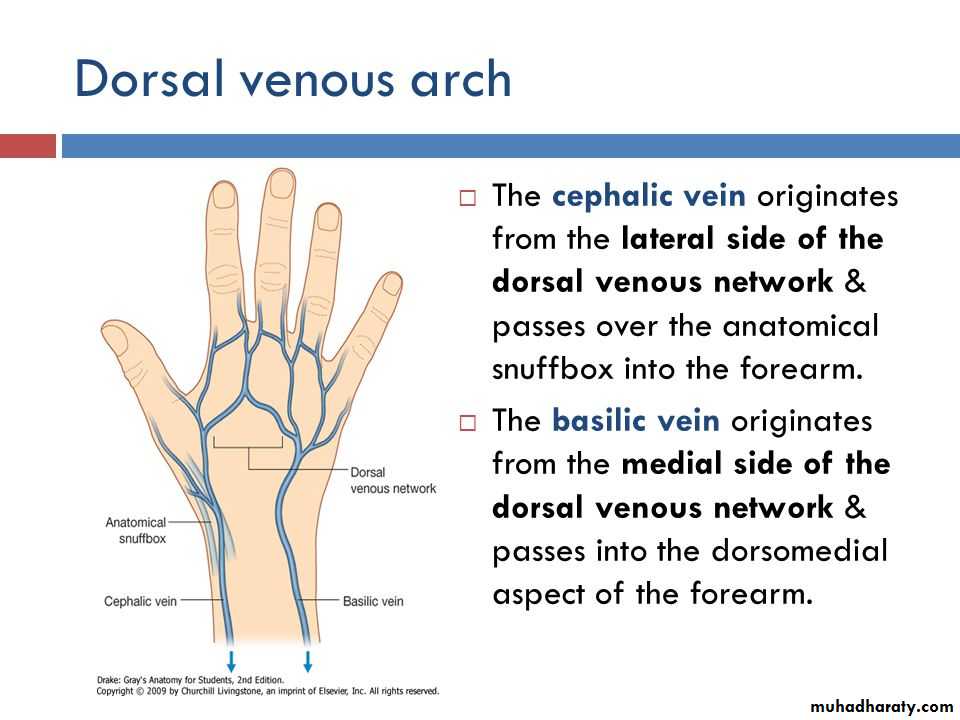
INTRODUCTIONTOANATOMY
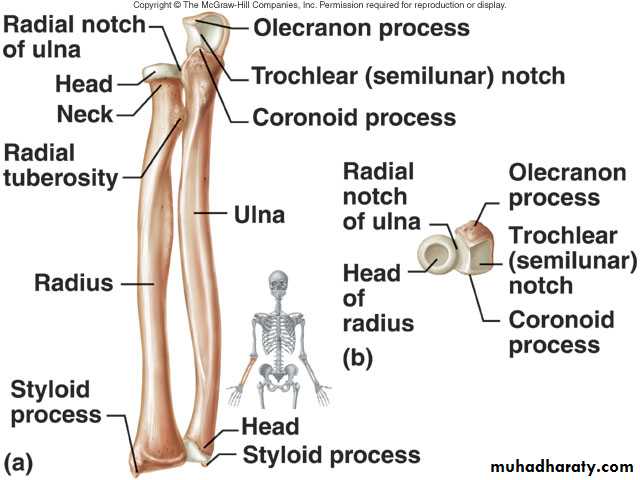
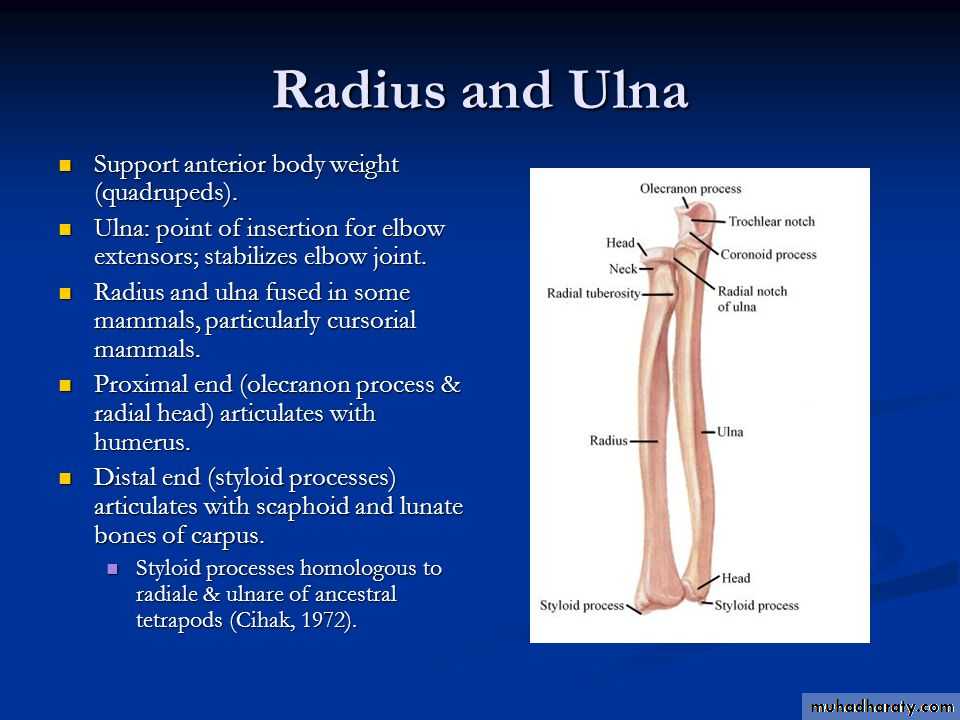
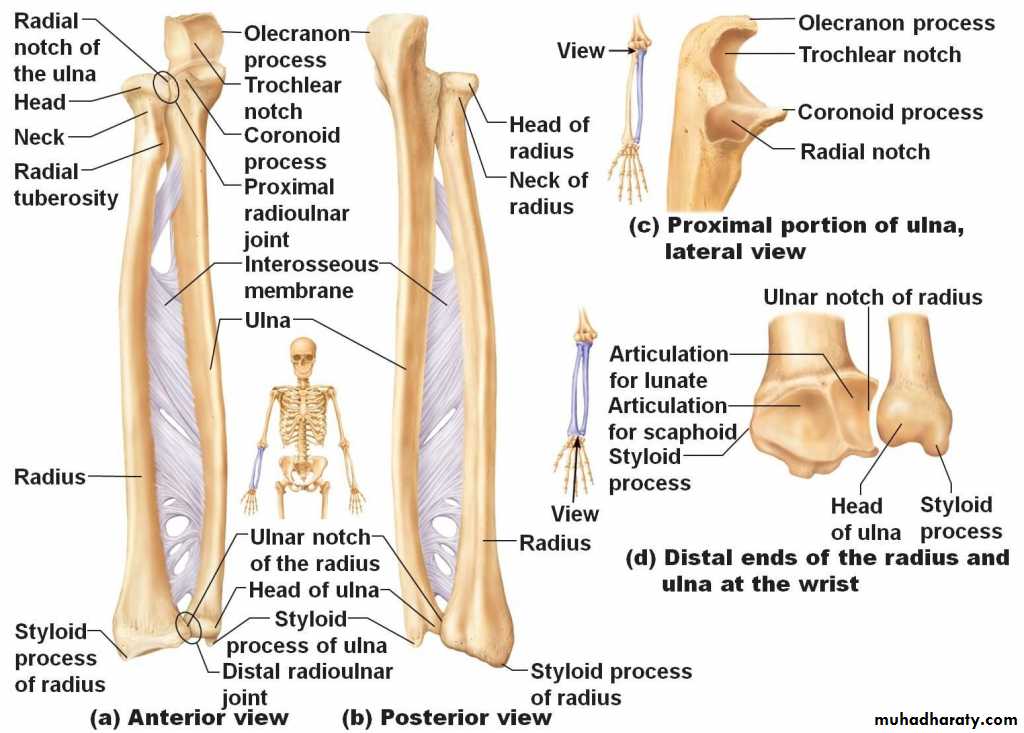
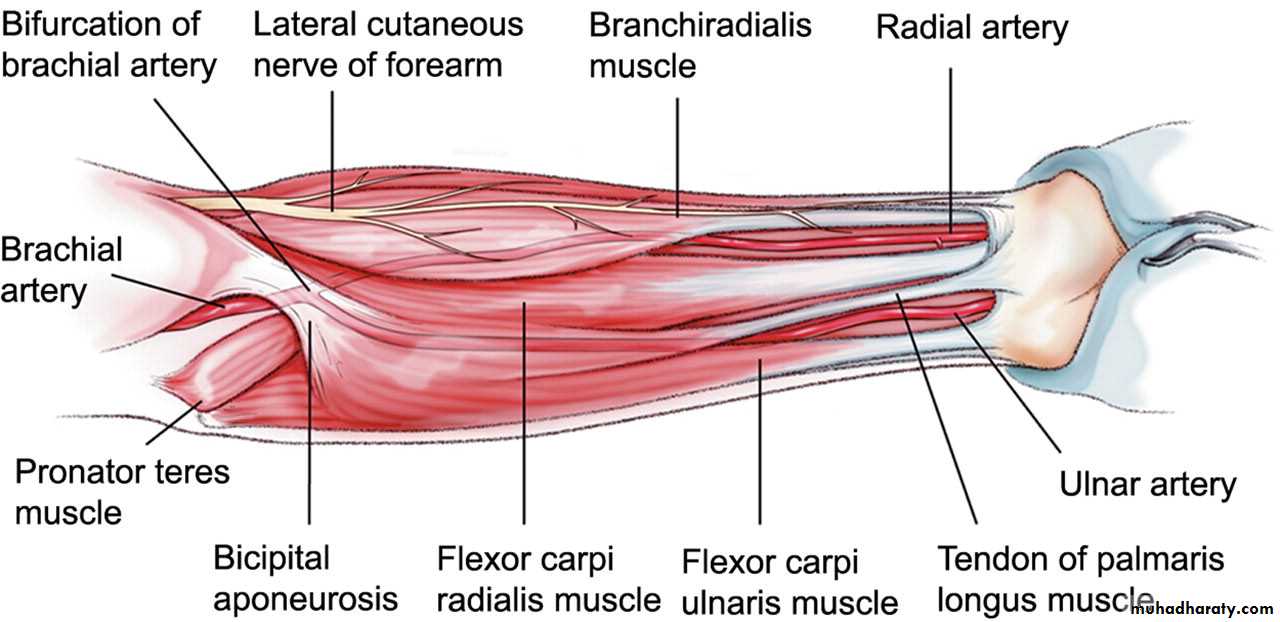
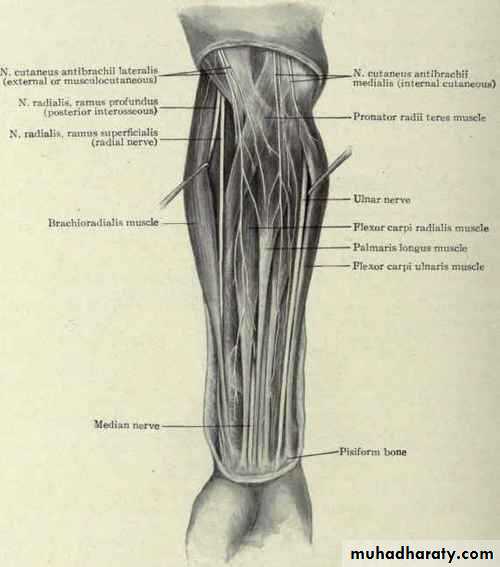
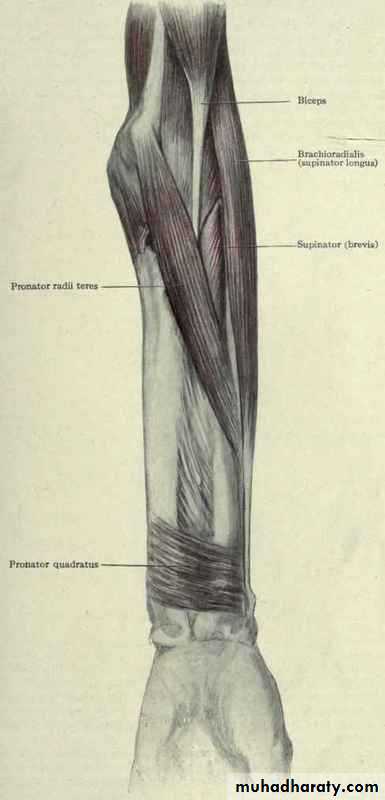
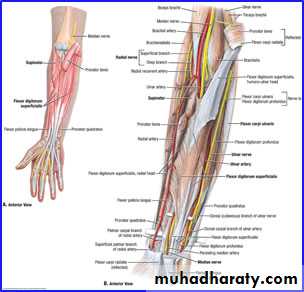
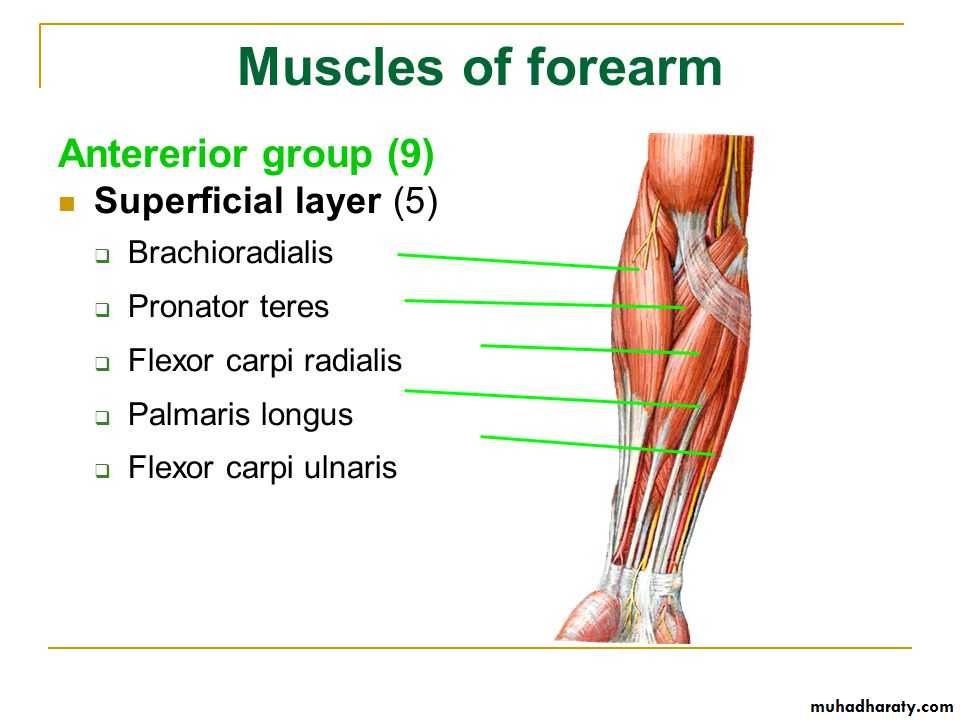
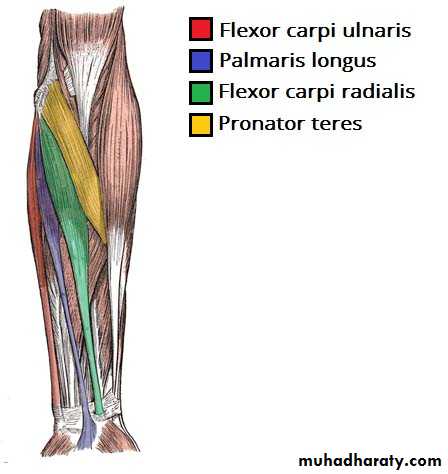
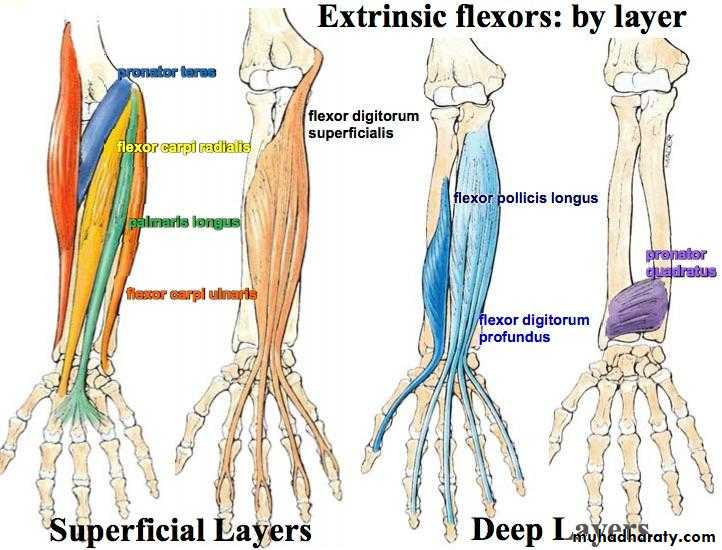
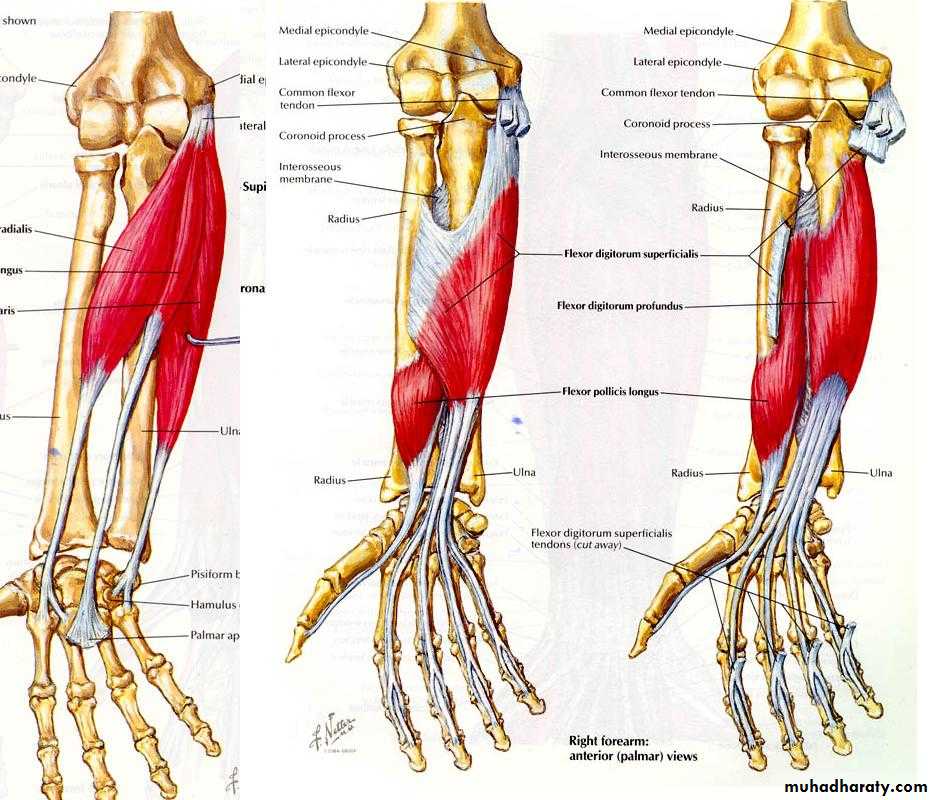
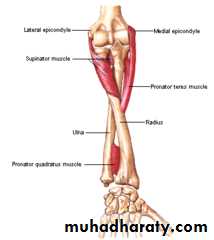
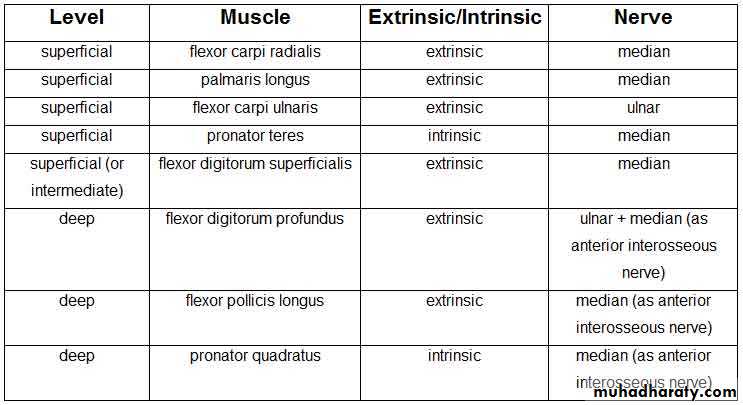
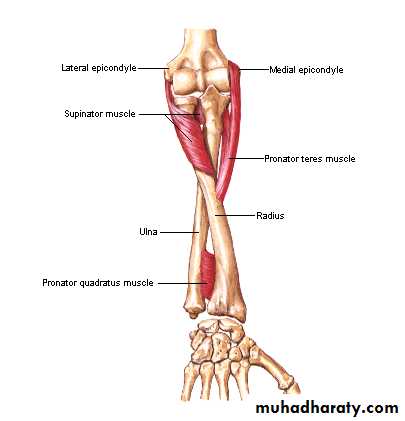
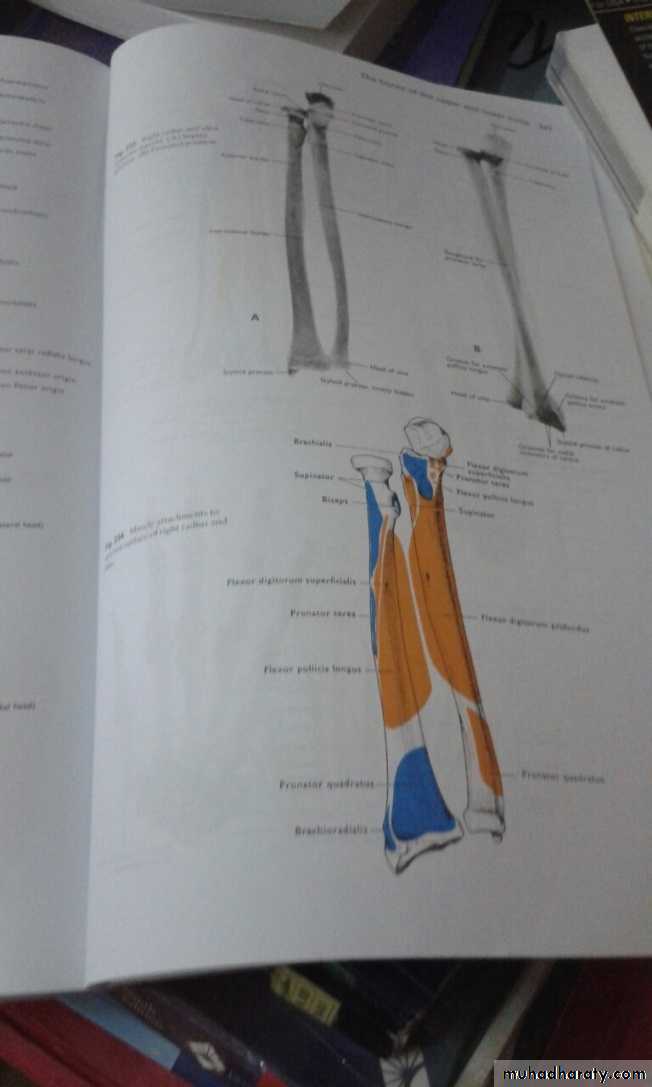
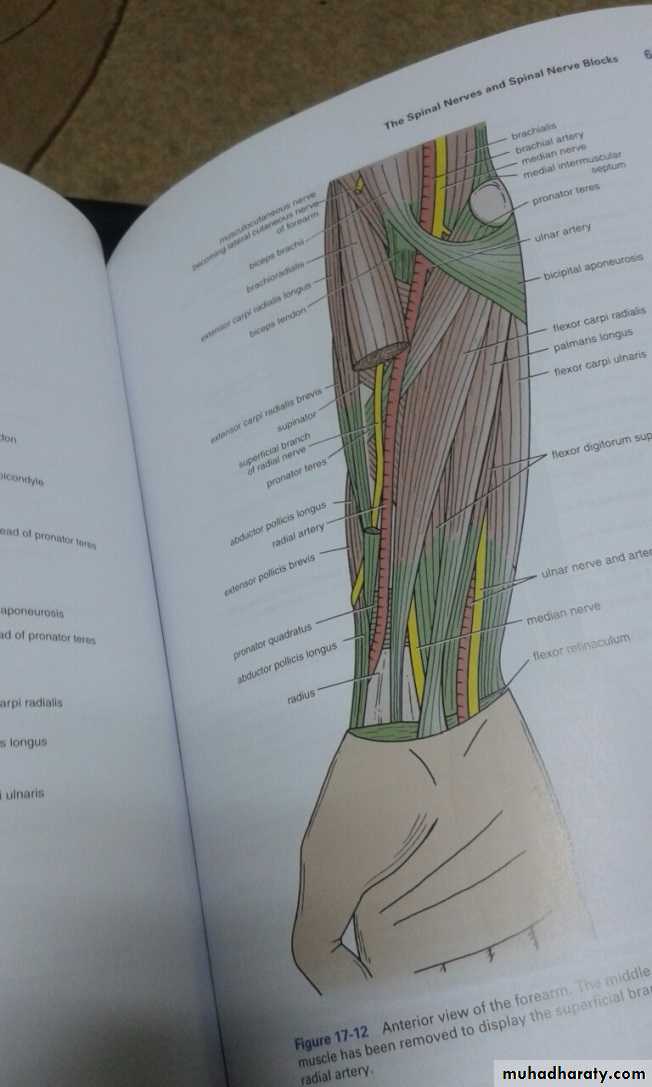
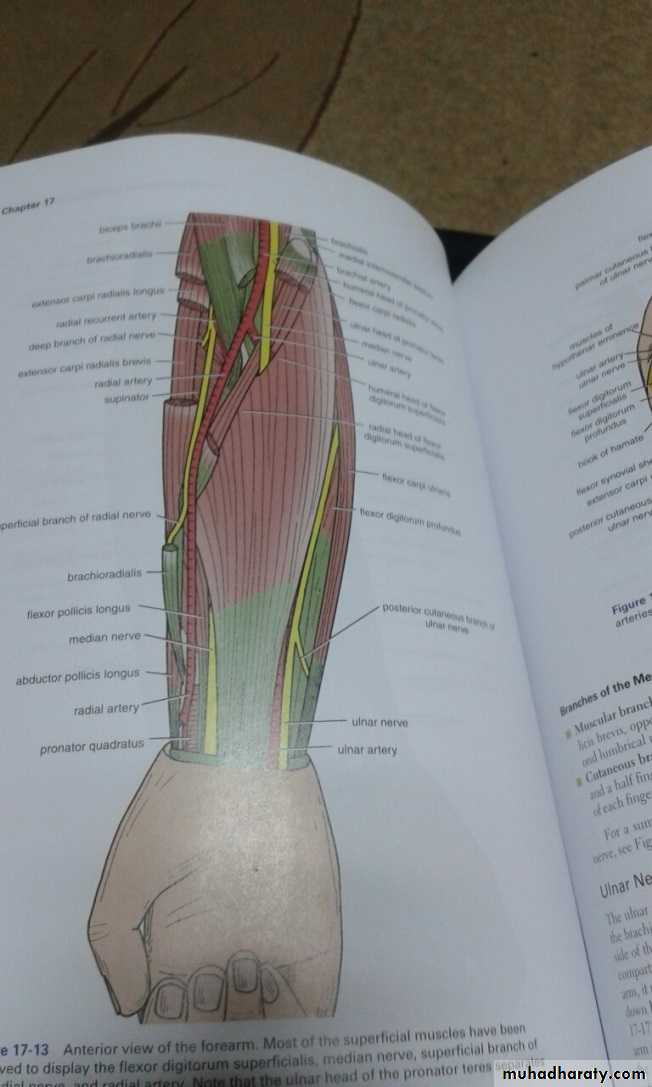
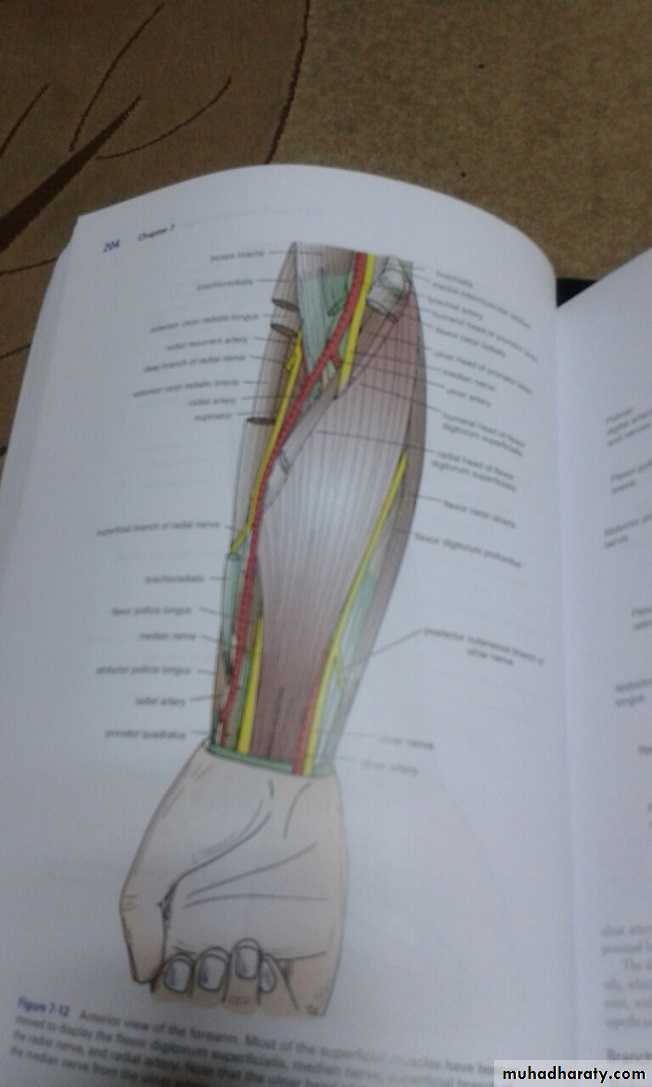
أ.د.عبد الجبار الحبيطيIs the anteromedial compartment of the F.A ,it includes 8 Ms ( 5 of them are superficial & 3 deep).The superficial are Pronater teres,Flexor carpi radialis,Palmaris longus,Flexor digitorum superficialis & Flexor carpi Ulnaris.The other 3 deep Ms are Flexor digitorum profundus, Flexor pollicis longus & Pronater quadratus Ms. Pronater teres takes origin by 2 heads , humeral & ulnar heads,the humeral head arises from medial epicondyle& medial supracondylar line ,while the ulnar head from medial side of Coronoid process of the ulna.The M is inserted into the lateral surface of the middle part of the shaft of the Radius bone.
