
Introduction to ANATOMY

OBJECTIVES
…
To define the anatomical position
To describe important planes & sections
To define certain terms in relation to position
& movements
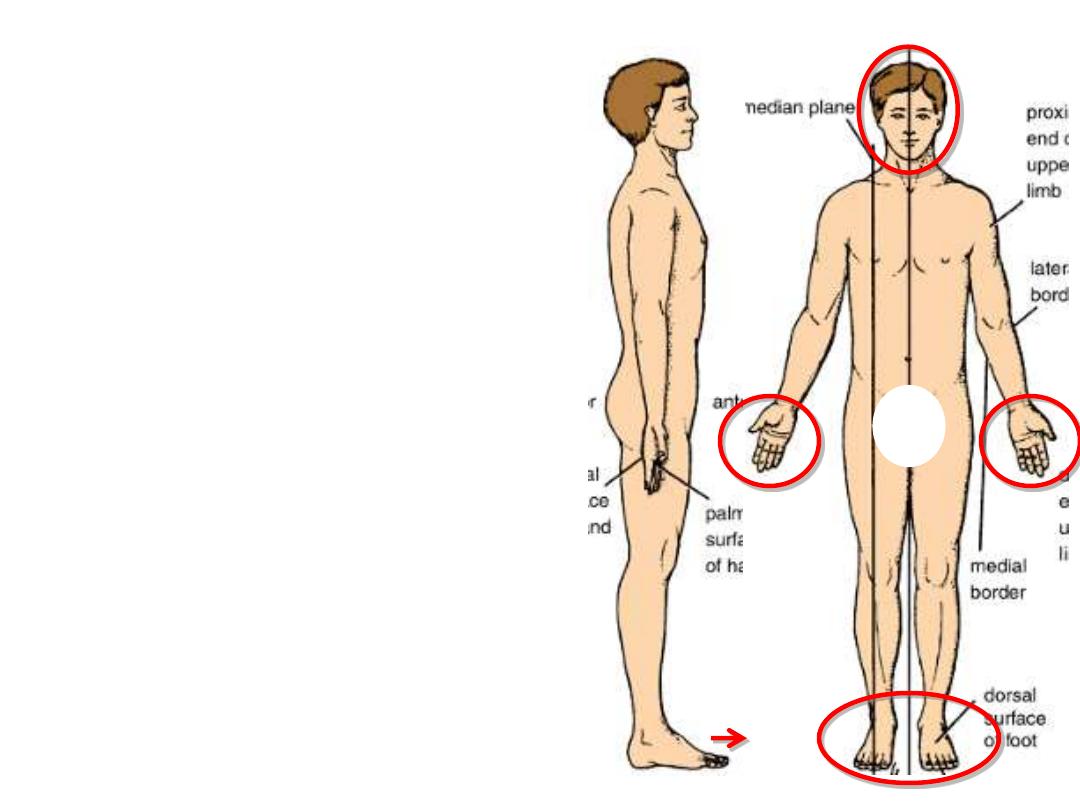
The anatomical position:
-This position is the standard reference
position of the body used to describe the
location of structures
-Standing upright
-Feet together
-Hands by the side
-Face looking forward
-Mouth is closed
-Facial expression is neutral
-Palms face forward with the fingers
straight
-Toes point forward
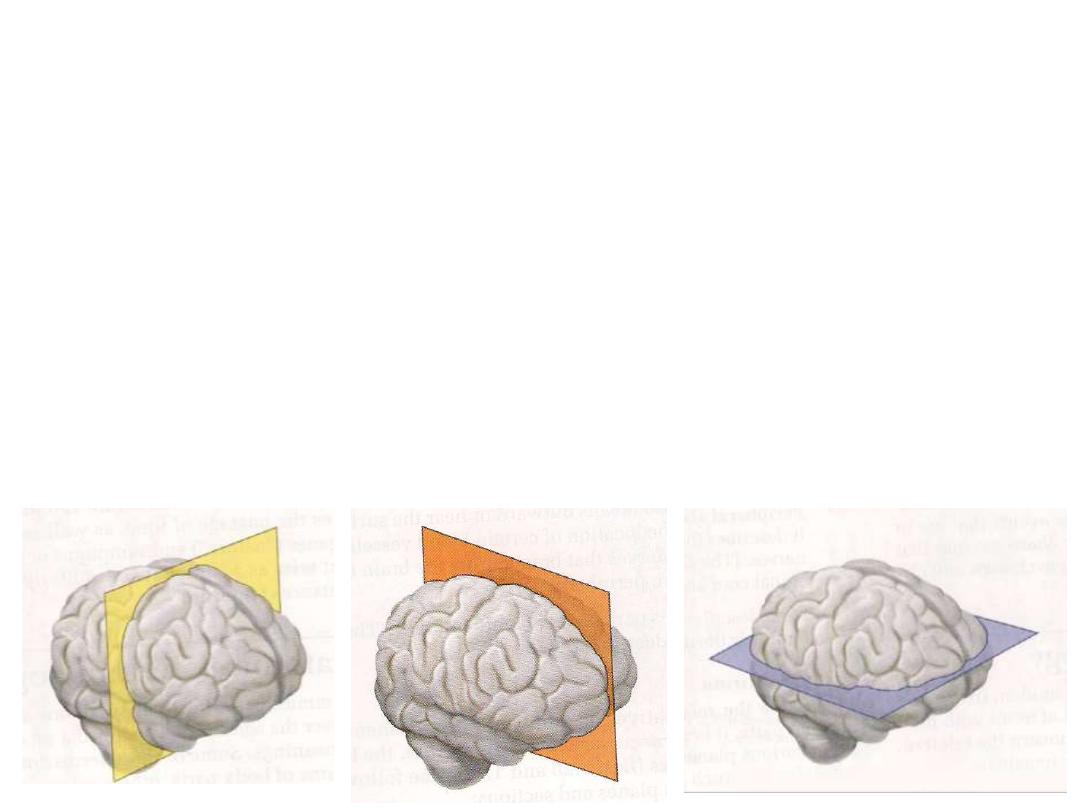
Anatomical planes:
1- Coronal planes
are oriented vertically and divide the body into anterior
and posterior parts.
