Leishmaniasis
Protozoan infection caused by Leishmania parasite which is spread by sandflies.
Family:
Genus: Leishmania
3 types of leishmaniasis:
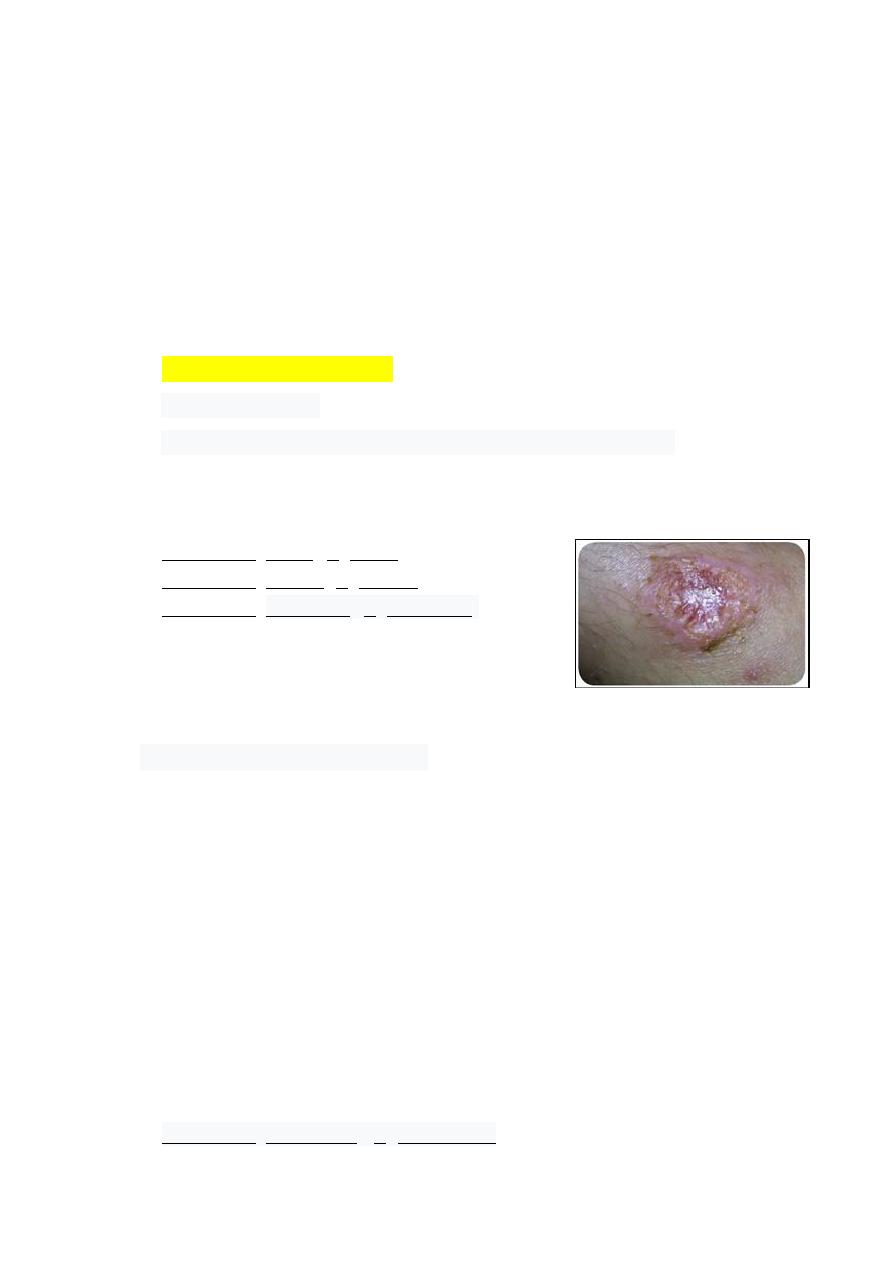
1- Cutaneous leishmaniasis
- The most common
- Affects the skin (face, arms, legs) causing skin sores or scars
- There may be a large number of lesions – sometimes up to 200 – which can cause
serious disability
- Leishmania major (L. major)
- Leishmania tropica (L. tropica)
- Leishmania aethiopica (L. aethiopica)
2- Mucocutaneous leishmaniasis:
The lesions can lead to partial or total destruction of the mucous membranes of
the nose, mouth and throat cavities and surrounding tissues. This disabling form
of leishmaniasis can lead to the sufferer being rejected by the community.
