
The forearm
Flexor compartment

OBJECTIVES
…
To list muscles of the anterior compartment of
the forearm
To describe the course of main arteries in the
region
To follow the main nerves in the region with
their branches
To relate to some clinical states
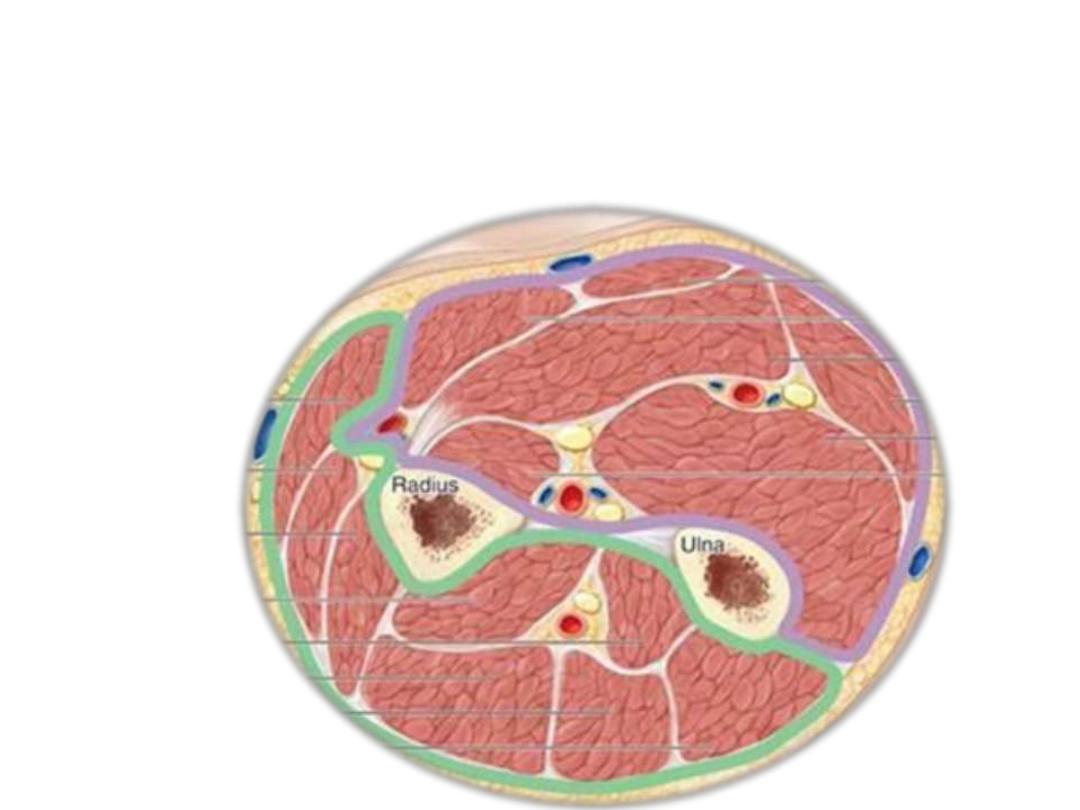
The forearm is divided into anterior (flexor) & posterior (extensor)
compartments by:
1- Medial intermuscular septum
2- Lateral intermuscular septum (very short)
3- Interosseoue membrane
1
2
3
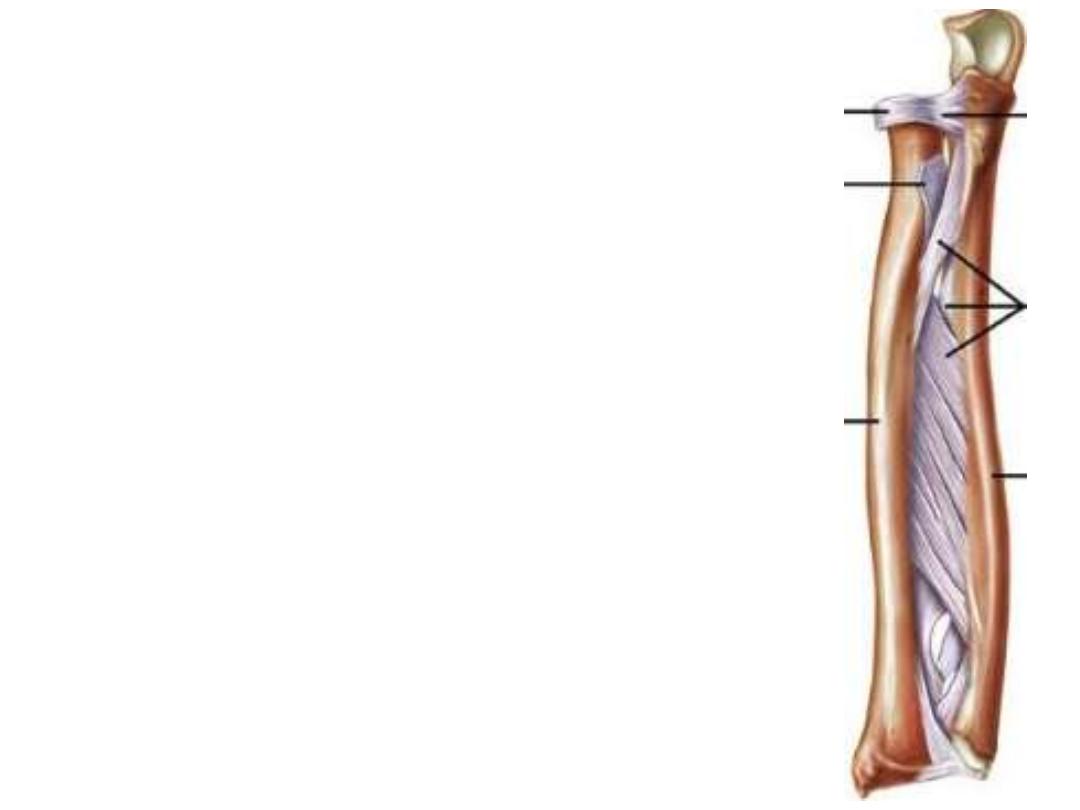
Interosseoue membrane:
- A
strong
fibrous
membrane
attaching
the
interosseous borders of the forearm bones to each
other
- Its fibers are directed downward & medially
transmitting force from radius to ulna (then to
humerus & scapula)