The Flexor Compartment of Forearm
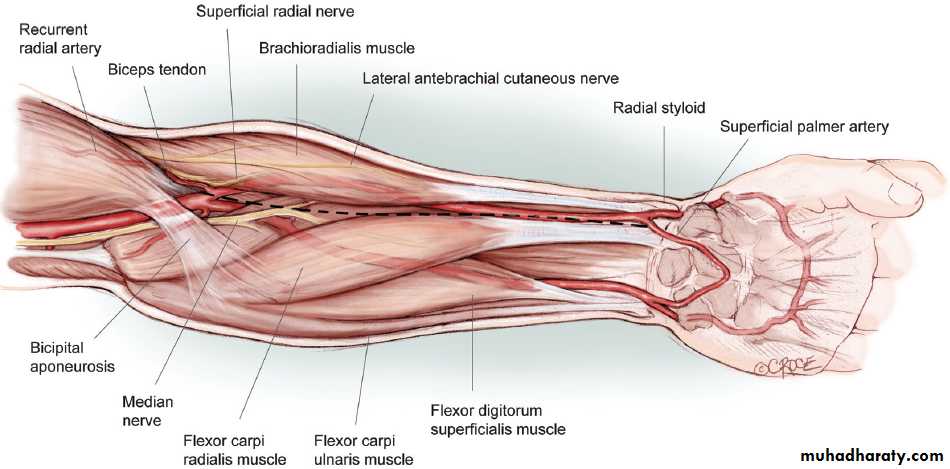
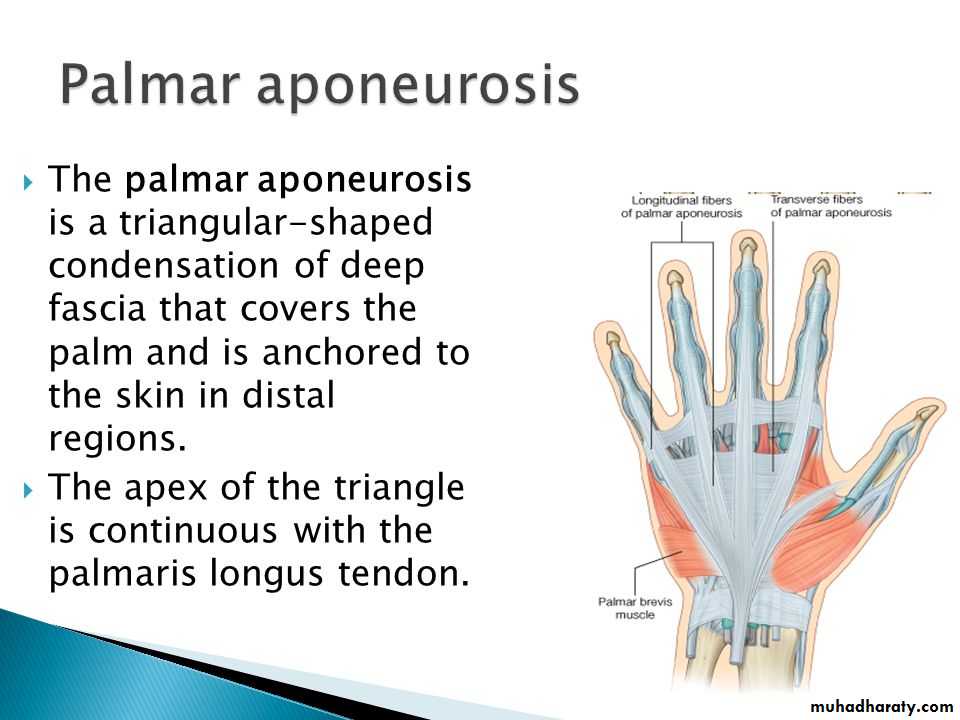
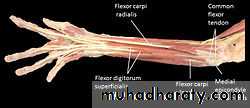
Flexor carpi radialis takes origin from the medial epicondyle of humerus& is inserted into th base of the 2nd metacarpal bone.Palmaris longus takes origin from medial epicondyle & inserts into palmer aponeurosis.
Flexor carpi ulnaris has 2 heads of origin a humeral head from medial epicondyle & ulnar head from medial side of olecranon process of ulna bone.The M is inserted into the Pisiform bone ( one of the carpal bones ).
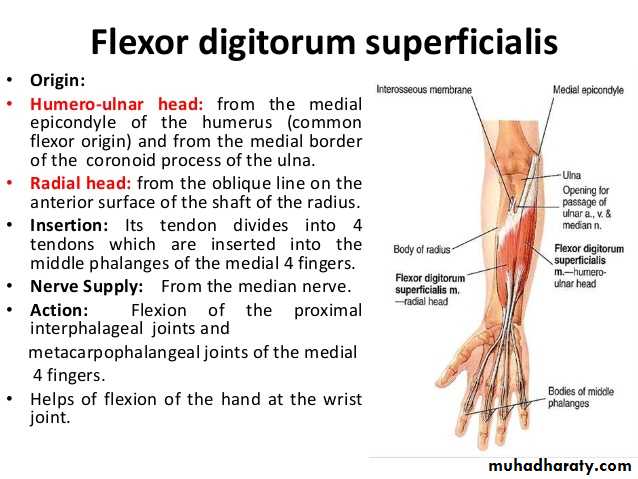
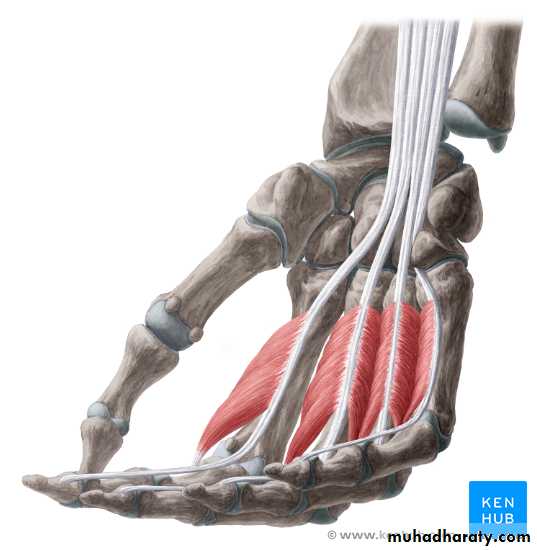
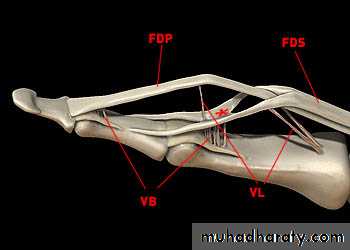
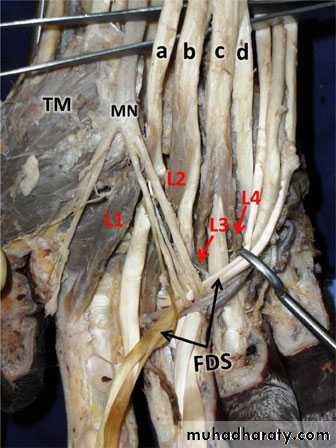
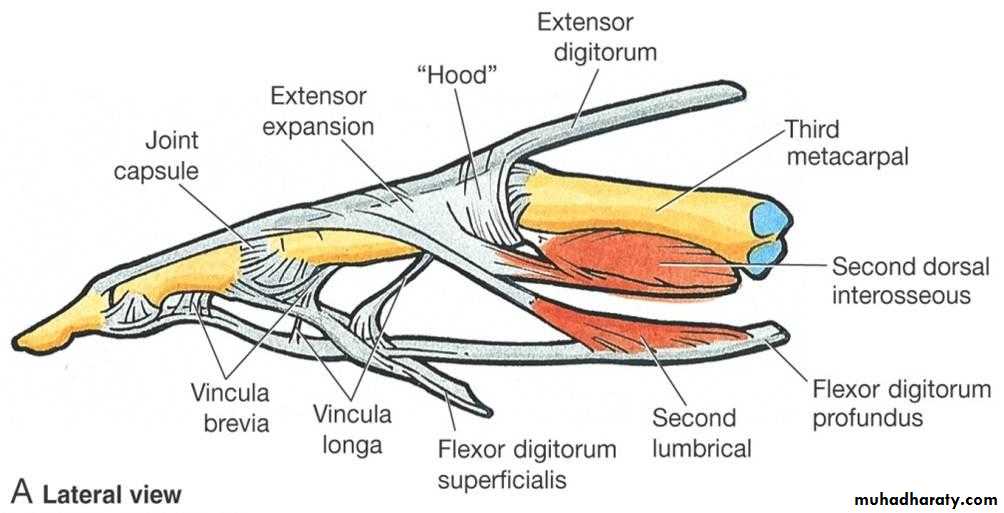
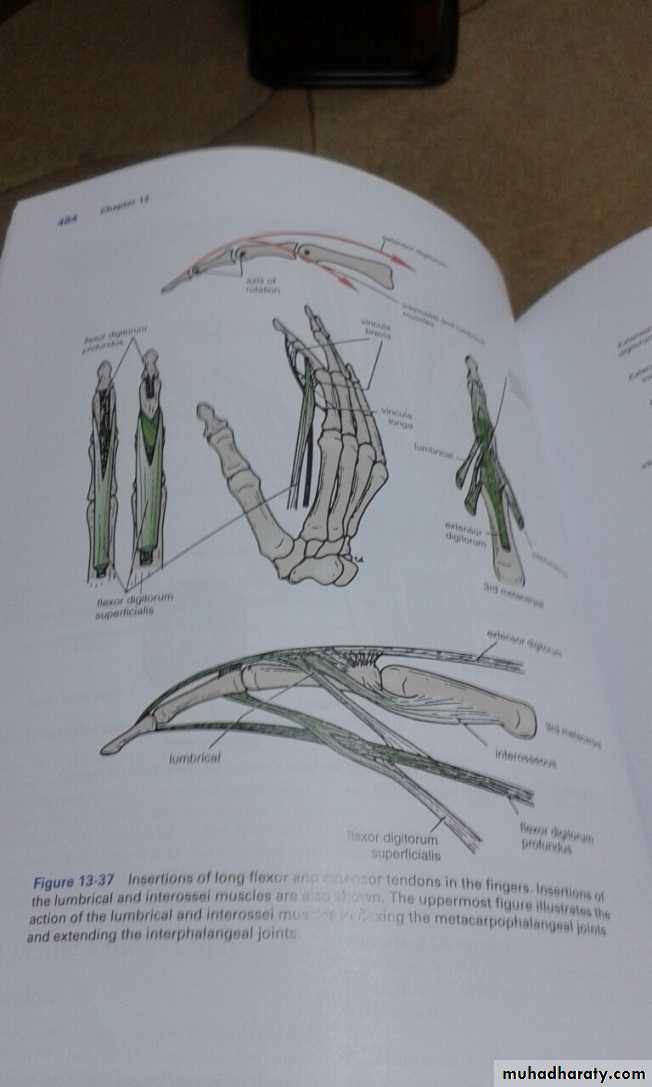
Flexor digitorum superficialis has 2 heads of origin too humeral & radial heads ,humeral from medial epicondyle,ulnar collateral ligament & medial margin of coronoid process of ulna bone.while the radial head arises from oblique line on the anterior surface of the radius bone.The M gives 4 tendons to the medial 4 fingers( each tendon inserts into the sides of the middle phalange of the corresponding finger).
Flexor digitorum profundus takes origin from the upper 3/4(three fourth)of anterior,medial &posterior surfaces of the ulna bone and from anterior surface of interosseous membrane.
The M gives 4 tendons to the 4 medial fingers ( inserts into the base of the distal phalanges).
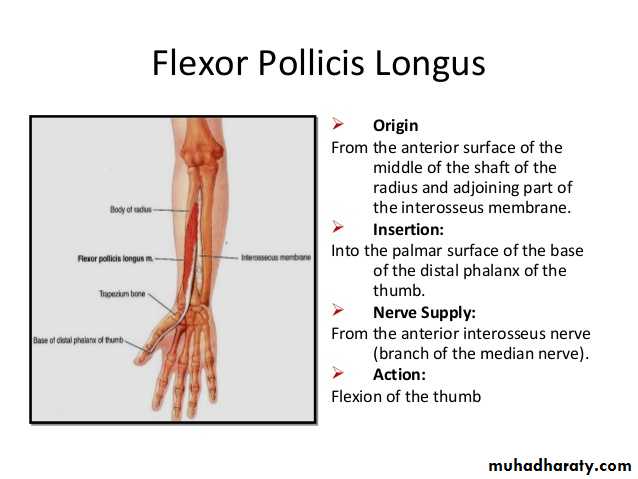
Flexor pollicis longus takes origin from middle 2/4 of anterior surface of Radius bone &interosseous membrane.The M inserts into the base of distal phalanx of the thumb.
Pronater quadratus takes origin from oblique line on the lower 1/4 of anterior surface of ulna bone & inserts into the lower 1/4 of anterior surface of the radius bone.
Notes :
1-The first 5 Ms are superficial group,while last 3 are deep group.
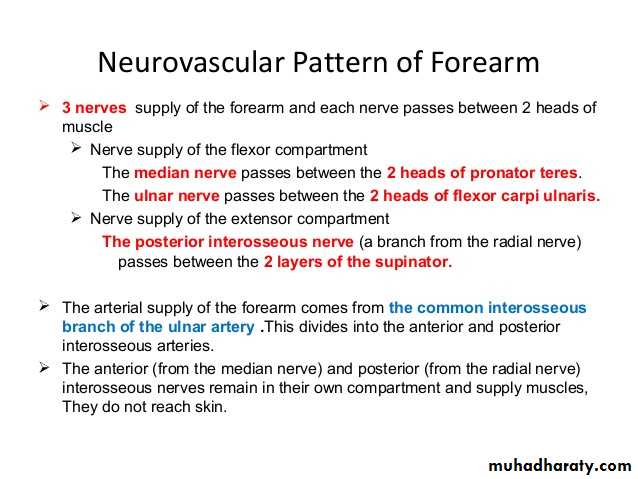
2- Four of them are innervated directly by median N ,two & half indirectly ( i.e via the anterior interosseous branch of the median N ).
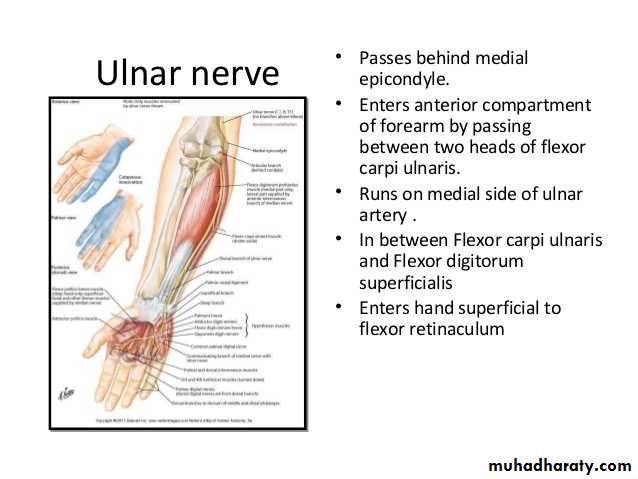
3-Flexor carpi ulnaris & medial half of Flexor digitorum profundus are supplied by the ulnar nerve.