Symptoms usually appear one to five years after skin lesions heal. These are
primarily ulcers in the mouth and nose or on the lips. Other symptoms may
include:
- stuffy or runny nose
- nose bleeds
- difficulty breathing
- Leishmania braziliensis (L. braziliensis)
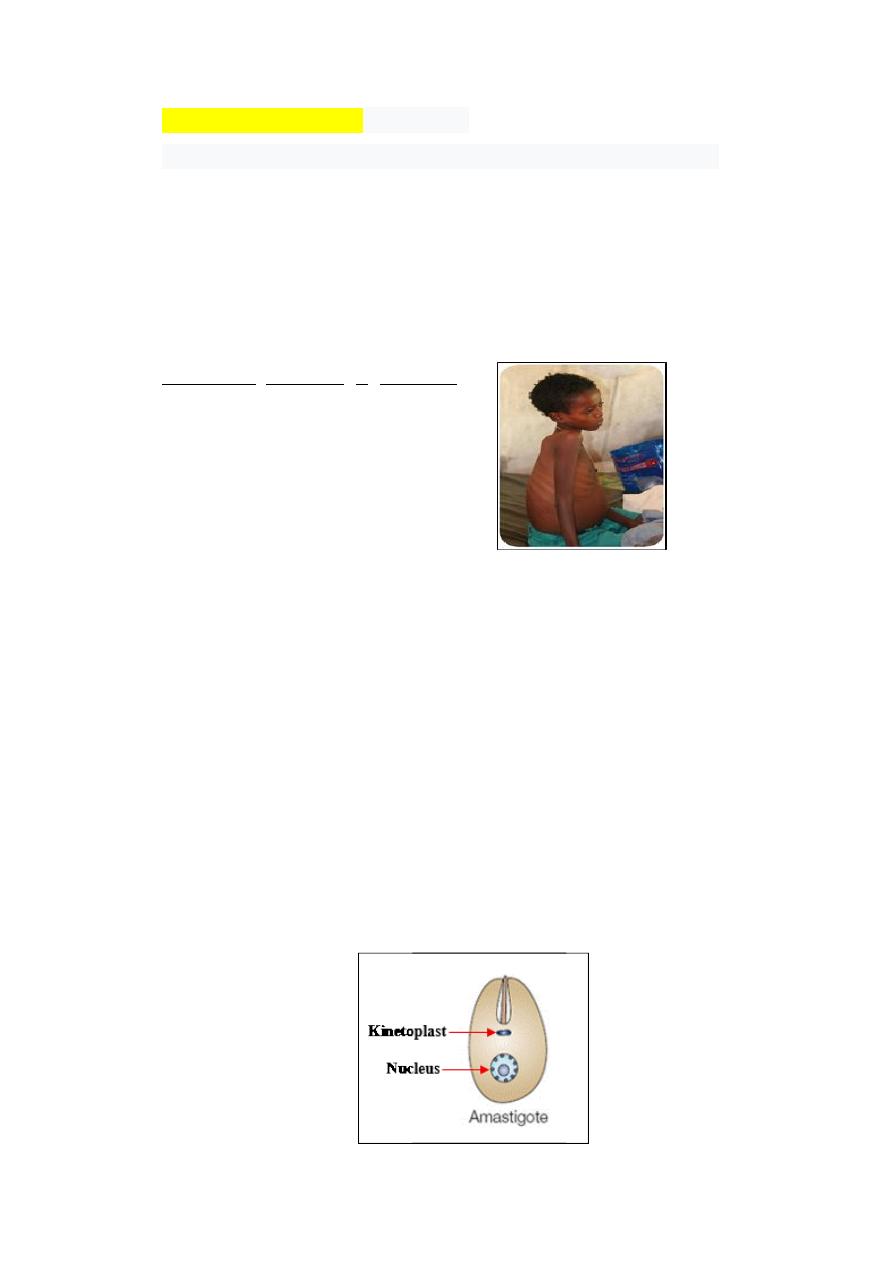
Visceral leishmaniasis (Kala azar)
- Affects internal organs (spleen, liver, bone marrow, lymph nodes)
- anaemia
- enlarged liver and spleen
- fever
- Weight loss
- weaker inflammatory response (due to the loss of phagocytes)
- Leishmania donovani (L. donovani)
Morphology & life cycle
- 2 hosts Vertebrate (human and animals) and invertebrate (sandfly)
- 2 morphology stages:
Amastigote: is the intracellular, oval shape, non-motile form in the vertebrate
host, and it divides by longitudinal binary fission at 37
o
C, 3-6 um in length and
1.5-3.0 um in width. The amastigote is also called the Leishman-Donovan
(LD) body. The amastigote is not really lack the flagellum, it is simply that the
flagellum does not extend beyond the body surface and by light microscopy
cannot be seen.
