
Breast Feeding


Normal Growth
• All babies tend to lose 5-10% of birthweight over first few days and
regain it by about 10
th
day.
• Feeding requirement is 150ml/Kg/day
• Normal weight gain 30g/day for first 6 months.
• Most babies double their birthweight by 4-5 months and treble by
one year.
Breast milk is the natural foods for full term
infants during the first months of life
Definition
Breastfeeding Advantages for Baby Nutritional benefits
Protein (whey)
• Easy digestible
• Rapid gastric emptying
• High biological value
• Non-protein nitrogen & free a.a for growth
Fat
• 50% of calorei
• Human milk also contains bile salt-stimulated
lipase
, which kills
Giardia lamblia and Entamoeba
histolytica.
so 92% of triglycerides are digested and absorbed.
• human milk contains twice as much of the more absorbable
olein
.
• EFA (DHA, AA)….Cholesterol synthesis
CHO
Lactose
1.
Energy (glucose & galactose)
2.
Enhance ca absorption
3.
Amylase: digest. Of starch & oligosaccharides.
Oligosach.=prebiotics (GOS)
which are the main substrate for normal flora
(Lactobacillus bifidus )

Composition of breast milk vs cows milk
• Carbohydrate:
Human milk 7% lactose & (10% glycoproteins)
cow milk 4.5% lactose
Protein: Human milk contains 1-1.5%, or
1.5g/100kcal.
80% whey protein (lactalbumin) is soluble and easy to be digested.
20%casein
While Formula contains up to
3g/100kcal,
ratio depends on manufacturer.
The predominant whey protein is β-lactoglobulin
• Fat
Oleic acid is more easily absorbed & there is twice as much in breast milk.
• Minerals
Cows milk contains more of all the minerals (esp. sodium, calcium and
phosphate) except iron and copper.
• Vitamins
Cows milk is low in vitamin C and D but more thiamine and riboflavin.
Immunological Contents of Breast Milk
• Immunoglobulins (IgA, IgG, IgM, leukocytes, cytokines)
• Host resistance factors (Complement macrophages, lymphocytes, lactoferrin,
iron binding protein and has an inhibitory effect on the growth of
Escherichia
coli
in the intestine), Lactobacillus bifidus (probiotics) .
• Anti-inflammatory components
• Enzymes: catalase, histaminase, lysozymes, lacto-peroxidase
• Antioxidants: ascorbic acid, alpha-tocopherol
• Prostaglandins
• Interleukin-6 (Stimulates an increase in mononuclear cells in breast milk).
• Decreased incidence and/or severity of otitis media, diarrhea, lower
respiratory infections, bacteremia, bacterial meningitis, botulism, urinary tract
infections, and necrotizing enterocolitis.
• Less hospitalization in first 6 months.
• Possible protective effect against sudden infant death syndrome, type 1
diabetes, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, lymphoma, allergies, and chronic
digestive diseases.

