Infant Nutrition
Objectives
1. To know about nutritional requirements for optimal growth & well being in infancy.
2. For better understanding of breast feeding regarding mechanism of lactation, composition,
adequacy, advantages, preparation of the lactating mother, problems encountered,&
contraindications.
3. Comparison between breast milk and cow’s milk regarding composition, nutritional outcome,
complications,& preparation of formula.
4. Special formulas like soy protein, lactose free,& hypoallergenic formulas.
5. Weaning.
Good nutrition is essential for:
1. Survival
2. Physical growth
3. Mental development
4. Health and well-being
Nutritional requirements
Age dependent (the younger the child the higher their energy needs per kilogram body weight).
Generally the average term baby needs in the first year of life :
Fluid 100-150 ml/kg
Calories 100 -120 kCal/kg
Protein 1.5-2 g/kg
Na 1.5 mmol/kg
K 3 mmol/kg
Premature babies may have increased needs regarding water, energy, protein, and bone
minerals to deal with their rapid growth.
Breast feeding
World Health Organization (WHO) strongly advocates breast-feeding as the preferred feeding
for all infants. The success of breast-feeding initiation and continuation depends on multiple
factors, such as:
• Education of mother
• Hospital breast-feeding practices and policies.
• Routine and timely follow-up care
• Family support .
The WHO recommends exclusive breast-feeding for the first 6 months of life.
Fifth stage Lec-
Dr.Athel
Pediatric
26/12/2016

Six months is the recommended age for the introduction of solid foods for infants.
Breastfeeding (and/or breast milk substitutes, if used) should continue beyond the first six
months, along with appropriate types and amounts of solid foods
Contribution of Breast-feeding to Health :
1. Infectious and allergic disease:
Human milk feeding decreases the incidence and severity of diarrhea, respiratory illnesses,
otitis media, bacteremia, bacterial meningitis, and necrotizing enterocolitis. •
Anti infective properties: Macrophages, lymphocytes and polymorphs, Secretory IgA,
Lysozyme, Lactoferrin (an iron containing growth factor that enhances the growth of
lactobacilli which create acidic medium that inhibits the growth of E.coli.),& anti-viral
agents.
Decreased atopic diseases and infantile colic compared to formula fed .
2. Breast-feeding and cardiovascular health
Meta-analyses have shown that breast-fed infants in industrialized countries have lower plasma
cholesterol in adult life, lower systolic blood pressure and are less obese.
3. Breast-feeding and neurological development:
There are beneficial effects of feeding preterm infants with human milk on long-term
neurodevelopment (IQ) in preterm infants.
Breast feeding strengthen the psychosocial mother-infant relationship.
4. Maternal benefits:
Decreased risk of postpartum hemorrhages, more rapid uterine involution
Longer period of amenorrhea, and decreased postpartum depression.
There is an association between a long lactation and a significant reduction of hypertension,
hyperlipidemia, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes in the mother.
Cumulative lactation of more than 12 months also correlates with reduced risk of ovarian
and breast cancer.
Adequacy of milk intake
Urine output: a well-hydrated infant voids six to eight times a day. Each voiding should soak,
not merely moisten, a diaper, and urine should be colorless.
Stool : By 5 to 7 days, loose yellow stools should be passed at least four times a day.
Growth: Rate of weight gain provides the most objective
indicator of adequate milk intake.