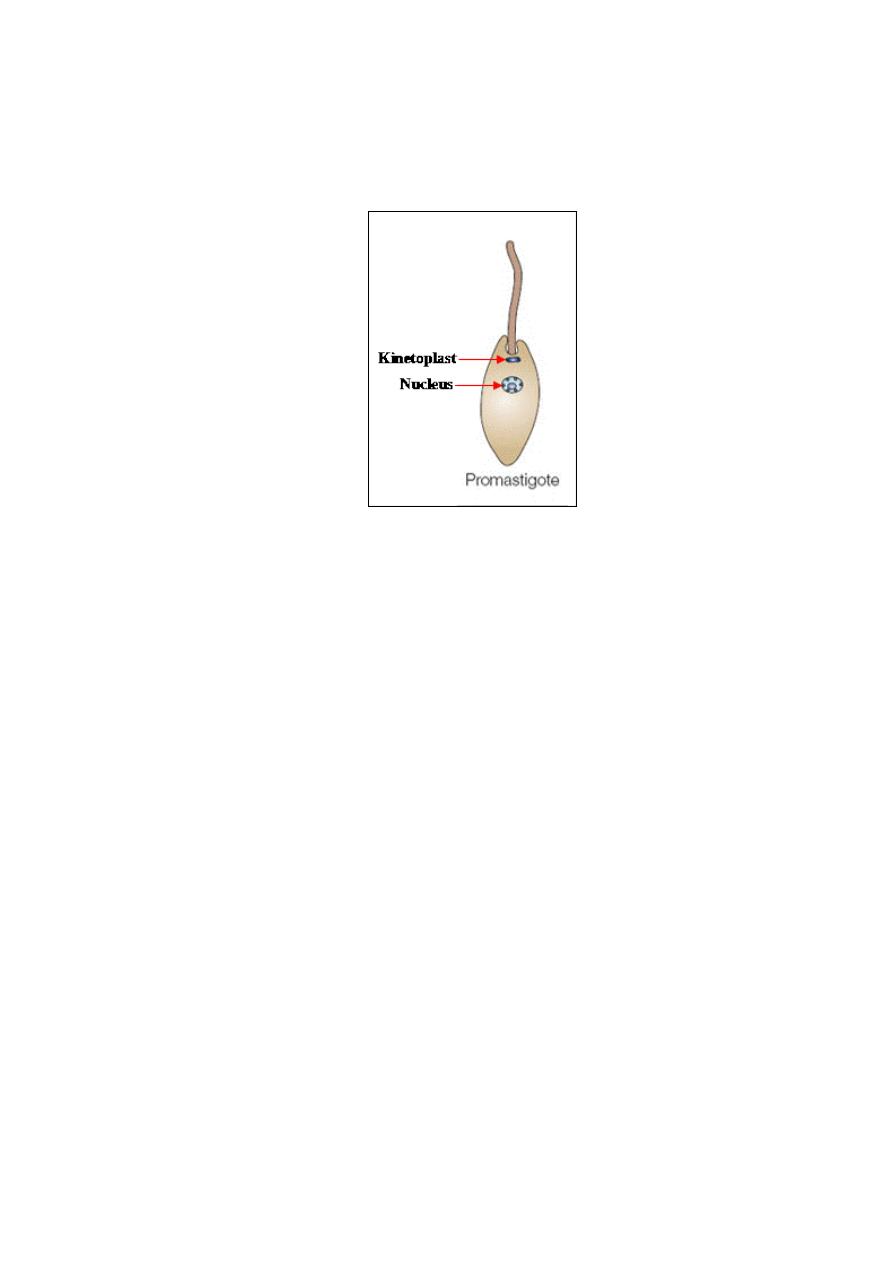
Promastigote:
is the
extracellular, larger and more elongated (spindle shape),
motile form in the invertebrate host (sandfly), and grows and divides by
longitudinal binary fission at 27
o
C in the sandfly.
Definitive host:
Promastigotes are injected by sandfly through the human skin during its blood
meal. Some promastigotes may enter the blood stream directly where some are
destroyed by macrophages. But many are also taken up through phagocytosis to
the liver, spleen and bone marrow. Then the amastigotes undergo cell division
using simple binary fission. Multiplication continues until the host cell can no
longer hold and ruptures. Each individual amastigote is then capable of invading
fresh cells. As a result, the entire tissue is progressively infected and destroyed.
