Clinical biochemistry second stage lecture 7 Dr.Thana Alsewedy
1
Inborn error in metabolism of amino acids
of
olic disorders
are metab
Inborn errors of amino acid metabolism
.
amino acids
.
synthesis and degradation
which impair the
in
Abnormality in
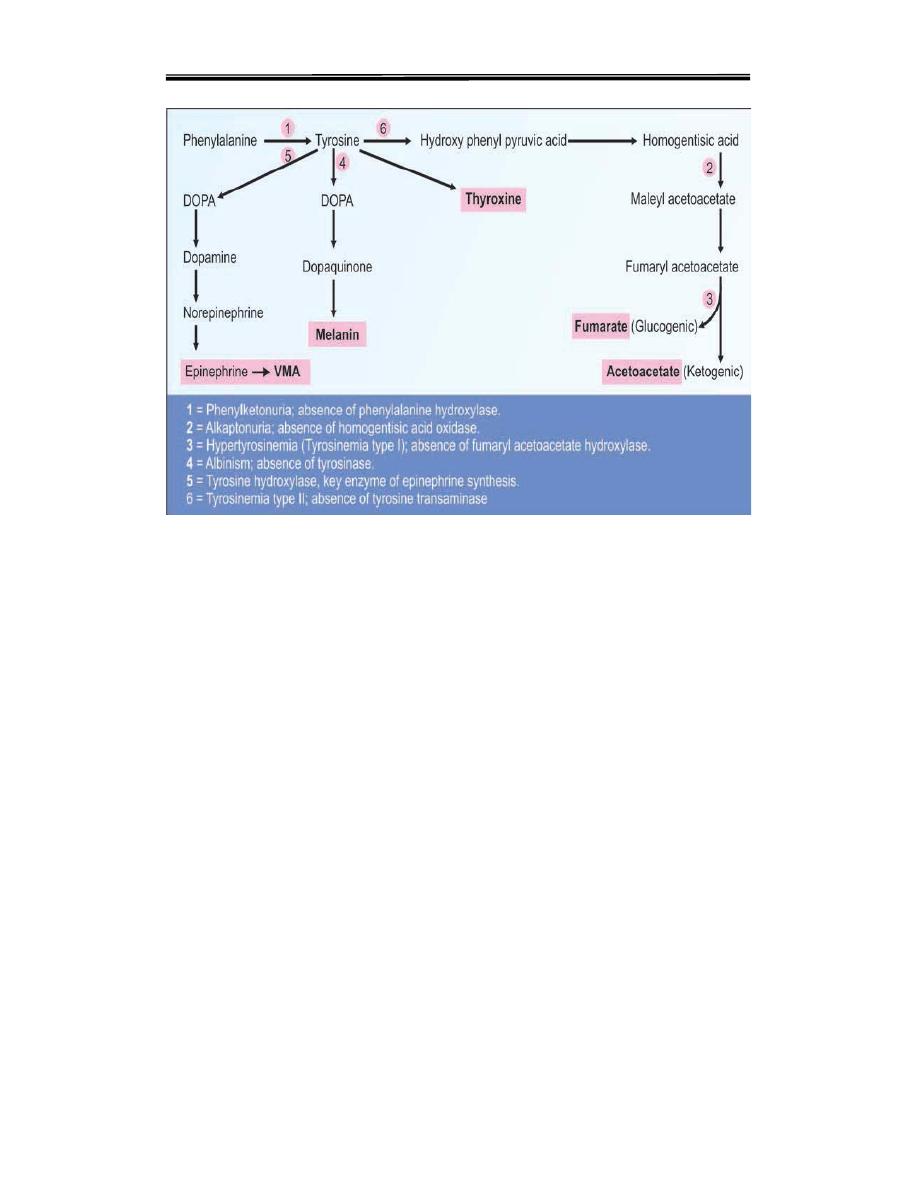
phenylalanine and Tyrosine metabolism
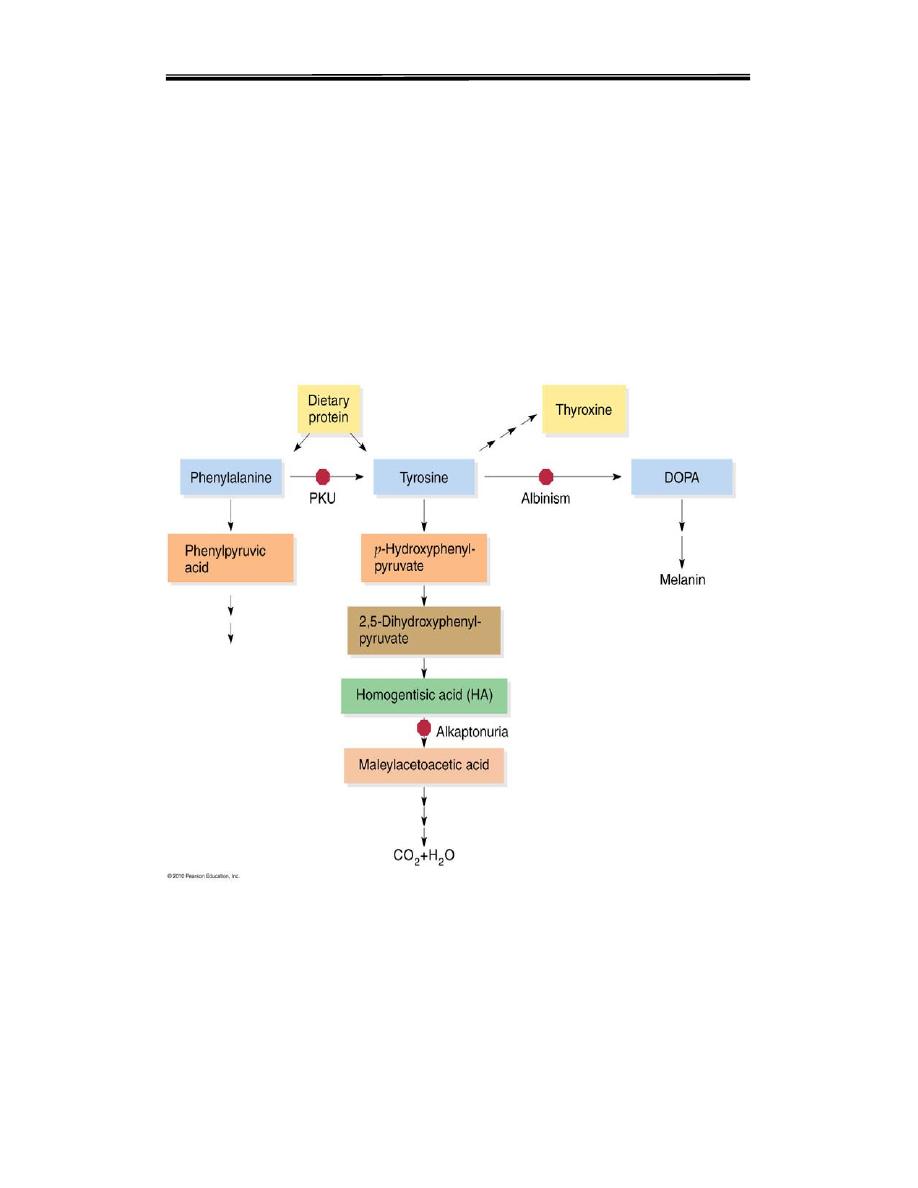