- Gives attachment to some muscles in the forearm
- It is considered as a fibrous joint (middle RU joint)
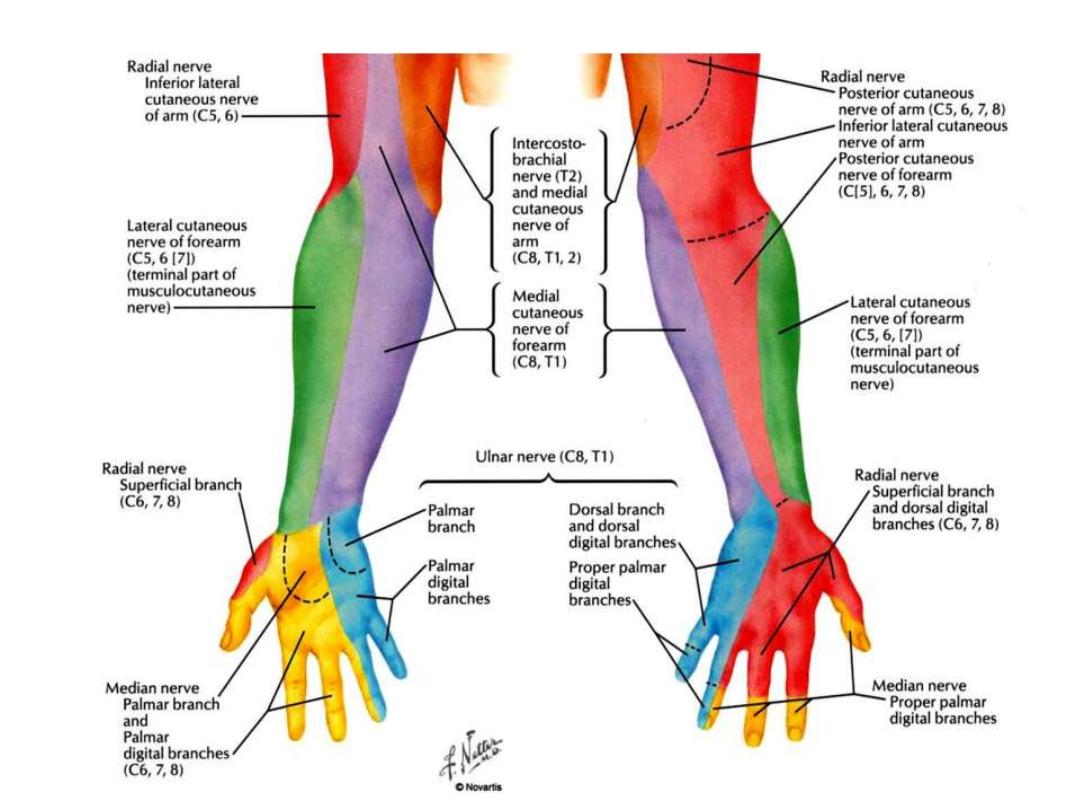
Cutaneous innervation:
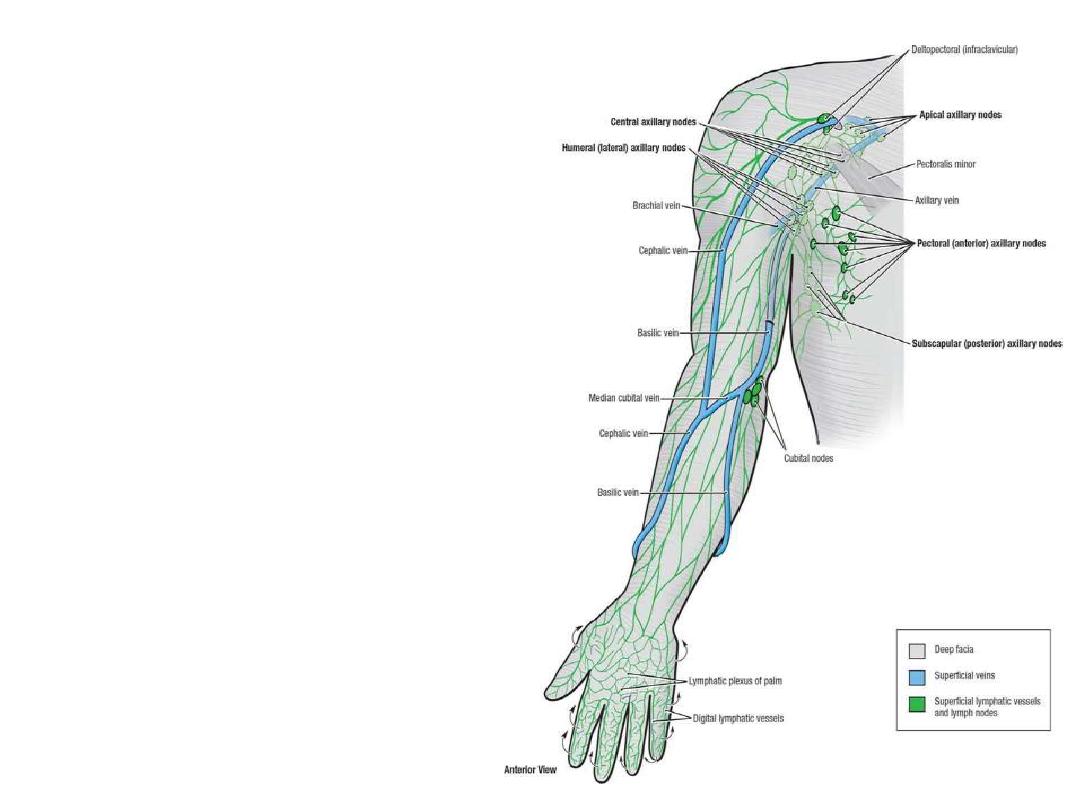
Lymphatics of the forearm:
Deep lymphatics:
Accompany arteries
Drain to the axillary nodes
Superficial lymphatics:
-Accompany superficial veins
-Those with cephalic vein drain to
the
deltopectoral (infraclavicular)
nodes
-Those with basilic vein drain to the
supratrochlear
nodes
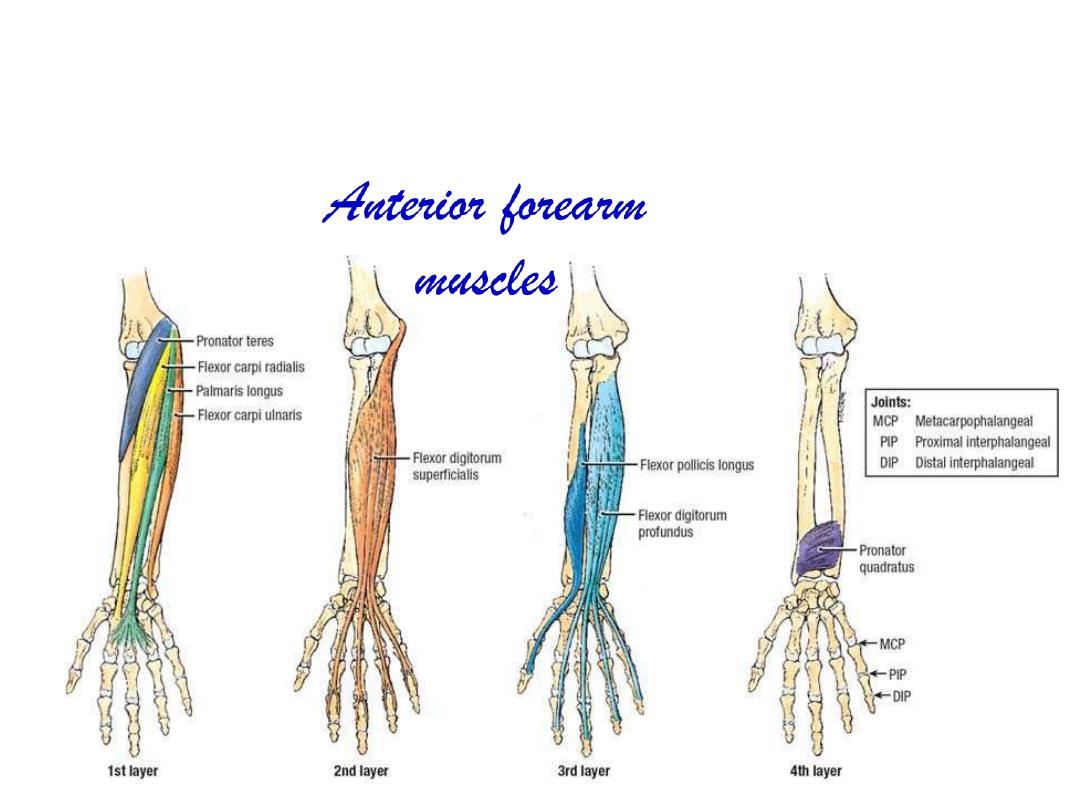
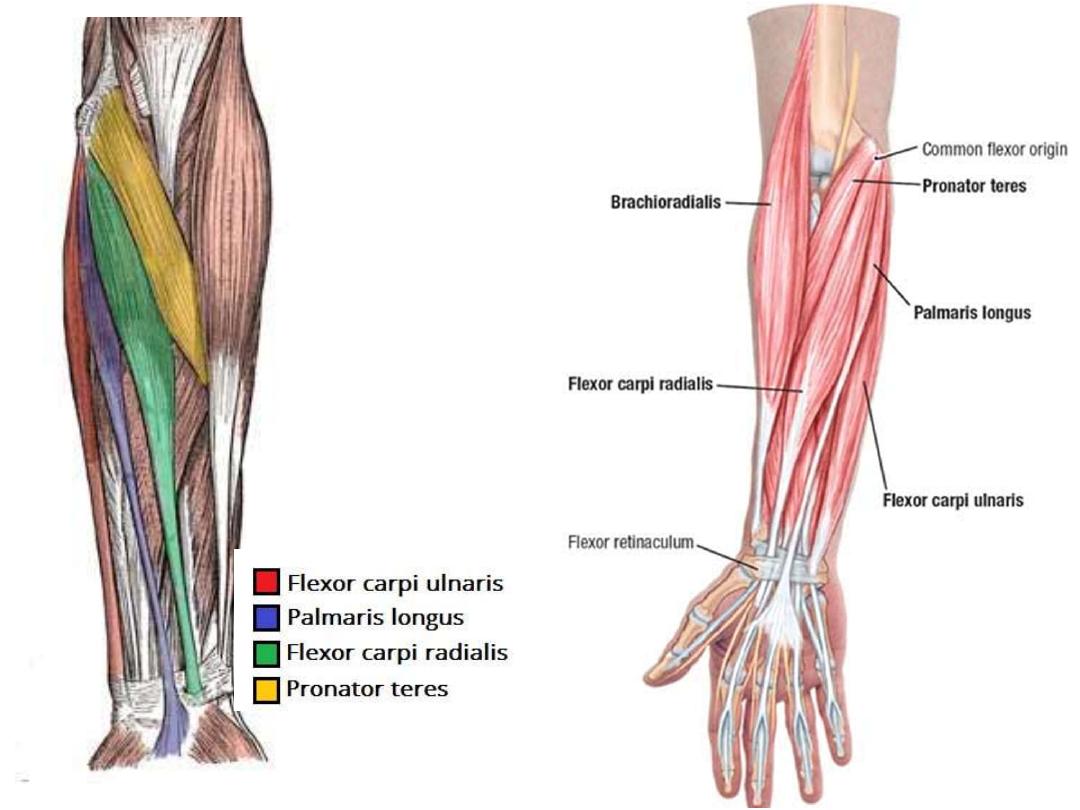
Superficial Layer:
Pronator teres
Flexor carpi radialis
Palmaris longus
Flexor carpi ulnaris
Intermediate layer
Flexor digitorum superficialis
Deep layer:
Flexor pollicis longus
