By:Dr.Yossra K.Al-RobaiaayAssistant professorFICMS (FM)
Epidemiologic Measures Of AssociationEpidemiologic Measures of Association
• AssociationA statistical relationship between two or more variables
• Risk
• Probability conditional or unconditional of the occurrence of some event in time
• Probability of an individual developing a disease or change in health status over a fixed time interval, conditional on the individual not dying during the same time period
Association between exposure & Disease
Question:Is there an excess risk associated with a given exposure?
Objective:
To determine whether certain exposure is associated with a given disease
Methodology:
Use one of the epidemiologic study designsCohort
Case-control
2*2 table
Cohort Study
Assess the cumulative incidence (Ie) of disease in an exposed group
Assess the cumulative incidence (Io) of disease in unexposed group
e.g. Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Risk among Smokers
1-year risk of CHD among smokers (Ie)*
CHD
Yes No Total
Smokers 84 2916 3000
Ie = 84/3000 risk of CHD among smokers)
CHD Risk among non-smokers1-year risk of CHD among non-smokers (Io)
CHDYes No
Non-smokers 87 4913 5000
Io= 87/5000=17.4/1000/yr (1-yr risk of CHD among non-smokers)
• Risk Difference(attributable risk):
It’s the absolute effect of the exposureDifference of two risks (Risk Difference)*
Ie- Io = 28.0 – 17.4 = 10.6
the excess of MI cases that attributed to smoking
• AR% used to find the % of the event or outcome that can be prevented if we eliminate the exposure.
AR%= (AR/Ie)*100
=10.6/28 *100
= 37% of MI can be prevented if we stop smoking
• Past surgery HCV status
HCV+ HCV-• Yes 59 48
• No 54 168
• 113 216
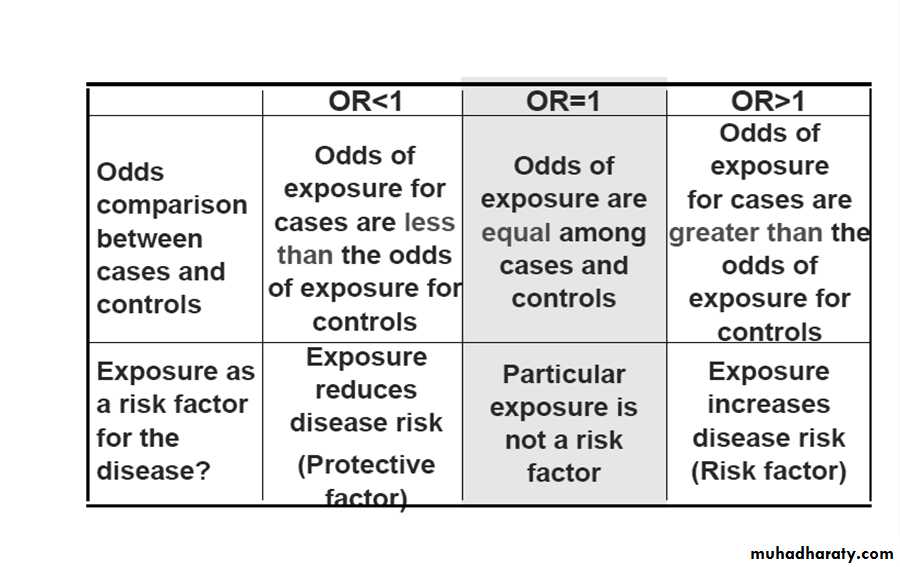
• OR= a.d/c.b
= 59* 168/ 54*48
=9912 / 2592
= 3.8
In cohort:
RR= Ie/Io = a/(a+b) / c(c+d)AR=Ie – Io = a/(a+b) - c(c+d)
AR%= AR/Ie *100 = Ie – Io /Ie *100
In case control:
OR = a.d/b.c
AR%=OR -1/OR *100
Relative Risk (RR
In a study, the incidence of pellagra among mill workers was 9/1000. The incidence among those who did not work in the mill was 44/1000 calculated :
The relative risk
• Relative Risk = Risk Ratio = 9 / 44 = 0.2
i.e mill workers had a protective effect from pellagra .
• Example
• In a case control study to evaluate the relation between smoking and MI• A total of 789 case and control
• Smoking seen in 157 of 366 cases
• Smoking seen in 110 of 423 control
Calculate OR And explain the results
• SMOKING MI +ve MI -ve
Yes 157 110• No 209 313
• 366 423
• OR= a.d/c.b
= 157* 313/ 209*110
= 49141/ 22990
= 2.13
• Smokers have risk of 2.13 times to develop MI than nonsmokers.
