
Infant milk formula
manufacturing
1-Dry blending…… ingredients in powder
forms
Advantages .. More affordable , less energy.
Disadvantages:No heat treatment to these
ingredient so any microbial contamination in
these raw material may be present in finish
products.
2- Wet blending – spray drying…the
ingredeients are blended together in the
following series..
12/20/2016
Infant milk formula
1

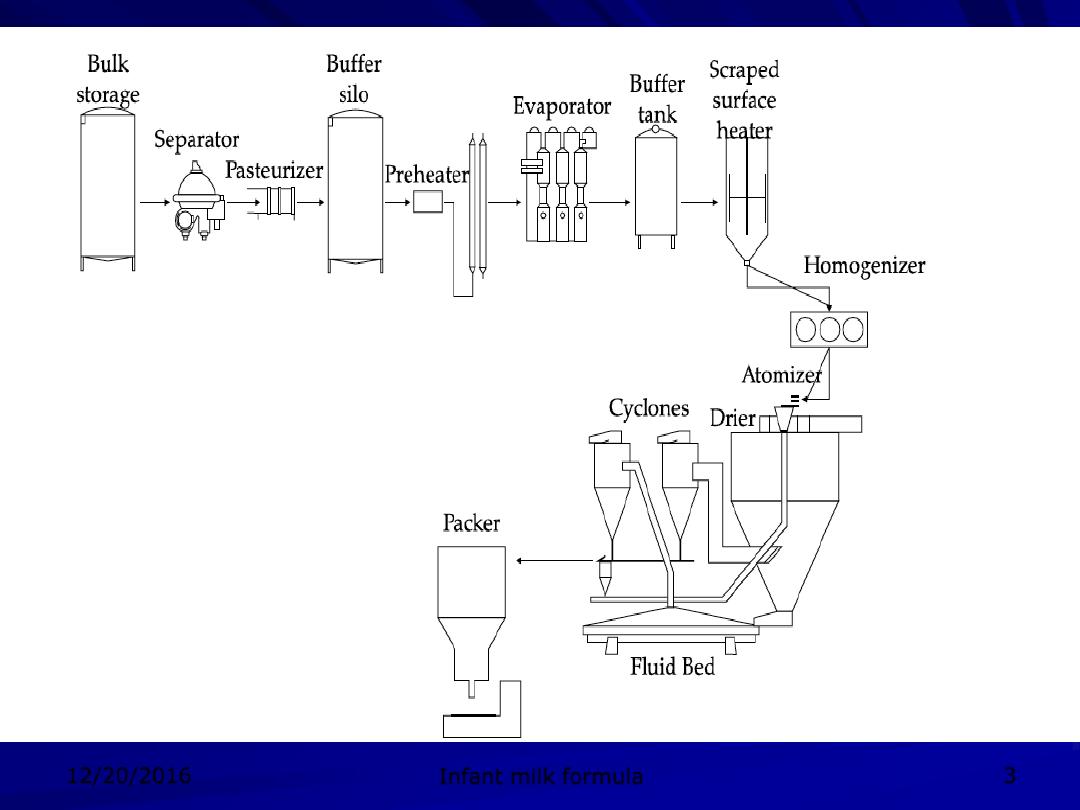
Reception of raw milk and storage in silo
Pasteurization
Cream separation
Homogenization
Addition of micronutrients and blending.
Homogenization
Concentration and vaporization
Spray drying
Packaging
12/20/2016
Infant milk formula
2
12/20/2016
Infant milk formula
3
12/20/2016
Infant milk formula
4

Out lines
:
1-The definition of formula feeding.
2-Reasons of choosing formula feeding.
3-Types of formula feeding.
4-Forms of formula.
5-Types of formula.
6-Advantages & disadvantages of formula feeding.
7-The equipment..
8-Basic principles of preparation a formula.
9-Ways to prepare a formula.
10-Preparation of formula .
11-The technique of feeding.
12-Common mistakes in formula feeding.

What is formula
feeding?
It is a food product designed to provide the
nutritional needs of newborns & infants.
Infant Formula
Product intended for use by infants that
simulates human milk or is suitable as a
complete or partial substitute for human milk

Reasons for choosing formula-feeding
include:
1-There is an inadequate supply of maternal breast
milk.
2-The baby is sucking inefficiently.
3- Some parents want to know exactly how much
their baby is receiving at each feeding, and
formula/bottle-feeding allows exact measurement.
4-To avoid the transferring of certain drugs from
the mother through the breast milk to the infant.
5-A practical alternative for mothers who may not
be able to breastfeed due to work schedules.
6-Death of the mother.
7-Institutions.
8-Infant's metabolic disorders
.