Flexor digitorum profundus
Pronator quadratus
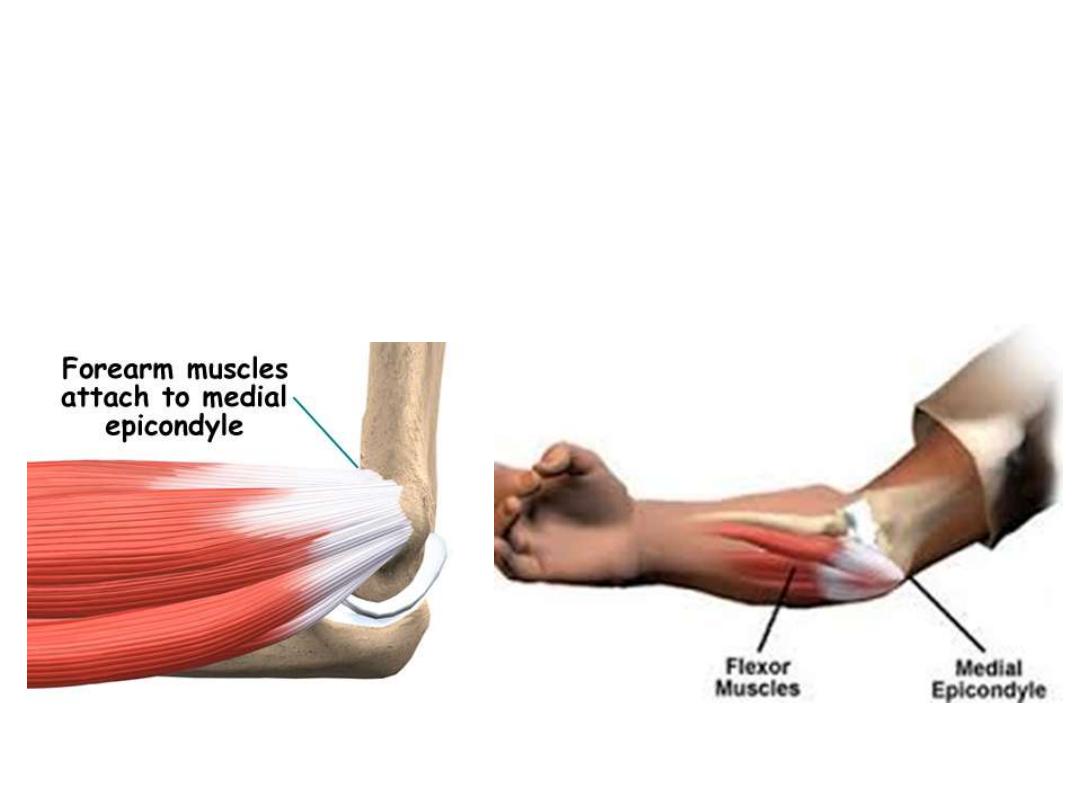
The common flexor tendon:
• The front of the medial condyle of humerus
• Gives attachment to the superficial layer of anterior forearm
muscles
Muscle
Common
origin
Additional
origin
Insertion
Innervation
Action
Pronator
teres
Common
flexor
tendon
Coronoid
process
Lateral surface &
mid-shaft of radius
Median
nerve
[C6,C7]
• Elbow flexor
• Pronator of RUJ
Flexor
carpi
radialis
-
Base of
metacarpals II and
III
• Wrist flexor
• Abductor
Palmaris
longus
-
Palmar
aponeurosis
Anchors skin of the
hand
Flexor
carpi
ulnaris
Posterior
border of
ulna
Base of metacarpal
V
Ulnar nerve
[C7,C8, T1]
• Elbow flexor
• Wrist flexor
• Adductor
Muscles of the superficial layer:
