
Toxoplasmosis
Protozoan infection caused by Toxoplasma parasite
Family: Sarcocystidae
Genus: Toxoplasma
Toxoplasma gondii (T. gondii)
- Obligate intracellular
- Infecting all warm blood animals
- Domestic cats are the only definitive hosts (multiply asexually)
Morphology
Toxoplasma can convert into various cellular stages
:
1- Tachyzoite:
- crescentic in shape
- motile
- pointed anterior end and a rounded posterior end
- spherical or ovoidal nucleus near the pointed end
- quickly multiplying (responsible for expanding the population of the
parasite in the host)
- spread throughout the body via the blood stream
- Tachyzoites stage-convert to Bradyzoites to form tissue cysts.

2- Bradyzoite:
- Similar to tachyzoite
- the parasite make up tissue cysts (during the chronic infections)
- the slowly dividing stage
- when an uninfected host consumes a tissue cyst, bradyzoites released from
the cyst infect intestinal epithelial cells before converting to the
proliferative tachyzoite stage. Following the initial period of proliferation
throughout the host body, tachyzoites then convert back to bradyzoites,
which reproduce inside host cells to form tissue cysts in the new host.
3- Oocysts:
- spherical or ovoid
- non-infectious (outside host) in the soil
- develop only in the intestine of the definitive hosts – cats
- the parasite develop into 2 sporoblast which converted into sporocysts
surrounded by wall (environmentally resistant).
- Each sporocyst contains 4
sporozoites (the infective form)
- The sporozoites are released inside the intermediate host
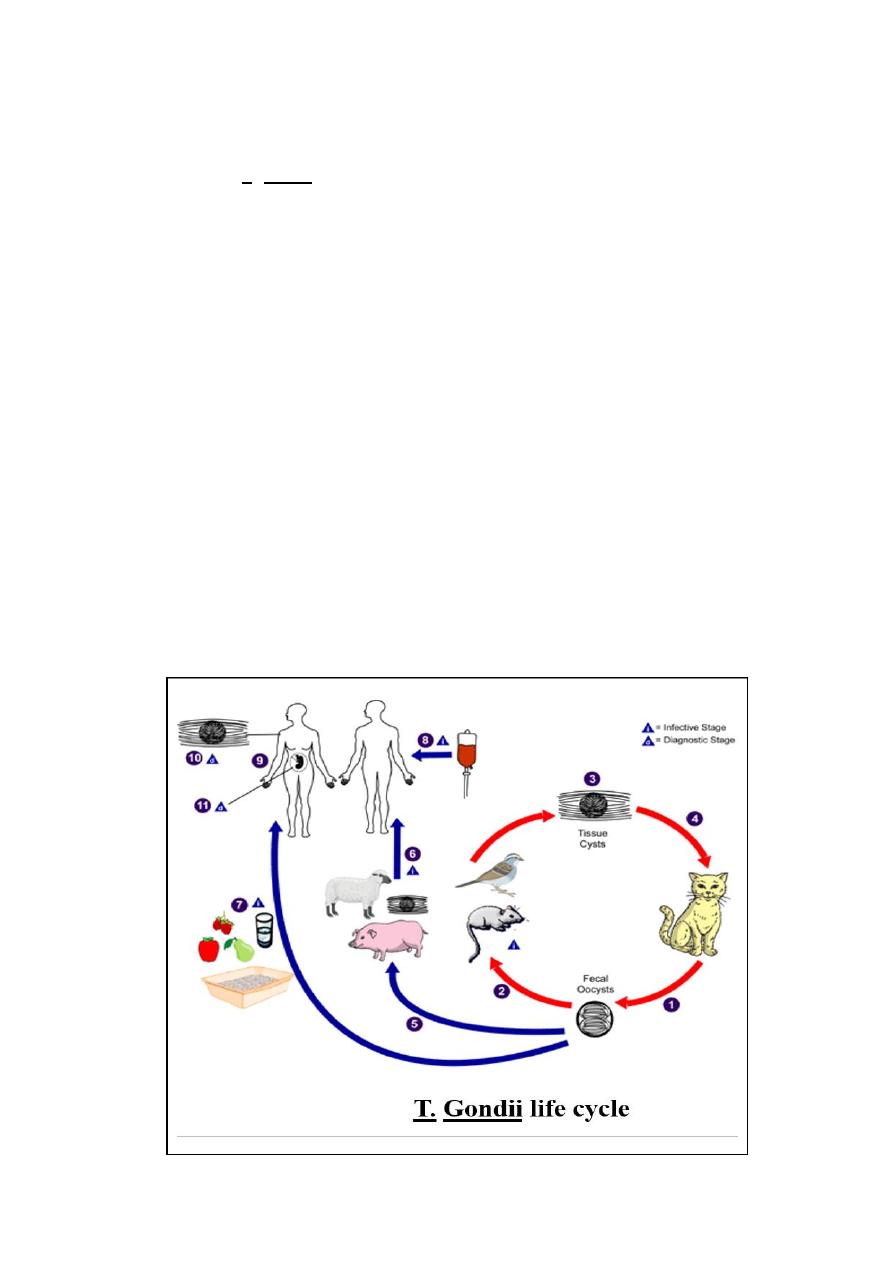
Life cycle
The life cycle of T. gondii consists of two stages asexual and sexual:
Asexual stage:
-
takes place in the intermediate hosts, which are mammals or bird
-
During this stage rapid intracellular growth of the parasite as tachyzoite takes place
(generation time in vitro is 6 – 8 hr). The oval or crescent – shaped tachyzoites can
infect and multiply in almost any nucleated mammalian or avian cell (acute infection)
-
Convert to bradyzoites (tissue cyst) to avoid the host immune response, limit the
acute stage and establish a chronic infection
.