Standard Formula Features
Breast milk
– 20cal/oz
– Human milk fat
– Lactose
– whey:casein 70:30
9 g/L
– Iron 0.3mg/L
– Vitamin D 21 IU/L
– 260 mOsm/kg H
2
0
Infant formula
– 20cal/oz
– Soy, coconut, sunflower, palm
– Lactose
– 60:40,
15 g/L
– Iron 12mg/L
– Vitamin D 405 IU/L
– 265-300 mOsm/kg H
2
0

The types of formula feeding:
A-Complementary feeding:
(each feed)
breast is given 1st until it is emptied then
formula is given to complete the feeding.
B- Supplementary feeding:
formula is
given to substitute one or more feeds.
C-Substitutive feeding:
no breast
feeding ,formula only.

Forms of formula:
Formulas come in three basic forms:
1-Ready-to-use formula
no mixing or
measuring required, just open and serve recycle all of
the cans or bottles. Once opened, it must be used within
48 hours.
2-Liquid concentrate formula
requires
you to mix equal parts of water and formula, so read the
instructions on the container carefully.
3-Powdered formula.
is the most economical
choice, and you must follow the directions exactly, but it
has a one-month shelf life after the container has been
opened.

Categories of Infant formulas
Standard
– Enfamil, Dovamil,Dovelac
Soy
– Isomil, Prosobee.
Protein hydrolysates
– Pregestimil, Nutramigen, Alimentum, Dovagentle.
Elemental
– Neocate, Elecare
Premature
– Enfacare, DovaCare.
toddlers formula , Dovelac 3, Enfagrow.
Specialized
– Modified for specific medical indication
Metabolic, renal, GI disorders
gatagories of formula
There's a formula to suit every baby's needs.
1-Cow's-milk-based formula:
Most formula available like
Dovelac ( France)
Guigoze (Swiss)
Enfamil & Dovamil (USA)
2-Soy-based formula:
If the baby has
galactosemia like prosbee.

3-Lactose-free formula: If the baby has lactose-
intolerance(inability to digest lactose like S26 Lactose
free (LF) & Dovediar .
4-Formulas for premature
and low-birth-weight babies:
These formulas often contain more
calories, protein, calcium, Vitamin D
& Essential Fatty acids (DHA,ARA)
with nucleotides like Dovacare.

Preterm Requirements
The aim of feeding premature babies is to achieve a rate
of growth which is similar to intra-uterine growth at the
same gestational age. Preferably the feed should be of
constituents that do not load the metabolism and
promote development of gastrointestinal function.
Special Needs
1)Glycogen stores are small. Minimal fat stores.
Reduced response to hypoglycaemia.
2)Increased energy requirements (100-120 kcal/kg/day)
3)Higher protein synthesis than term infants.
3)Nervous system potentially at risk if inadequate
nutrition provided(poly unsaturated fatty acids)

5-Hydrolyzed formula: In these formulas, the protein is
broken down into smaller parts that are easier for the
baby to digest than larger protein molecules. The baby
may need a hydrolyzed formula if he has allergies or
trouble absorbing nutrients. The doctor may also suggest
trying a hydrolyzed formula if the baby has
, they are
either partial hydrolyzed like Enfamil & Dovamil gentle or
extensive hydrolyzed like Nutramigen.
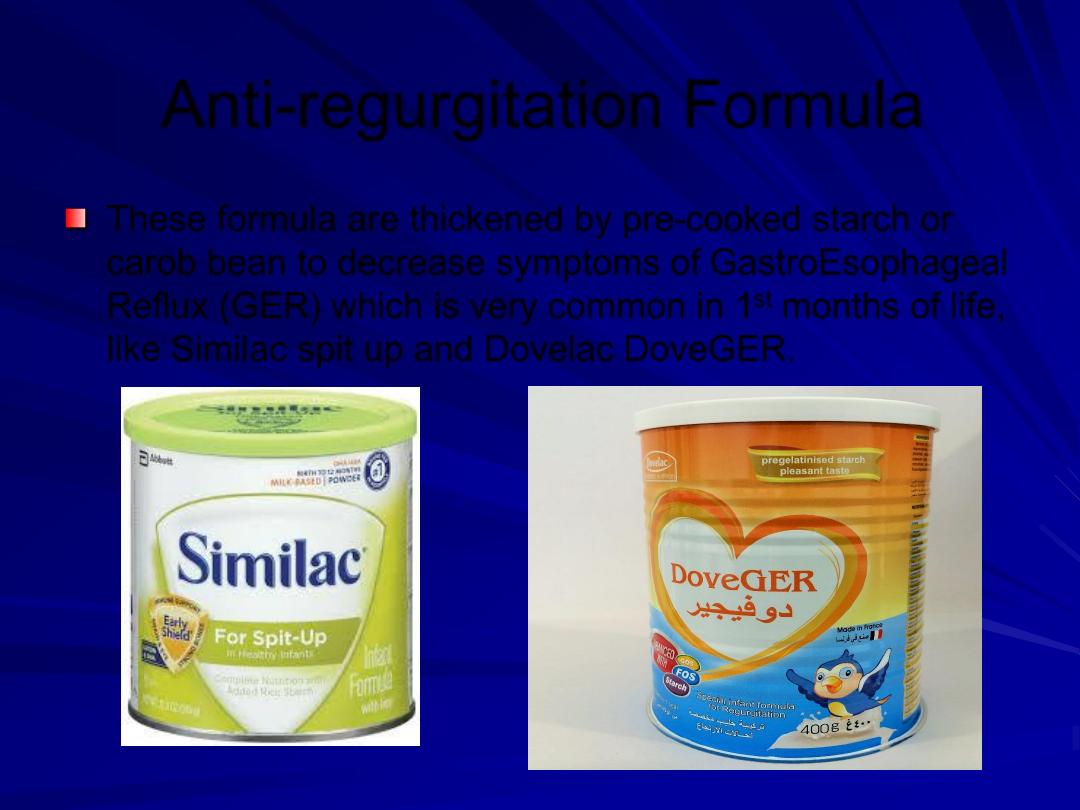
Anti-regurgitation Formula
These formula are thickened by pre-cooked starch or
carob bean to decrease symptoms of GastroEsophageal
Reflux (GER) which is very common in 1
st
months of life,
like Similac spit up and Dovelac DoveGER.