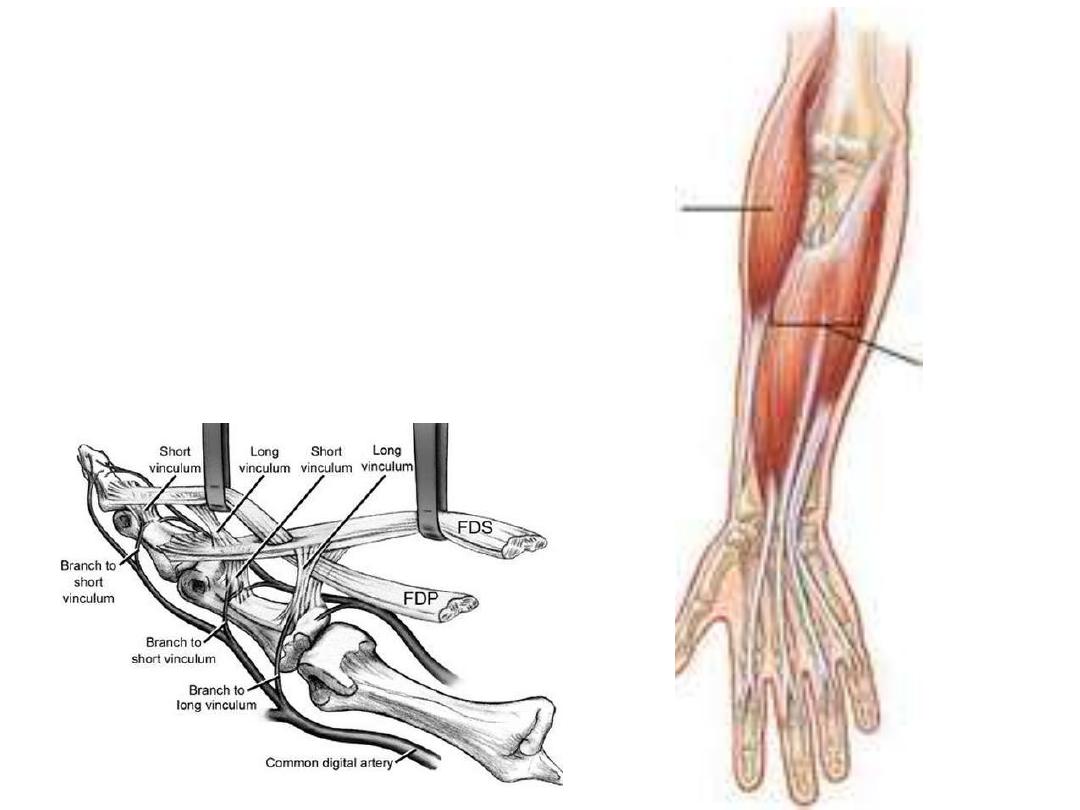
Flexor digitorum superficialis:
Origin:
- Common flexor tendon
- Oblique line of radius
Insertion:
Bifid tendon in the middle
phalanges of medial 4 fingers
Innervation:
Median nerve (C8 & T1)
Action:
Flexion of the wrist, MPJ & PIPJ
of the medial 4 fingers
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Innervation
Function
Flexor
digitorum
profundus
•
Anterior surface of ulna
•
Interosseous membrane
Distal phalanges
of the medial four
fingers
C8 & T1
•
Lateral ½: median n.
•
Medial ½: ulnar n.
Flexor of the
wrist, MPJm PIPJ
& DIPJ
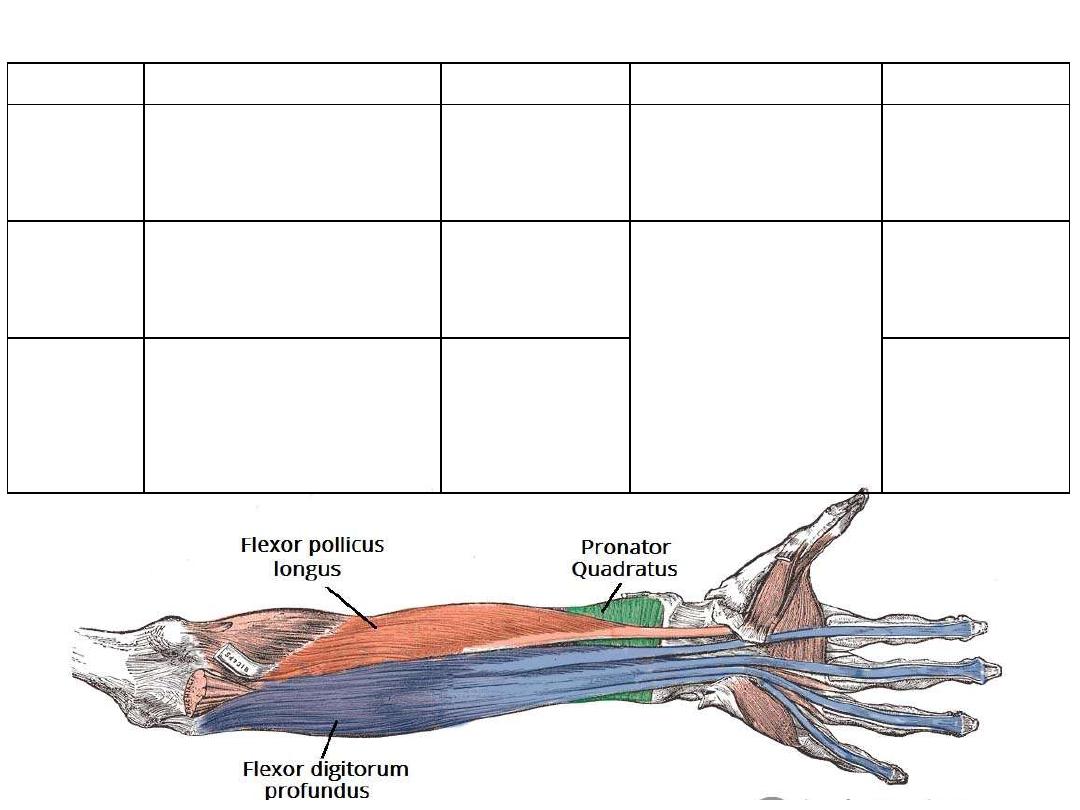
Flexor
pollicis
longus
•
Anterior surface of radius
•
Inter-osseous membrane
Distal phalanx of
thumb
Anterior interosseous n.