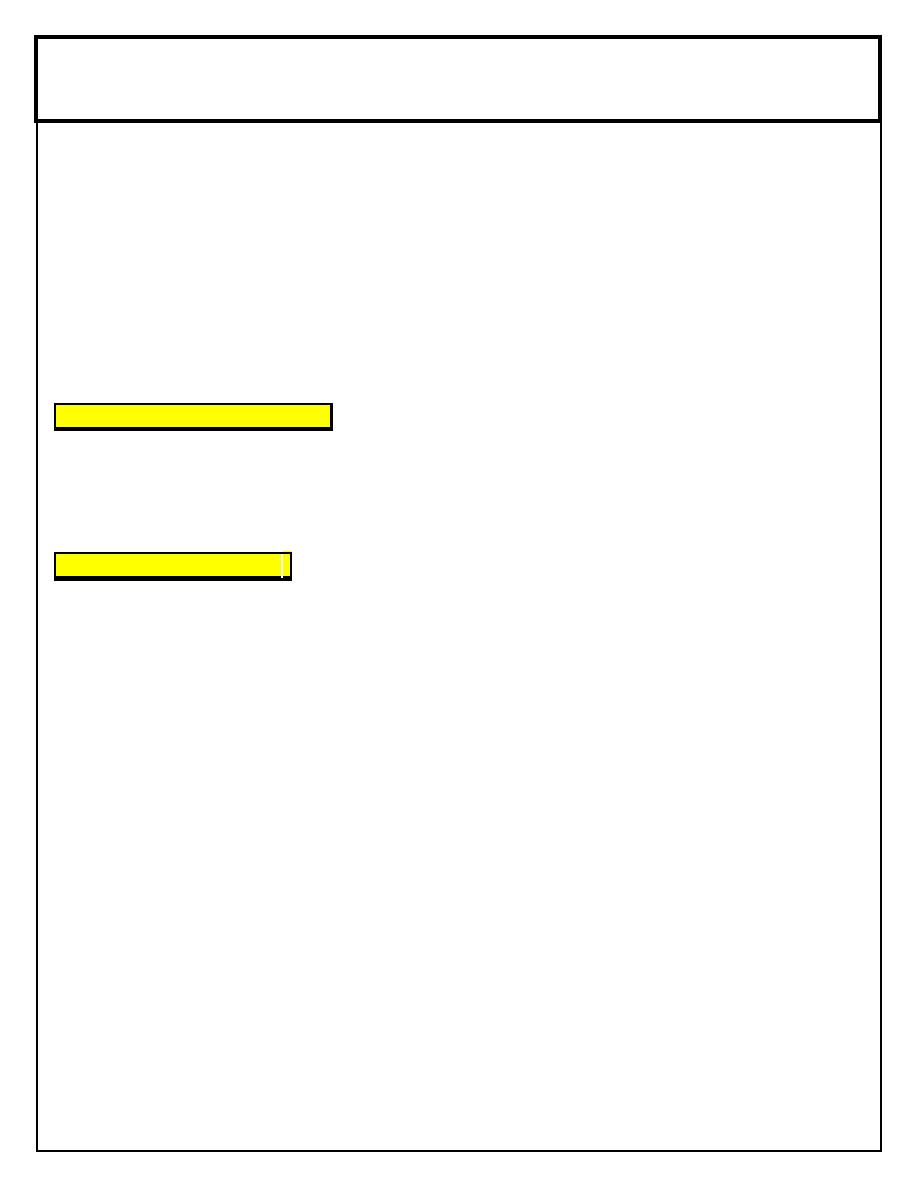
Let down reflex:
Breast milk production& secretion :
Prolactin released in response to sucking drives milk synthesis.
Oxytocine released in response to sucking stimulate the “let-down reflex”.
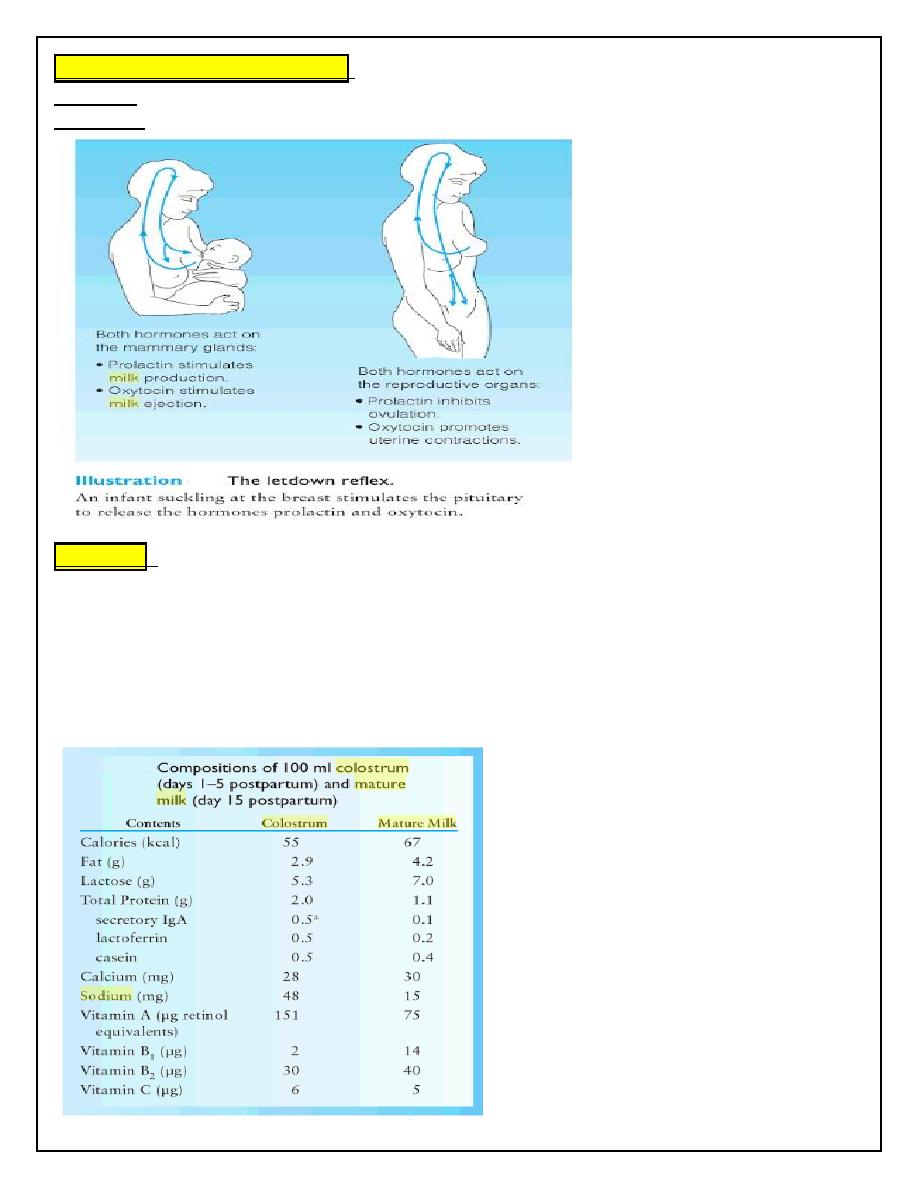
Colostrum :
•
For 2-4 days post delivery.
•
Contains more sodium
•
High in vit A and vit K
•
More protein & IgA than mature milk
•
Less fat and carbohydrate
• Colostrum is followed by transitional milk
•
Mature breast milk is established by 4th week

Common Breastfeeding Problems :
Breast tenderness, engorgement, and cracked nipples are the most common problems
encountered by breastfeeding mothers.
Engorgement
One of the most common causes of lactation failure, should receive prompt attention because
milk supply can decrease quickly if the breasts are not adequately emptied. Applying warm
or cold compresses to the breasts before nursing and hand expression or pumping of some milk
can provide relief to the mother and make the areola easier to grasp by the infant.
Nipple tenderness
Severe nipple pain and cracking usually indicate improper latch-on. Proper sucking should
include the areola as well.
Treatment include proper positioning of baby.
Additional measures include:
1.exposing the nipples to air.
2.Applying pure lanoline emollient .
3.Avoiding soaps and shampoos for cleaning.
4.Frequent changing of nursing pads.
5.Nursing more frequently by proper position of the baby.
Problems that may be encountered in breast fed babies :
1. Vitamin K deficiency
2. Hypernatremia at end of first week in babies due to insufficiency.
3. Breastfeeding jaundice (in the first week)& Breast milk jaundice .
Contraindications
– HIV (IN Western COUNTRIES)
– CMV, HSV (if lesions on breast)
– HBV
– Acute maternal disease if infant does not have disease (tuberculosis, sepsis.
– Breast cancer
– Substance abuse
_ GALACTOSEMIA& PKU.
Breast feeding is not contraindicated in mastitis.