Other Benefits of Breastfeeding:
7
•
water 87.5%
•
Low renal solute
•
Enhance intestinal maturity (GF & Hormones)
•
Psychological adv. ( bonding & mutual benefits)
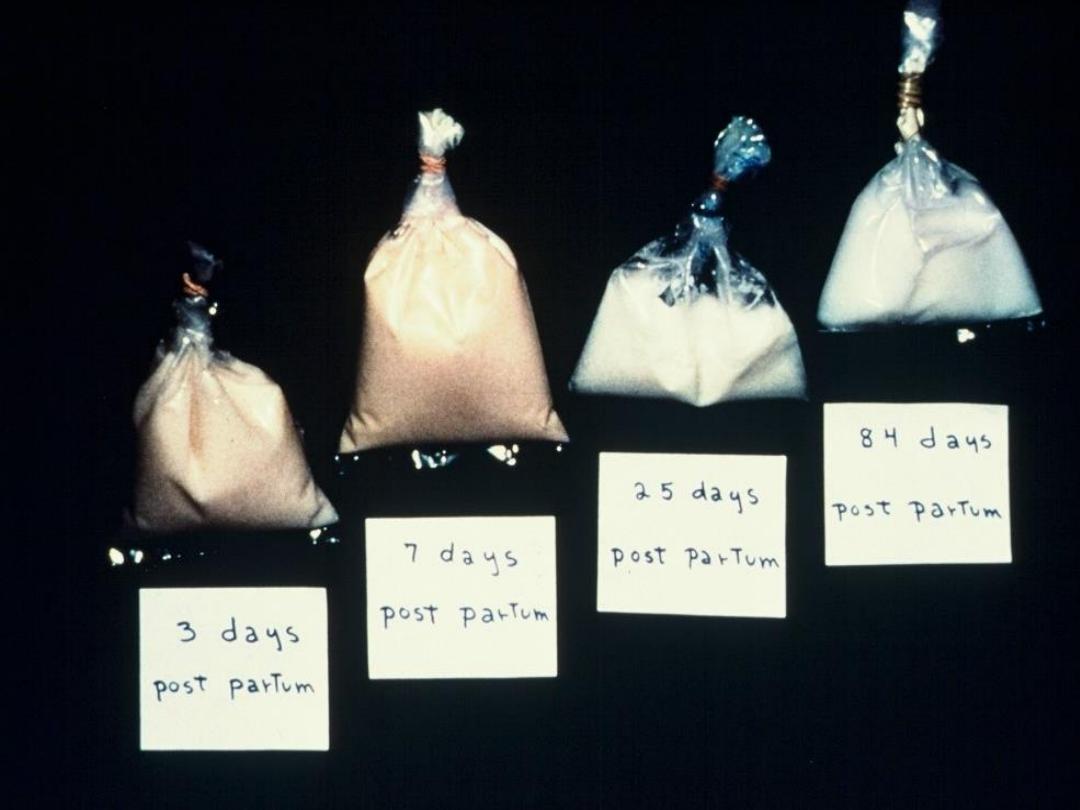
Breast milk composition change with
each feeding , BF course , term vs. preterm
Colostrum: small amount during days 3 to 5
High in protein, immunoglobulins and minerals,
Low in lactose and fat
Transitional milk: produced during days 6 to10
High in fat, lactose
Lower in protein and minerals
Mature milk: available by 2 weeks post-partum (Provides 20-22 kcal/ounce)
Average secretion: 750 mg/d
60-80% whey protein, 40% lactose, 50% fat
Growth factor Low in vitamin D

Slide 2b

Factors effect production of breast milk
1.
Mechanical factors ( empting of breasts)
2.
Psychological factors ( no factor is more important than mother’s
being happy and relaxed state of mind)
3.
Anatomical factors9 breast engorgement and nipple retraction).
4.
Endocrine factors ( Prolactin, oxytocin & thyroxine).
5.
Maternal drugs, smoking and alcohol.
6.
Maternal diet & hygiene
•
Avoid Tomatoes, anion, cabbage, spices, berries, caffeine &
chocolate.
•
Breast should be washed once a day, nipple kept dry.
7.Baby causes like ( Nasal obstruction, oral stomatitis, poor sucking,
cleft lip/palate).