[C7,C8]
Flexor of IPJ of
the thumb
Pronator
quadratus
Anterior surface of ulna
(distal part)
Anterior surface
of radius (distal
part)
•
Pronator
•
Opposes the
bones to each
other
Muscles of the deep layer:
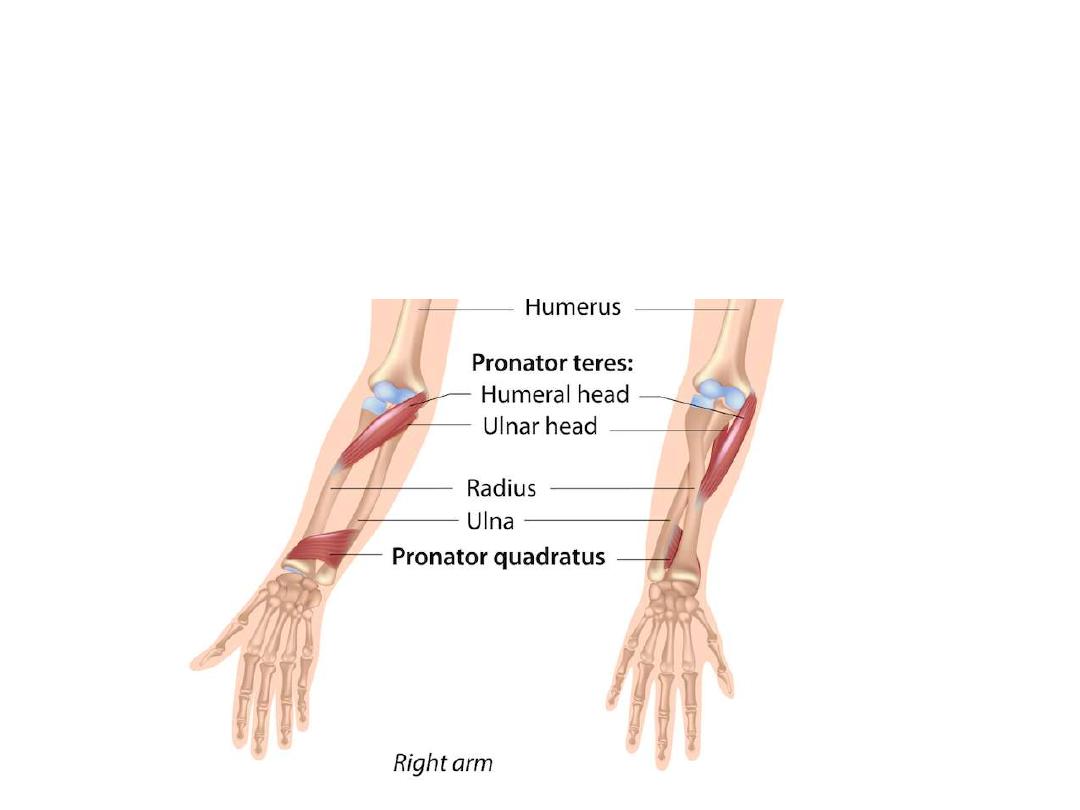
Pronation
Is the movement by which the radius rotates at the RU joints around
the ulna
Pronator teres & quadratus assist each other in doing this movement
Pronation
Supination
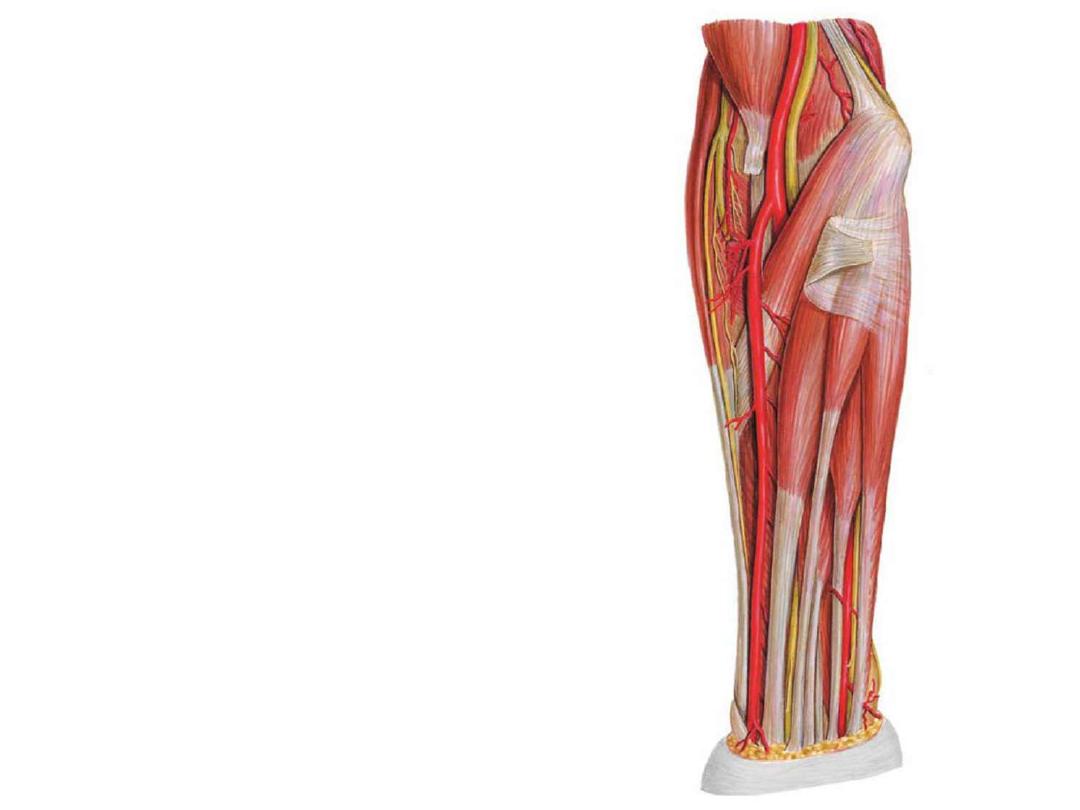
Vessels of the forearm:
Radial artery:
-Originates from the brachial artery at
the neck of the radius
- Lies deep to the brachioradialis muscle
in the proximal forearm
-In the distal forearm, it lies between
brachioradialis & FCR
-The radial pulse can be felt by gently
palpating the radial artery against the
underlying muscle and bone.