2- Sagittal planes
are oriented vertically and divide the body into right and
left parts.
The plane that divides the body into equal right and left halves is termed the
median plane.
3- Transverse, horizontal, or axial planes
divide the body into superior and
inferior parts.
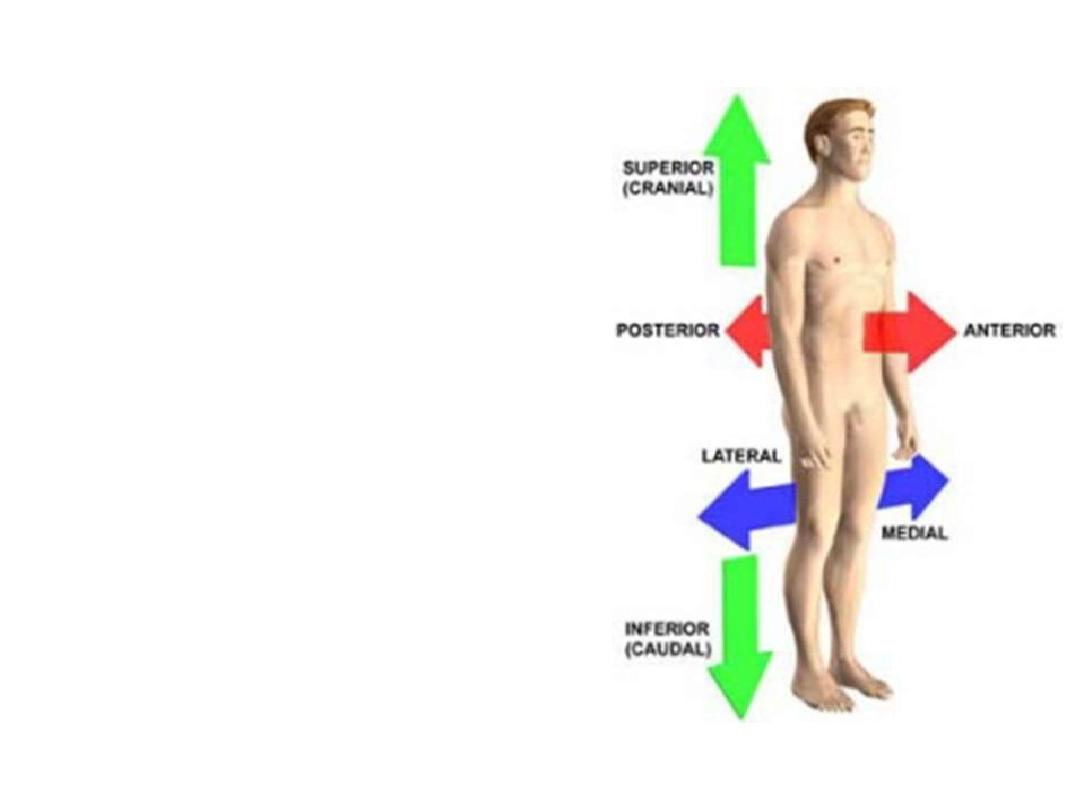
Terms of relationship:
These are terms used to describe the
location of structures relative to the body
as a whole or to other structures
1- Anterior & posterior:
describe the
position of structures relative to the
'front' and 'back' of the body:
. Anterior; nearer to the front
. Posterior; nearer to the back
In the trunk (ventral-dorsal)
In the palm (palmar-dorsal)