Asexual stage:
-
takes place in the intestine of the definitive host (feline family) domestic cast
-
bradyzoites or Oocysts are ingested by a feline, formation of Oocysts processed in
the epithelium of the small intestine.
-
The Oocytes,
sporocyst and sporozoites
then released in the faeces of the feline to
the environment

Toxoplasmosis has three stages:
1- Acute toxoplasmosis:
- tachyzoites are present
- sometimes asymptomatic in healthy adults
- symptoms are often influenza-like:
swollen lymph nodes, headaches, fever, and fatigue or muscle aches and pains
that last for a month or more.
infants infected via placental transmission may be born with either of these
problems, or with nasal malformations.
2- Latent toxoplasmosis:
- only bradyzoites (tissue cysts) are present
3- Cutaneous toxoplasmosis
- skin lesions may occur in the acquired form of the disease.
Transmission
Humans get infected by:
- blood transfusion or organ transplantation (very rare)
- consuming undercooked, infected meat (especially lamb, pork and venison)
- ingesting water, soil (for example, putting dirty fingers in your mouth) or
anything else that has been contaminated with cat faeces
- mother-to-child transmission. A pregnant woman, who has just been infected
with Toxoplasma gondii can pass the infection to her unborn baby (congenital
infection). She might not have any symptoms, but the unborn child might suffer
and develop disease.
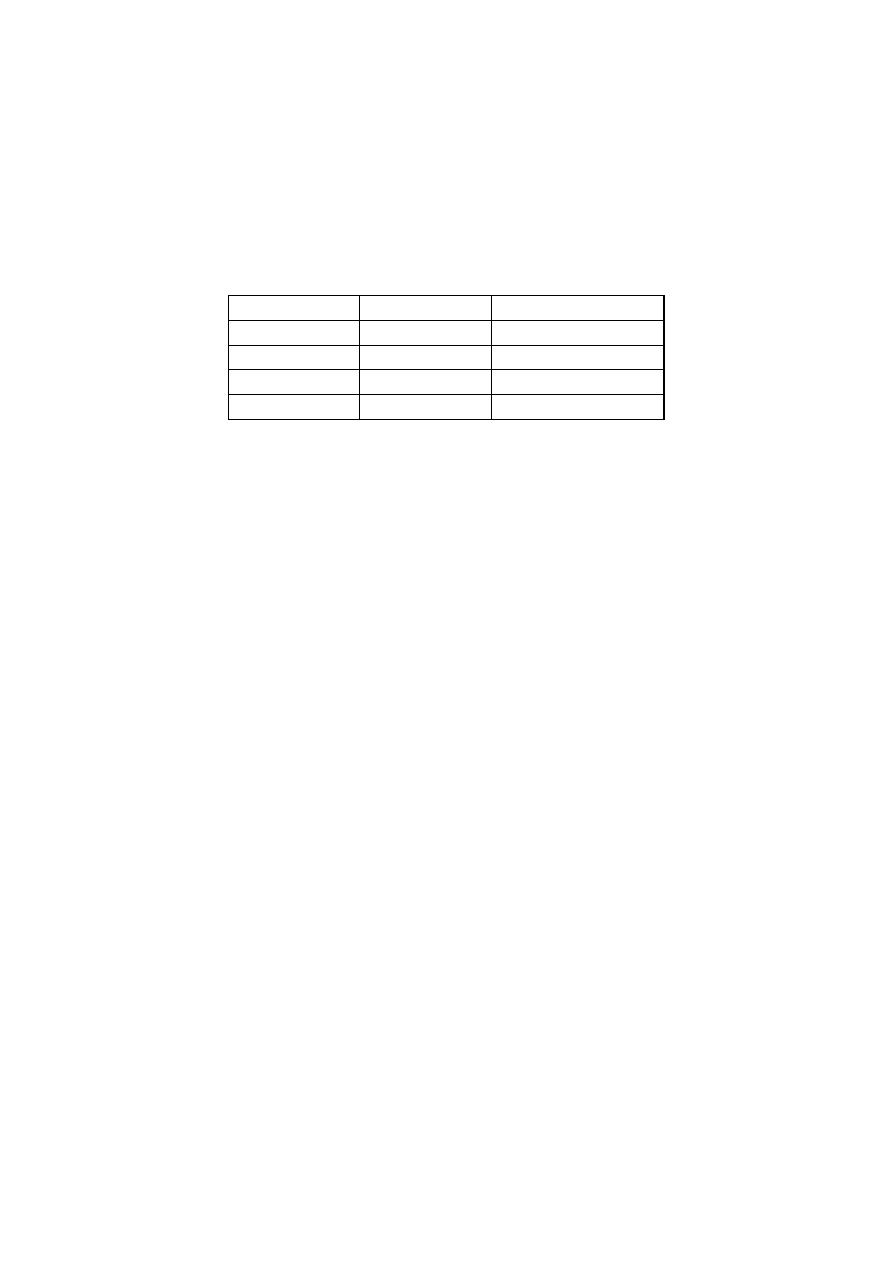
Diagnosis
- indirectly by serologic tests through detecting immunoglobulin antibodies (IgG
and IGM)
- IgM antibodies can be detected in the first week of infection (peak 2-4 weeks)
- IgG can be detected later (peak 2-4 months), last for many years
IgM
IgG
-ve
-ve
No infection
+ve
+ve
Acute infection
+ve
-ve
Acute infection
-ve
+ve
Chronic infection
Treatment
Trisulfapyrimidines or sulfadiazine, plus folic acid