-The radial artery leaves the forearm,
passes around the lateral side of the
wrist
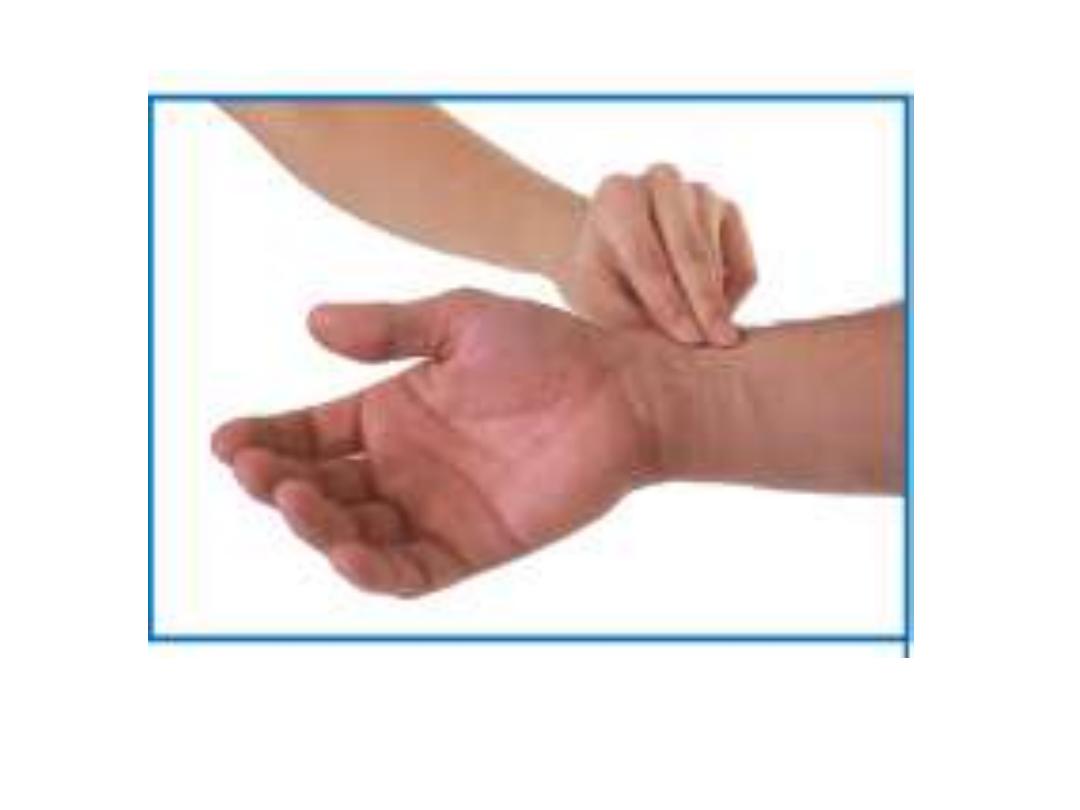
Radial pulse
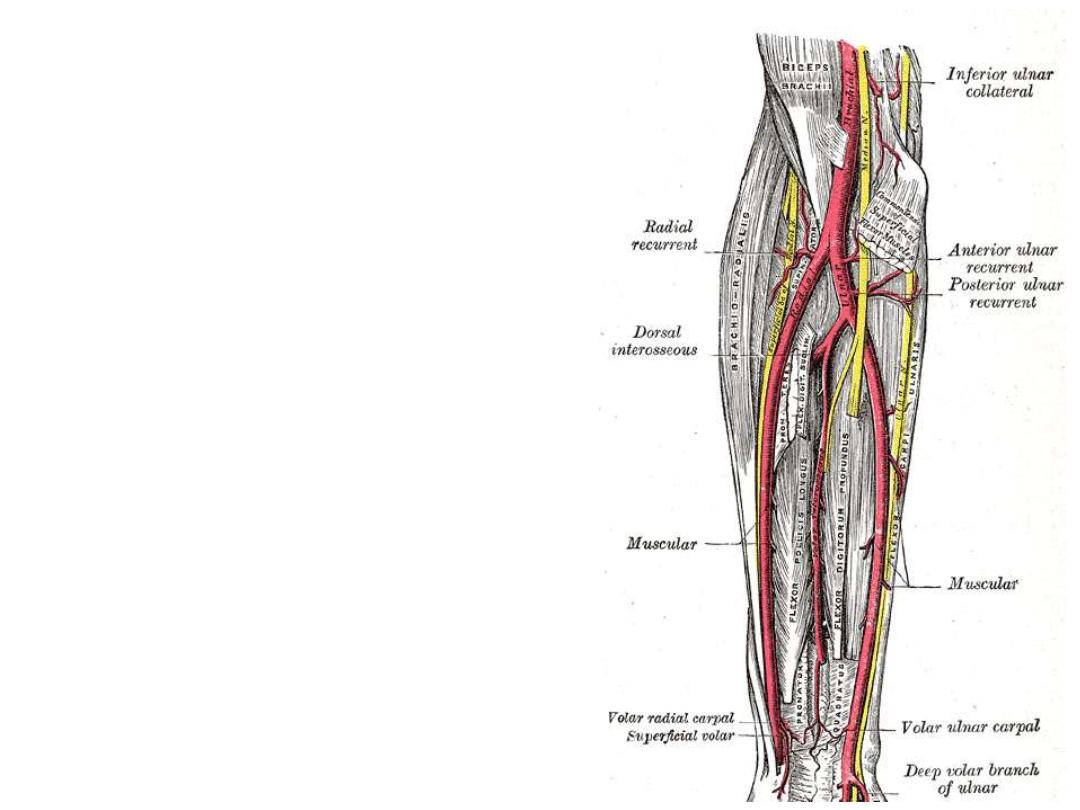
-Branches:
Radial recurrent artery; enters the
anastomosis around the elbow joint
Muscular
Palmar carpal branch
Superficial palmar branch enters the
hand
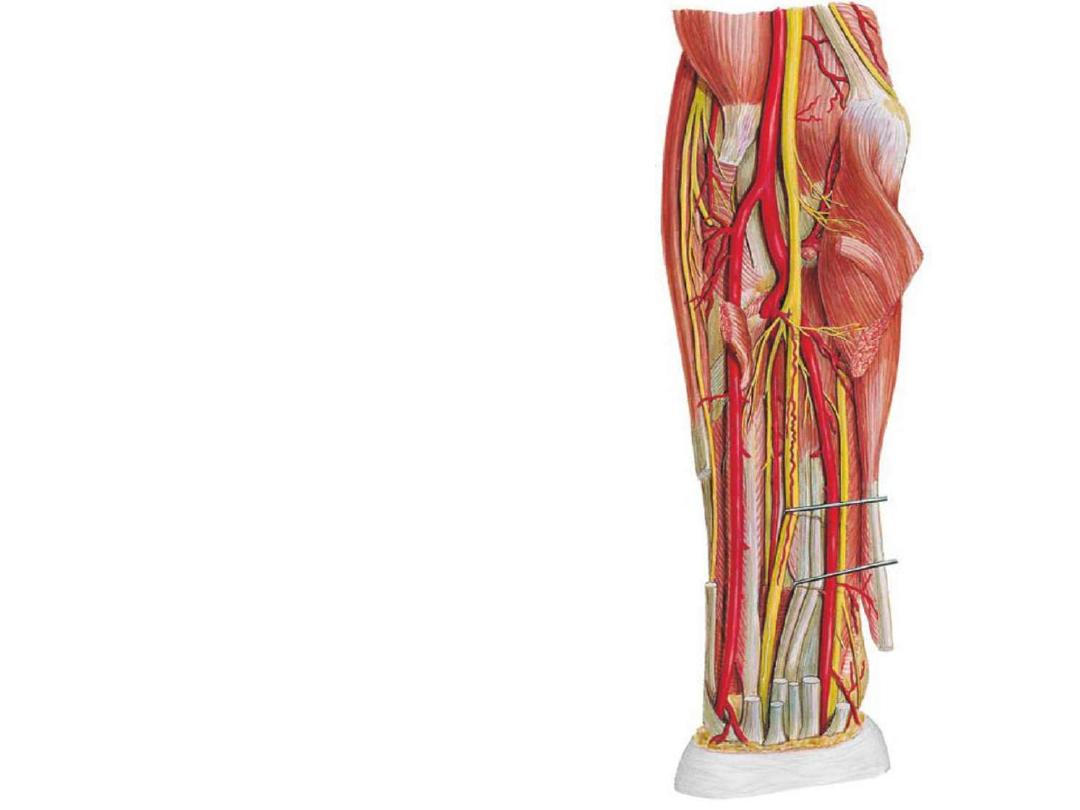
Ulnar artery:
-The ulnar artery is larger than the
radial artery
-Passes deep to the pronator teres
muscle
- In the distal forearm it remains
under flexor carpi ulnaris tendon,
and is therefore not easily palpable
-The ulnar artery leaves the forearm,
& enters the hand by passing lateral
to the pisiform bone
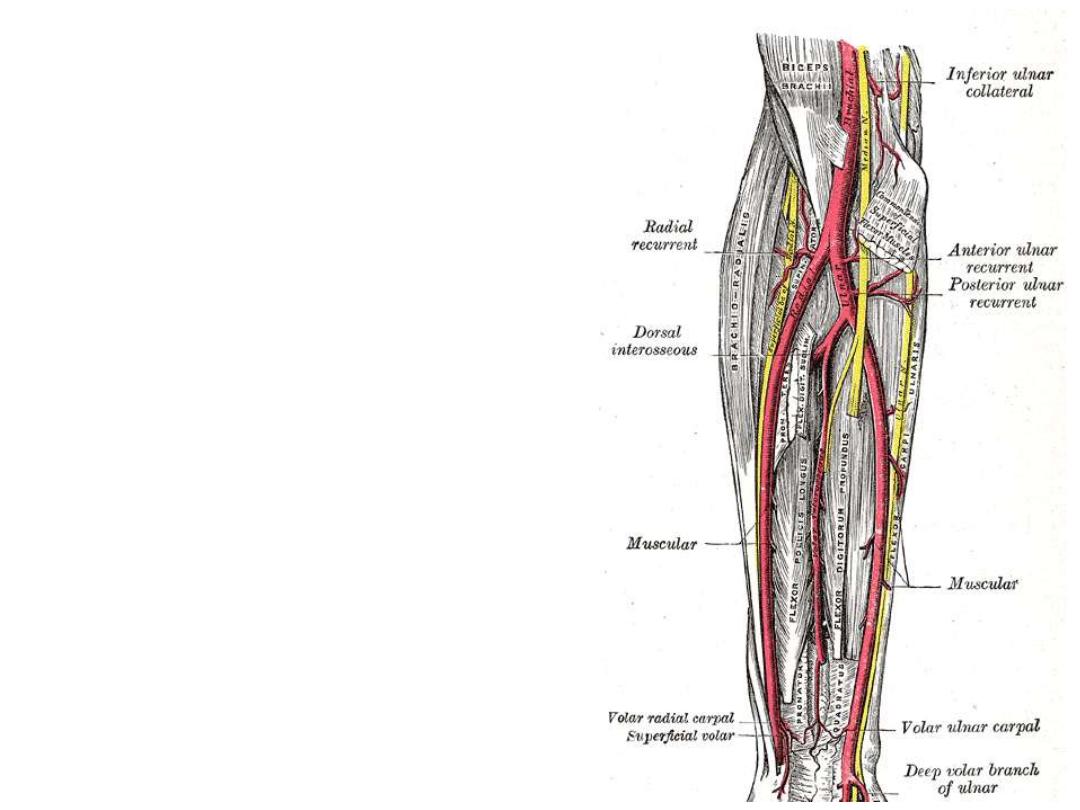
Branches:
Anterior & posterior ulnar recurrent