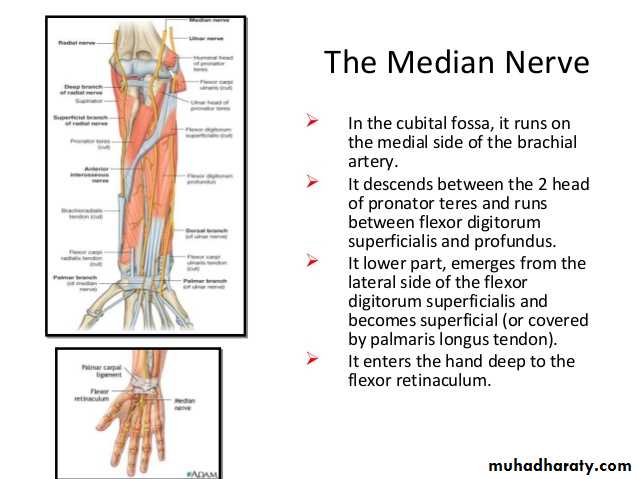
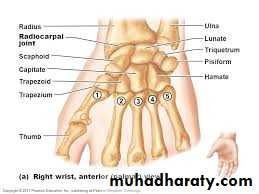
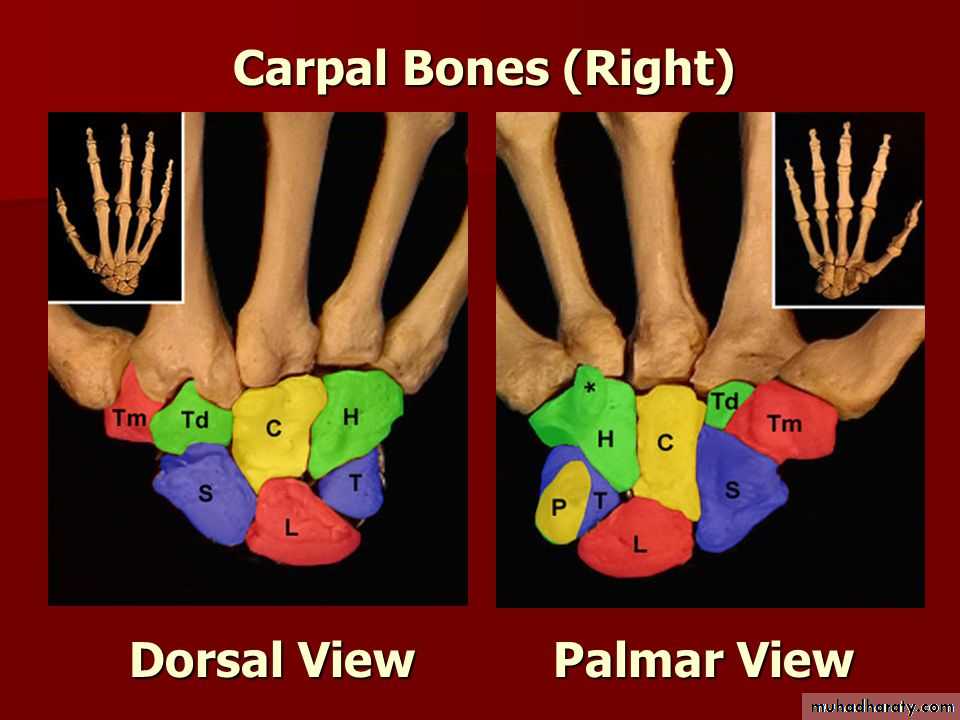
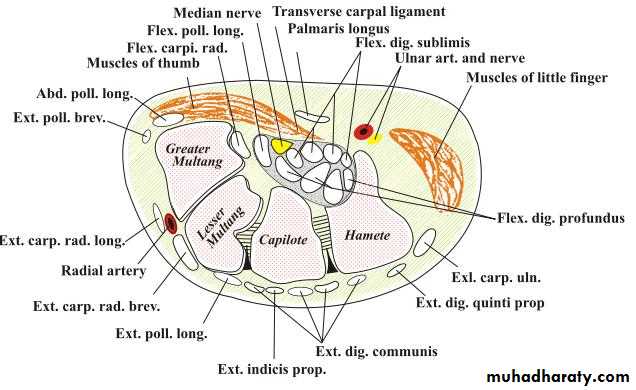
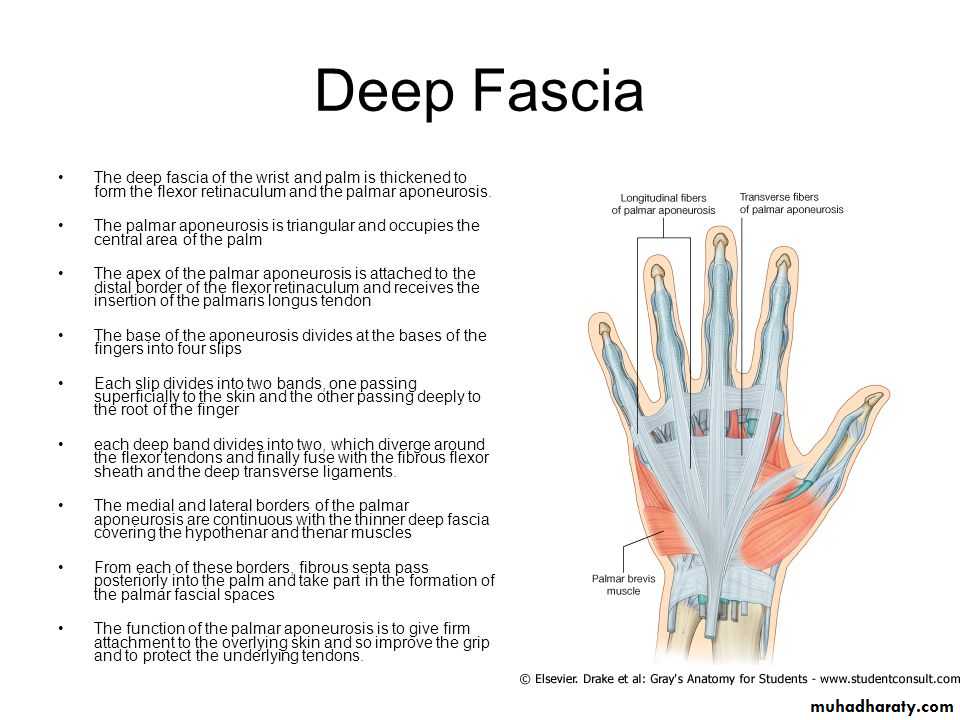
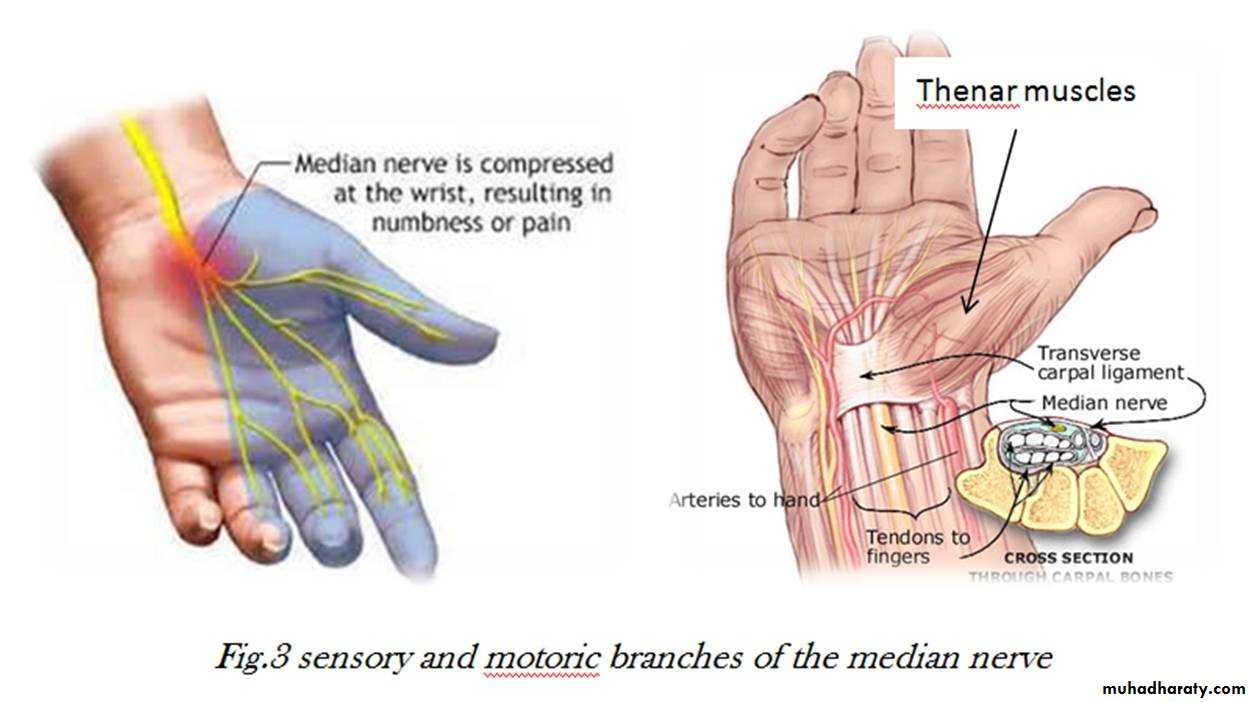
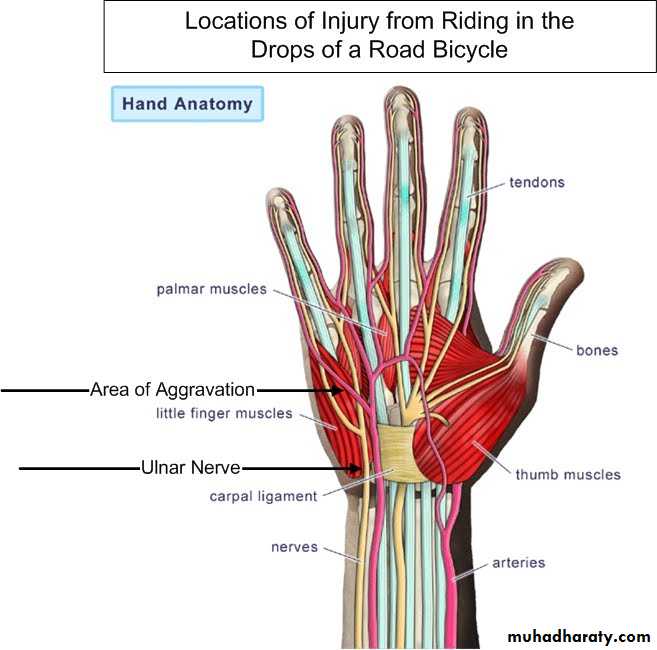
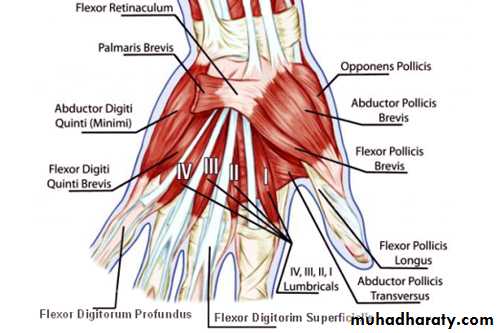
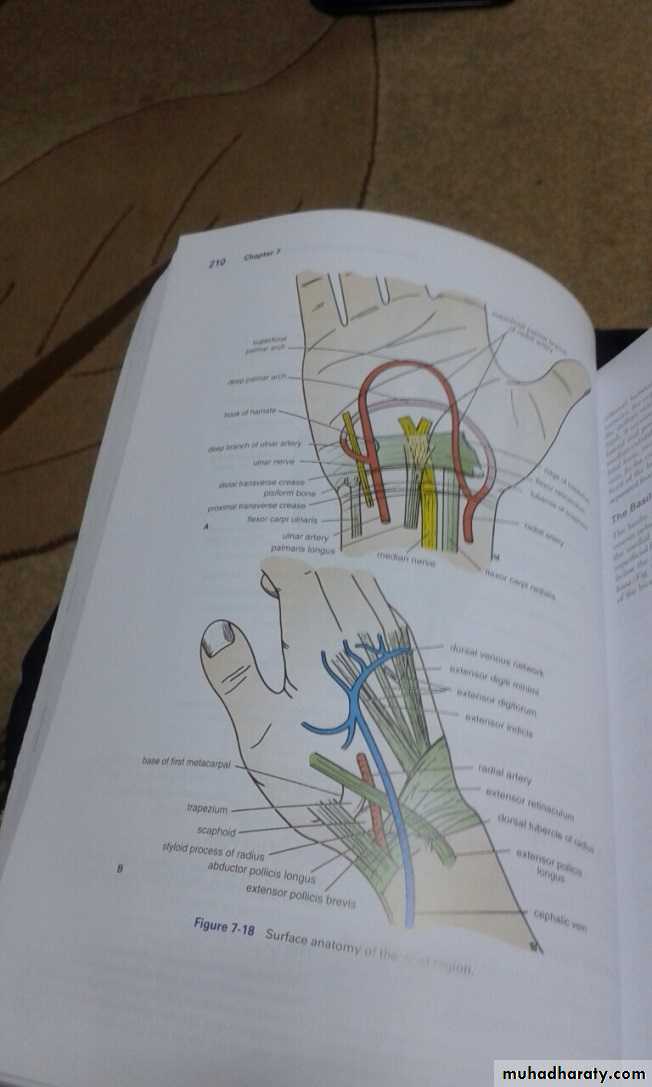
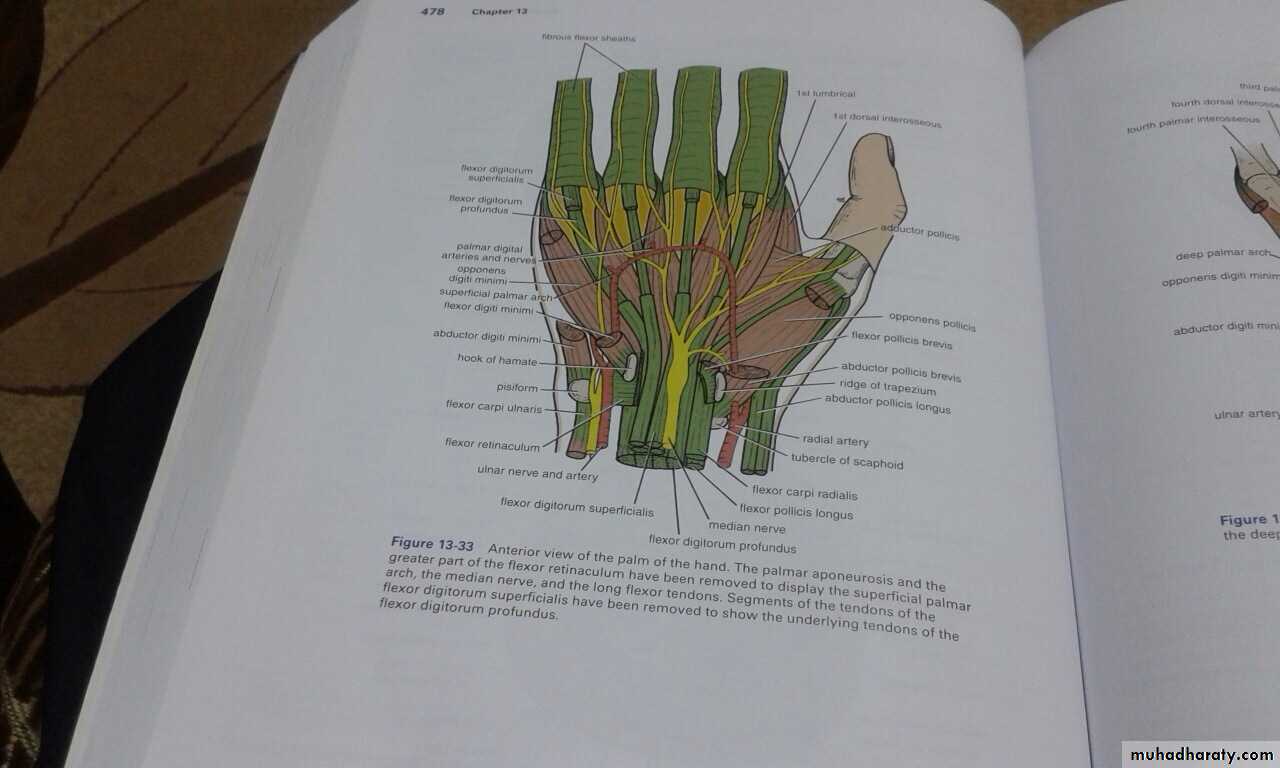
It is the thickened part of the deep fascia of the F.A located anteriorly at the junction between the F.A & palm of the hand in front of some carpal bones.It is attached to pisiform & hook of hamate medially,while laterally attached to scaphoid & trapezium ,this fibrous retinaculum bridges over some carpal bones forming a fibro—osseous tunnel known as the carpal tunnel through which pass the following structures:
THE FLEXOR RETINACULUM
1- Four tendons of Flexor digitorum superficialis.2-Four tendons of Flexor digitorum profundus.
3-Tendon of Flexor pollicis longus .
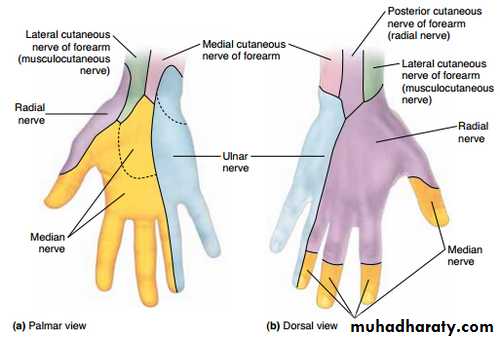
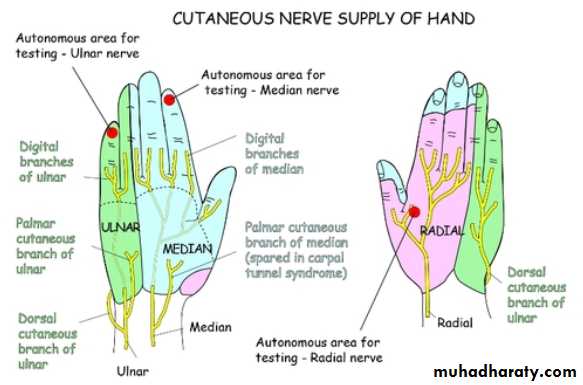
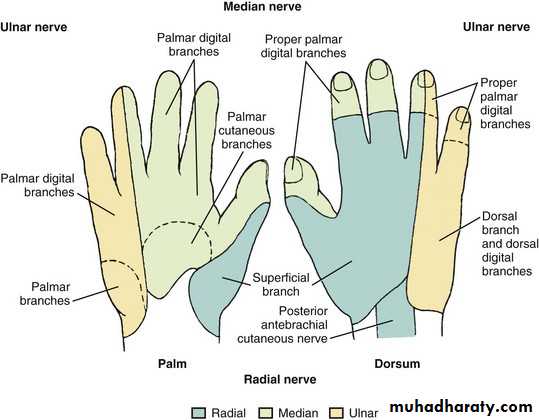
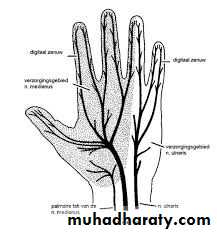
4-The Median nerve.Thus the median N is liable for compression in certain circumstances leading to what is called Carpal Tunnel Syndrome.
The following structures cross superficial to Flexor Retinaculum:
1-Tendon of palmaris longus M.2-The Ulnar Nerve.
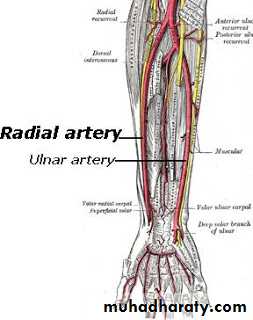
3-The Ulnar Artery.
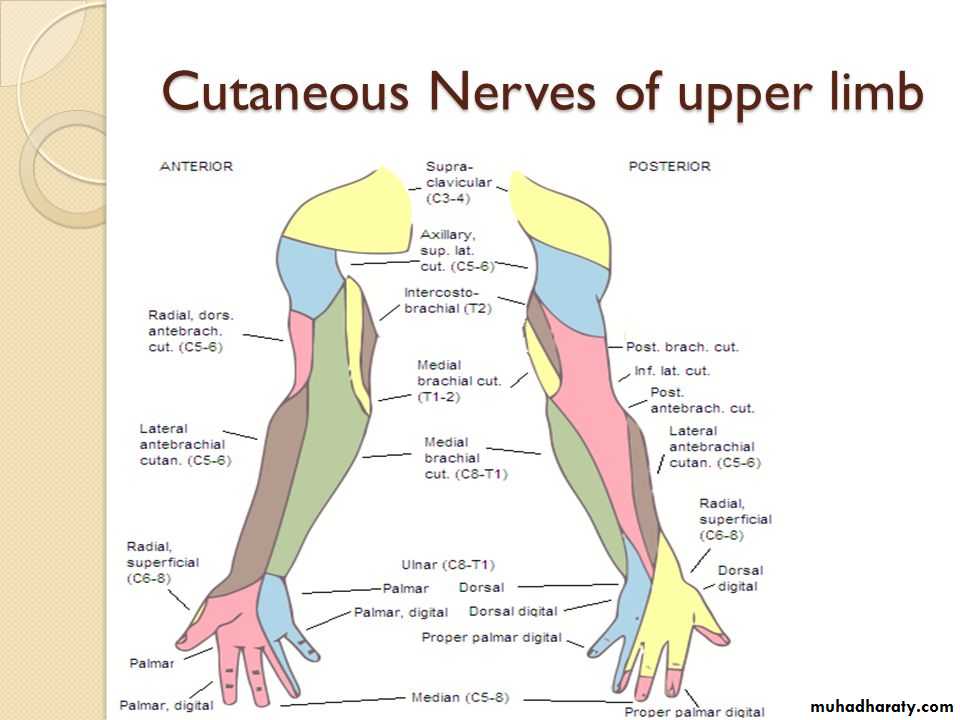
4-Palmer cutaneous branch of the Median nerve.
5-Palmer cutaneous branch of the Ulnar nerve.
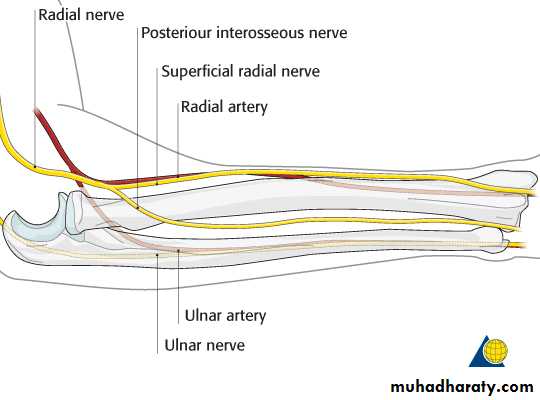
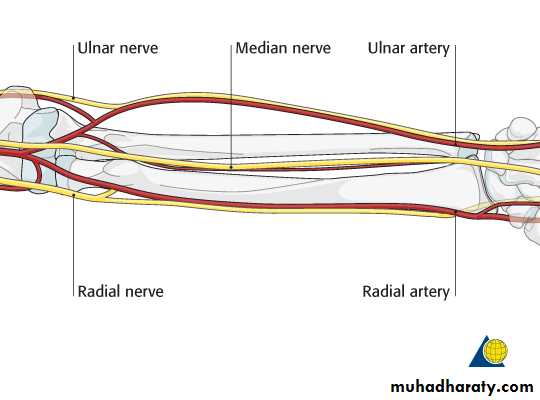
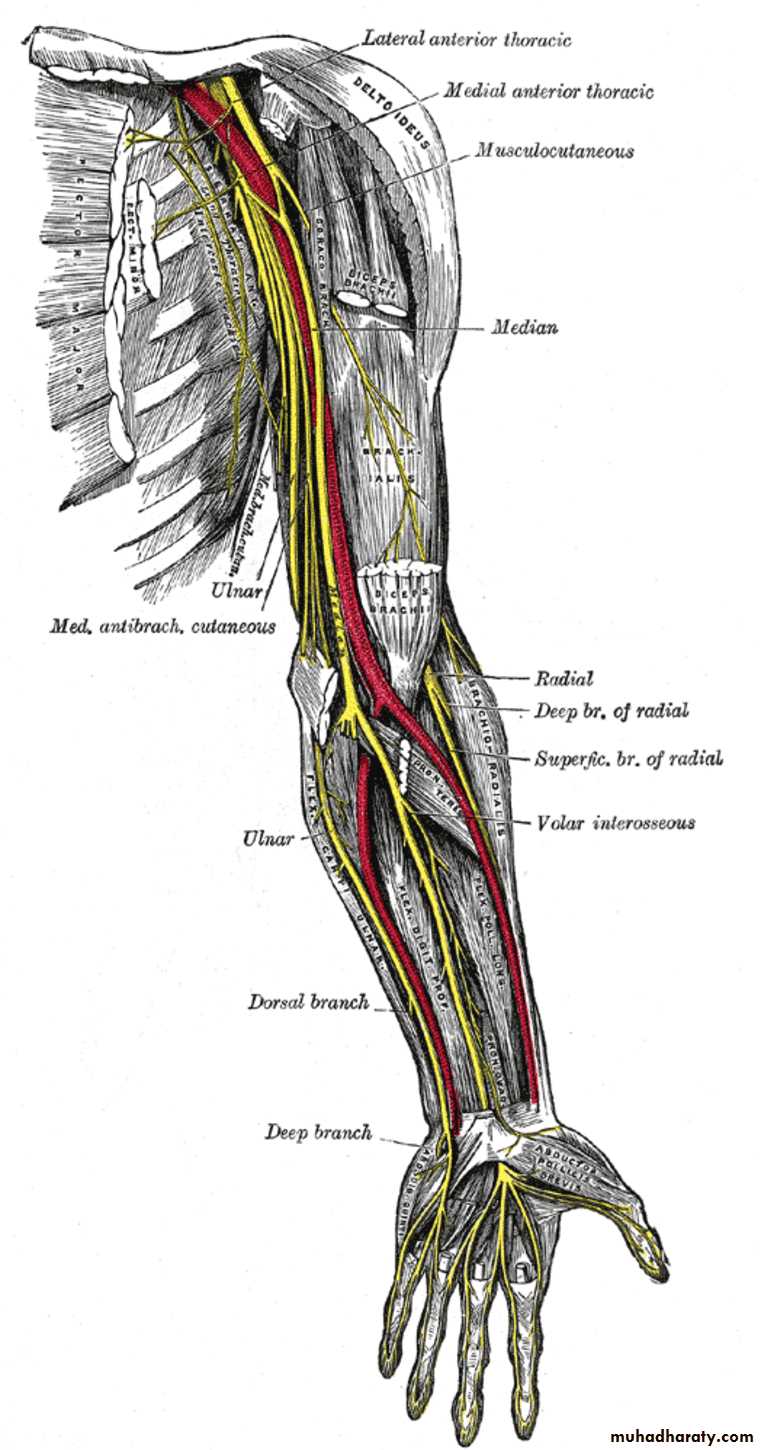
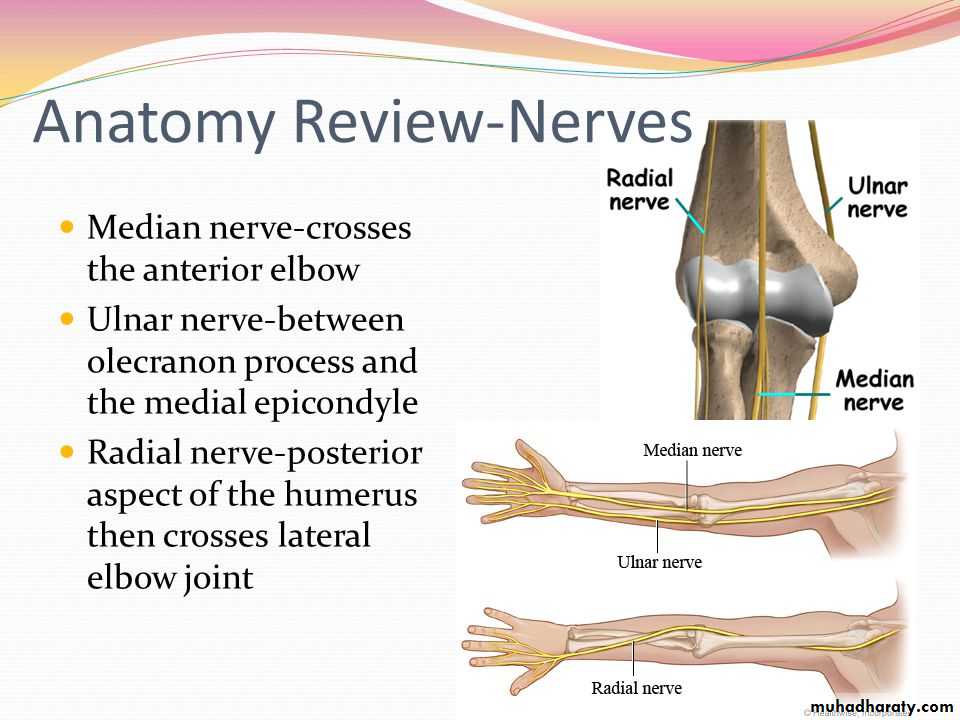
Is one of the branches of the medial cord of the Brachial plexus,it doesn’t supply any structure in the arm,just above the middle part of the Arm it pierces the medial intermuscular septum of the Arm( accompanied by both superior & inferior Ulnar collateral As ).It leaves the Arm by passing behind the medial epicondyle of the humerus to reach the F.A,it passes between the 2 heads of Flexor carpi ulnaris to reach F.A. In the F.A it descends under cover the Flexor carpi ulnaris M accompanied by the Ulnar A .It supplies Flexor carpi ulnaris & medial half of Flexor digitorum profundus M,then at the lower part of the F.A it gives dorsal ulnar cutaneous branch which goes to the back of the hand to supply sensations .Just before it leaves the F.A it gives palmer cutaneous branch which passes superficial to the Flexor retinaculum to reach the Palm of the hand.
