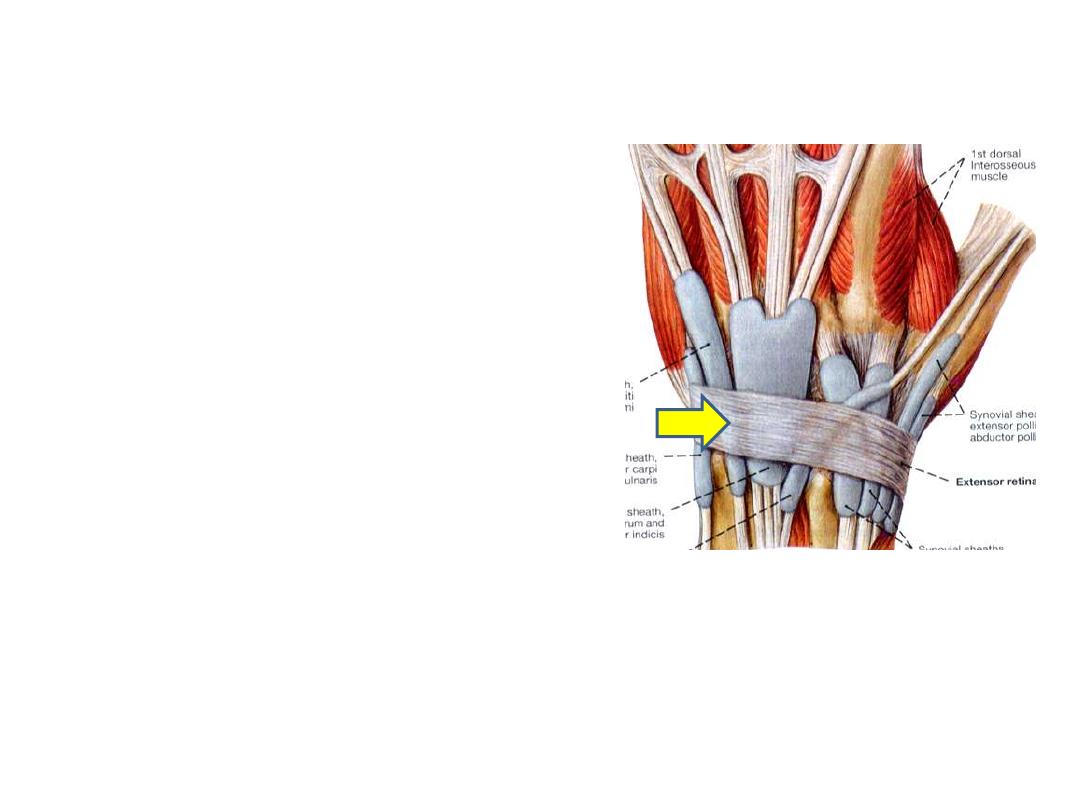
The extensor retinaculum:
A thickened part of deep fascia that
holds the tendons of the extensor
muscles in place.
It is a strong, fibrous band, extending
obliquely downward and medially
across the back of the wrist
The ER is attached laterally to the
lateral margin of the radius.
Medially, it is not attached to the ulna,
its medial attachment is to the most
medial of the carpal bones, the
triquetrum & pisiformis. It is also
attached to the ridges on the dorsal
surface of the radius.