Evaluating the Pregnant Woman
• Consider physical obstacles
• Physical examination of breasts and nipples.
• Inverted or flat nipples.
• Use breast shells for 6-8 weeks before delivery.
• Breast cancer-avoid pregnancy and lactation for 5 years.
• Encourage communication and support
• Misinformation, fears, self assurance.
• Father’s and family’s attitudes.
• Prenatal referral to lactation consultants/educators.
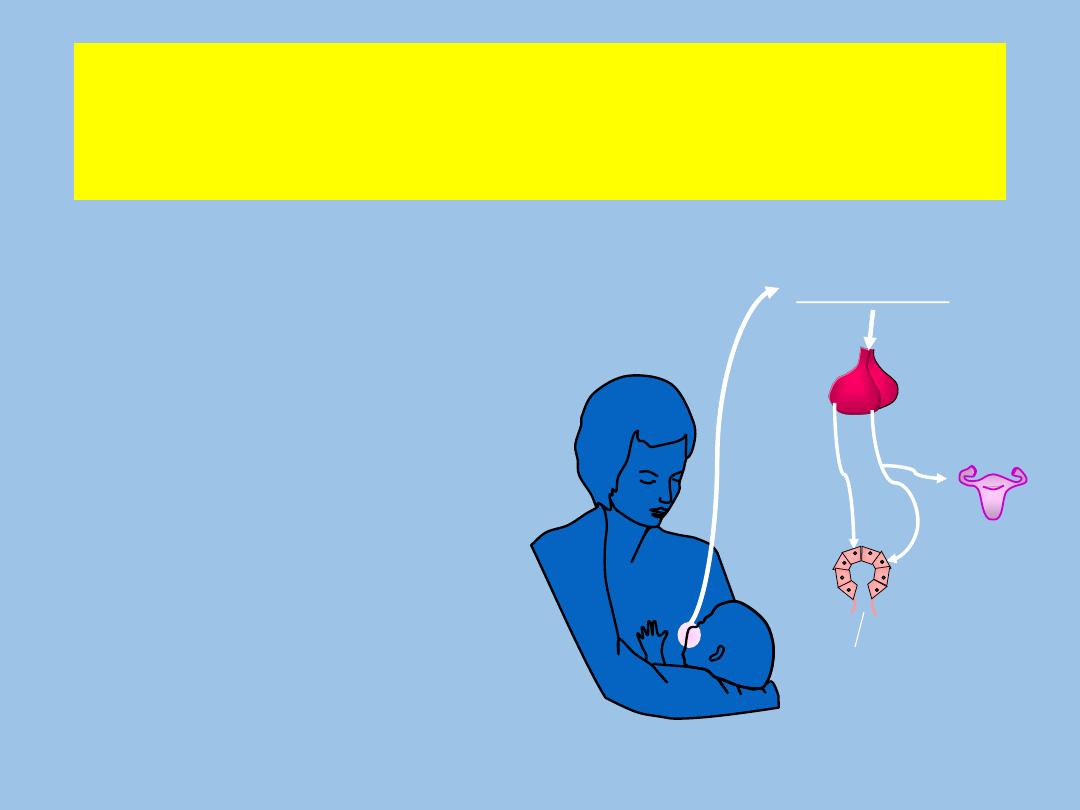
Physiology of Lactation
Suckling stimulates nipple
--->pituitary gland secretes
oxytocin--->let down reflex results
in milk ejecting cells contract
forcing milk from milk cells into
milk ducts.
Milk pools in lactiferous sinuses
under the areola. Suckling
stimulates milk to come from the
nipple.
Hypothalamus
Prolactin
Lacteal
Uterus
Oxytocin
Myoepithelial
Cell
Pituitary Gland

When to Breastfeed
• Initiate feeding as soon as possible after delivery when the baby
and mother condition allow usually within 1-4 hours after birth.
• Signs of hunger include:
• Alertness, increased activity, mouthing and rooting
• Feed on demand at least every 3 hours.
• 5-10 minutes per breast for first few weeks.
• Breast milk empties from stomach in 1.5 hours.
• Not unusual to breast feed every 2 to 3 hours or
8 to 12 times in a 24 hour period.
• Do not give glucose water to infant.
• After feeding held erect on mother shoulder to rub and eructate
swallow air.
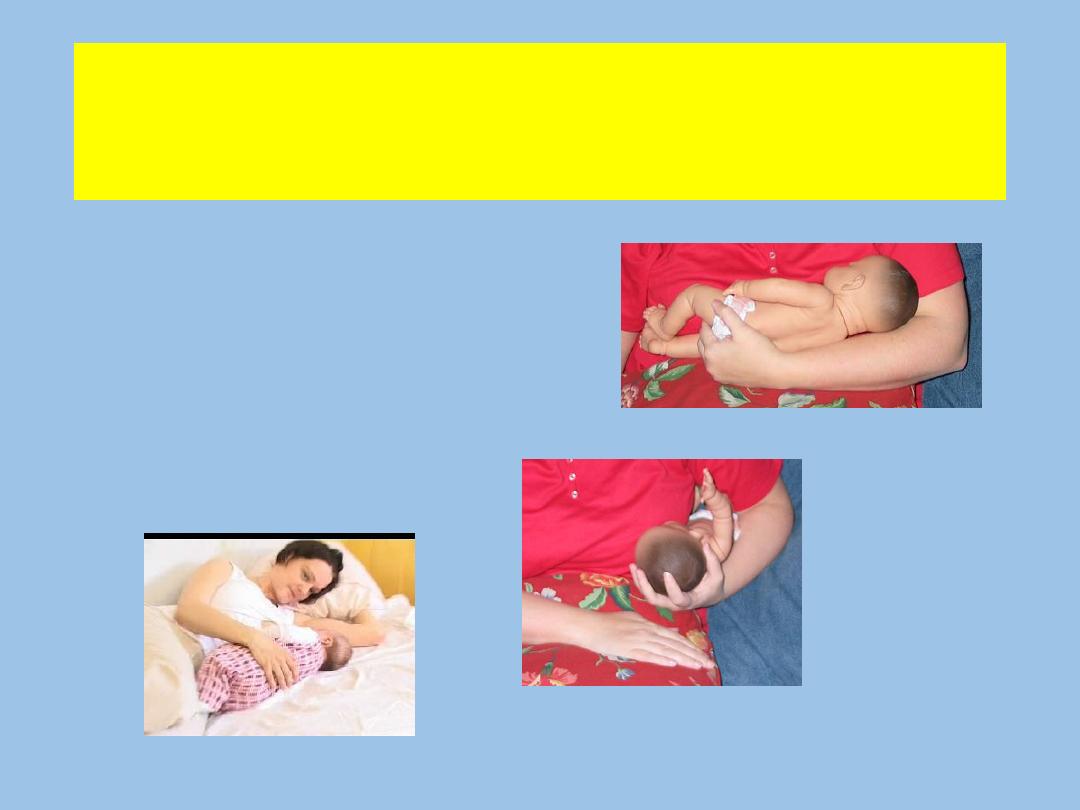