The Ulnar Nerve
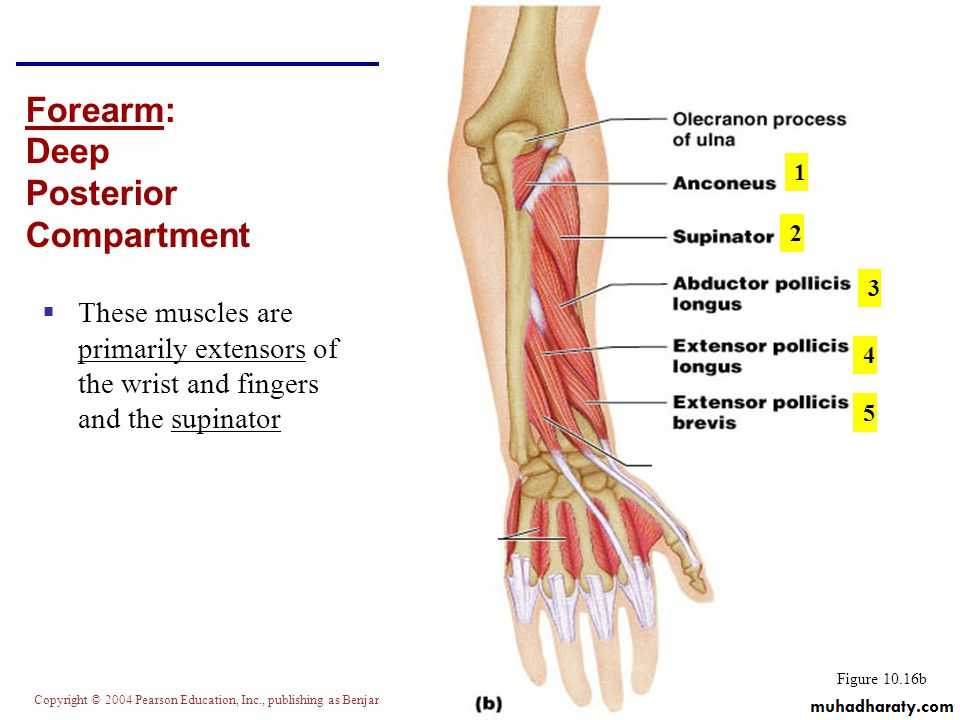
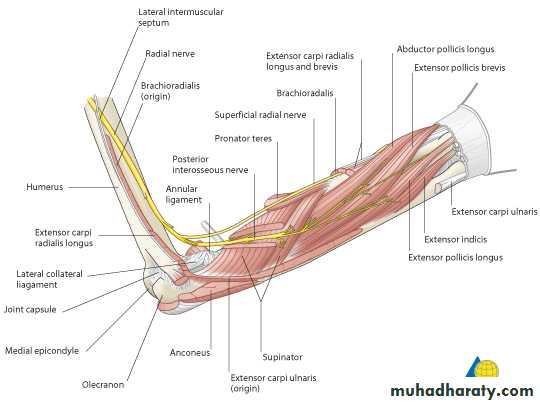
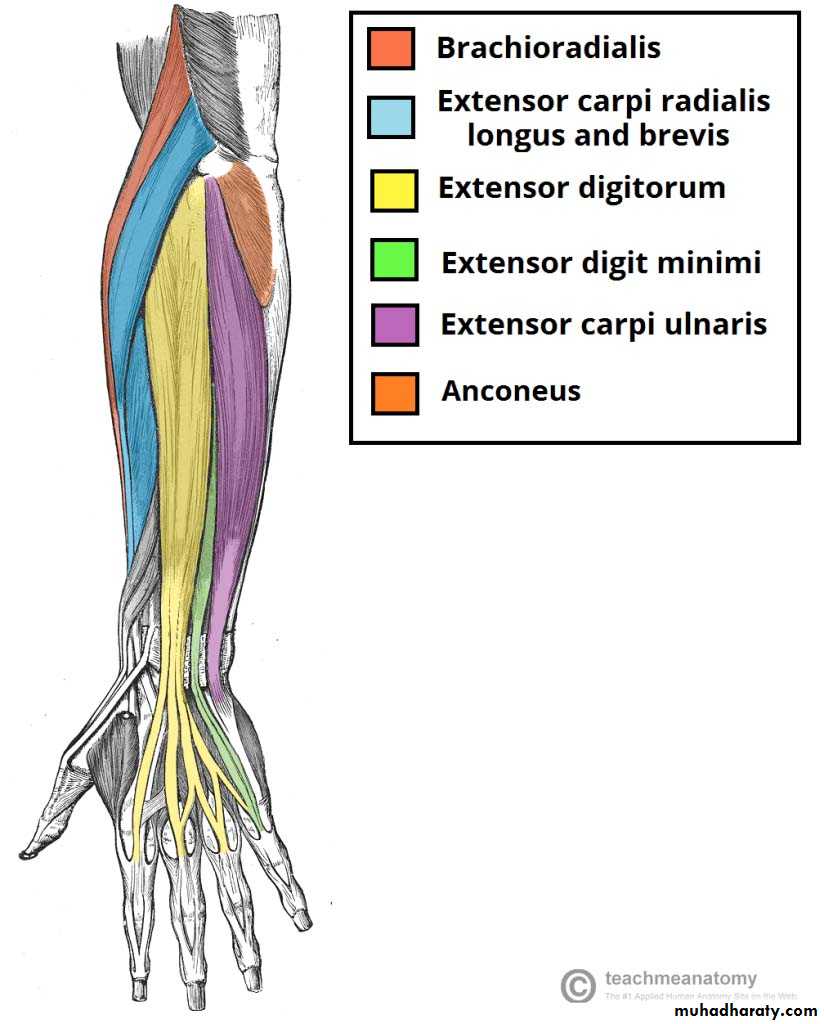
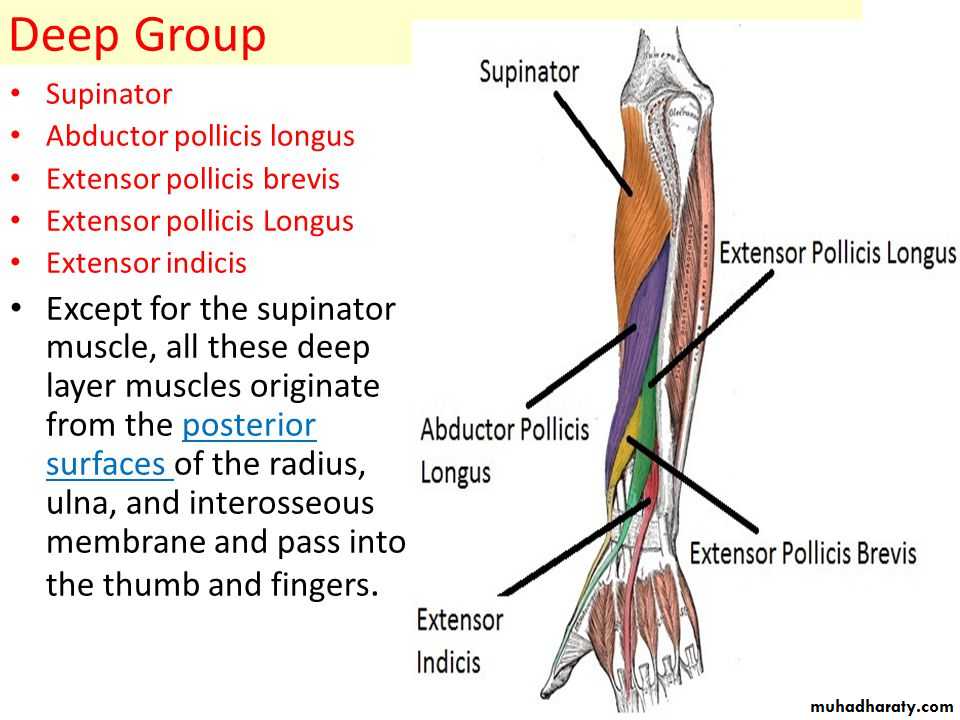
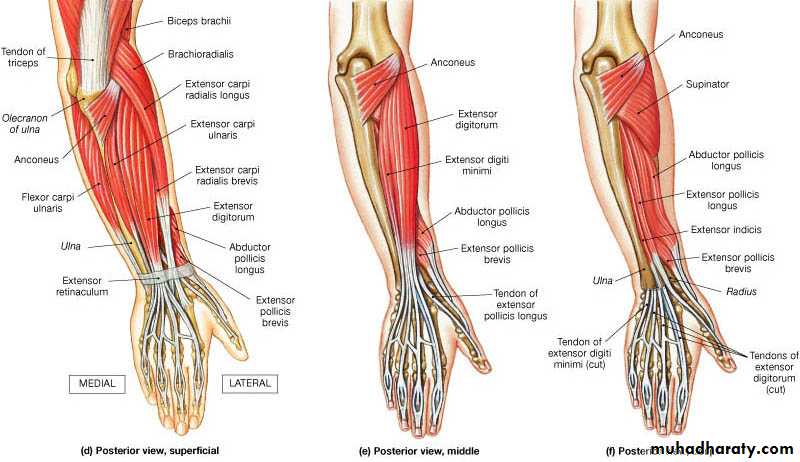
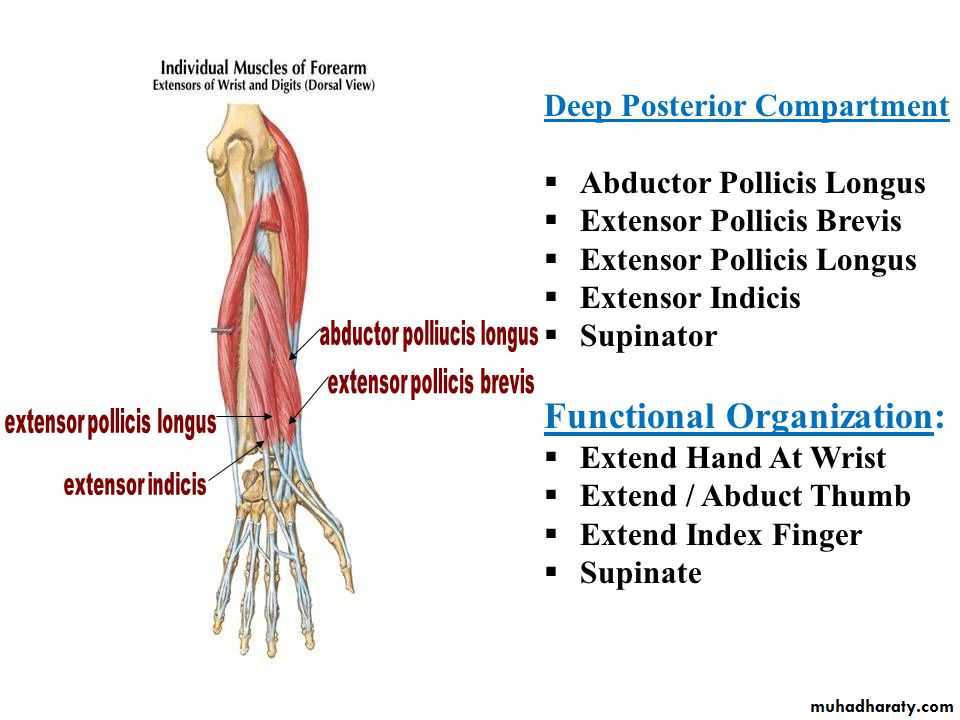
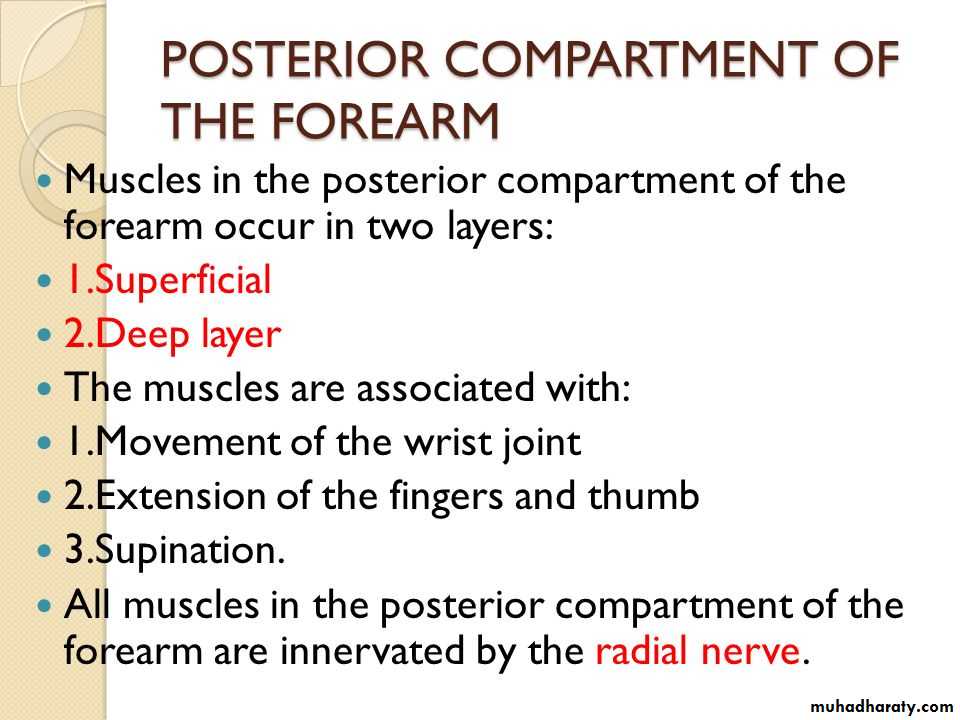
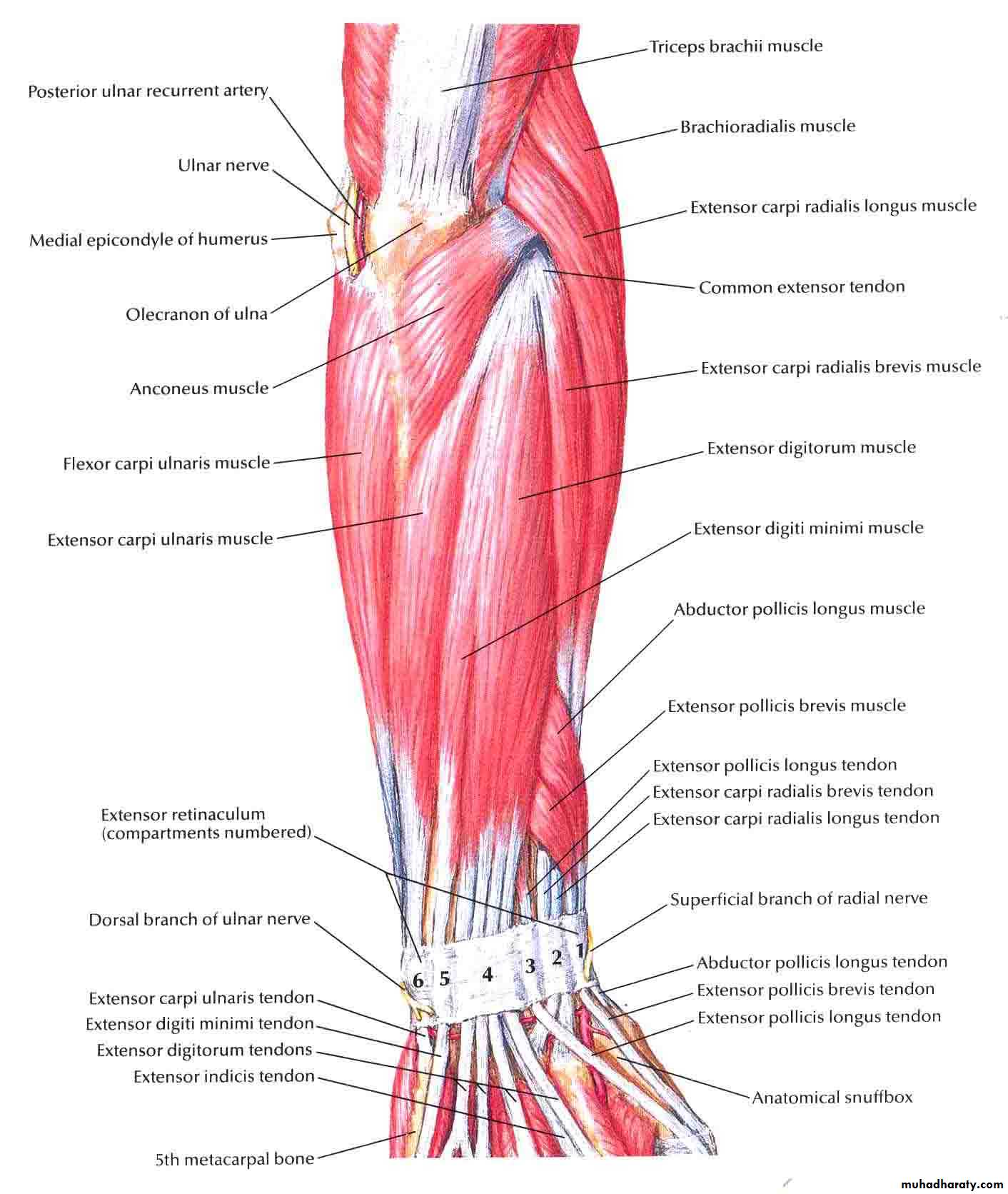
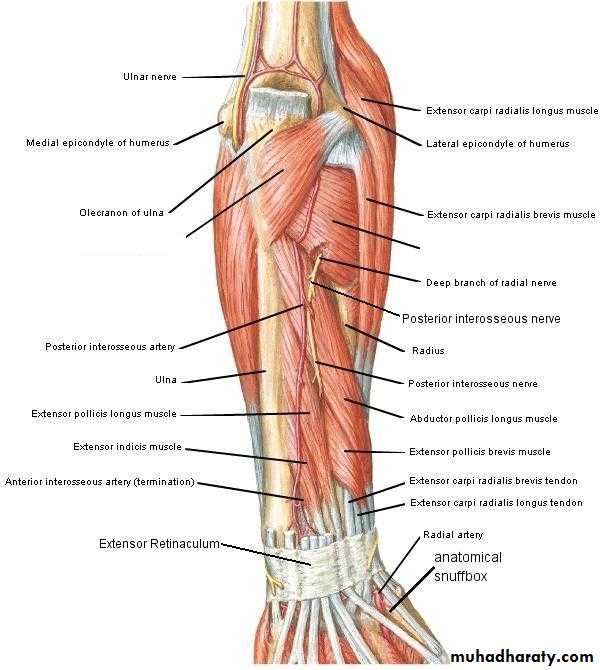
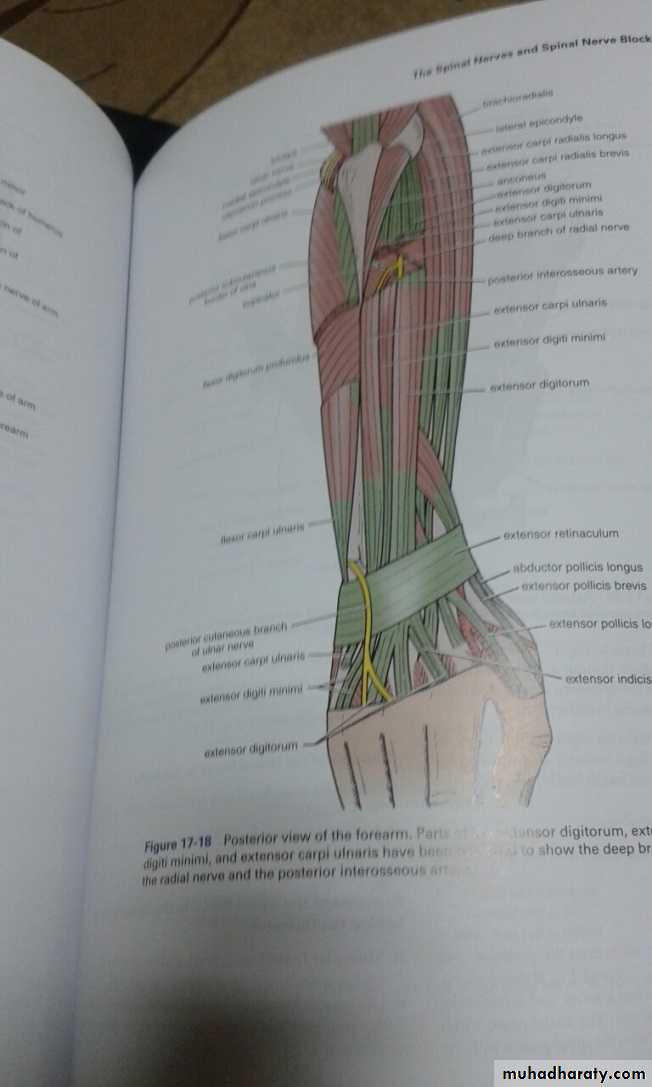
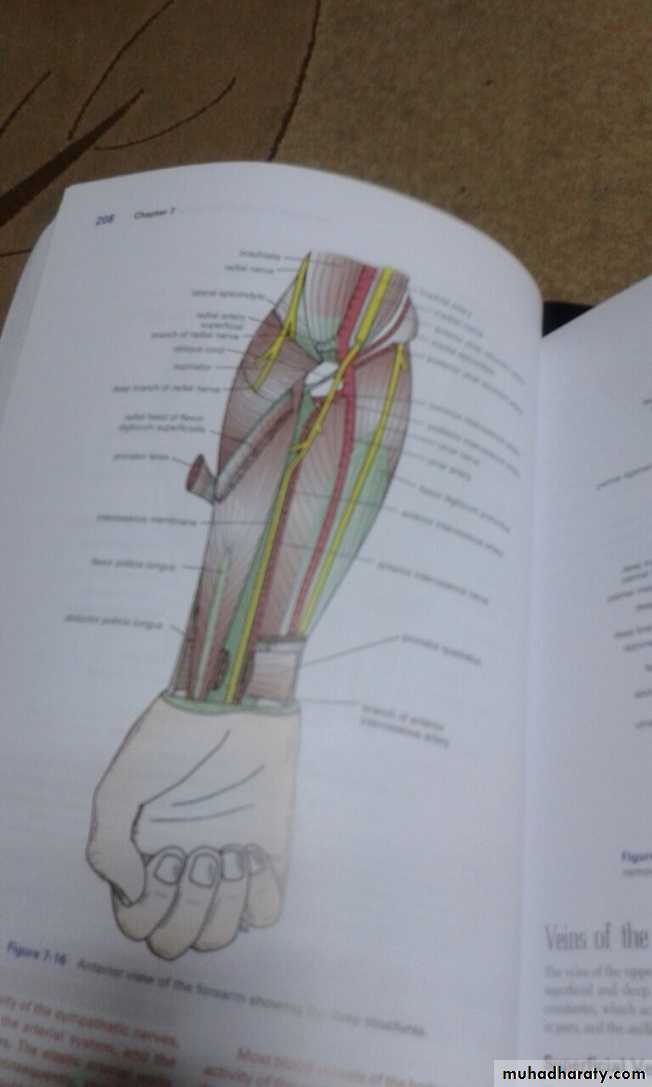
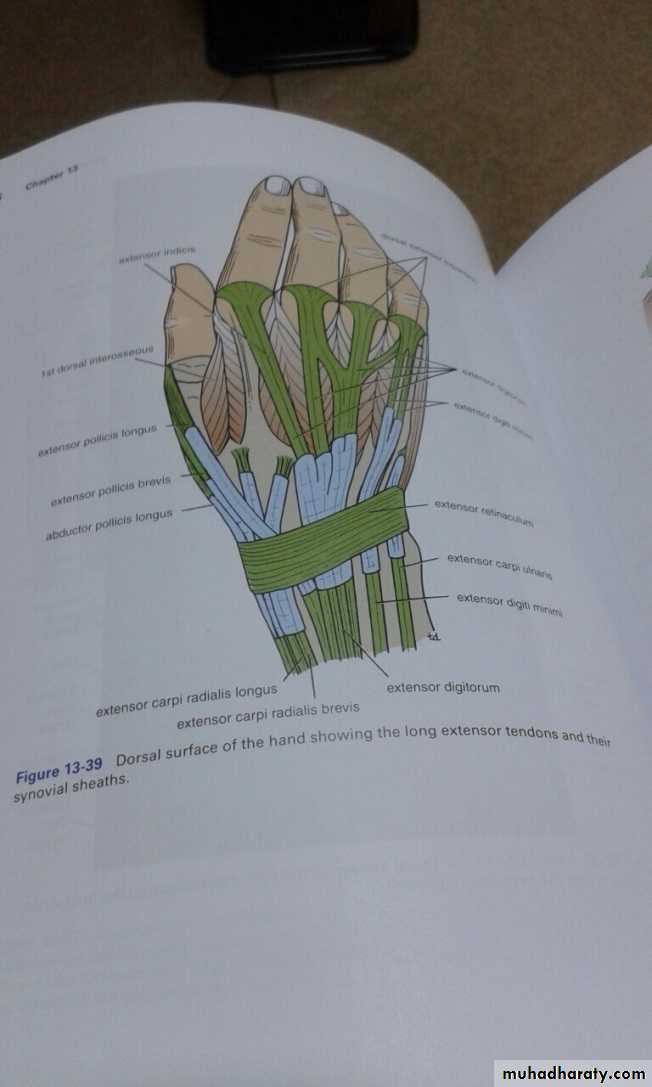
It includes 7 superficial & 5 deep Ms .The superficial are Brachioradialis,Extensor carpi radialis longus, Extensor carpi radialis brevis,Extensor digitorum,Extensor digiti minimi ,Extensor carpi ulnaris & Anconeus muscles.The Deep group includes Abductor pollicis longus,Extensor pollicis brevis, Extensor pollicis longus , Extensor indices & Supinator Ms
Posterior compartment of Forearm
The Brachioradialis takes origin from upper two thirds of lateral supracondylar ridge& lateral intermuscular septum.It is inserted into the lateral side of Radius bone.