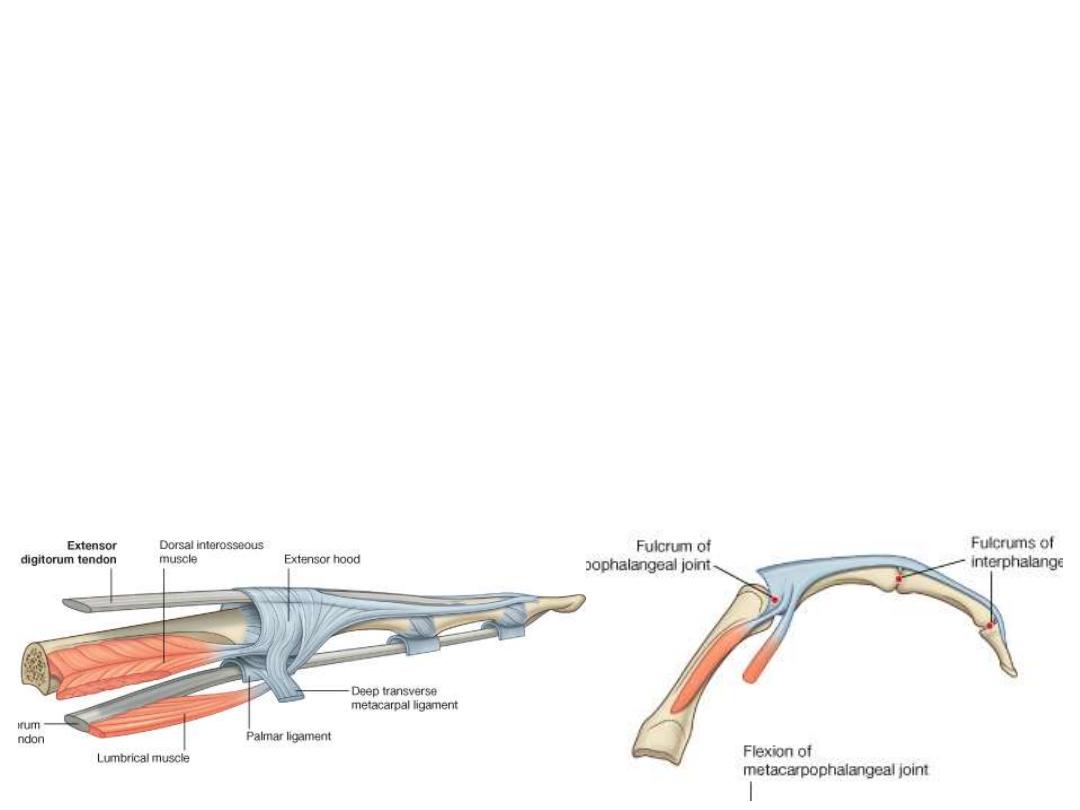
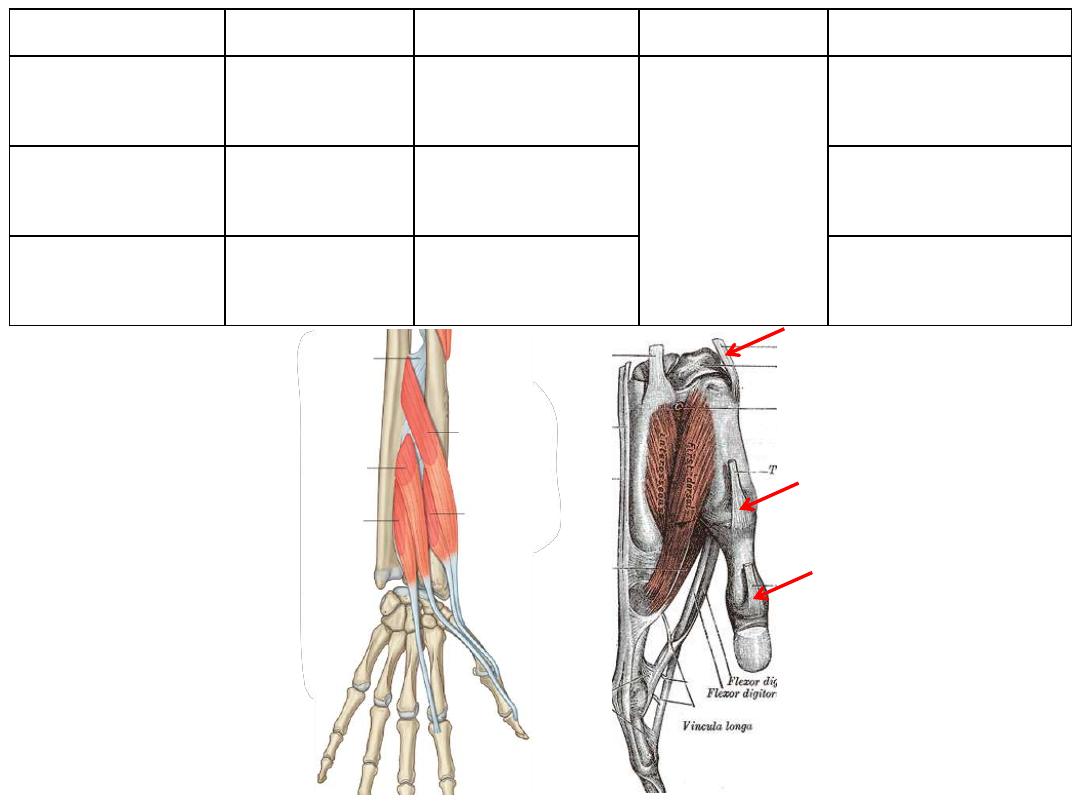
The extensor hoods (Dorsal digital expansions):
• Tendons of ED & EPL as they pass onto the dorsal aspect of the digits they
expand over the proximal phalanges to form this complex structure
• Tendons of EDM, EI & EPB join these hoods
• Each extensor hood is triangular in shape, with:
• Apex attached to the distal phalanx;
• Central region attached to the middle phalanx (in the thumb to proximal
phalanx)
• Corner of the base wrapped around the sides of the MPJ & are attached to