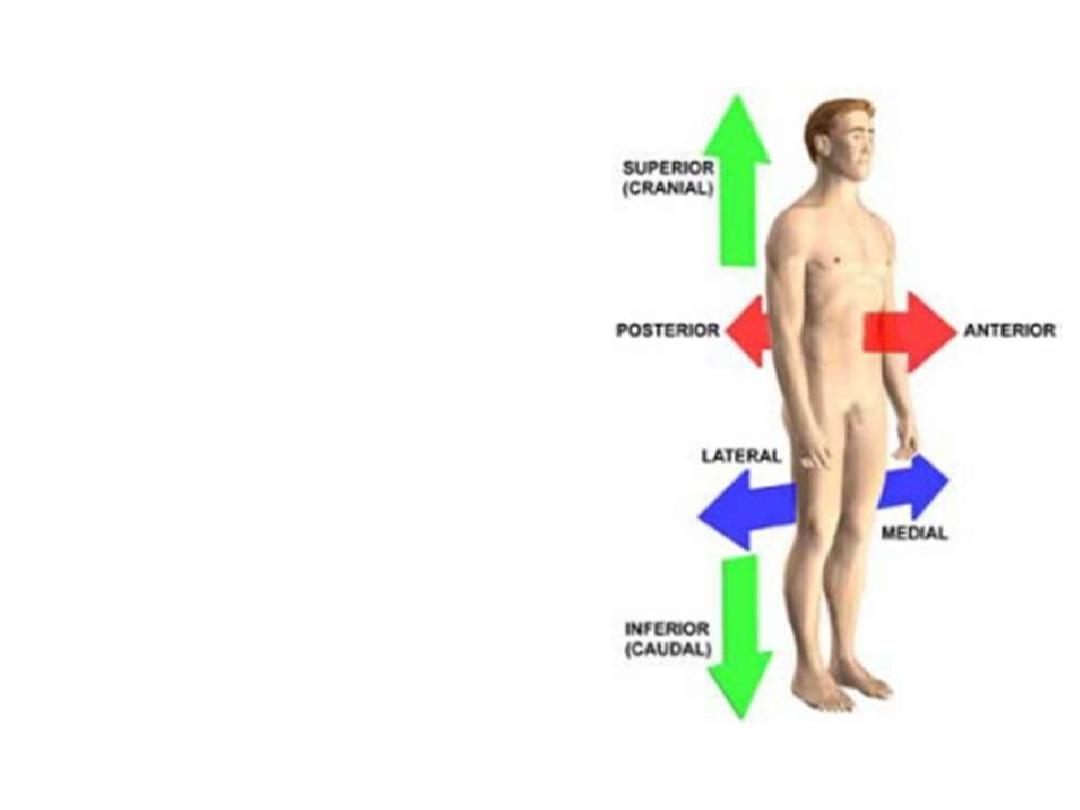
2- Medial and lateral:
describe the
position of structures relative to
the median plane
. Medial; nearer to the median
plane
. Lateral; away from the median
plane
3- Superior and inferior:
describe
structures in reference to the
vertical axis of the body.
. Superior; nearer to the vertex
. Inferior; nearer to the sole
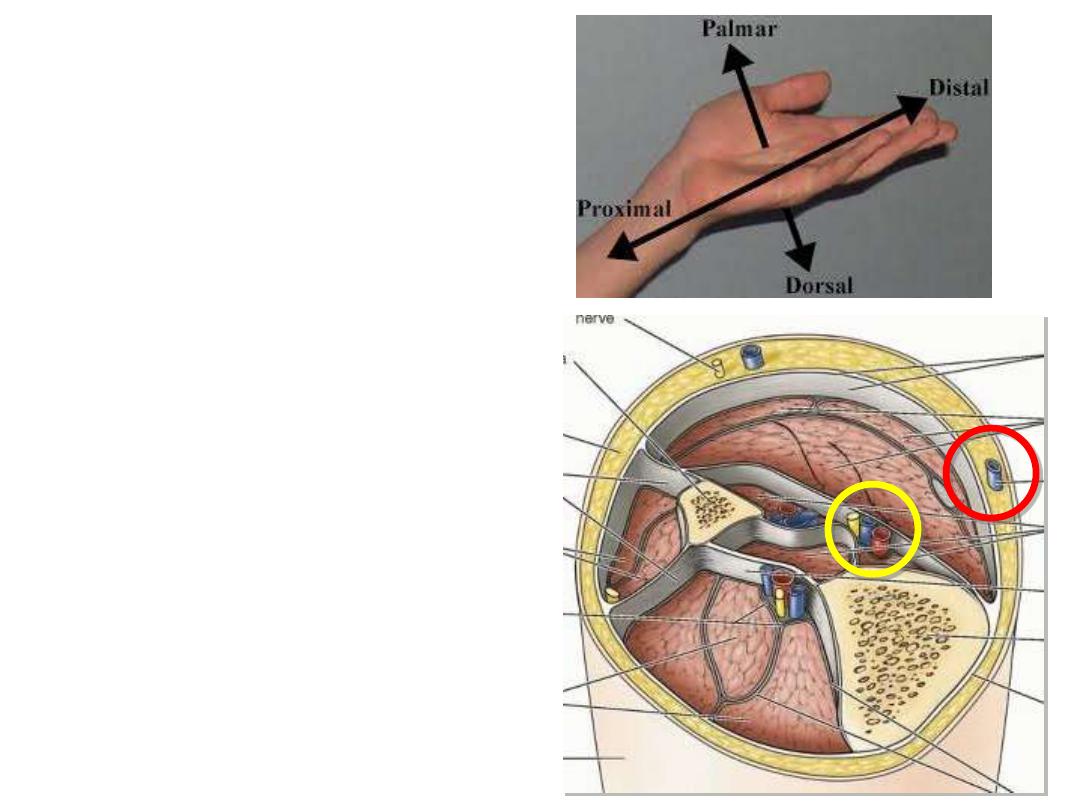
4- Proximal & distal:
used with
reference to the origin or attachment of
a structure, particularly in the limbs.
. Proximal; nearer to origin
. Distal; away from origin
5- Superficial & deep:
used to describe
the relative positions of structures with
respect to the surface of the body.