1- PHENYL KETONURIA (PKU)
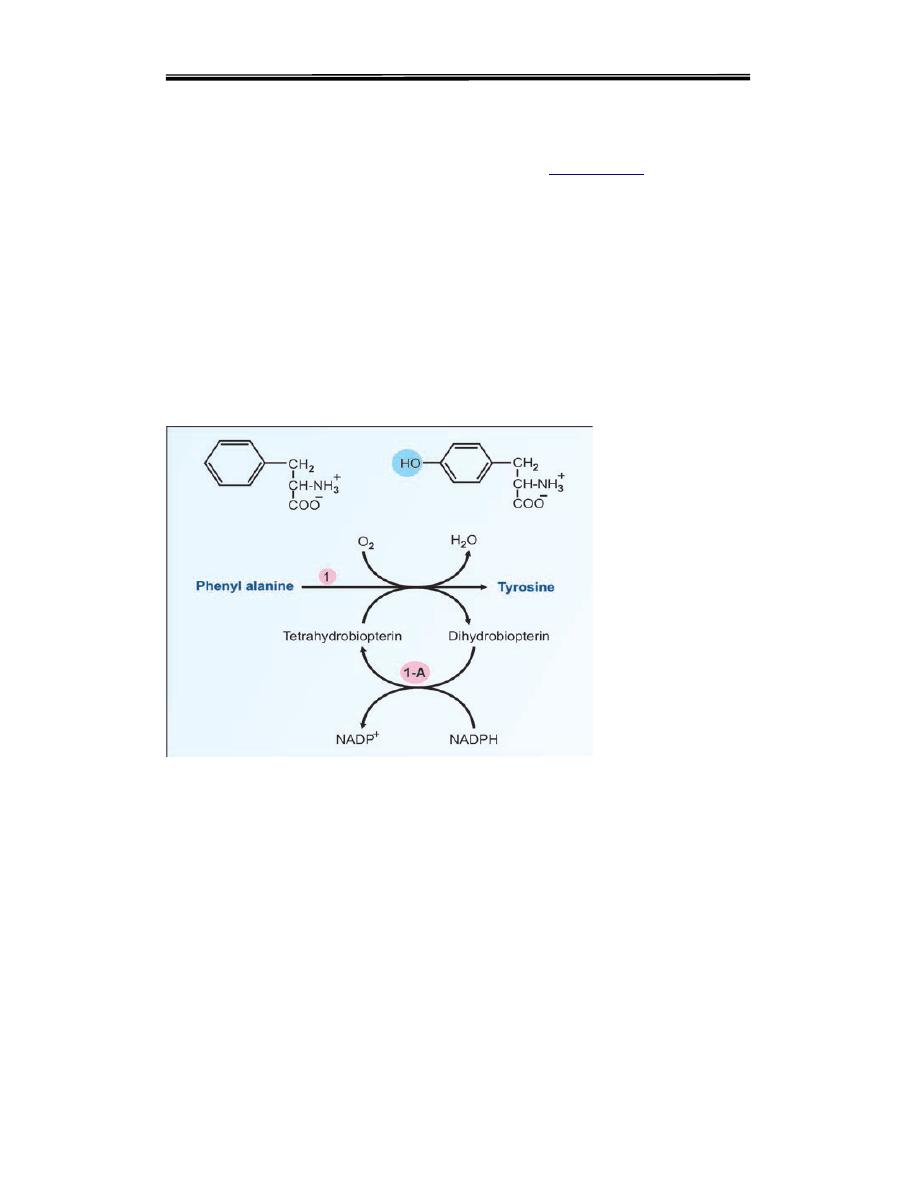
Deficiency of phenyl alanine hydroxylase (Fig.17.1) is the cause for this
disease. The genetic mutation may be such that either the enzyme is not
synthesized, or a non-functional enzyme is synthesized.
Phenyketonuria (PKU) is a genetic disorder that is characterized by an
inability of the body to metabolize phenylalanine, caused by a deficiency
in Phenylalanine Hydroxylase (PAH) enzyme or The defect is due to
deficiency of dihydrobiopterin reductase.an enzyme that catalyzes the
regeneration of tetrahydrobiopterin (cofactor of PAH)
4. Biochemical Abnormalities
A. Phenylalanine could not be converted to tyrosine. So phenylalanine
accumulates. Phenylalanine level in blood is elevated.