deep ligaments of the palm
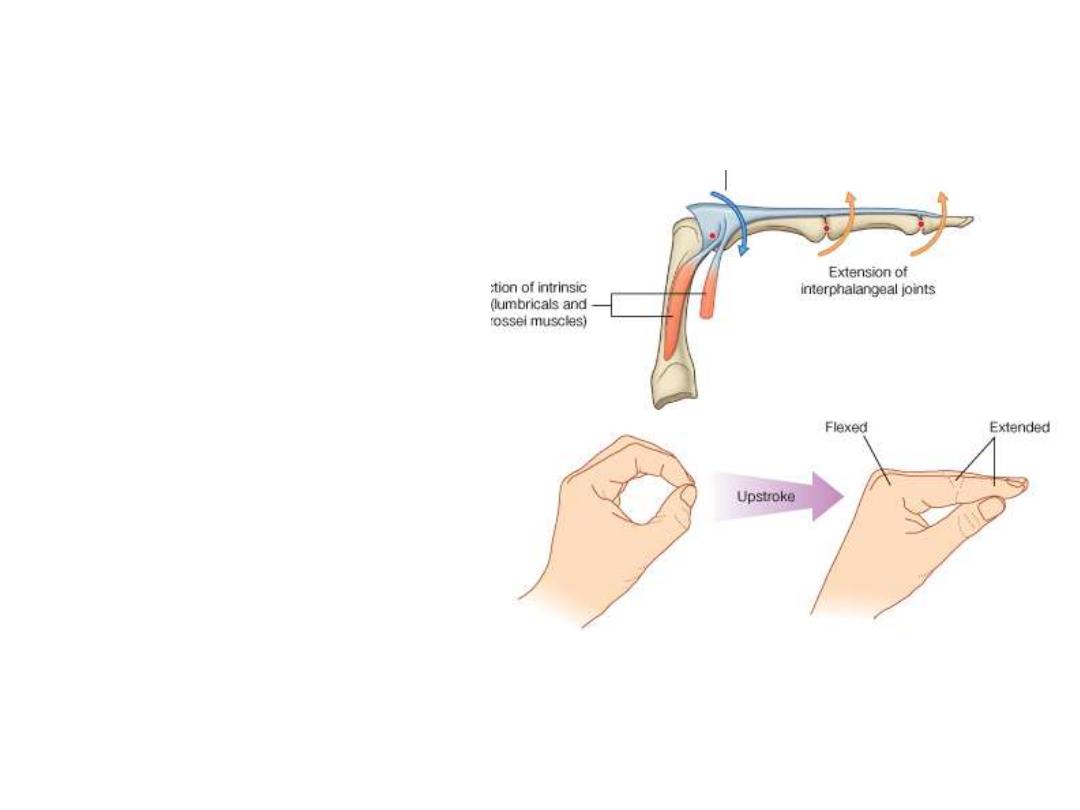
• In the medial 4 fingers, the
lumbrical, interossei are attach to
the extensor hoods
• In the thumb, the adductor
pollicis and abductor pollicis
brevis muscles insert into it
• Because these muscles pass
anterior to the MPJ, they flex
these joints
• Simultaneously, the force is
transferred dorsally through the
hood will extend the IPJ
• This movement is peculiar for the
action of palm muscles through
the extensor hoods