MOVEMENT DISORDERS
DYSTONIA:Paroxysmal, unprovoked, painful contraction of agonist & antagonist muscles around joint, affecting limbs or trunk.
Causes: - genetic
-drug induced
-task specific
Treatment:
AnticholinergicsBotulinum toxin
Deep Brain Stimulation
SPASM:
Painful, Sudden contraction of muscle or group of muscles. (Muscle cramp)usually provoked by strenuous exercise.
MYOCLONUS
Sudden, shock like jerky movement of a limb or part of body.
Spontaneous or stimulus induced.Of cortical or spinal pathology
CLONUSIs repetitive, rhythmic, jerky, involuntary contractions & relaxations (3-8)Hz around a joint.
Seen in UMNS with DTR examination & in epilepsy.
TREMORRhythmic oscillatory movement, that is best classified :
Rest tremor when occurs in limb in rest.Action tremor: Postural tremor
Intention Tremor.ATHETOSIS:
Abnormal, slow, sinusoidal, writhing distal movements.
Usually results from basal ganglial lesion.CHOREA
Rapid, irregular, involuntary, proximal movements that may affect different body parts.Involuntary movements are often superimposed by voluntary ones (Semipurposeful).
Lesion in basal gabglia (caudate).• BALLISMUS
Unilateral, violent (ballistic), choreaic, proximal movements.Lesion usually subthalamic vascular in nature.
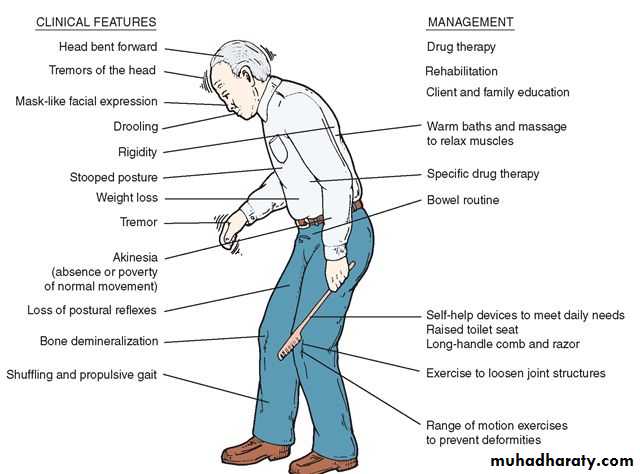
PARKINSON DISEASEIdeopathic, neurodegenerative disorder affecting the basal ganglia characterized by dopaminergic loss & imbalance between dopaminergic & cholinergic systems.
Prevalence: 1-2/1000,
M=F.
WITH INCREASNG AGE increase the prevalence.
Clinical Presentation
NMS Non Motor Symtoms:Precede the onset of motor symptoms by years: anxiety & depression.
REM sleep behavioural disorderBecome increasing disabling as PD progress.
• Motor Symtoms:BradyKinesia: (hallmark)
Slow movements, reduction (hypokinesia) in automatic movements.
Mask face, slow monotonus speech (hypophonia), drooling saliva.
Mayerson sign. Glabellar Tap.
Difficult shoelace tying & buttoning.
MicrographiaTremor
Rest tremor (pill rolling) or Counting tremor.4-6 Hz increases at times of emotional stress & improve during voluntary movements..
• RigidityIncreased muscle tone of lead pipe quality in limbs & when mixed with the tremor
(Cog wheel Rigidity).Flexed posture (Camptocormia).
• Postural instability & abnormal gait:Slow, shuffling, narrow based gait. Loss of arm swing
Difficulty in getting up from bed.
Difficulty in initiation & stoppage (Festinations)
Difficulty on turning.• INVESTIGATIONS
Diagnosis is clinical.Neuroimaging is NORMAL & rarely helpful
Functional CT or MRITREATMENT
1-Physiotherapy & EducationOccupational therapy
Speech therapy
• 2-Drug therapy: (symptomatic)
- Dopaminergic Supplementation: (hypokinesia)C
Sinemet LEVO DOPA:
Madopar
Dopa Agosists: Pramipexol
RopinirolCOMT inhibitors: Entacapone
MAO-B inhibitors: SelligilineAmantadine
b- Anticholinergics: (tremor & rigidity)
1Procyclidine
Trihexphenidyl
Benztropine
3- Surgery:
drug resistantThallamotmy &