. Superficial; nearer to surface
. Deep; away from surface
6- External & internal:
used to describe
the position in relation to the center
. External; away from center
. Internal; nearer to center
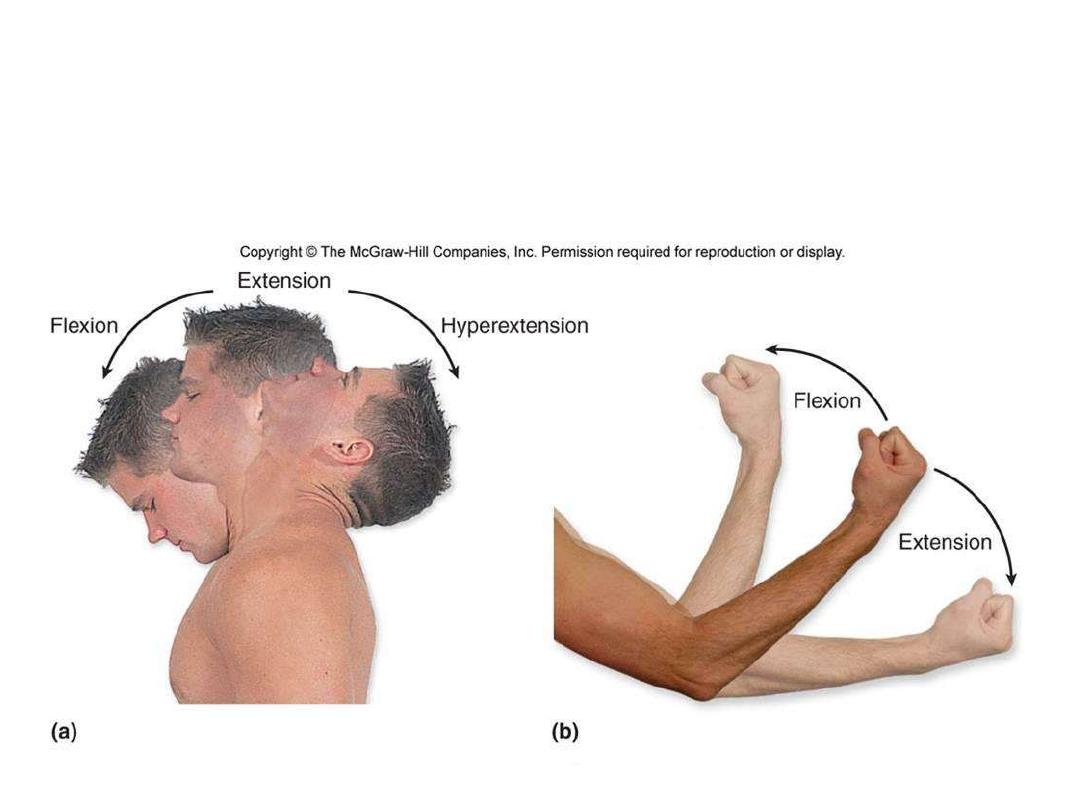
Terms of laterality:
1- Bilateral;
paired structures present on both sides (kidneys)
2- Unilateral;
unpaired structure present on one side (spleen)
3- Ipsilateral;
relating things to the same side of the body