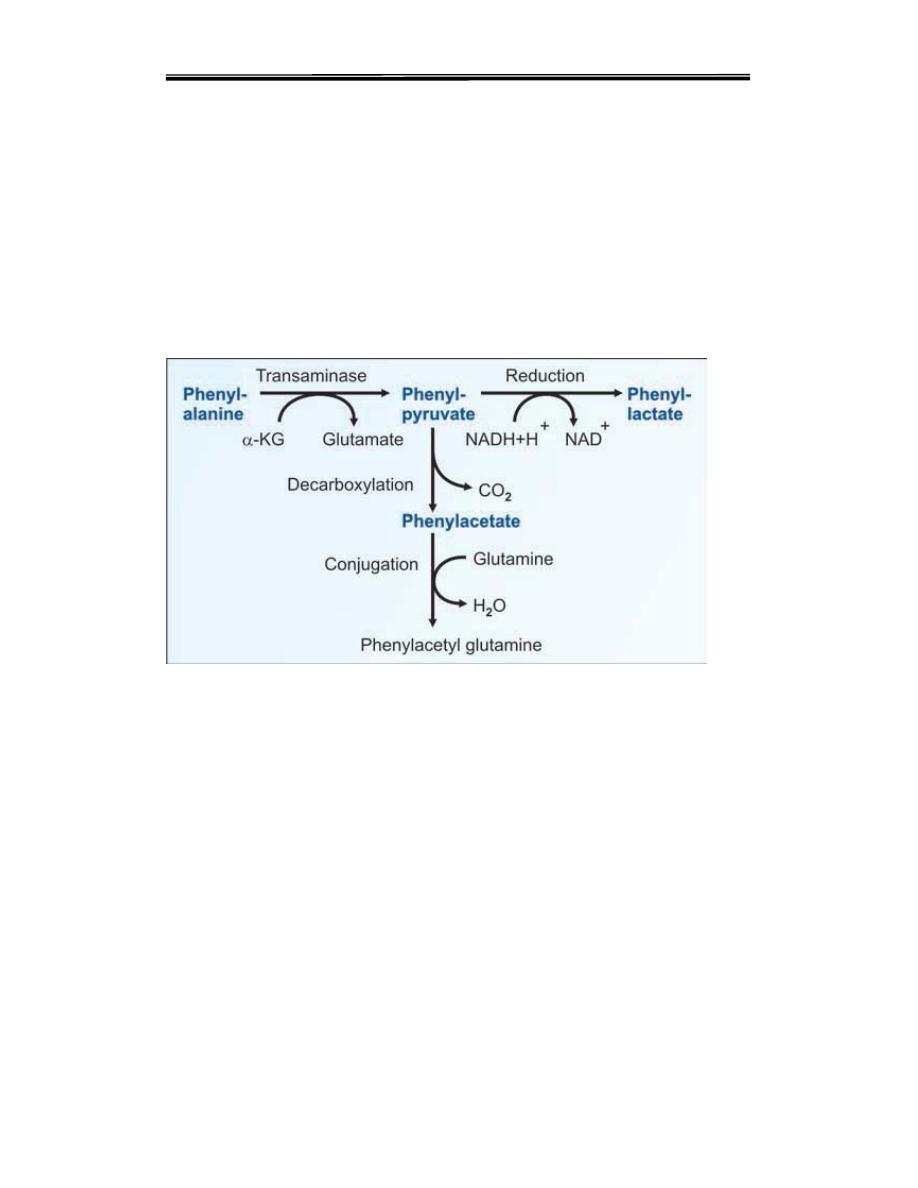
B. So alternate minor pathways are opened accumulation of too much
phenylalanine and its toxic metabolities phenylpyruvic acid, phenyllactic
acid and phenylacetic acid. which becomes a major donor of amino
groups in aminotransferase activity and depletes neural tissue of α-
ketoglutarate. Absence of α-ketoglutarate in the brain shuts down the
TCA cycle and the associated production of aerobic energy, which is
essential to normal brain development.
Phenyl ketone (phenyl pyruvate), phenyl lactate and phenyl acetate are
excretedin urine.