Specialized formula:
Similac PM 60/40
– For infants with hypocalcemia
due to hyperphosphatemia
or impaired renal function.
Metabolic Formulas
– PKU, MSUD, tyrosinemia,
homocystinuria, glutaric aciduria,
PPA/MMA, urea cycle

toddlers formula
These formula have a growth recipe enrich with all vitamins
and minerals to enhance appetite in this age in addition to high concentration
of Iron to prevent Iron deficiency anemia like Nido, Dovelac 3 & enfagrow.
There are six main ingredients in
formula
• Macronutrients
1-carbohydrates
2-protein
3-Fat
• Micronutrients
4-Vitamins
5-Minerals
6-Others

1-Formula-fed babies often need to eat less frequently than do
breastfed babies because breast milk moves through
more quickly. Thus, breastfed babies may
become hungry more frequently.
2-A The entire family can involved in all aspects of the baby's
care, including feedings. The mother can therefore get more
rest.
3-Allows exact measurement of how much of food the baby is
receiving at each feeding.
4-The mother does need not to care about what she eating.
The advantages of formula :

The dis-advantages:
1-The formulas are expensive.
2-The lack of maternal infection-fighting
antibodies that are in breast milk R\T that the
baby will get sick easly.
3-No formula can exactly duplicate the ideal
composition of breast milk.
4-The formula may will be difficult to digest.
Weaning
During infancy is necessary to enable transition from milk feedings to other table foods and is
important for nutritional and developmental reasons
At this stage increasing
need for energy so more
solid foods should be added.
with growth, babies required
more food items
such as minerals and vitamins, that cannot
be supplied by milk.
to
train GIT digest
starch, and other solid foods.
to
induce independence
using spoon and cup, by himself.
Commence weaning at 4-6months old and increase so that by 12 months solids are the main part
of the diet with milk to drink along side.
The most commonly fed complementary foods between
4 and 11 mo
of age are infant
cereals
.
introduction of
complementary foods
(solid and liquid foods other than breast
milk or formula, also called
weaning foods
like cereals, vegetables, fruit,
soups, egg, etc. )
Aims

Important Principles for Weaning
Begin at ≈ 4-6 mo of age
Avoid foods with high allergenic potential (cow's milk, eggs, fish, nuts,
soybeans).
At the proper age, encourage a cup rather than a bottle.
replacing
one meal
for milk fed.
gradual increase
in amount of new food.
the
presentation of food
is important (colored dishes, spoon..).
I
ntroduce 1 food at a time and avoid sugar, salt & honey.
Energy density should exceed that of breast milk.
foods (meat, iron-supplemented cereals) are required.
Zinc intake should be encouraged with foods such as meat, dairy
products, wheat, and rice.
Phytate (tea) intake should be low to enhance mineral absorption.
Breast milk should continue to 12 mo; formula or cow's milk is then
substituted.
Give no more than 24 oz/day of cow's milk.
Fluids other than milk & water should be discouraged.
Give no more than 4
–6 oz/day of fruit juices. ( No soda, Pepsi, 7 up etc.)