4- Contralateral;
relating things to different side of the body
Lesion produces ipsilateral symptoms
(Green)
Lesion produces contralateral symptoms
(Red)
Terms of movement:
1- Flexion (bending)
– extension (stretching)
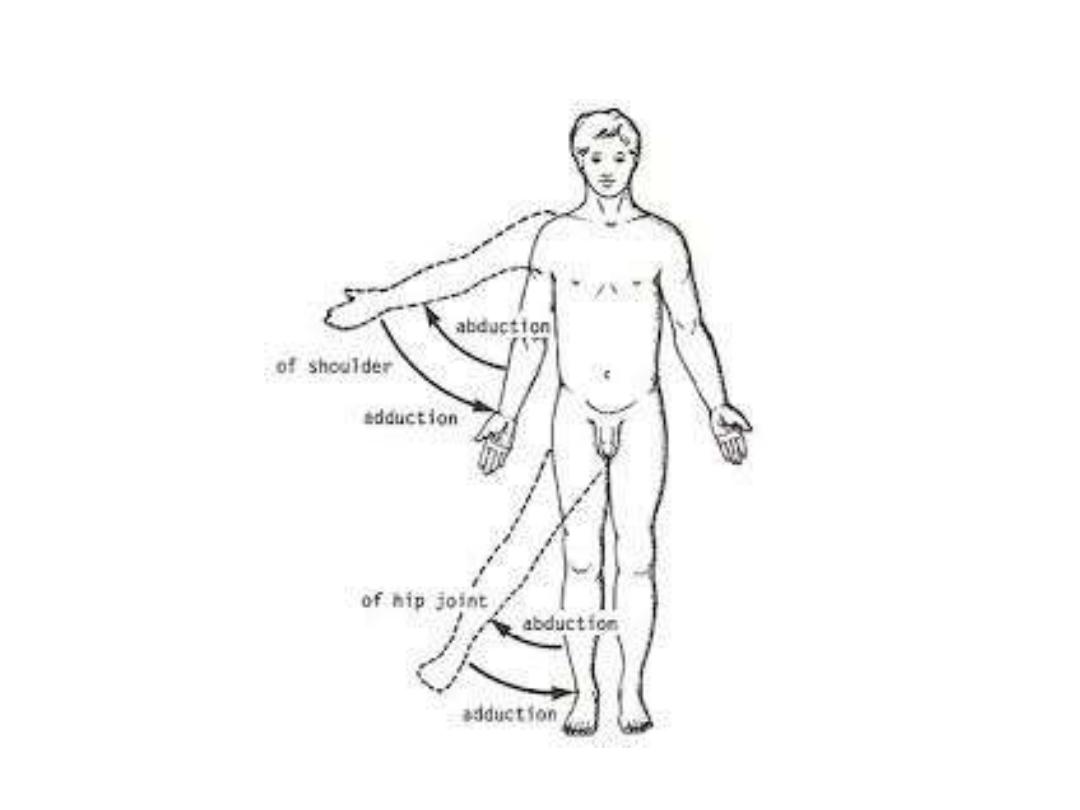
2- Adduction (towards)
– abduction (away)
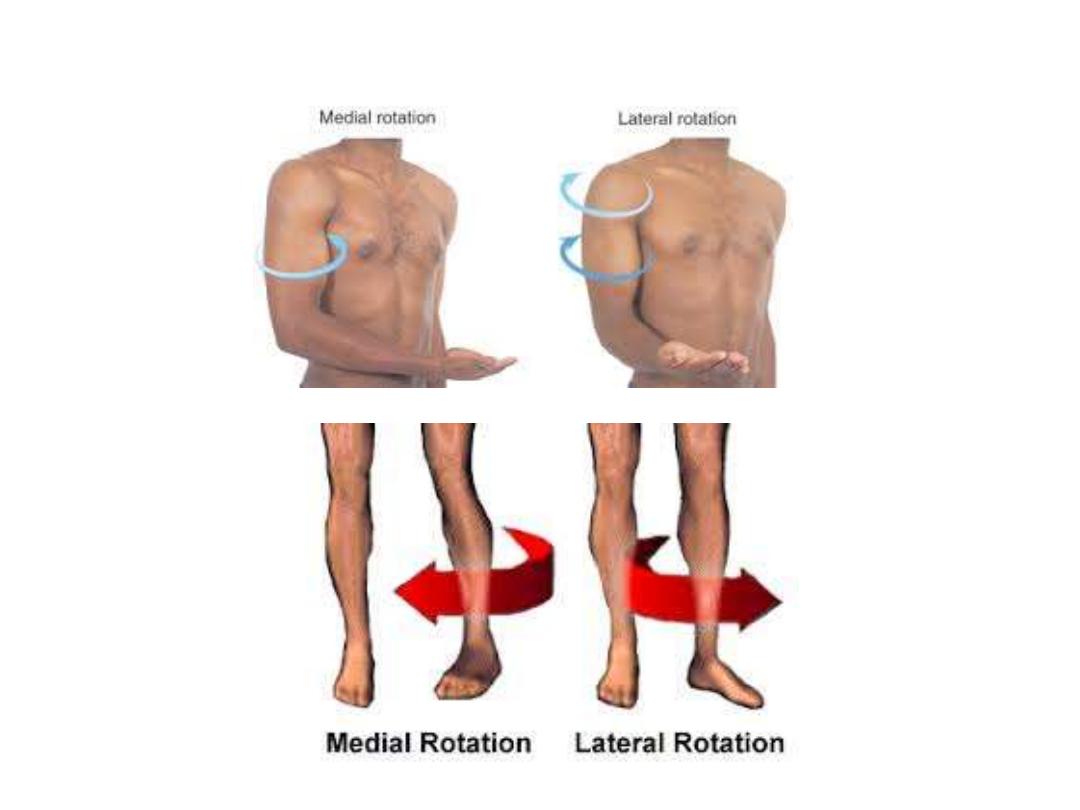
3- Rotation (medial & lateral)
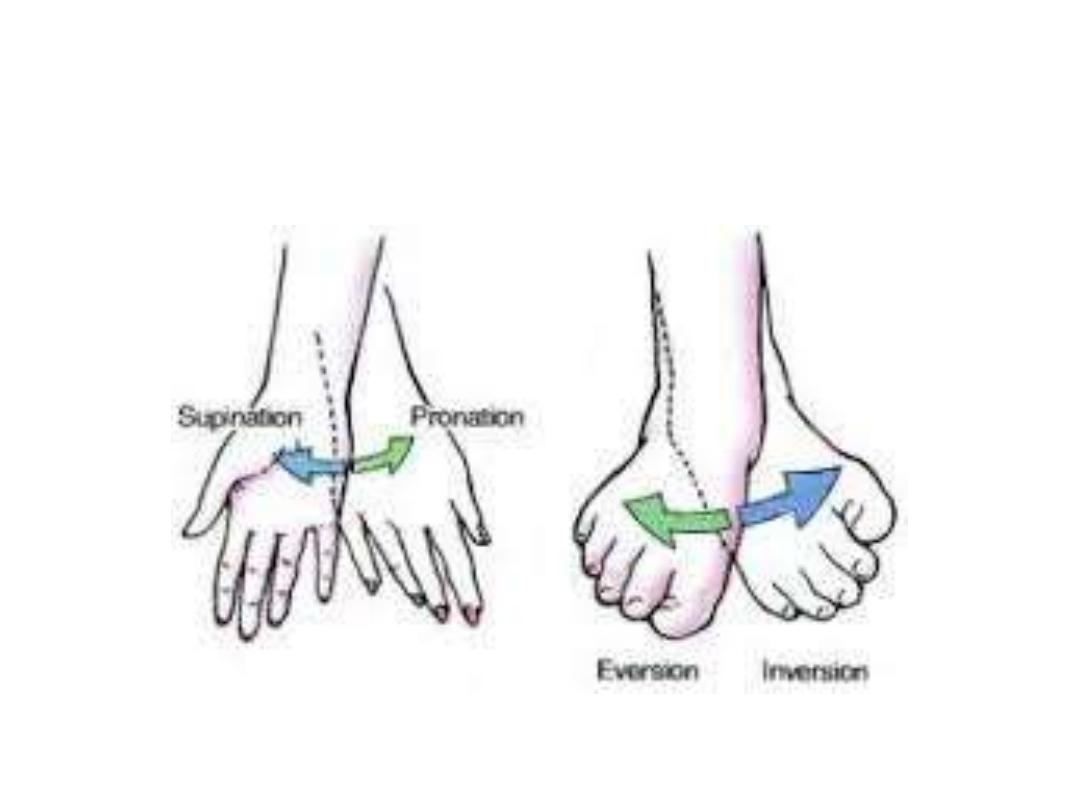