Clinical biochemistry second stage lecture 7 Dr.Thana Alsewedy
2
Clinical Manifestations
A. The classical PKU child is mentally retarded
B. Agitation, hyperactivity, tremors and convulsions are often manifested.
This may be because phenylalanineinterferes with neurotransmitter
synthesis. Since tetrahydrobioptrerin is the co-enzyme
required for serotonin and dopamine, the decreased level of these
neurotransmitters may also result in the neurological symptoms.
C. The child often has hypopigmentation, explained by the decreased
level of tyrosine.
D. Phenyl lactic acid in sweat may lead to mousy body odor.
6. Laboratory Diagnosis
Blood phenylalanine: Normal level is 1 mg/dl. In PKU, the level is >20 mg/dl.
2-Tyrosinemia
Tyrosine is an amino acid which is found in most animal and plant
proteins. The metabolism of tyrosine in humans takes place in liver
Tyrosinemia is caused by an absence of the enzyme fumarylacetoacetate
hydrolase (FAH) which is essential in the metabolism of tyrosine. The
absence of FAH leads to an accumulation of toxic metabolic products in
various body tissues, which in turn results in progressive damage to the
liver and kidneygiving a raised level of tyrosine in blood and urine
clinical symptoms include moderate mental retardation, characteristic eye
and skin lesions and disturbance in fine coordination.
3-Alkaptonuria (Black urine disease)
An inherited defect in the phenyl a lanine – tyrosine pathway involves a
deficiency in the enzyme that catalyses the oxidation of homogentisic