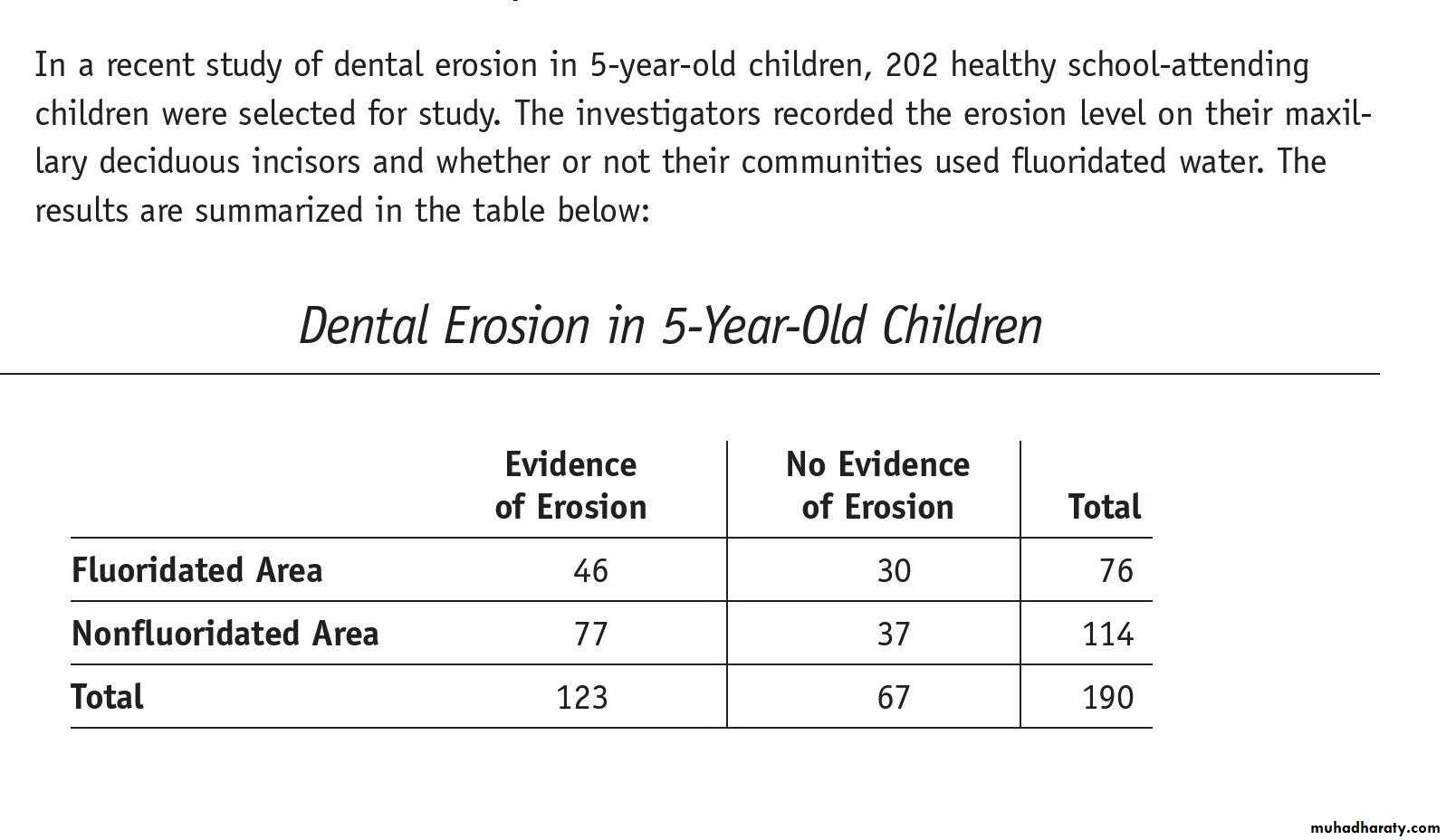
QUIZ. In a recent study of dental erosion in 5-year-old children, 202 healthy school-attending
children were selected for study. The investigators recorded the erosion level on their maxillary
deciduous incisors and whether or not their communities used fluoridated water. The results are summarized in the table below:
a. What is the incidence rate of erosion over the five years for the two groups of children?
(You may assume their teeth were free of erosion at birth.)
b. What is the rate difference between the fluoridated areas and not fluoridated areas?
c. What is the relative risk for those in the nonfluoridated group?
d. Based on your data above, does fluoridation appear to confer a risk of increased dental erosion or a protective tendency? Justify your response by appealing to the numeric value you calculated in part c.