Extensor carpi radialis longus takes origin from lower third of lateral suracondylar ridge & lateral intermuscular septum.It inserts into the base of 2nd metacarpal bone.
Extensor carpi radialis brevis arises from lateral epicondyle& radial collateral ligament.It is inserted into the base of the 3rd metacarpal bone.
Extensor digitorum takes origin from lateral epicondyle .It gives 4 tendons to the medial four fingers on the back& insert via extensor expansion to middle & distal phalanges.
Extensor digiti minimi takes origin from lateral epicondyle too.Its tendon join the tendon of extensor digitorum for the little finger.
Extensor carpi ulnaris takes origin from lateral epicondyle & posterior border of Ulna bone.It is inserted into the medial side of the base of 5th metacarpal bone.
Anconeus takes origin from lateral epicondyle & inserts into the lateral side of Olecranon process& upper one fourth of posterior surface of Ulna bone.
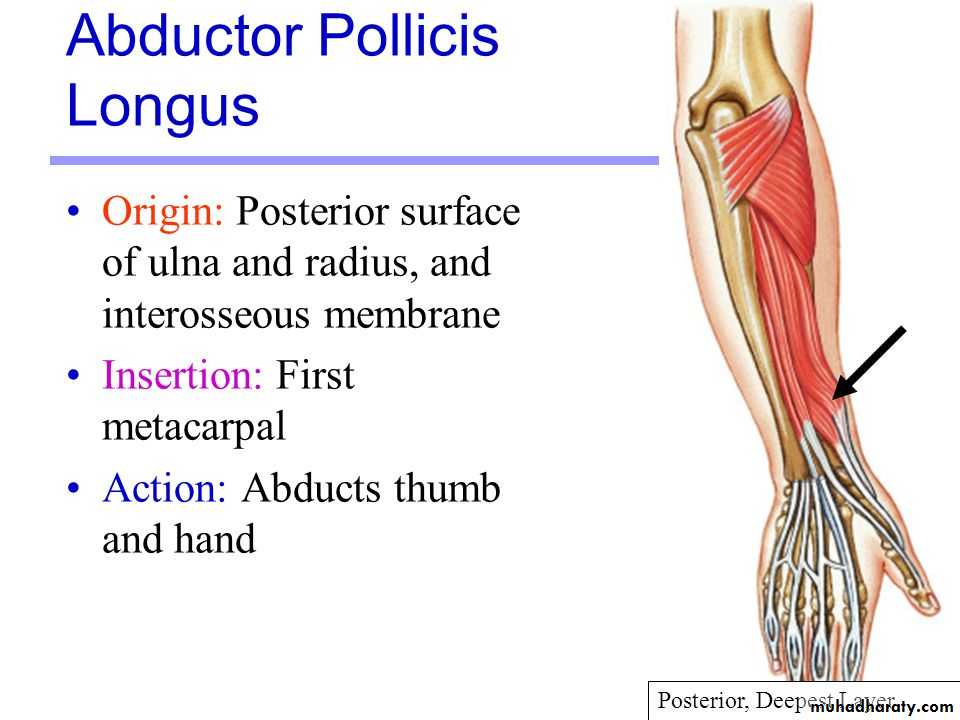
Abductor pollicis longus takes origin from posterior surface of Ulna & Radius below the Anconeus.It is inserted into the base of 1st metacarpal bone.
Extensor pollicis brevis takes origin from posterior surface of Radius & from interosseous membrane.It is inserted to the base of the proximal phalanx of the Thumb.
Extensor pollicis longus takes origin from posterior surface of Ulna & interosseous membrane .It is inserted to the base of the distal phalanx of the Thumb.
Extensor indices takes origin from posterior surface of Ulna & interosseous membrane. Its tendon goes with the tendon from extensor digitorum for the index finger & joins its extensor expansion .
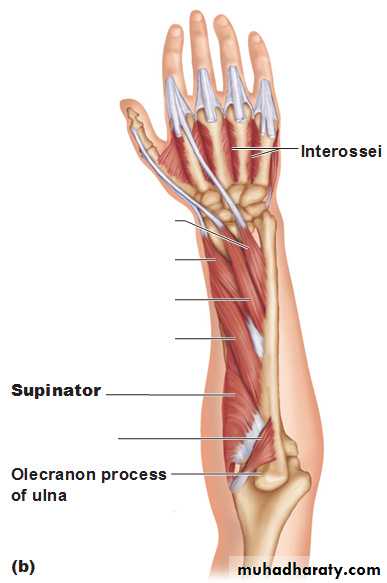
Supinator takes origin from many sites as lateral epicondyle , Radial collateral ligament , annular ligament of superior Radio-ulnar joint & from Supinator crest of Ulna bone.It wraps round the upper third of Radius to get insertion to the posterior surface ,lateral & anterior surfaces of the upper third of Radius bone.Note the following for innervations:
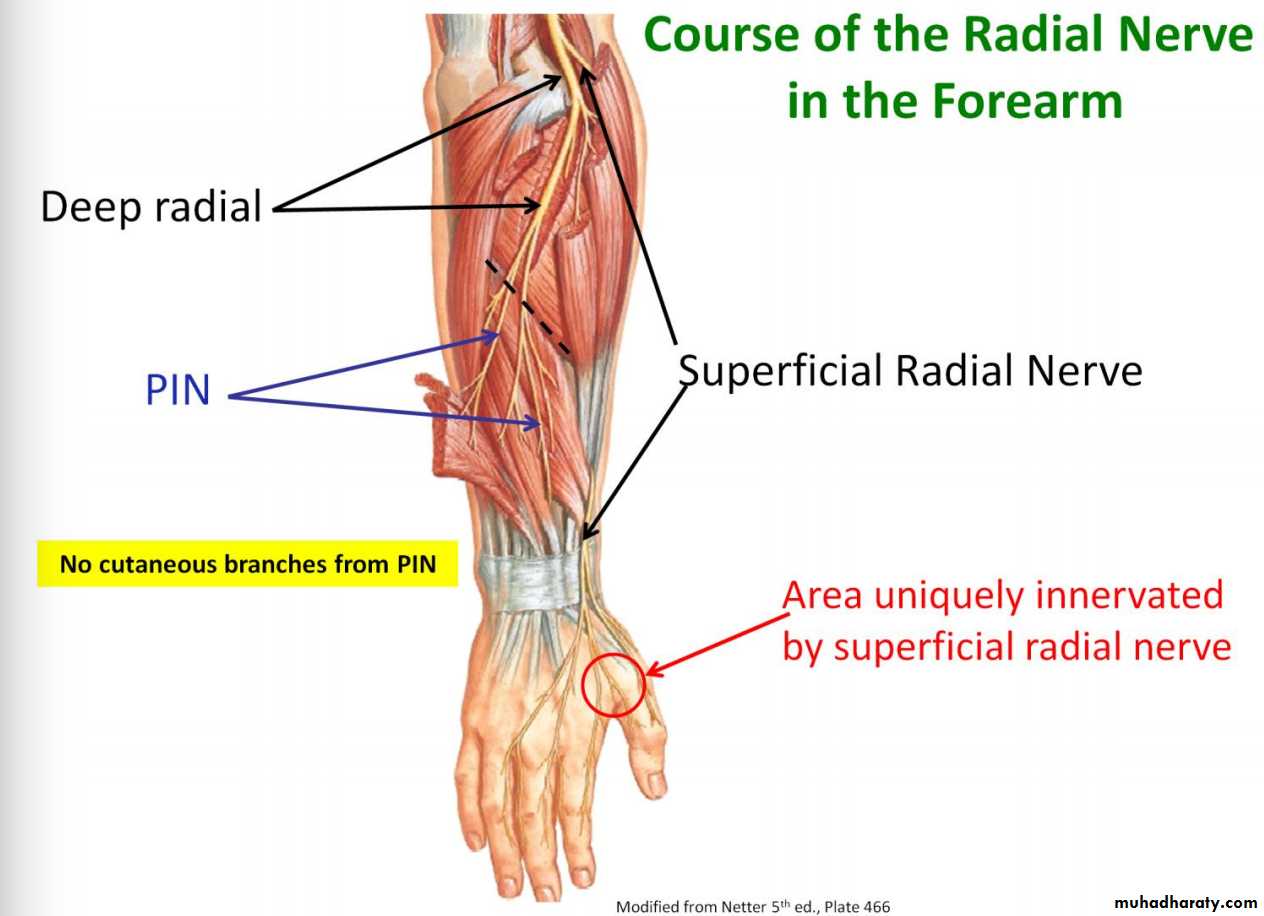
1-Brachioradialis & Extensor carpi radialis longus from Radial nerve before its division.
2-The Supinator by deep branch of Radial N as it pierces its substance.
3-Anconeus by the nerve to Anconeus given off by Radial N as it runs in Spiral groove.4-All the rest of the Extensor Ms are supplied by the posterior interosseous N which is the direct continuity of the deep branch of Radial N as it leaves the substance of Supinator M to run on the posterior surface of the interosseous membrane.
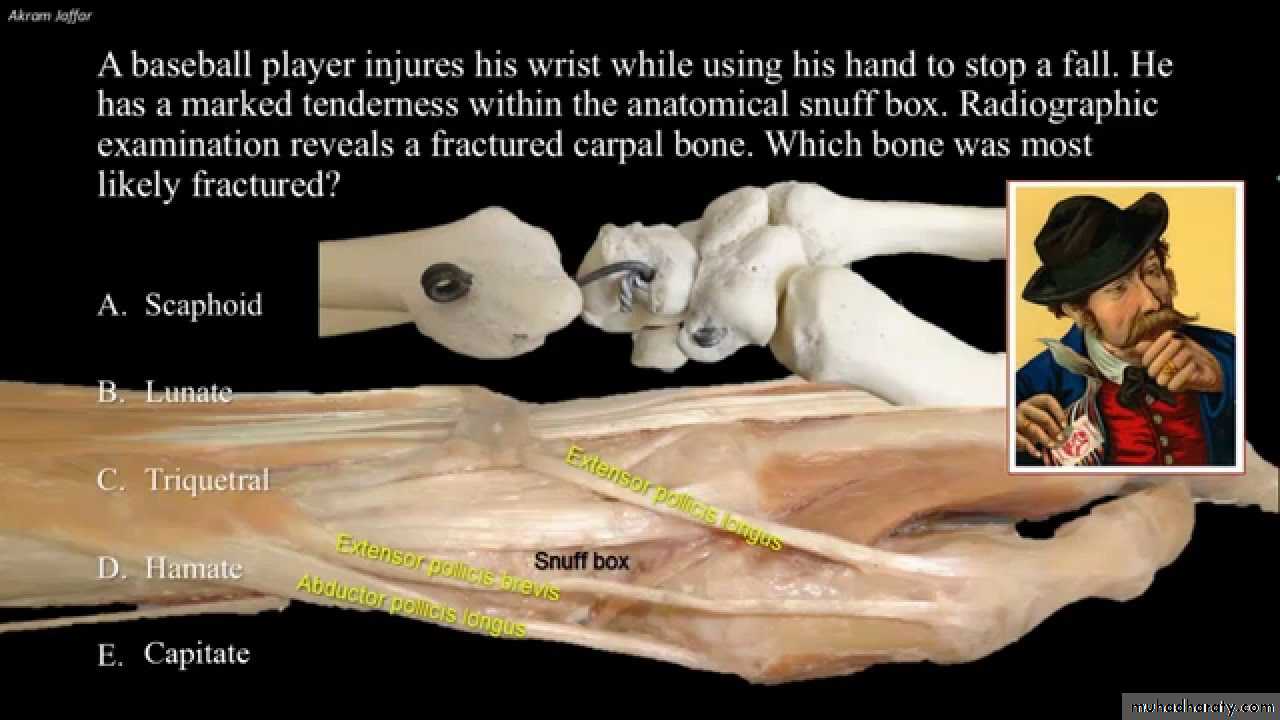
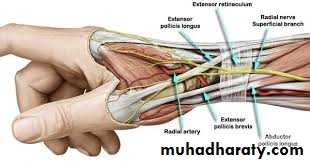
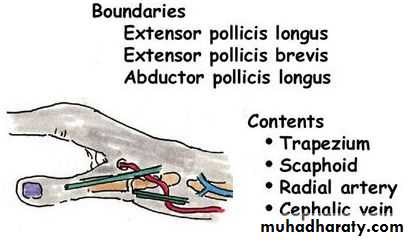
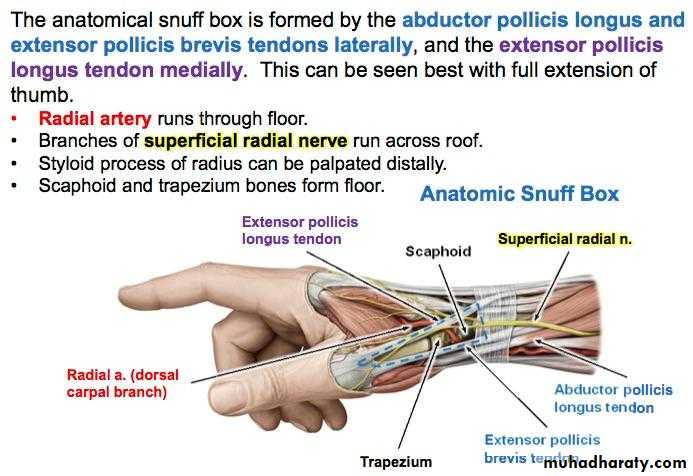
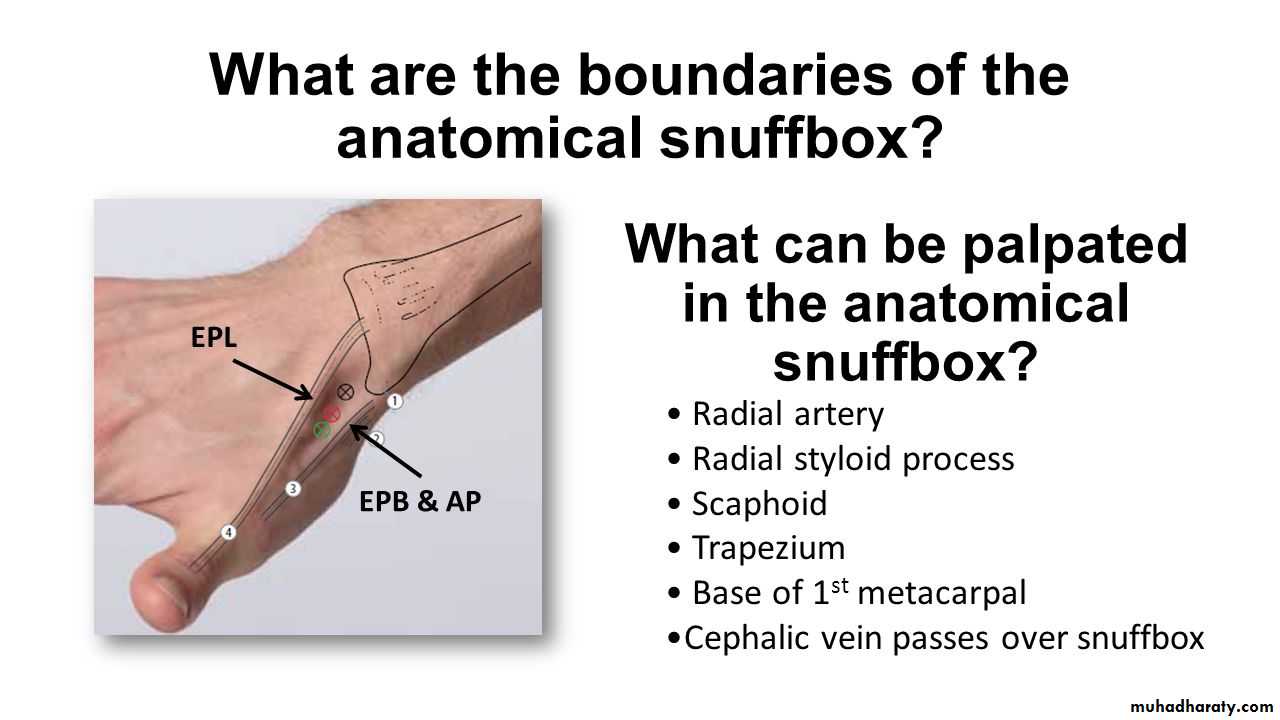
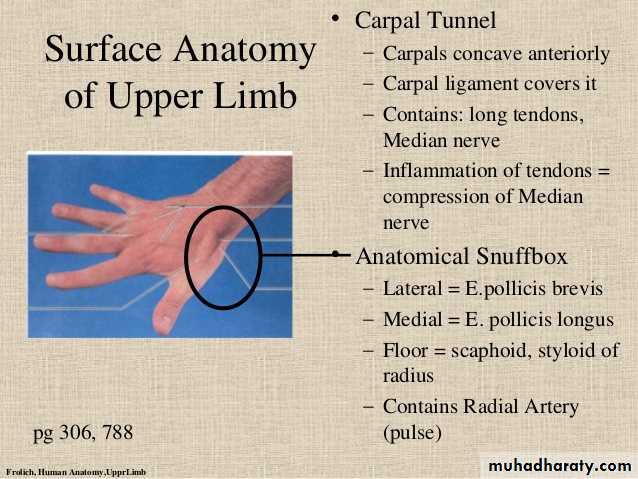
Is seen at the base of the Thumbposteriorly,it is bounded laterally ( or anteriorly )by the tendons of Abductor pollicis longus & that of Extensor pollicis brevis,while medially ( or posteriorly) by the tendon of Extensor pollicis longus.Its roof is formed by the skin & fascia being crossed superficially by the terminal branches of superficial branch of Radial N & the beginning of Cephalic vein,where as its floor is formed by Scaphoid bone + Styloid process of the Radius bonelying on them the Radial artery ( feel pulsation here).
THE SNUFF BOX
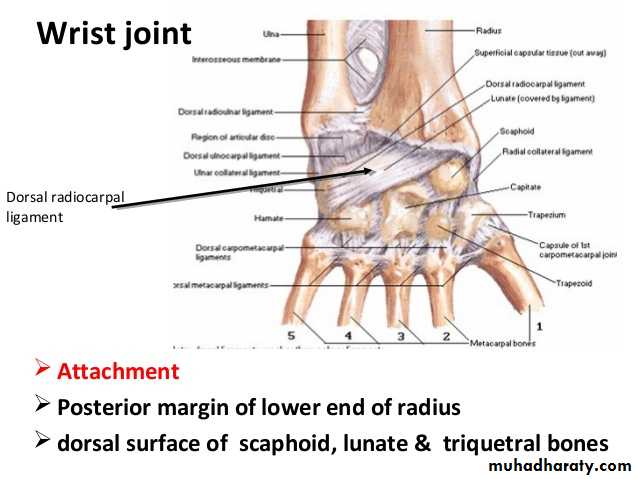
Exactly like the Flexor Retinaculum on the back of the Wtist region at the junction between back of F.A & Dorsal aspect of the Hand.It is attached to the lower end of anterior border of Radius ( laterally ) & to the Pisiform + Triquetral boneswith the Styloid process of Ulna ( medially ).Deep to it the extensor tendons pass via 6 compartments.