Drugs :
Absolute contraindications: Relative contraindications:
Antineoplastics
Neuroleptics
Radiopharmaceuticals
Sedatives
Ergot alkaloids
Tranquilizers
Iodide/mercurials
Metronidazole
Atropine
Tetracycline
Lithium
Sulfonamides
Chloramphenicol
Steroids
Cyclosporin
Nicotine
Alcohol
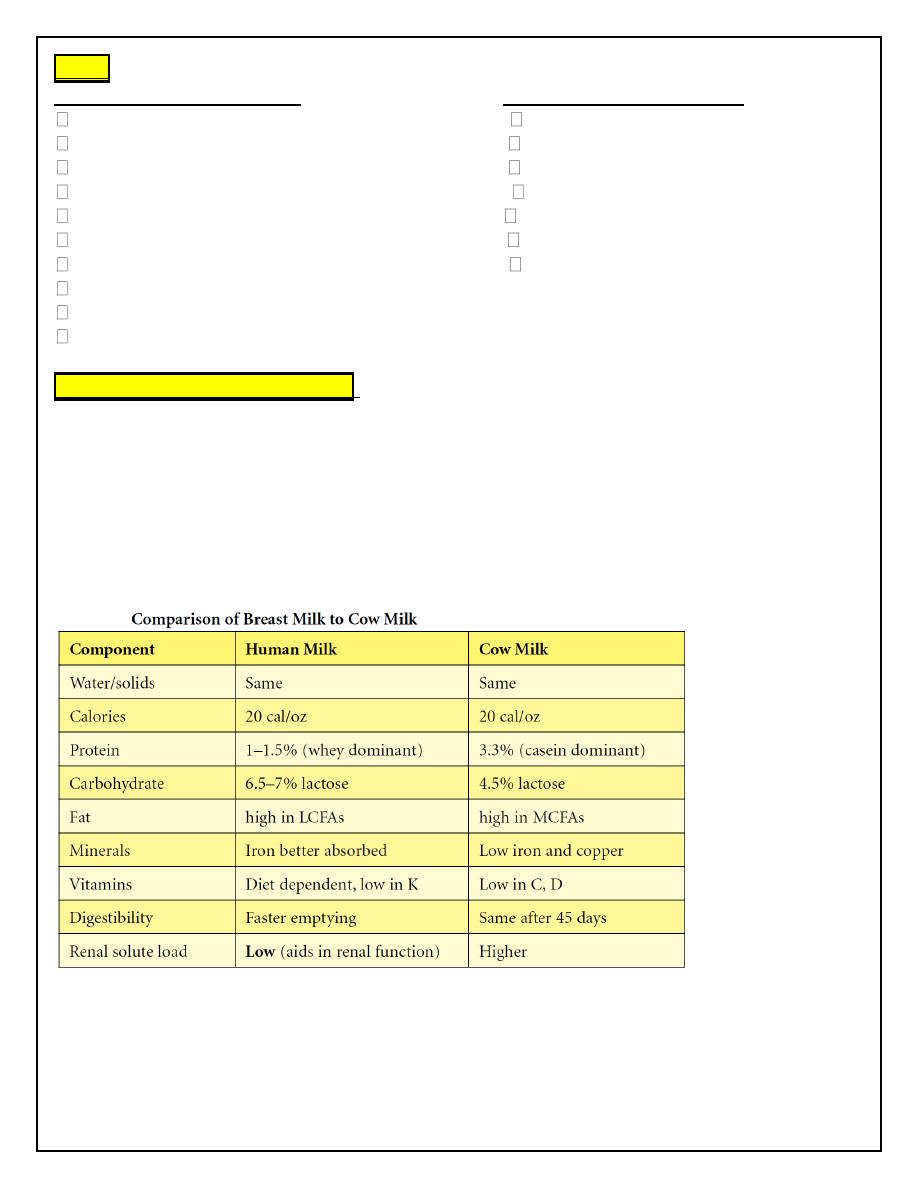
BREAST MILK SUBSTITUTES :
Infant formulas (modified cows milk) are suitable from birth and are usually based on cows
milk (unmodified)
Whey based milks are usually first choice if not breast feeding
Casein based milks are suggested for hungrier babies
Soya infant milks
Follow on formulas: higher iron content than cows milk
Specialised formulas for those who are preterm or have medical conditions (lactose free,
phenylalanine free)

SOY PROTEIN FORMULAS : ( Isomil,nursoy…)
- Similar to cows milk but protein derived from soya with lactose replaced with other
carbohydrates (glucose syrups)
- Indicated in Galactosemia, Lactose intolerance,& Cows milk allergy.
- Soya milks contain phytoestrogens which may increase the risk of breast cancer. So it should
be used only when strictly indicated and no proper substitute exists .
Preparation of milk should follow hygienic measures to decrease the risk of contamination .
1. Hands should be washed properly.
2. Feeding bottles should be boiled for several minutes.
3. Only boiled water should be used.
4. Number of feeding bottles= No. of feeding +1.
COMPLEMENTARY FOODS & weaning
By approximately 6 months, complementary feeding of semisolid foods is suggested. By this
age, an exclusively breastfed infant requires additional sources of several nutrients, including
protein, iron, and zinc.