Proper Positioning of the Infant
• Cradle position
• Football hold
• Lying down
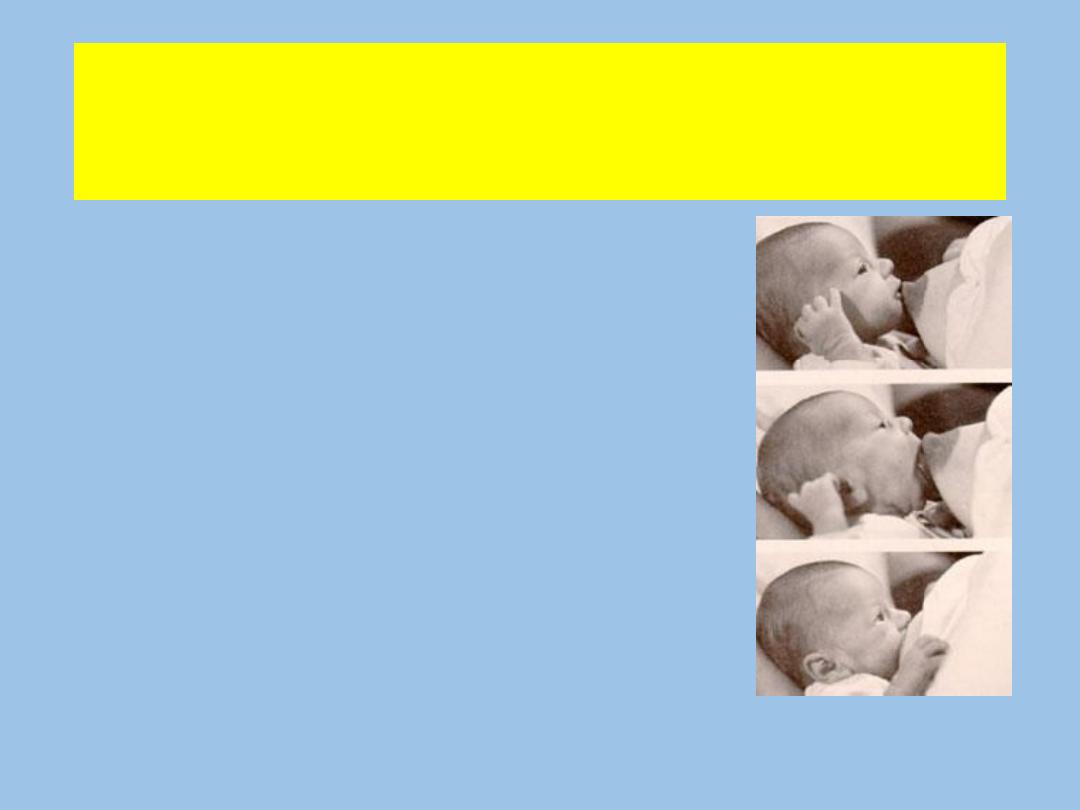