Intermediate host:
Once the amastigotes are ingested, they undergo further development only in
the digestive tract of the female sandfly. Then they undergo structural
modification into flagellated promastigotes, becoming larger and considerably
elongated, and multiply by binary fission.
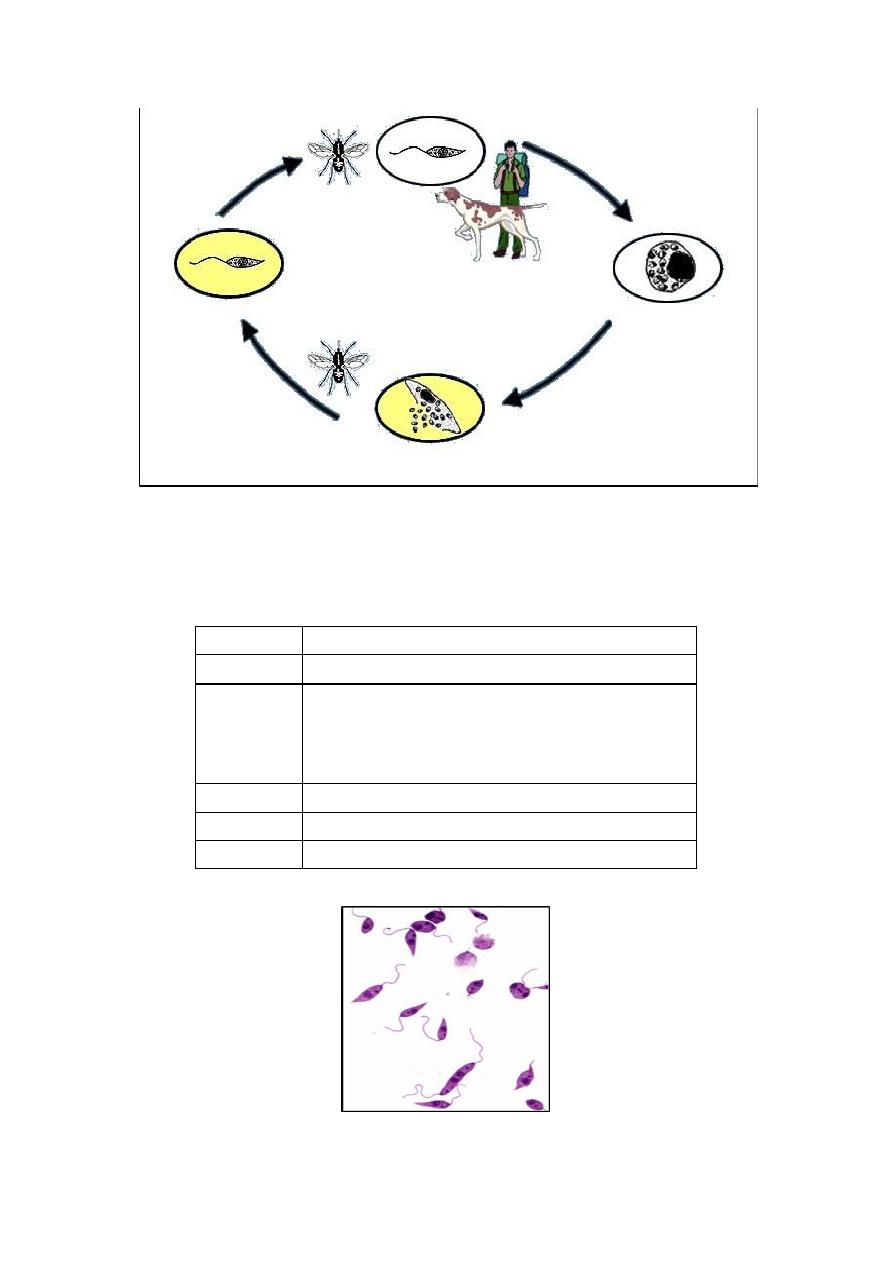
Diagnosis: (Microscopic examination)
Trophozoite
Specimen Blood, tissue smear,
Method
Leishman stain:
Add 7-8 drops of the stain and
leave for 1-2 minutes. Then add 12-15 drops of
buffered distilled water, mix thoroughly, leave for 4
– 8 minutes.
Diseases
Leishmaniasis
Seen
Amastigote stage
Treatment
Amphotericin B