branches to the elbow anastomosis
Muscular arteries
Common interosseous artery which
divides into anterior and posterior
interosseous arteries
The anterior interosseous artery
passes on the interosseous membrane
and supplies muscles of the deep
compartment of the forearm with the
bones of the forearm
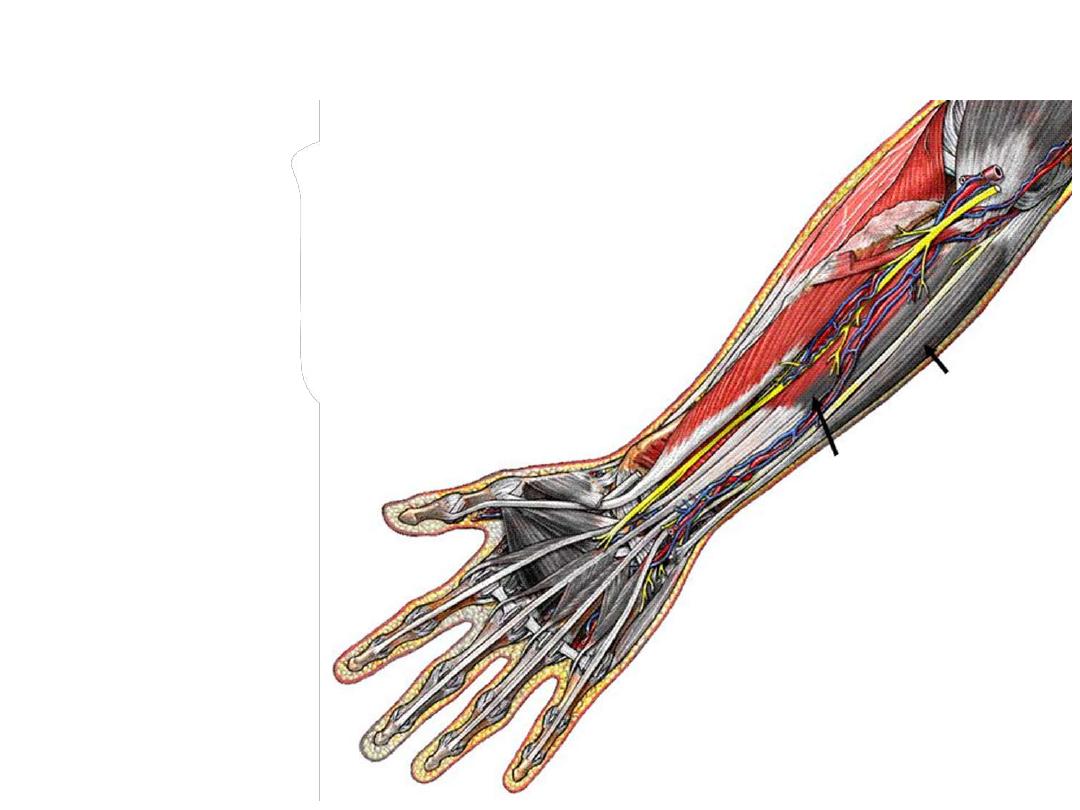
Nerves:
Median nerve:
-Leaves the cubital fossa by passing between
the two heads of the pronator teres
-Passes deep to flexor digitorum superficialis
-Just proximal to the wrist, it becomes between
the tendons of the FCR & FDS muscles
-Enters the hand by passing deep to the flexor
retinaculum
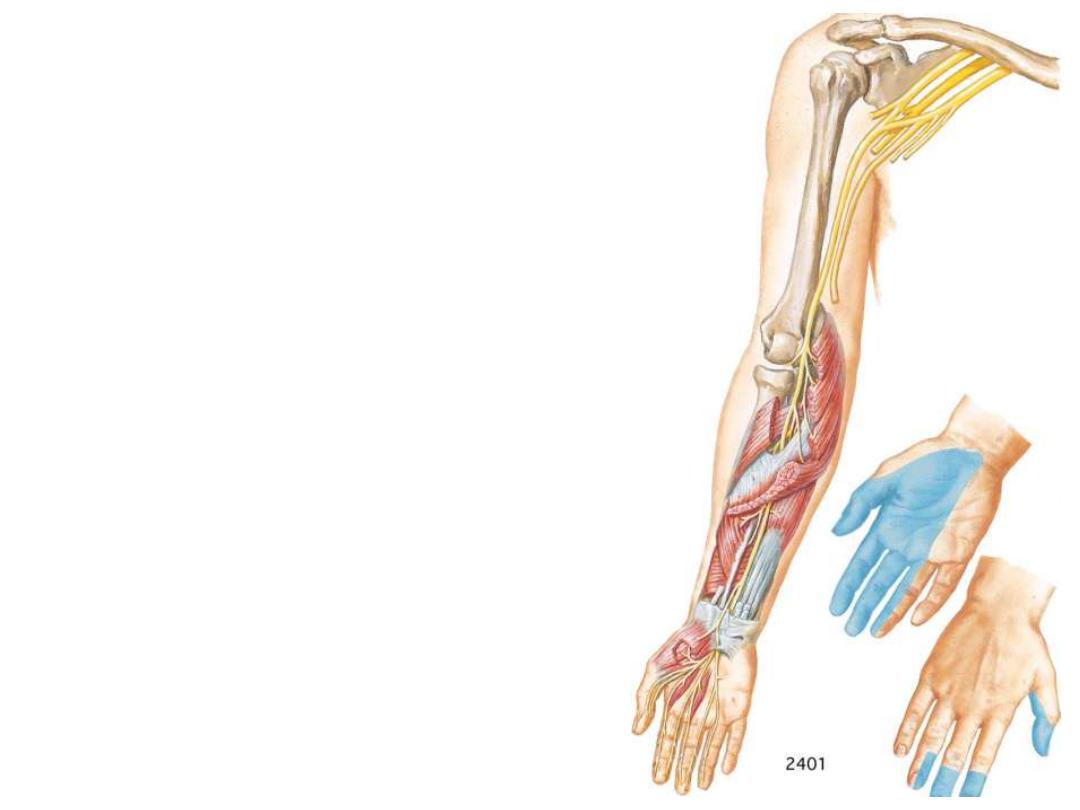
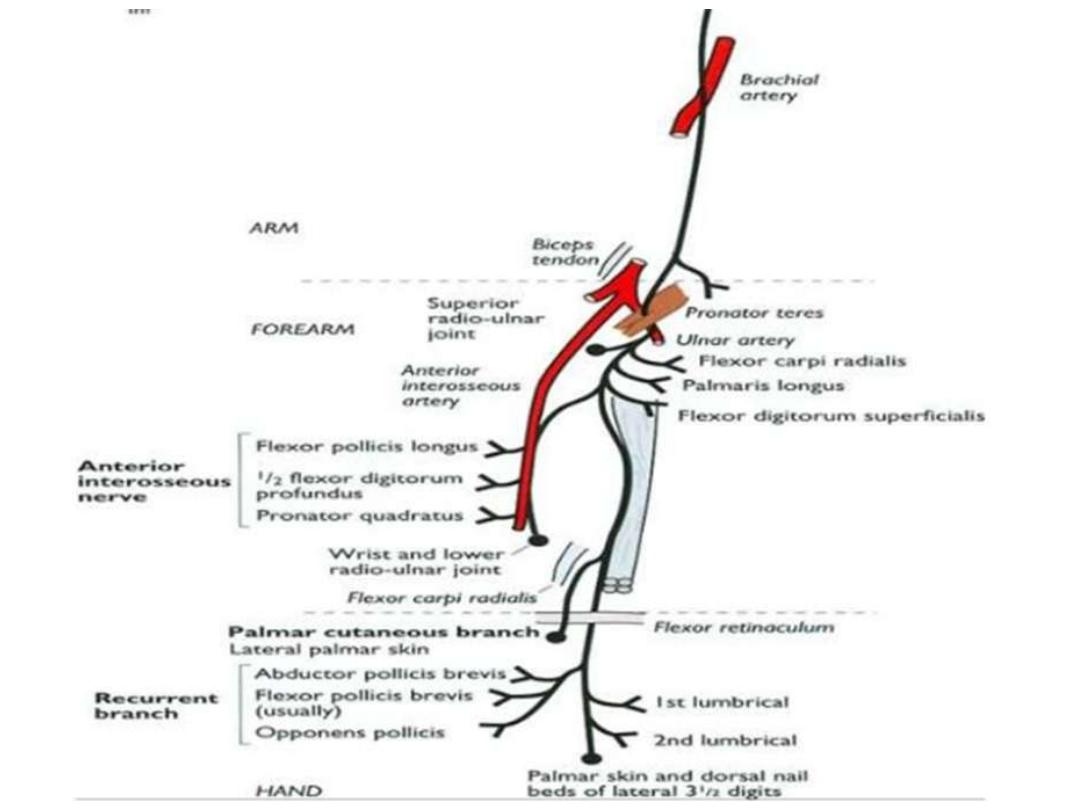
Branches:
The anterior interosseous nerve;
which innervates the muscles in the