4- Pronation
– supination
5- Eversion - inversion
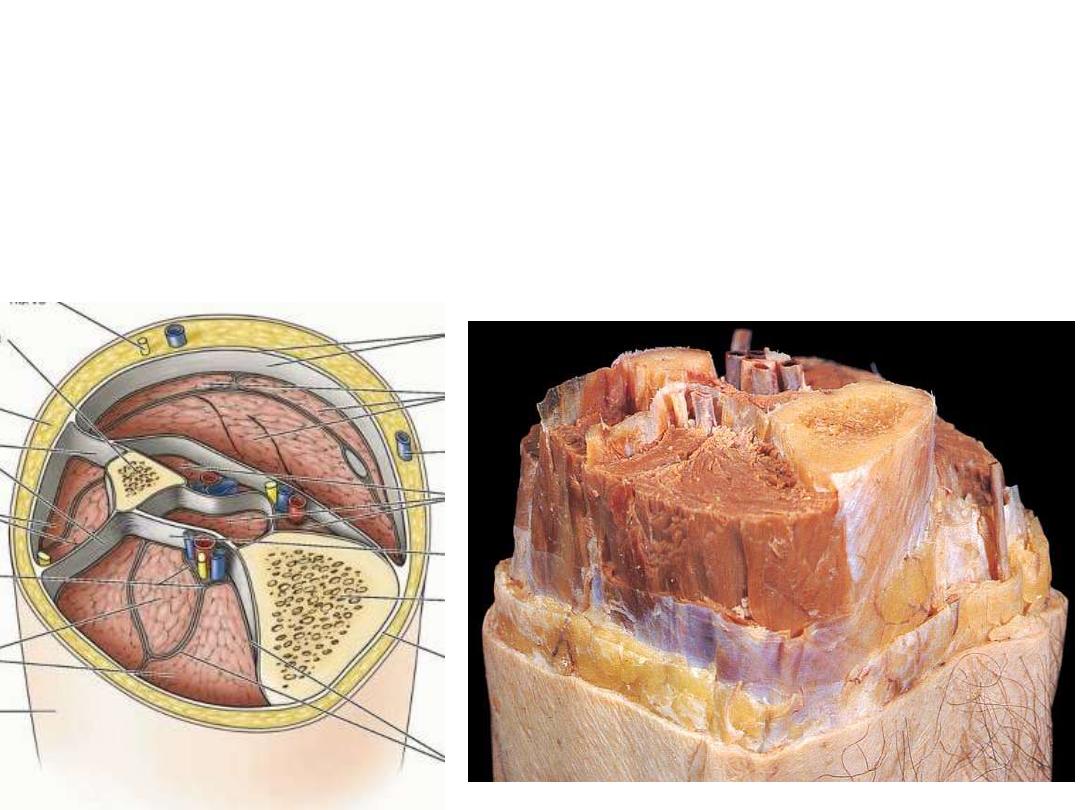
Fascia:
•Superficial: usually fatty
•Deep: mostly membranous
Reflects neurovascular & lymphatic supply
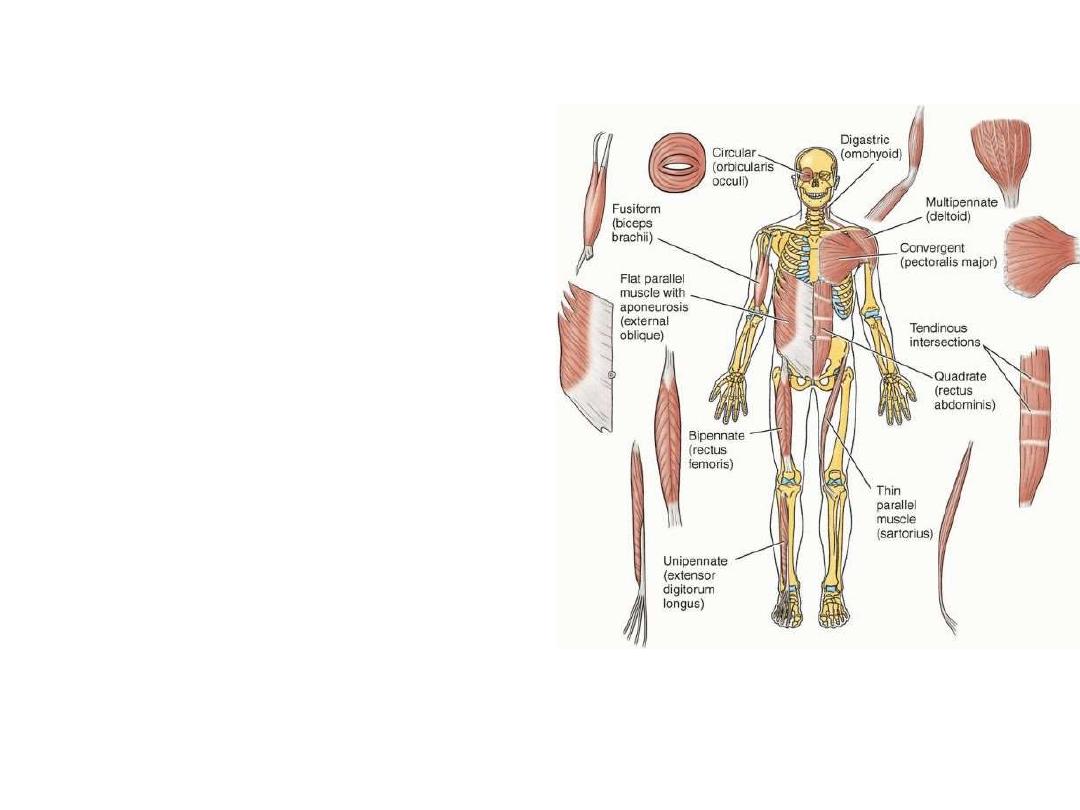
Muscles:
-
Muscles are for movement
-
Movements could be skeletal or visceral
-
They do so by a process called contraction
-
Contraction is shortening of the fibers which
form the muscle