acid (an intermediate in the metabolic breakdown of tyrosine and
phenyalanin).
Clinical biochemistry second stage lecture 7 Dr.Thana Alsewedy
3
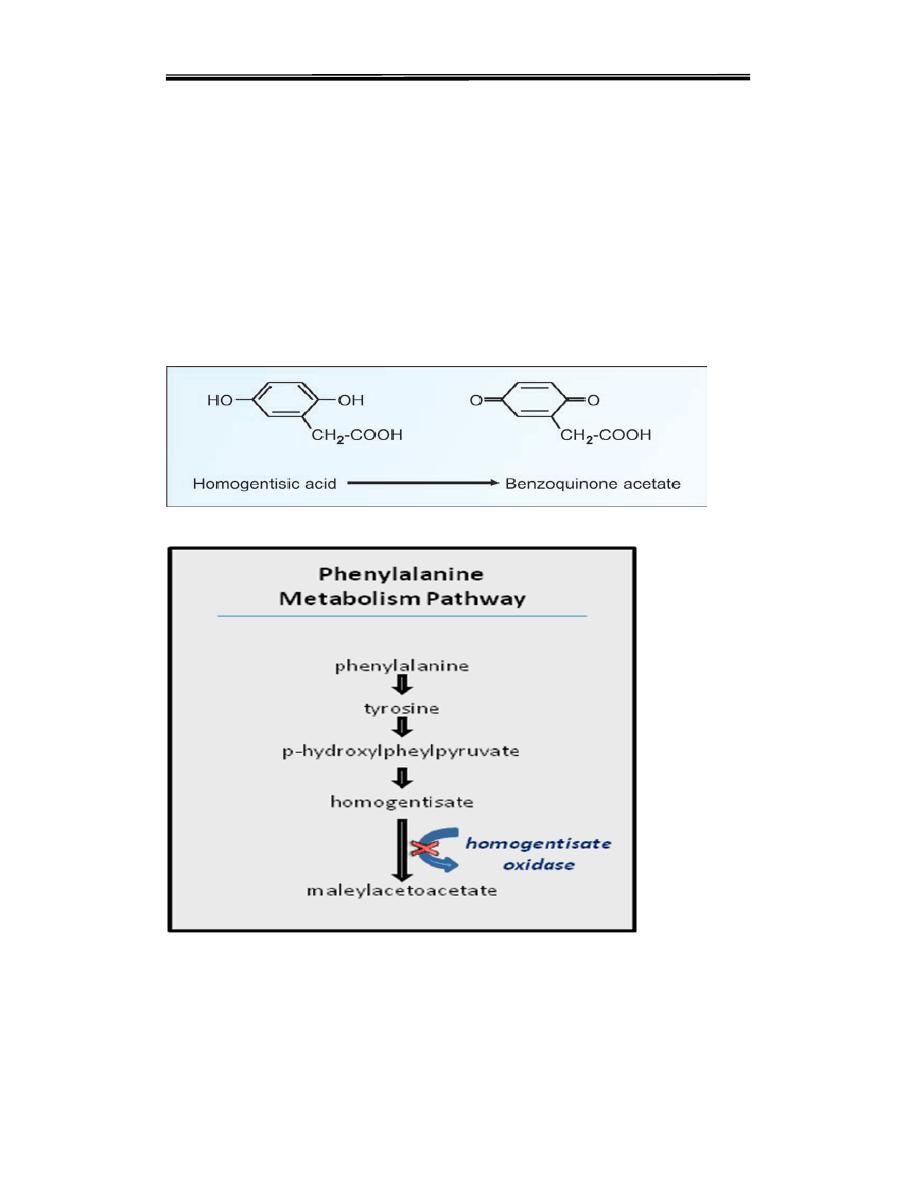
Alkaptonuria is caused by the lack of an enzyme called homogentisic
dioxygenase (HGD). This condition occurs 1 in 1,000,000 live birth
homogentisic acid accumulates and gets excreted in urine where the urine
turns black on standing. There is a form of arthritis in late cases and
generalized pigmentation of connective tissues; this is believed to be due
to the oxidation of homogentisic acid by polyphenol oxidase
forming benzoquinone acetate that polymerises and binds to connects
tissues molecules. Patients usually lead a normal life but have develop
arthritis at adult .
It is compatible with fairly normal life. The only abnormality is the
blackening of urine onstanding. The homogentisic acid is oxidized by polyphenol
oxidase to benzoquinone acetate (Fig.17.6). It is then polymerized to black colored
alkaptone bodies.
Clinical biochemistry second stage lecture 7 Dr.Thana Alsewedy
4
4-ALBINISM
1. The Greek word, albino means white. Albinismis an autosomal
recessive disease with an incidence of 1 in 20,000 population (Fig.17.7).
Albinism – genetically determined lack or deficit of enzyme tyrosinase
Tyrosinase is completely absent, leading to defective synthesis of
melanin
.
3. The ocular fundus is hypopigmented and iris may be grey or red. There
will be associated photophobia, nystagmus and decreased visualacuity.