Latching on Properly
• Hold the breast in the opposite hand.
• Stroke the baby’s cheek or lips with the nipple to
get him to open his mouth (rooting reflex).
• Once his mouth is open, pull the baby towards the
breast, making sure that his head is facing the
breast and mother and baby are stomach to
stomach.
• Get as much of the nipple and areola into the
baby’s mouth as possible.
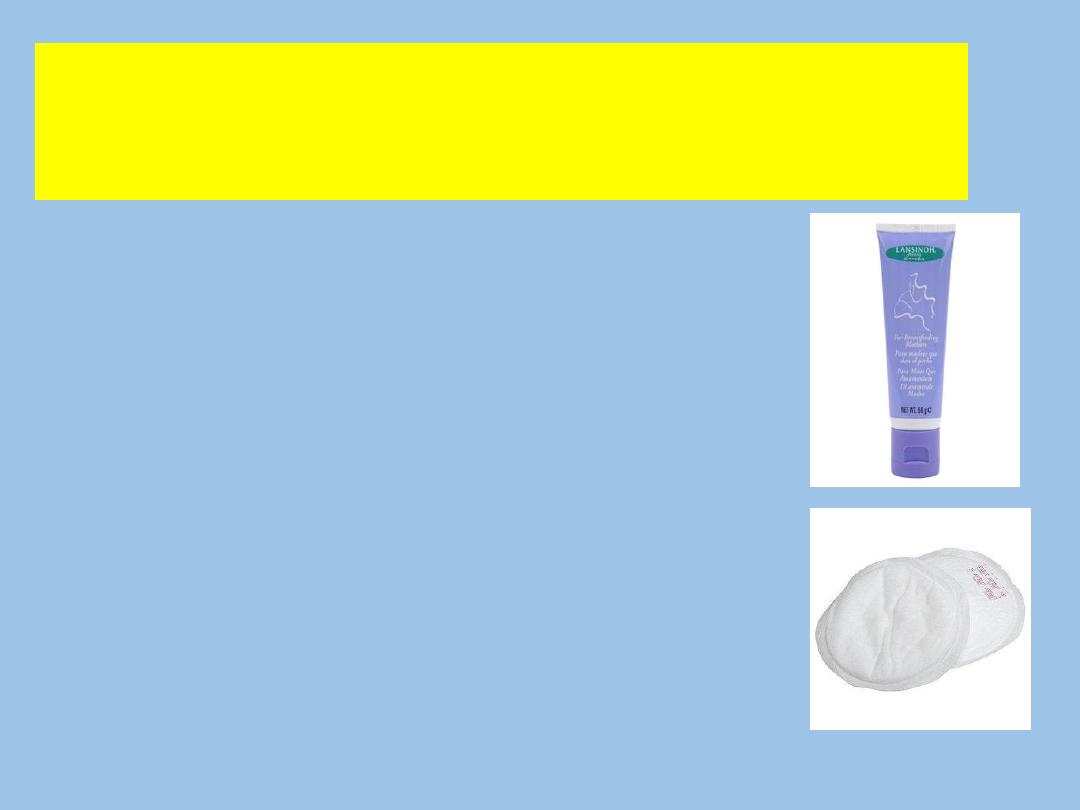
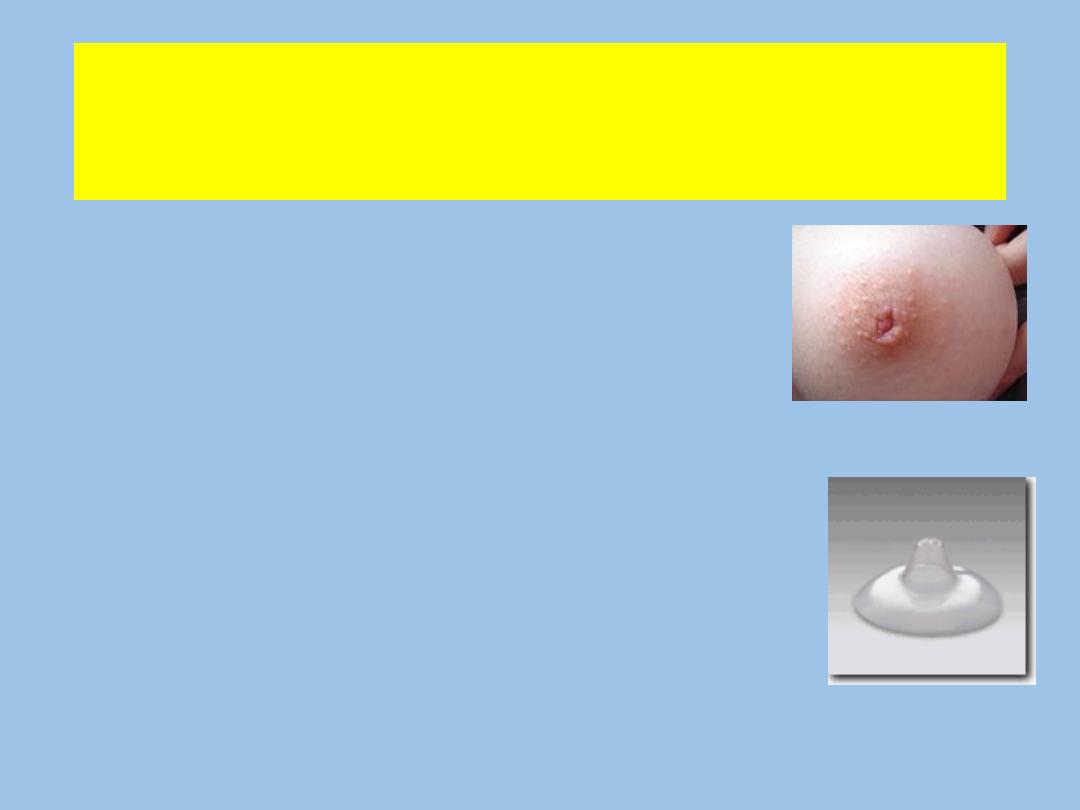
Care of the Breasts and Nipples
Demonstrate proper latch on and positioning.
Cleanliness and attention to fissures.
Use (pure lanolin) for cracked nipples.
Avoid soaps and other ointments.
Insert nipple shield into bra for irritated nipples.
Use breast pads for leakage and change often.