EXTENSOR RETINACULUM
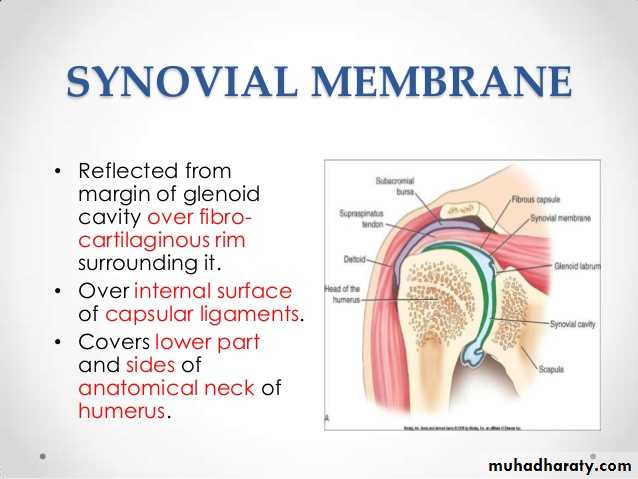
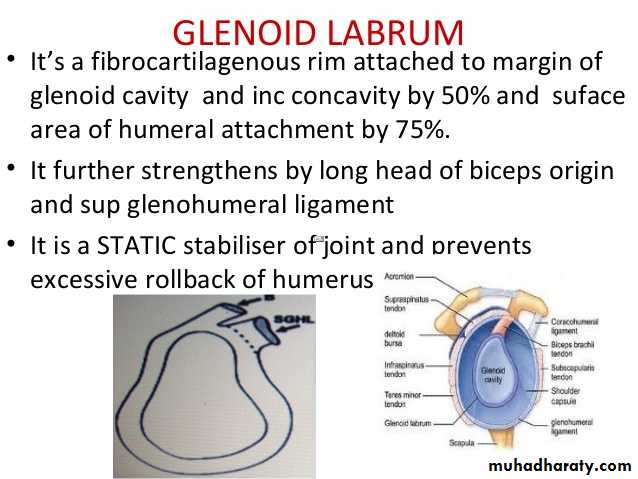
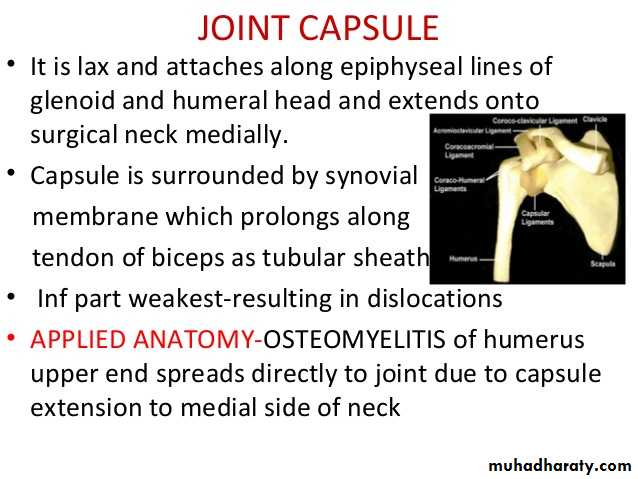
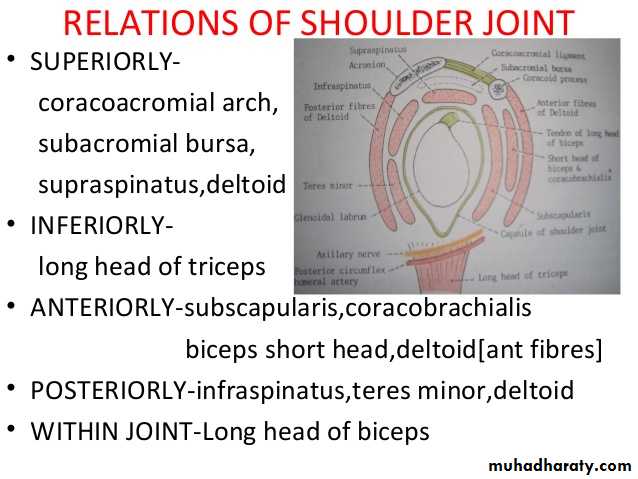
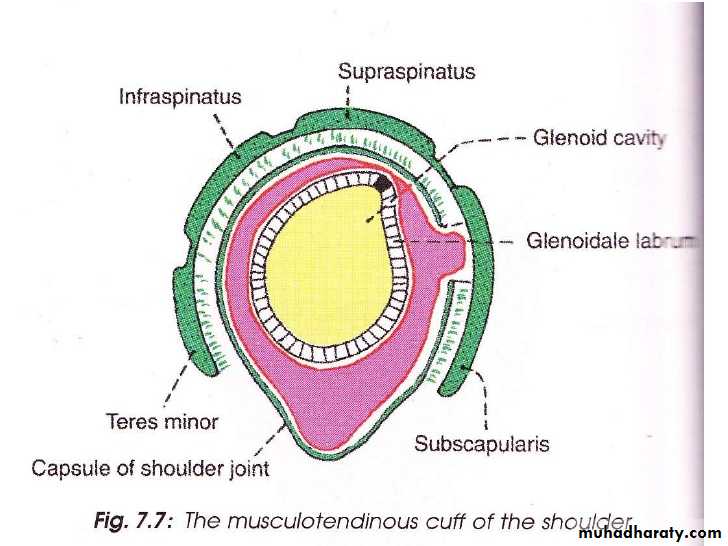
It is a synovial joint of ball & socket variety between the shallow glenoid cavity of Scapula & hemispheroidal head of Humerus ( both articular surfaces are covered by hyaline cartilage.The concavity of Glenoid fossa is deepened by a fibro-cartilagenous rim known as Glenoid labrum.The thin & lax capsule allows freedom of movements at the joint ,it is re-inforced by the tendons of the Rotator cuff Ms.The capsule is lined by from inside by synovial membrane which forms a cavity ( synovial cavity).The ligaments of the joint are:THE SHOULDER JOINT
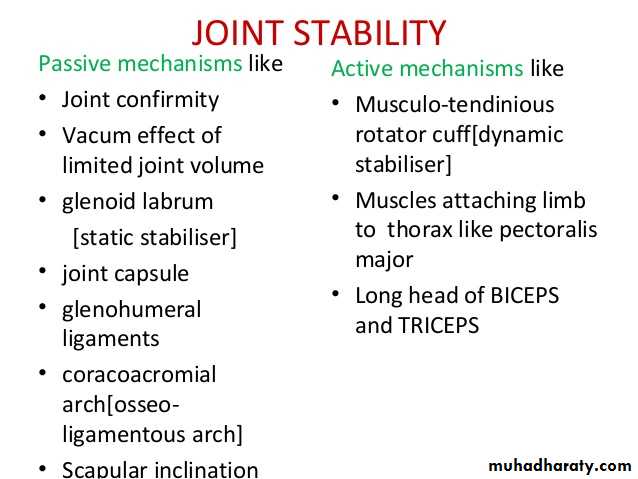
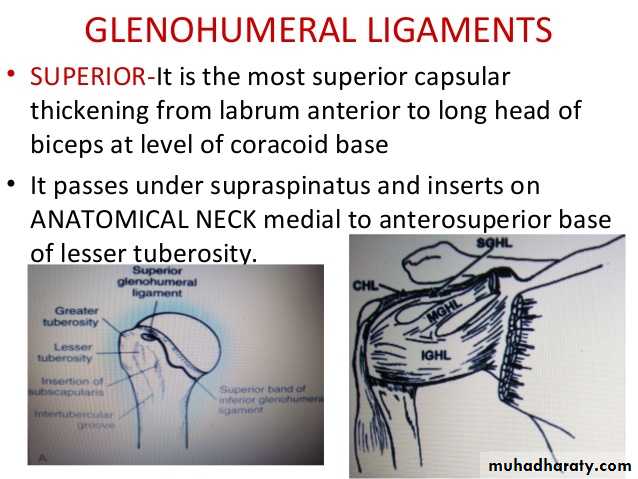
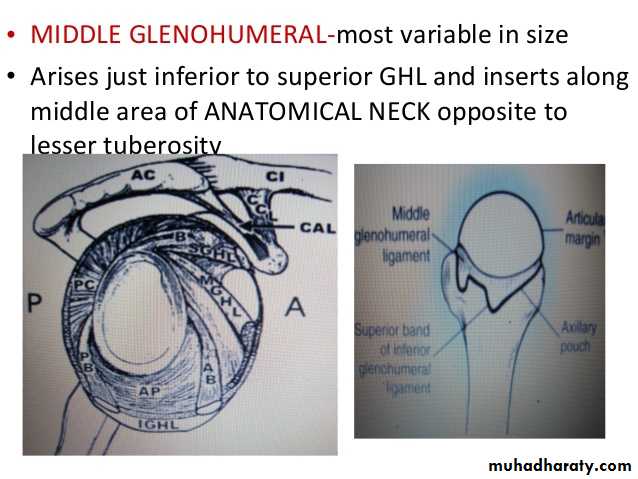
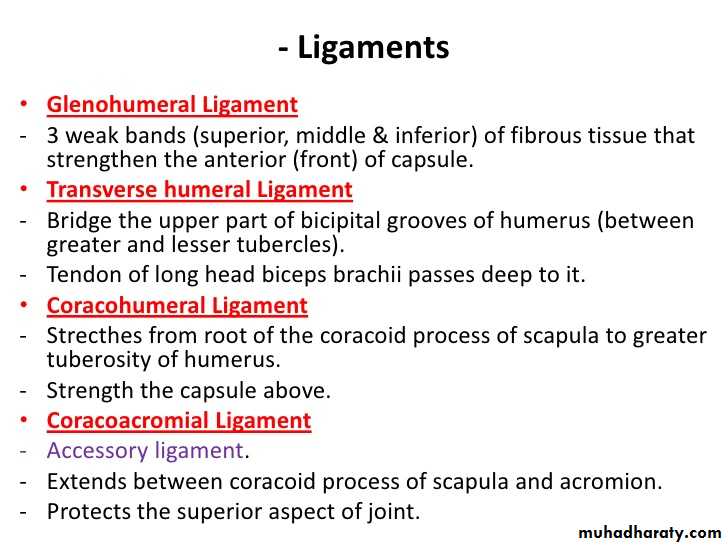
• 1- Glenohumeral ligaments which are 3 in number, superior ,middle & inferior (known as intrinsic ligaments).
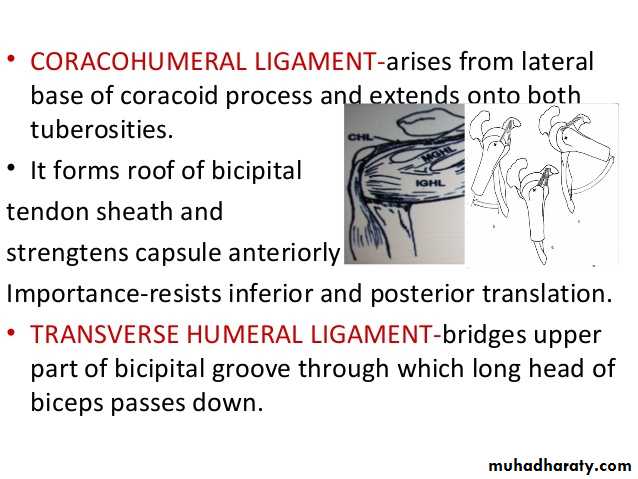
• 2- Coraco-humeral ligament( Extrinsic ligament ).It is a thick band from the root of coracoid process to the upper part of the front of greater tuberosity.
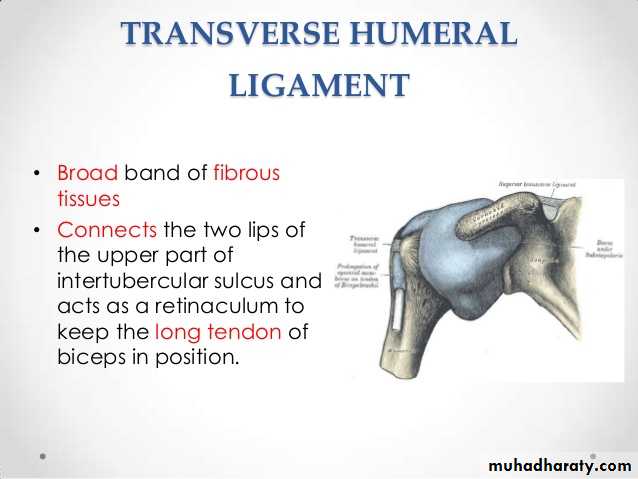
3- Transverse humeral ligament ( Extrinsic ) ,it stretches between the lips of Bicepital grooveof the humerus converting it into a canal for the passage of the tendon of long head of biceps.
• 4-Coraco-acromial ligament( accessory),its apex attached to the a cromion & its base attaches to the lateral border of the Coracoid process.
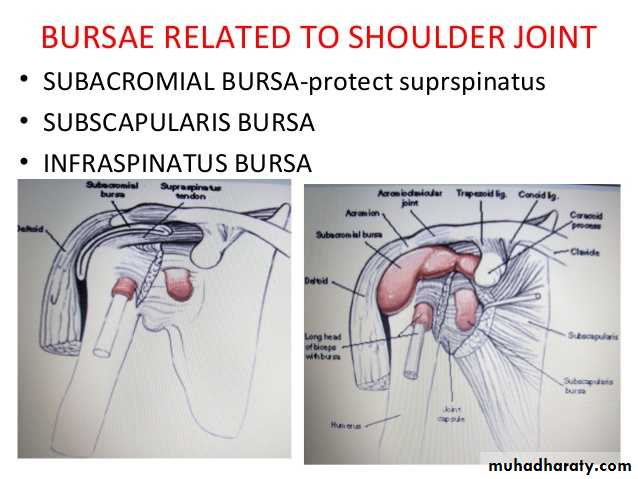
• 5-There are 4 bursae related to the joint ,these are the subscapular,infraspinatous, Subacromial & subcoracoid bursae.
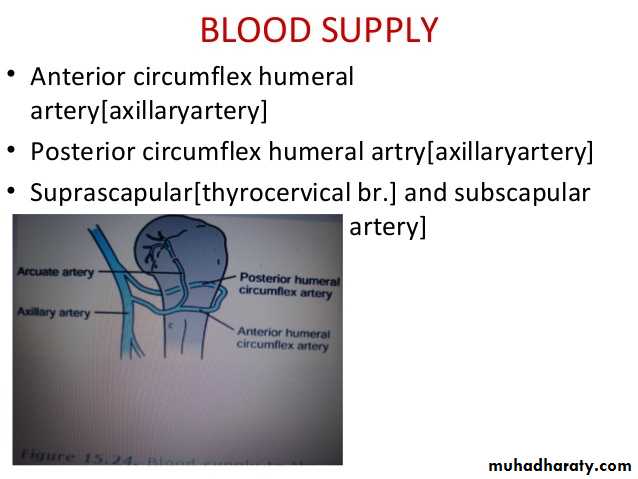
The joint receives articular ( sensory ) nerve supply from the Axillary & suprascapular nerves.It receives blood supply from anterior & posterior circumflex humeral ,and also from circumflex scaular & suprascapular arteries.The movements are as follows:
• 1-Flexion is performed by anterior fibers of Deltoid,clavicular head of pectoralis major,Biceps & Coracobrachialis muscles.
• 2-Extension by posterior fibers of Deltoid& teres major muscles.
• 3-Abduction by supraspinatous up to 18 degree,then by the lateral fibers of Deltoid from 18—90 degree.Beyond 80 degree occurs at the shoulder girdle due to rotation of scapula by Trapezius & Serratus anterior muscles.
• 4-Adduction by Pectoralis major & Latissimus dorsi muscles.
• 5-Medial rotation by Pectoralis major,anterior fibers of Deltoid& Subscapularis .
• 6-Lateral rotation by posterior fibers of Deltoid,infraspinatous & Teres minor Ms.
• 7-Circumduction is a combination of all the above movements.
• 1-Due to instability of the joint & laxity of the capsule,it is frequently lible to inferior dislocation( the capsule here is least protected by muscles.This dislocation may cause injury or pressure on the Axillary nerve.
• 2-Osteoarthritis & Rheumatoid arthritis which may needs artificial joint replacement,
• 3-Supraspinatous tendinitis is usually secondary to subacromial bursitis,thus results in the inability to initiate abduction.
Applied Anatomy:
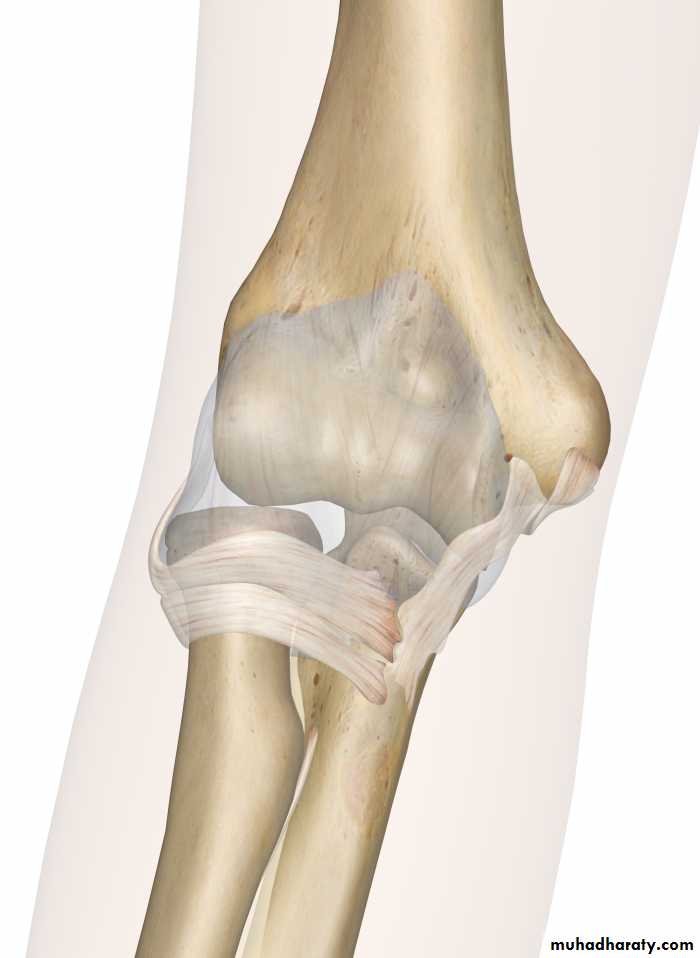
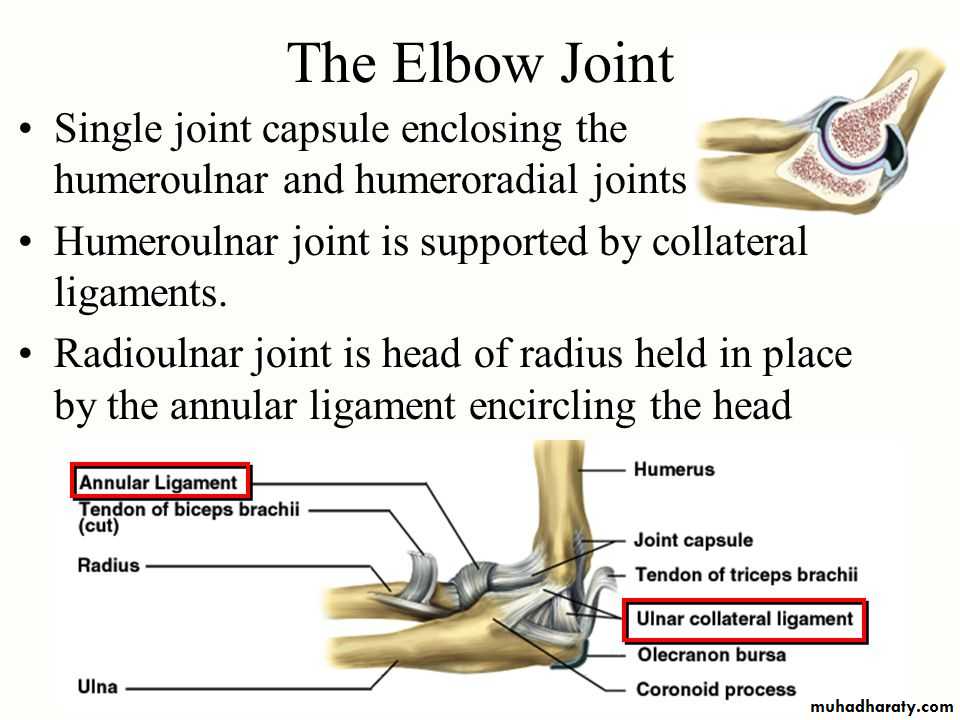
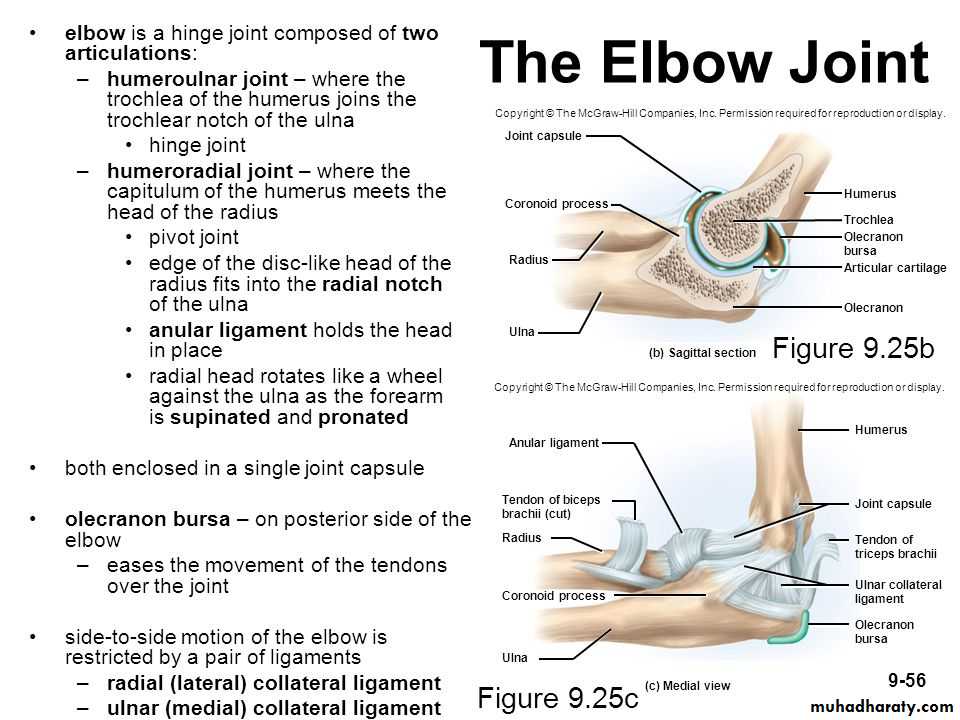
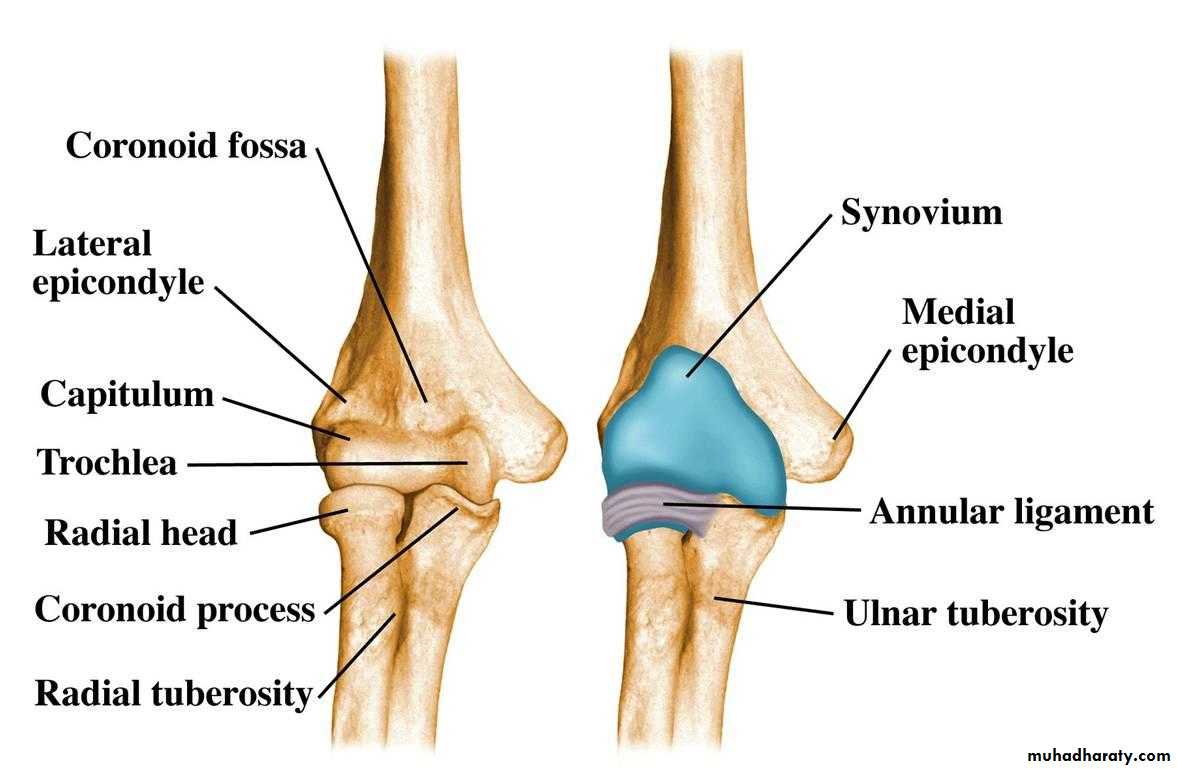
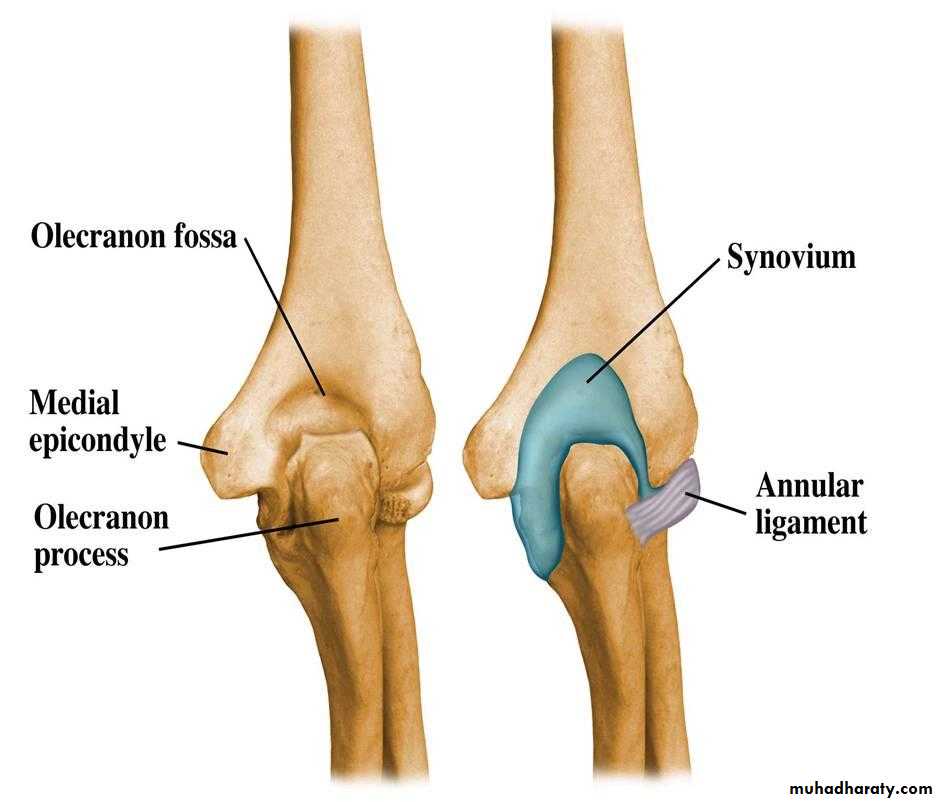
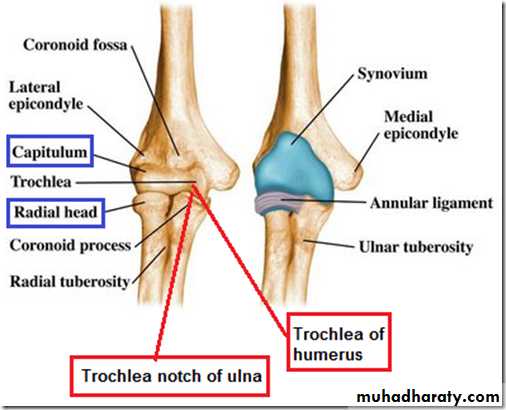
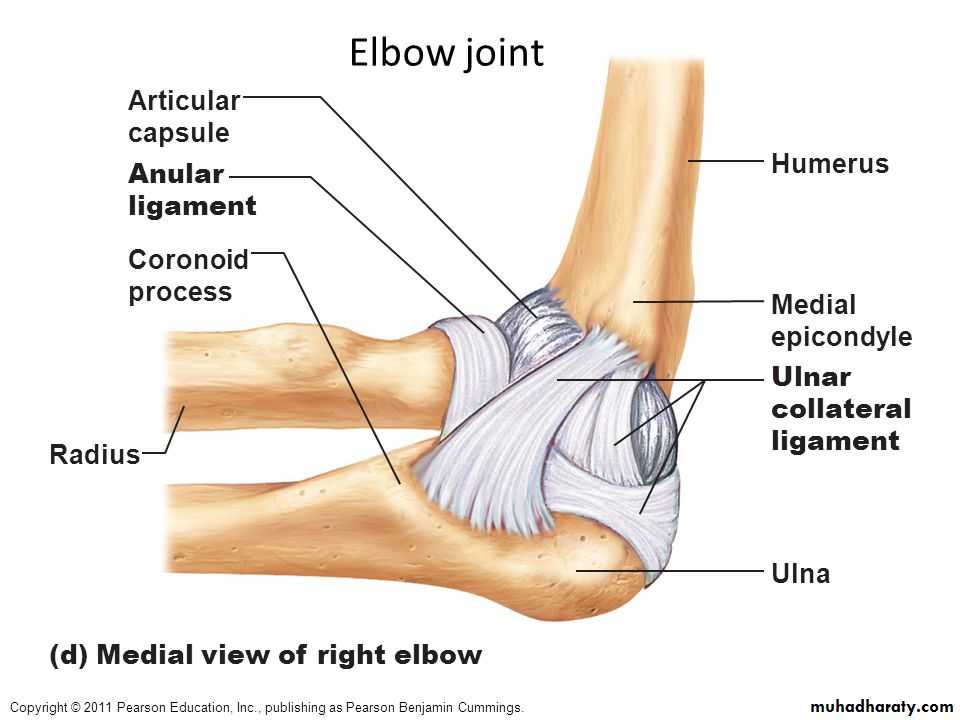
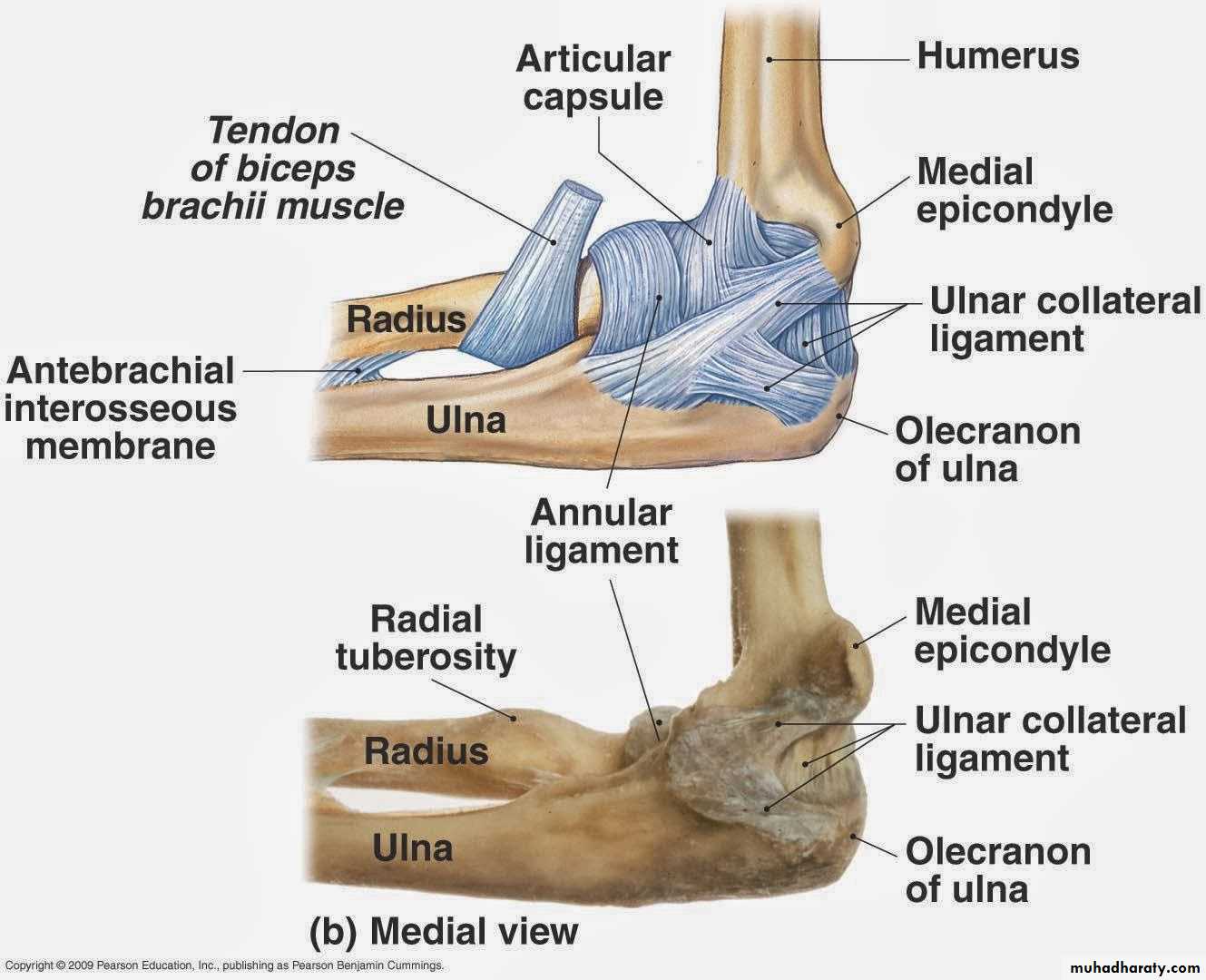
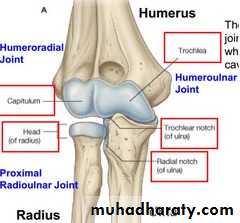
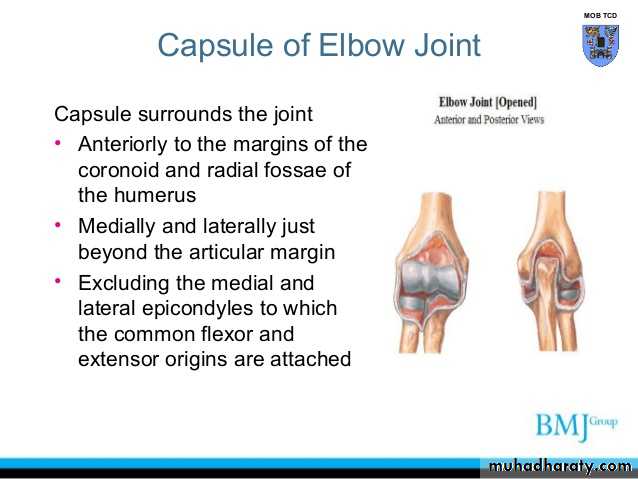
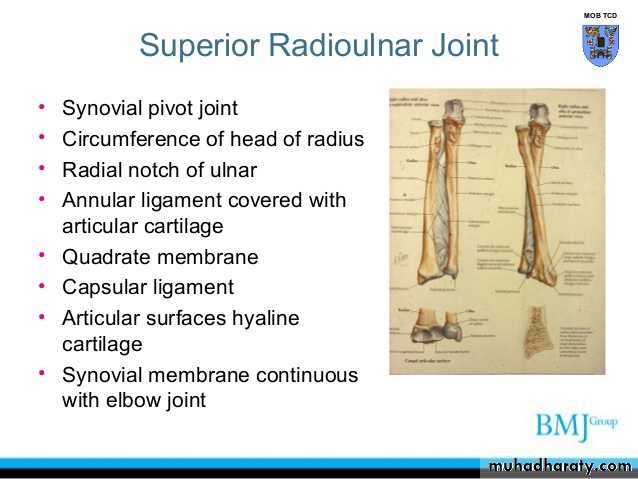