4. The skin has low pigmentation, and so skin is sensitive to UV rays.
The skin may show presence of naevi and melanomas. Hair is also white.
Clinical biochemistry second stage lecture 7 Dr.Thana Alsewedy
5
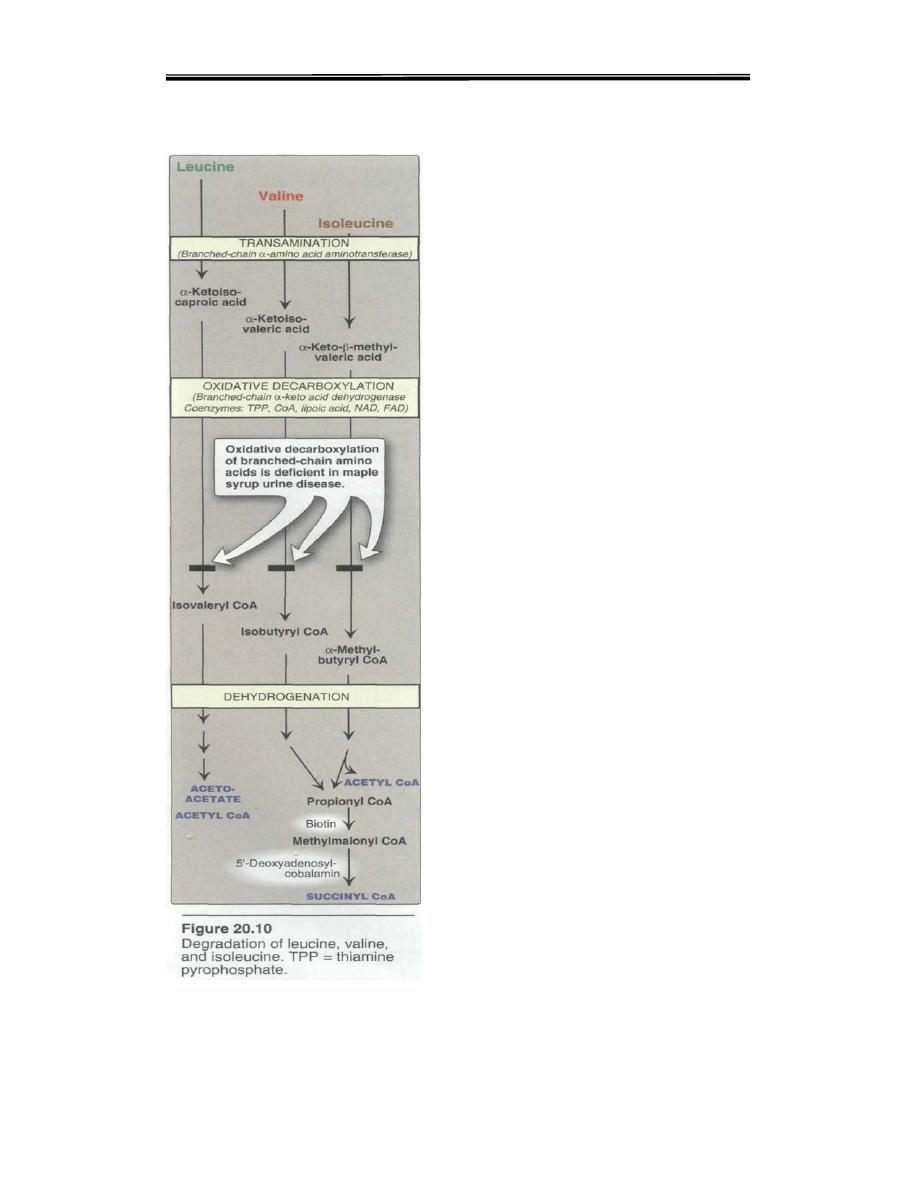
Branched chain amino acids Abnormality
Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD)
The normal metabolism of the branched chain amino acids Leucine,
Isoleucine, and valine Valine. (Val) (V) is glucogenic; Leucine (Leu) (L)
is ketogenic while Isoleucine (Ile) (I) is both ketogenicand glucogenic.
All the three are essential amino acids. Leucine is the major ketogenic
amino acid.These amino acids serve as an alternate source of fuel for the
brain especially under conditions of starvation.metabolism of these amino
acid involves loss of the α-amino acid by transamination followed by
oxidative decarboxylation of the respective keto acids
.
. The
decarboxylation step is catalysed by branched chain α keto acid
decarboxylase. In approximately 1 in 300,000 live birth in the general US
population are affected by this enzyme defect leading to ketoaciduria.
When untreated this condition may lead to both physical and mental
retardation of the newborn and a distinct maple syrup odor of the urine.
This defect can be partially managed with a low protein or modified diet.
In some instances,supplementation with high doses of thiamine
pyrophosphate is recommended
Thisis because the decarboxylation
requires thiamine.
.