Assessing Breastfeeding, signs of satisfaction
• Mom feels tugging on nipple without pain.
• Infant weight gain pattern consistent (20-30g/day).
• Infant should sleep for 2-4 hours.
• Voiding: 6-8 wet diapers/day.
• Stooling: generally more stools than formula.
• Feeding pattern-generally every 2-3 hours.
• Duration of feedings-generally 10 minutes/side.
• Activity and vigor of infant.

Nutritional Requirements During Lactation
• Breastfeeding is an anabolic state, resulting in increased energy and
nutrient needs:
• 500 kcal/day (birth to 6 mo)
• 400 kcal/day (7 - 9 mo)
• Protein, zinc, niacin, vitamins A, E, C requirements increase above
those in pregnancy. (
Protein = 71 g/day)
• Chronically low maternal iron, vitamin B, C, D, thiamin, and folate
intake leads to low content in breast milk.
Causes of breast feeding interruption.
1. Infrequent feeding
2. Failure to wake sleeping baby for feeding
3. Excessive use of pacifiers
4. Unware mother about frequent feeding
5. Intermittent bottle feeding ( Nipple confusion)
Contraindication to Breastfeeding
• Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
infection
• Human T-cell leukemia/lymphoma virus
HTLV-1
• Herpes simplex virus
• Known primary acute cytomegalovirus
infection
• Active acute Hepatitis B, C (potential
risk)
newly diagnosed
• Untreated active tuberculosis
• Galactosemia & PKU.
Breastfeeding is contraindicated in very few situations.
Diseases
Drugs &
Substance Abuse
1. Smoking should be avoided, as nicotine can cause:
• Vomiting, diarrhea and restlessness for the baby.
• Decreased milk production for the mother.
• May increase risk of SIDS.
• Opportunity to urge and instruct on smoking cessation.
2. Alcohol readily passes into breast milk and is neurotoxic.
3. Recreational and illicit drugs are a contraindication to breastfeeding
(Heroine, cocaine , etc)
4. radioactive agents used in diagnostics test.
5. tetracycline,
6. oral metronidazole,
7. Bromocriptine (hormone antagonist)
8. Cyclophosphamide/ Doxorubicin/ Methotrexate (antineoplastic agent)
9. Cyclosporine (immunosuppressant)
10.Ergotamine (migraine headaches)
11.Lithium (psychotropic agent)
Breastfeeding Recommendations
• “Exclusive breastfeeding is the ideal nutrition source and sufficient to
support optimal growth and development for the first six months of
life.”
• The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends
breastfeeding continue for at least the first 12 months.
• Add of vitamin K, D at birth , Parenteral administration of
1 mg of
vitamin K
1
at birth, after the first feeding is completed but within 6 hr
of birth, is recommended for all infants, and this is especially
important for those who will be breast-fed.
• Add Zinc & Iron or cereals at 4-6 months.