Classification:
1- Voluntary muscles (skeletal)
2- Involuntary muscles:
A) Cardiac muscles
B) Smooth muscles
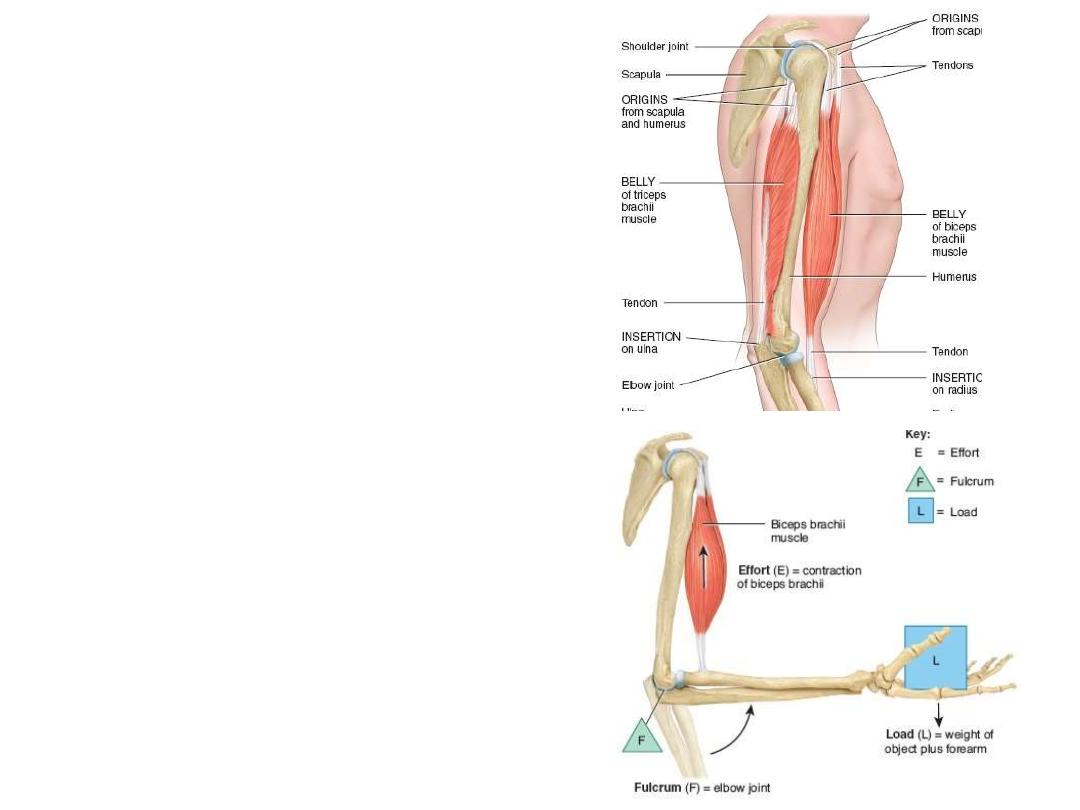
Terms related to muscles:
-Origin:
is meant to imply its more fixed
or central attachment
-Insertion:
the movable point
-Prime mover:
direct action performance
-Synergist:
assists the prime mover
-Antagonist:
opposes or inhibits the
prime mover
-Fixator;
a muscle which fixes certain