Clinical biochemistry second stage lecture 7 Dr.Thana Alsewedy
6
Clinical biochemistry second stage lecture 7 Dr.Thana Alsewedy
7
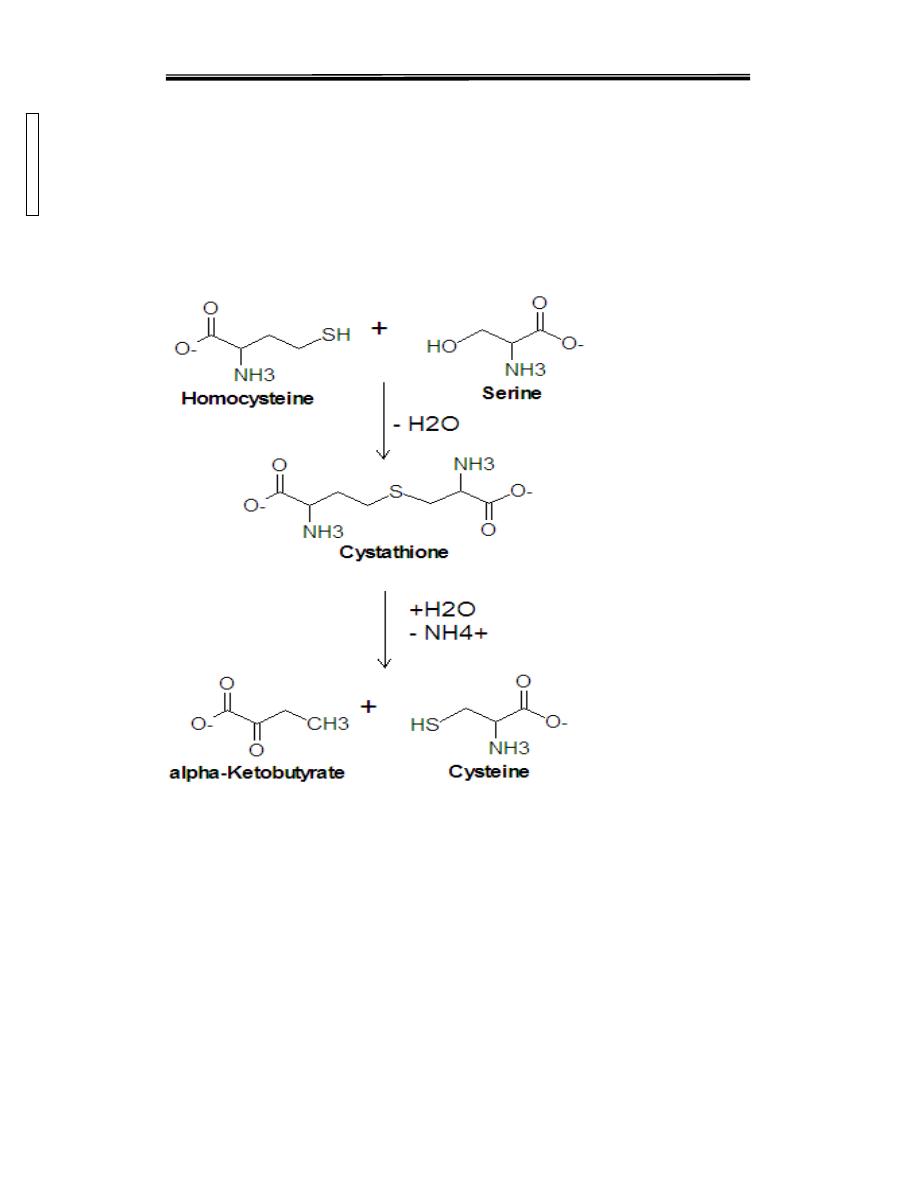
Homocystinuria
Genetic defects for both the synthase and the lyase enzymes involved in
conversion of methionine amino acid into cysteine amino acid. . Missing
or impaired cystathionine synthase leads to homocystinuria. High
concentration of homocysteine and methionine in the urine.
Homocysteine is highly reactive molecule. Disease is often associated
with mental retardation, multisystemic disorder of connective tissue,
muscle, CNS, and cardiovascular system
Cystinuria
Cystinuria is one of the inborn errors of metabolism. The disorder is
attributed to the deficiency in transport of amino acids
is an inherited
autosomal recessive disease that is characterized by the formation of
cystine(cysteine-S-S cysteine) stones in the kidneys, ureter, and bladder.
Cystinuria is a cause of persistent kidney stones. It is a disease involving
the defective transepithelial transport of cystine and dibasic amino acids
in the kidney and intestine, and is one of many causes of kidney stones .
N
o
r
e