Is a compound synovial joint of hing variety,includes 2 articulations a Humeroulnar & Humeroradial.The Trochlea of the humerus articulates with the Trochlear notch of Ulna.The Capitulum of Humerus articulates with head of Radius,they are covered by hyaline cartilage.The capsule is attached (above ) in front to the medial epicondyle&upper margins of Coronoid & Radial fossa,but from behind along the trochlear margin,margin of Olecranon fossa & over the Capitulum.Below along the margins of the Coronoid & Olecranon processes and to the Annular ligament around the head of the Radius.The inner surface of the Capsule & the 3 fossae are lined by synovial membrane.
THE ELBOW JOINT
Ligaments are the followings:
1-Ulnar collateral(Medial) ligament.It is triangular band with anterior,posterior & inferior thick bands and middle thin part.2-Radial collateral (lateral) ligament .It extends from lateral epicondyle of the Humerus to the Annular collateral ligament.
3-Anterior & posterior ligaments which strengthen the capsule in front &behind.
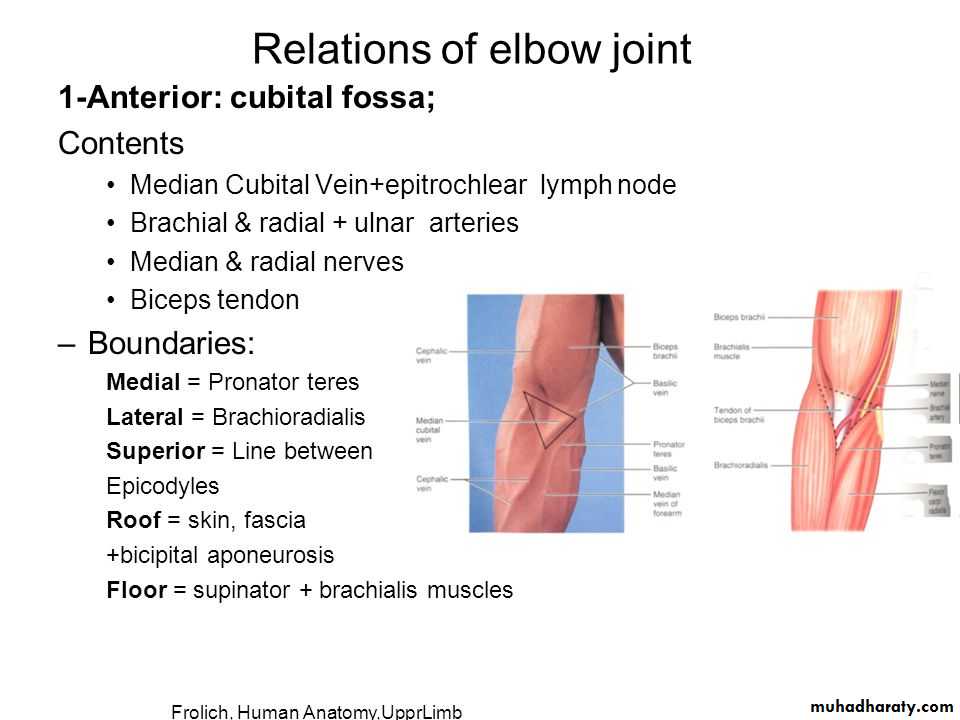
The main relations are as follows:
1-Anteriorly by Brachialis,tendon of Biceps,Median N & Brachial artery.2-Posteriorly by Anconeus & insertion of Triceps.
3-Medially by common Flexor origin & the Ulnar nerve.
4-Laterally by common Extensor origin & Supinator M.
The joint are supplied by articular (sensory) branches from Radial & Musculocutaneous nerves.The blood supply by branches from the anastomosis around the Elbow joint.The main movements at the joint are the followings:
1-Flexion movement is performed by Brachialis & Biceps .
2-Extension is performed by Triceps & Anconeus.
Applied Anatomy includes the following cases:
1-Dislocation which is usually a posterior one&is often associated with fracture of the Coronoid process.Here the Anatomical Triangular relation ship between the Olecranon & the 2 Epicondyles is lost.2- Subluxation of the head of Radius(pulled elbow) occurs in children when the F.A is suddenly pulled in Pronation movement.The head of the Radius slips away from the Annular ligament.The Elbow is kept fixed in slight Flexion & Pronation,while Supination is limited and is painfull.
3-Tennis Elbow.Any abrupt Pronation may lead to pain & tenderness over the lateral epicondyle.This is possibly due to the following factors:
A-The sprain of Radial collateral ligament.
B-Tearing of the fibers of Extensor carpi Radialis Brevis.
C-Inflamation of the Bursa related to M tendon.
4-Student's Elbow: Repeated excessive friction may cause inflammation of subcutaneous Olecranon Bursa.Gout may cause subcutaneous Bursitis.
5-Effusion of the joint,leads to distension which occurs posteriorly ,because here the Capsule is weak&the covering deep fascia is thin.Aspiration is done on any side of the Olecranon to remove the fluids.
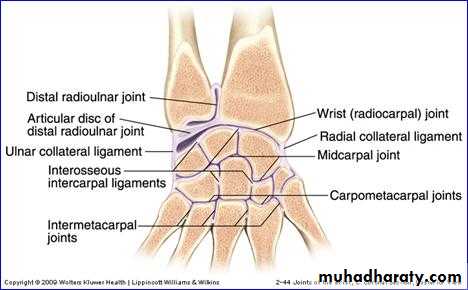
THE WRIST Joint
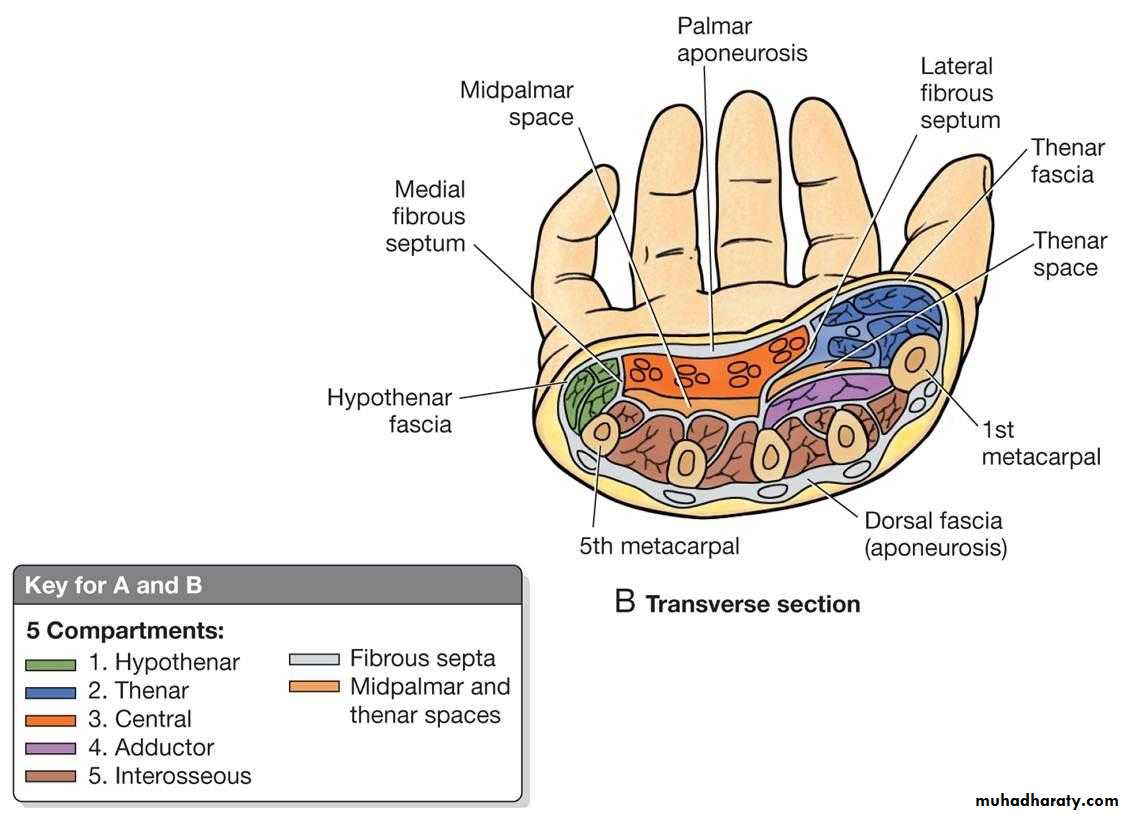
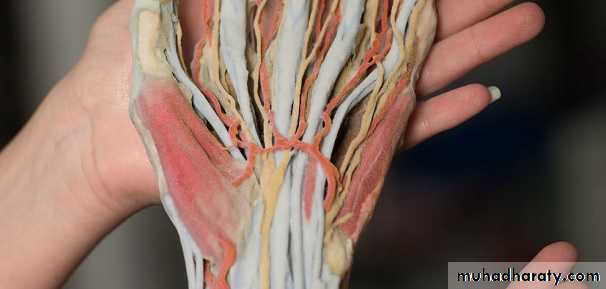
1-The Thennar Space deep to palmar palmar aponeurosis& along the flexor tendons of Index finger & in front of fascia covering Adductor Pollicis M.It is limited by the intermediate & lateral Palmar septae….
2-The Mid Palmar Space ,lies deep to palmar aponeurosis &along flexor tendons&in front of the fascia covering interossei between medial &intermediate palmar septae.
3-The Superficial Pulp Spaces.
The Spaces in The Palm
4-The Ulnar Bursa,alarge synovial space enclosing tendon of Flexor digitorum Profundus & Superficialis & extends to proximal third of the metacarpal bone.
5-The Radial bursa,around tendon of flexor pollicis longus,it continues distally to distal synovial sheath of the Thumb.
6-The Synovial Tendon Sheath of the digits.