parts to promote the action of the acting
muscle & reduce power loss
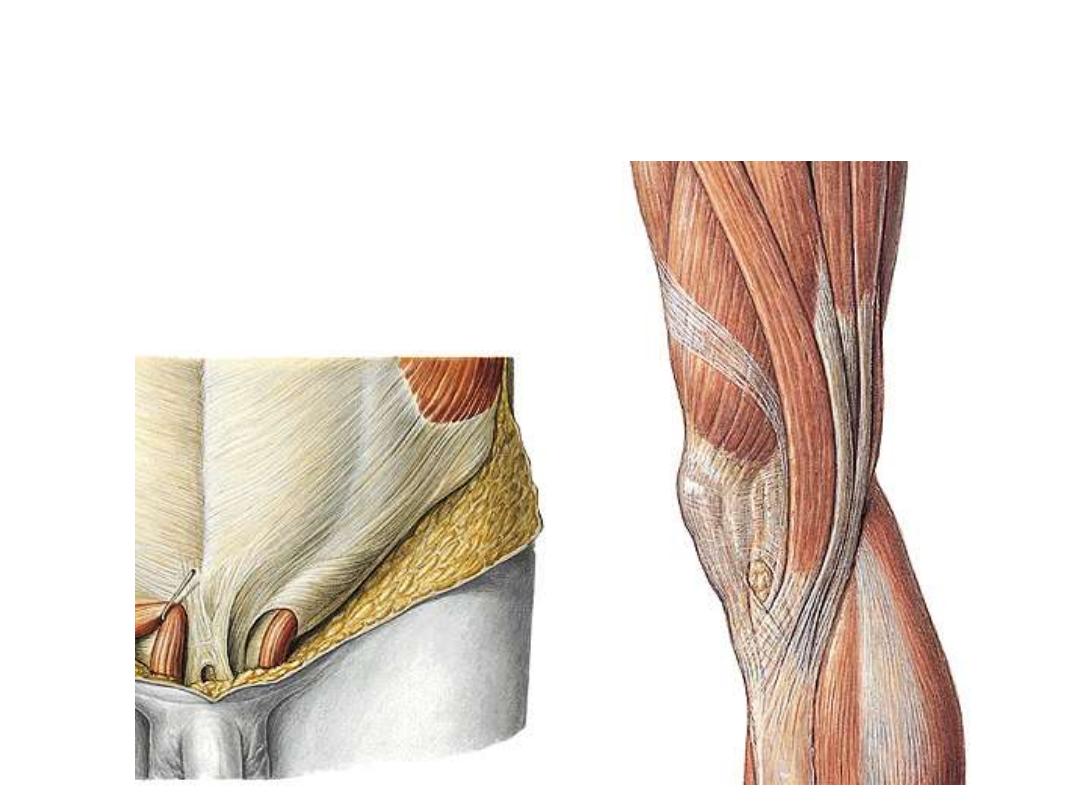
Muscle tendons:
White, glistening, inelastic fibrous cords which lie at muscle ends
Aponeuroses:
-The non fleshy part of flat muscles
-They appear white, glistening, parts
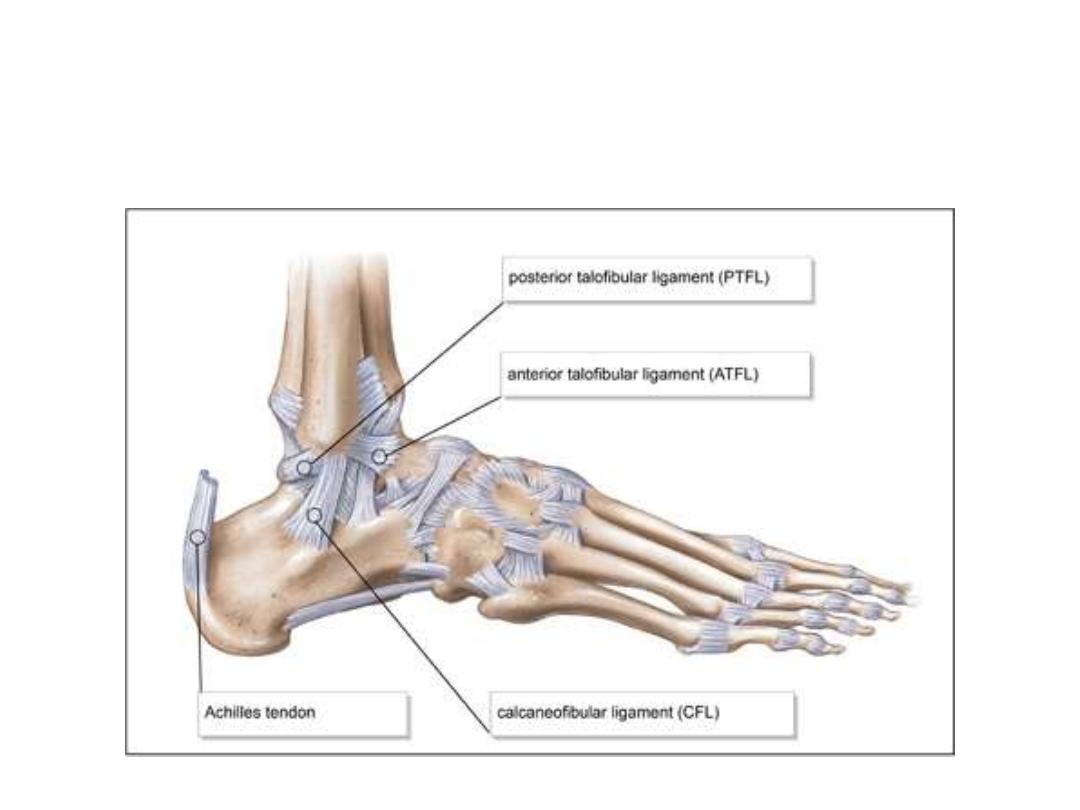
Ligaments:
-A ligament is a cord of connective tissue uniting two structures
-Usually associated with joints