deep layer & terminates as articular
branches to joints of the distal
forearm and wrist
Palmar branch; originates from the
median nerve just proximal to the
flexor
retinaculum
&
passes
superficially
into
the
hand
and
innervates the skin over the base and
central palm (spared in CTS)
Branches to the forearm muscles
except FCU & medial
½ of FDP
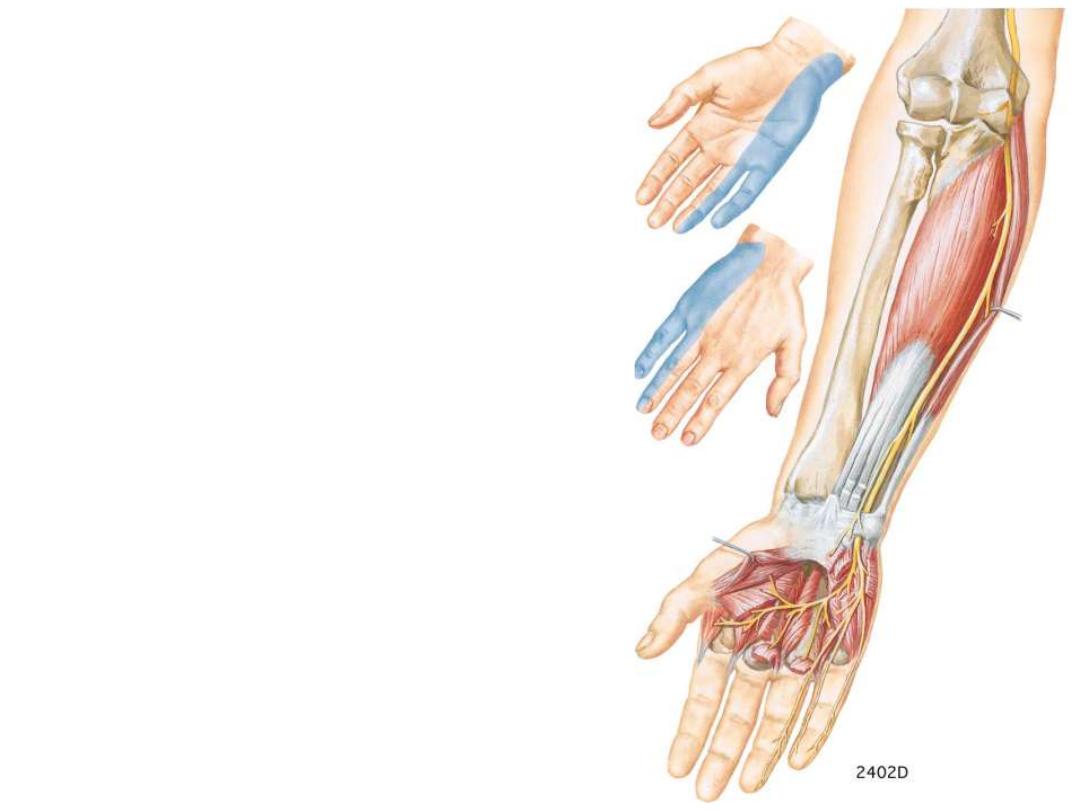
Ulnar nerve:
-In the forearm it lies under the flexor
carpi ulnaris
- The ulnar artery is lateral to the ulnar
nerve in the distal two-thirds of the
forearm, and both the ulnar artery and
nerve enter the hand by passing
superficial to the flexor retinaculum and
immediately lateral to the pisiform bone
Branches:
Muscular to FCU & medial
½ of FDP
Cutaneous branches to the medial
aspect of the hand & fingers