Continue------Spaces
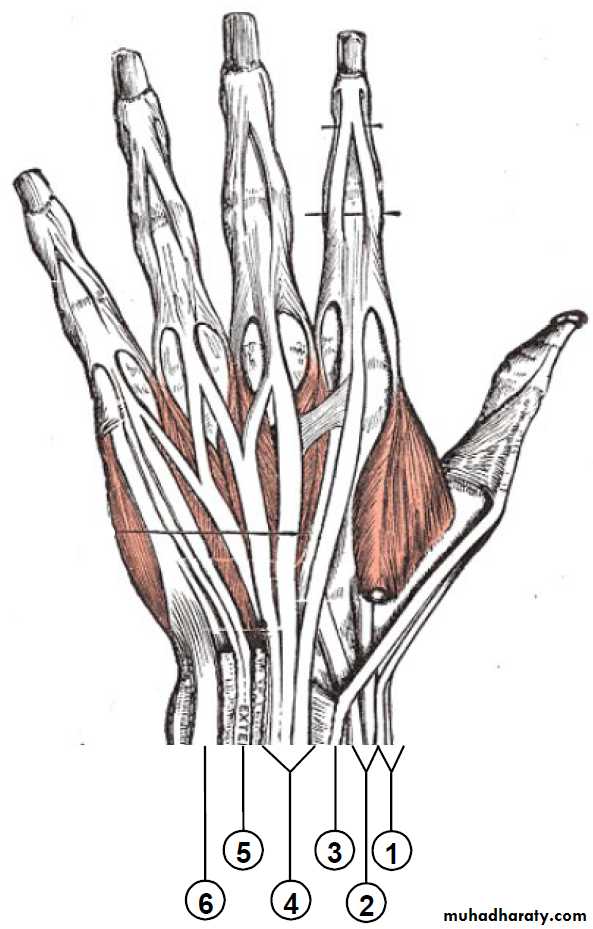
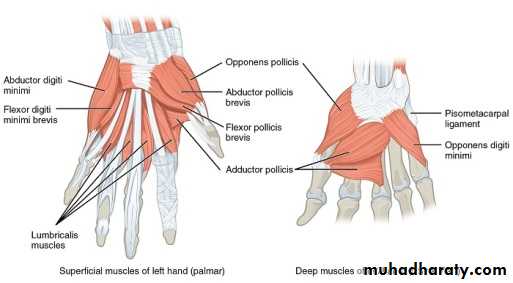
It includes 4 main Compartments as follows:
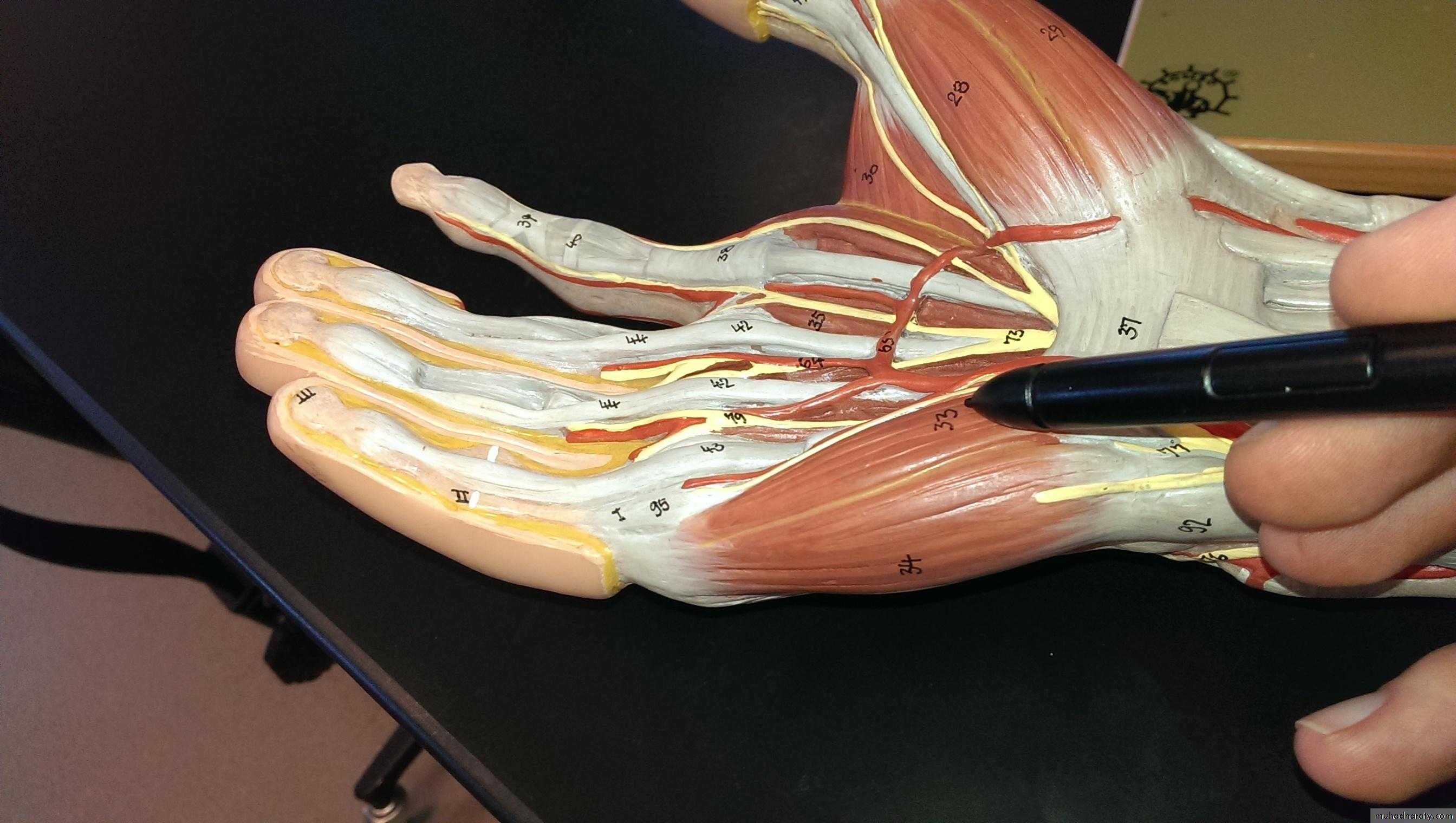
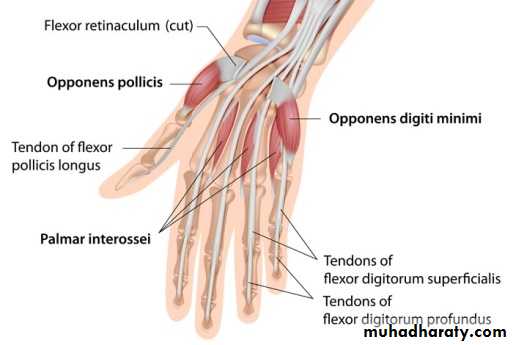
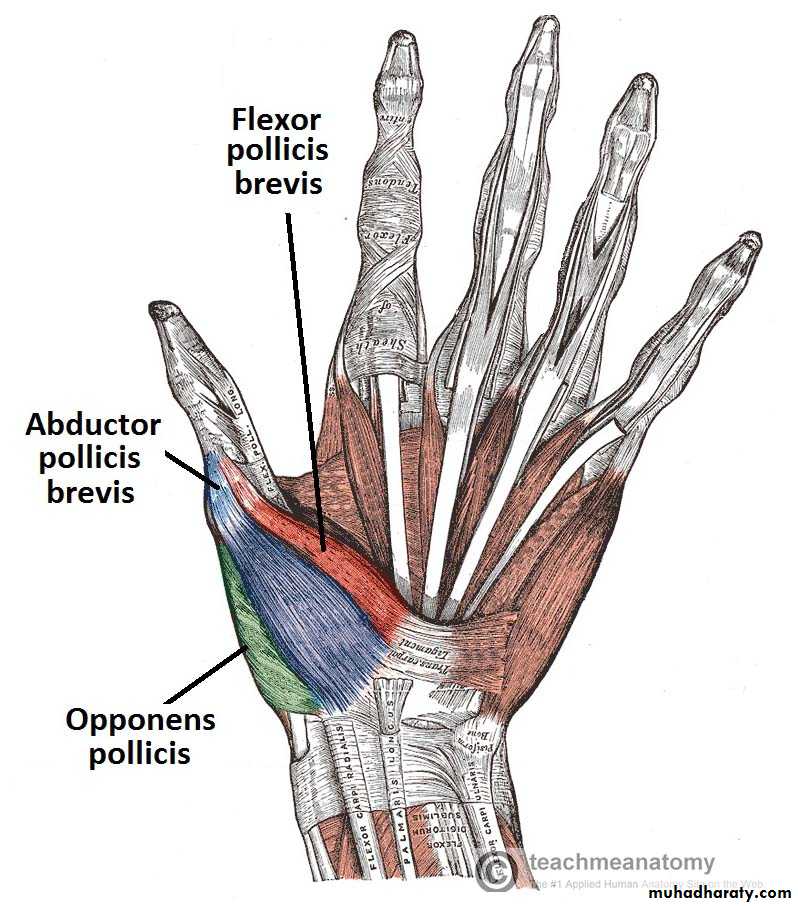
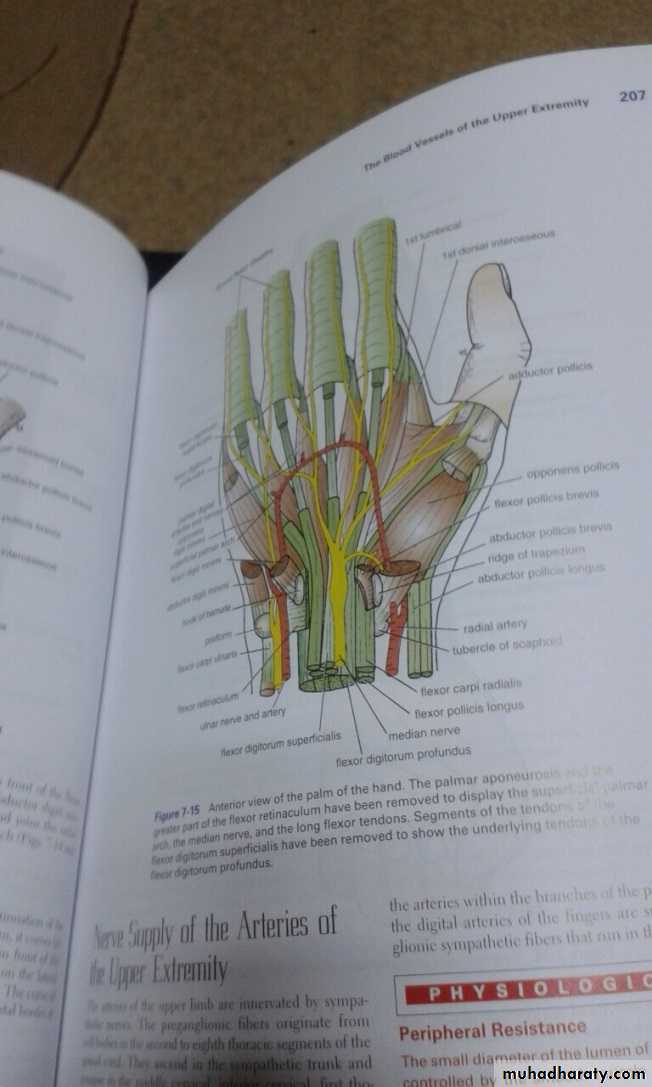
1-The Thenar Compartment ,has 3 muscles, Abductor &Flexor pollicic brevis + OpponencPollocis brevis.They are supplied by recurrent branch of the median nerve.
2-Hypothenar Compartment ,has 3 muscles , Abductor &Flexor digiti minimi brevis and Opponence digiti minimi .They are supplied by the Deep branch of the Ulnar Nerve.
Compartments of The Palm
3-The Central compartment contains :
A-Palmar Aponeurosis
B-Superficial Palmar Arterial Arch.
C- 4 tendons of Flexor Digitorum Superficials
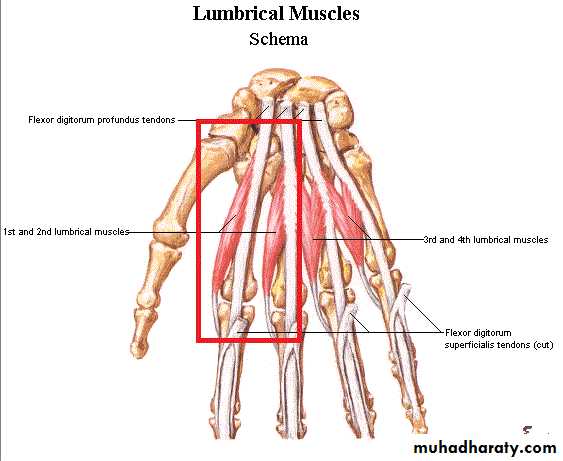
D- 4 Tendons of Flexor Digitorum Profundus & Associated 4 Lumbricals muscles.
E-The branches of the Median Nerve.
Continue-----Compartments
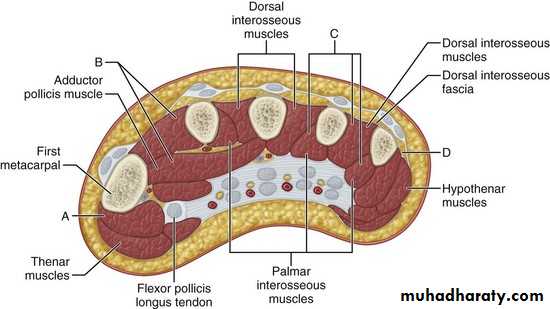
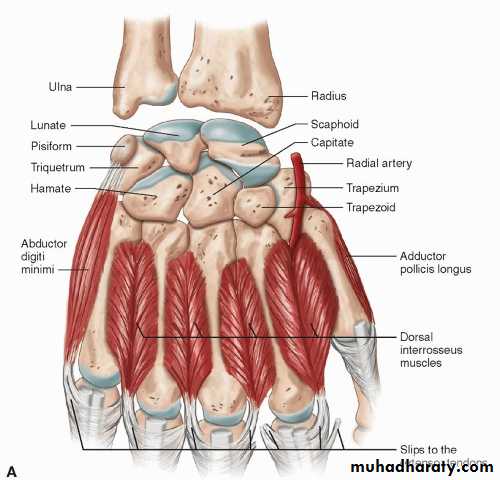
4-The Interosseous-Adductor Compartment contains the followings:A-The Adductor Pollicis muscle.
B- 4 Dorsal interossei muscles.
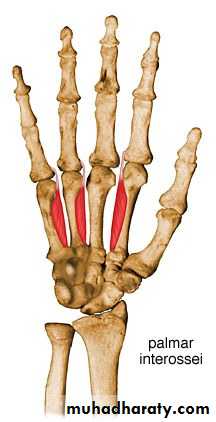
C- 3-4 Palmar interossei muscles.
D- The Deep Palmer Arterial Arch.
E- The deep branch of the Ulnar Nerve lies within the concavity of the Deep Arch.
F-The Metacarpal bones.
Continue on Compartments
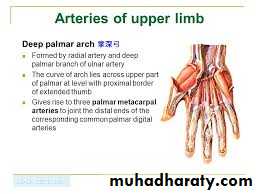
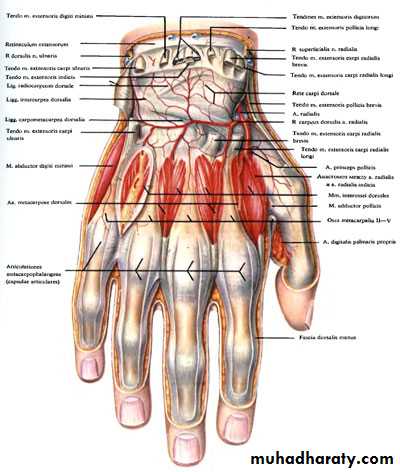
It gives the following branches :
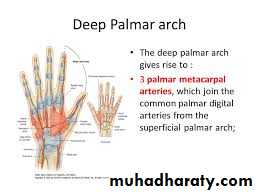
1- Three Palmar Metacarpal As runs on the 2nd- 4th interosseous spaces.2- Three perforating branches to connect with the Dorsal Arterial Arch on dorsal aspect of the wrist.
3-Recurrent branch.
Within the concavity of the deep Arch the deep branch of the Ulnar Nerve is found here
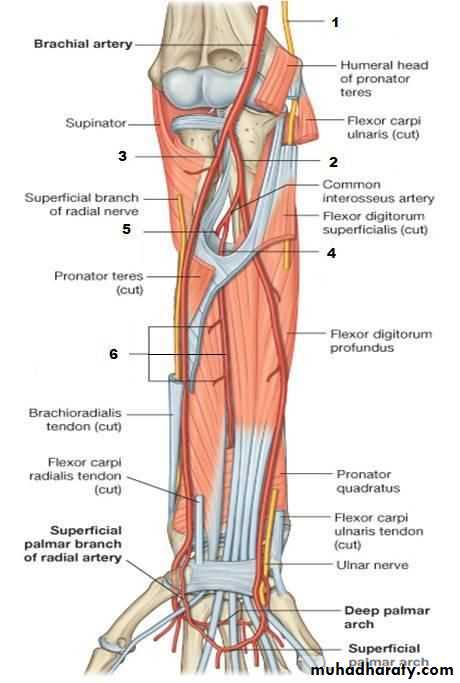
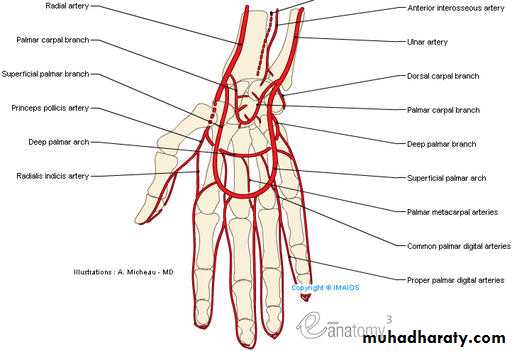
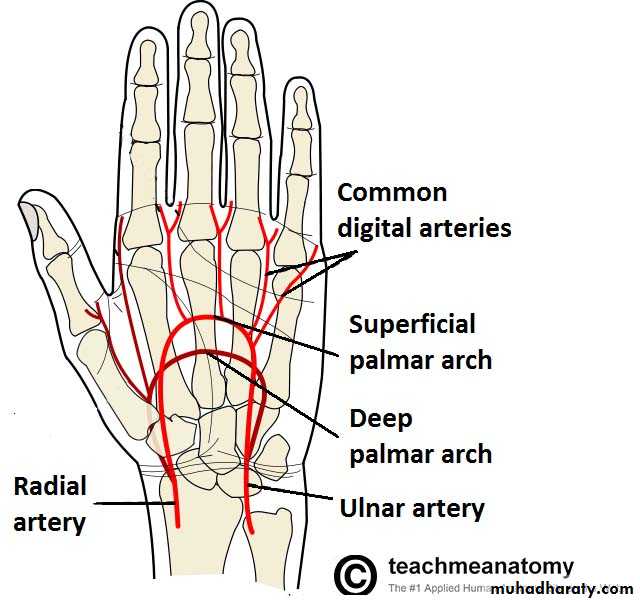
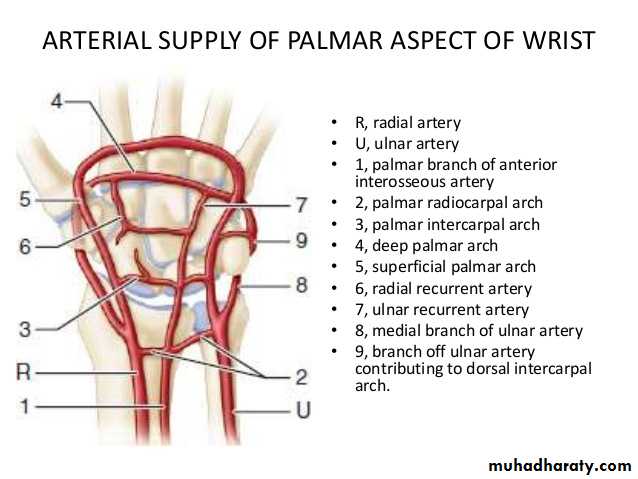
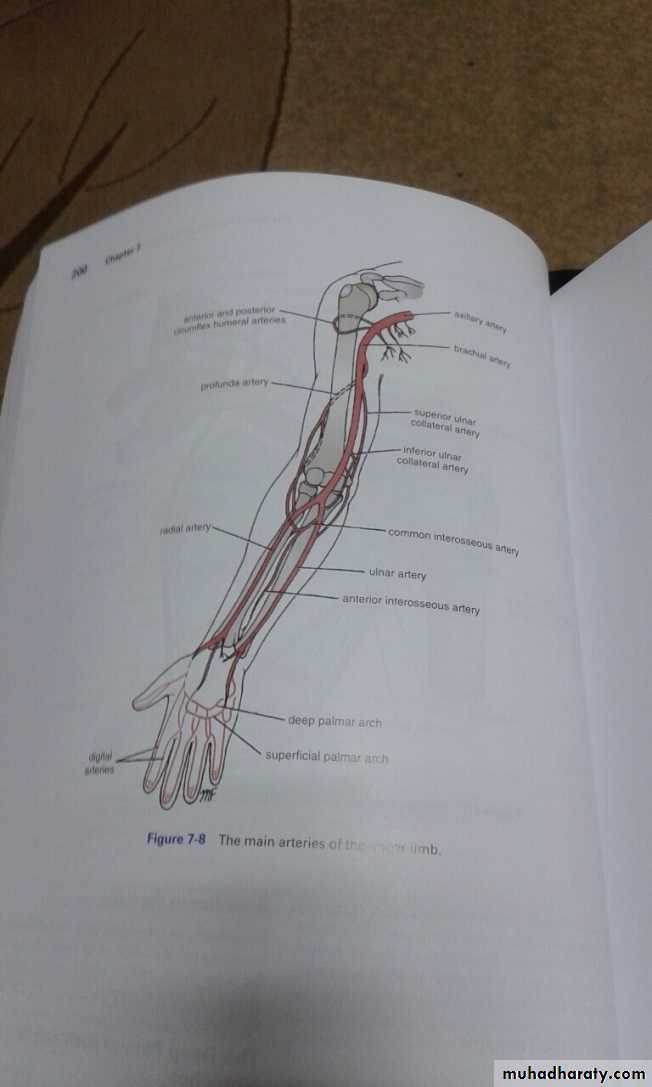
The Deep Palmar Arch
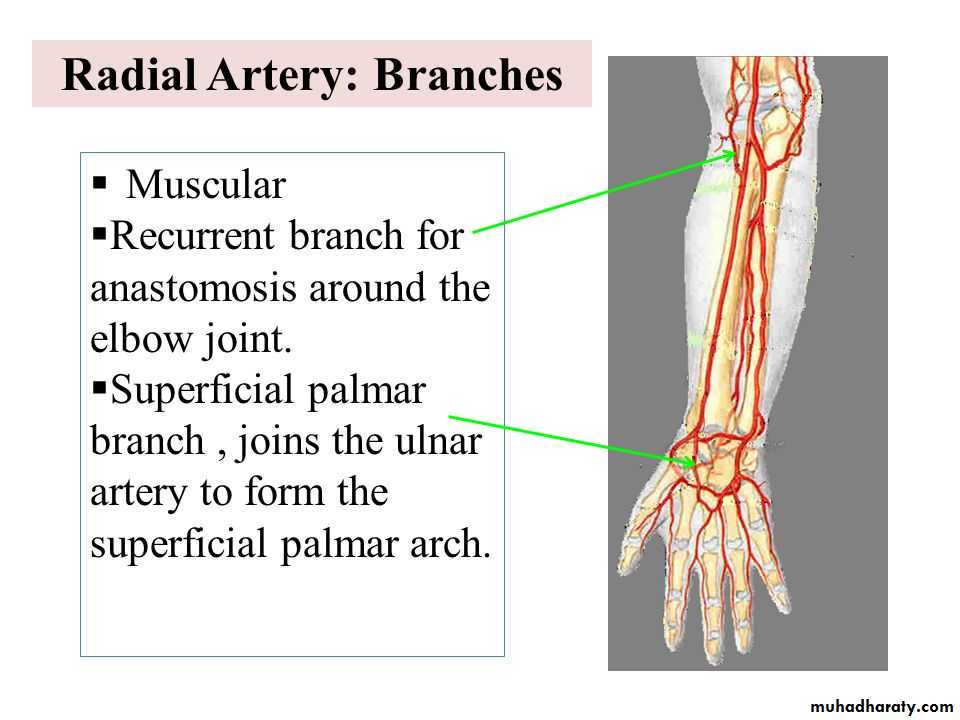
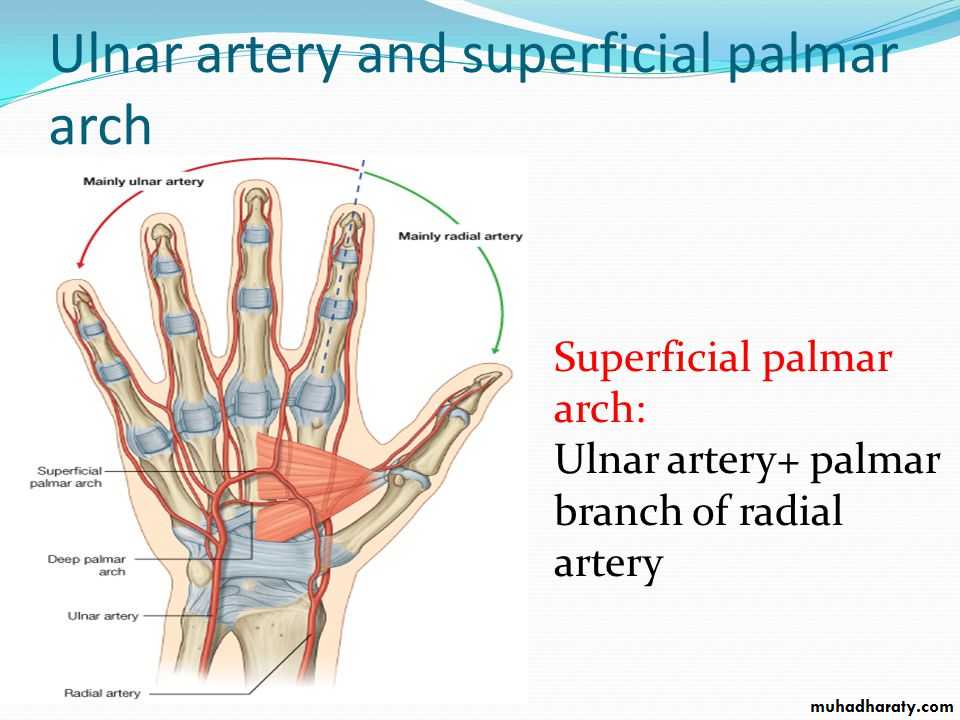
It is formed mainly by the superficial palmar branch of the Ulnar artery & is completed by the followings:
1-Superficial palmar branch of the Radial A.
2-The Princeps Pollicis A ( From R.A ).
3-The Tadialis indices A ( From the R.A )
It gives 4 common palmar digital branches, each of them will give 2 proper digital As to the sides of adjacent 2 fingers .
The Superficial Palmar Arch