Weaning
Soft lumps are often manageable from 6 months. Chewing encourages
development of speech muscles.
replacing one meal for milk fed.
CEREALS:
excellent for infants contain iron, B complex.
FRUITS:
have mild laxative.
raw ripe, banana is readily digested and enjoyed by most infants.
VEGETABLES:
good source of iron and other minerals and B complex vitamins.
add at 7m of age.
MEATS, EGGES, STARCHY FOODS:
egg and starchy food usually introduced during second 6m of life then
add potatoes, rice.

weaning
Should be
gradual
to prevent GIT upset
Do not rush or force-feed.
should
not be started
at convalescent
period of any disease.
should not
started if child is under
weight to avoid GIT upset.
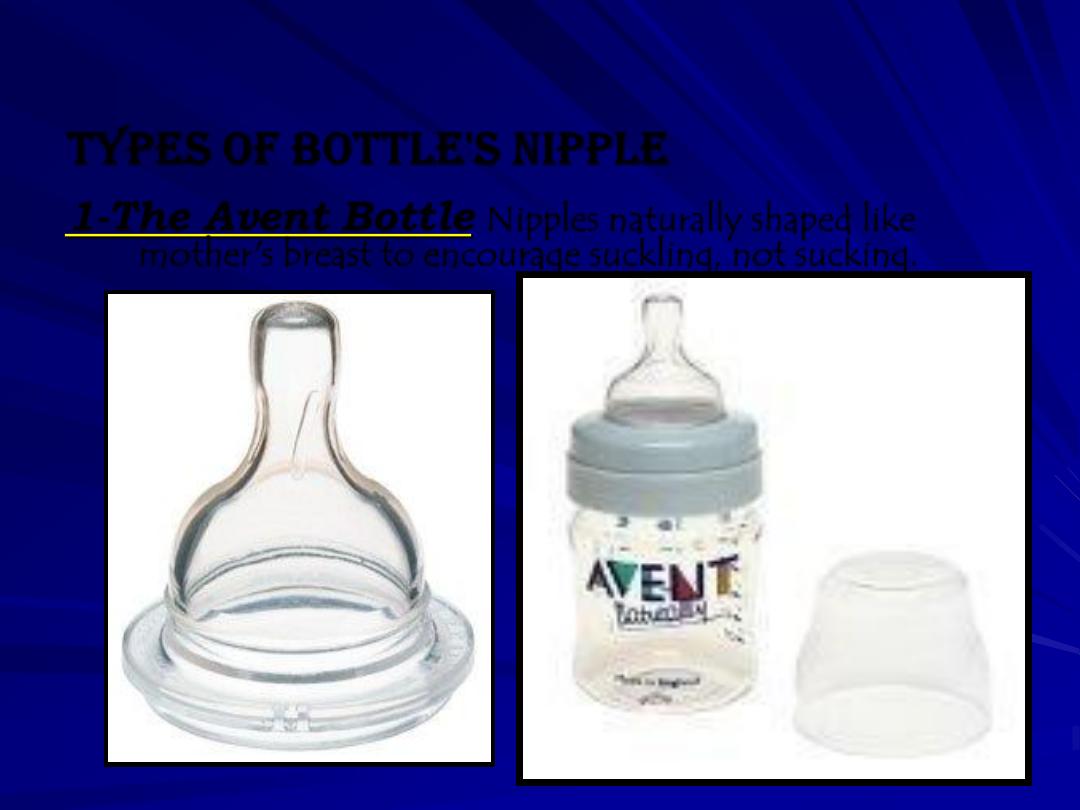
Types of bottle's nipple
1-The Avent Bottle
Nipples naturally shaped like
mother's breast to encourage suckling, not sucking.

2-Nipple Sampler including:
A-The level two nipple is for use when feeding infant ages 3
months and up.
B-The level three nipple is for use when feeding more
aggressive eaters.
C-The Y-cut/cereal nipples are for use when feeding cereal and
thick juices.

3-Preemie Flow Silicone Nipple
is for use when feeding
preemie babies& can be used for standard 4oz and 8oz
bottles.
4-
The NUK Silicone Orthodontic Nipples :
A-( If it silicone):
simulates the shape of
mother's breast during breastfeeding.
B-(If it latex):-
Nipples are Cross cut-
*simulates the shape of mother's breast during
breastfeeding & *encourage oral exercise and
slow intake.
N.B :It is best to use a nipple that is silicone,
rather than latex, to protect the baby from latex
allergens
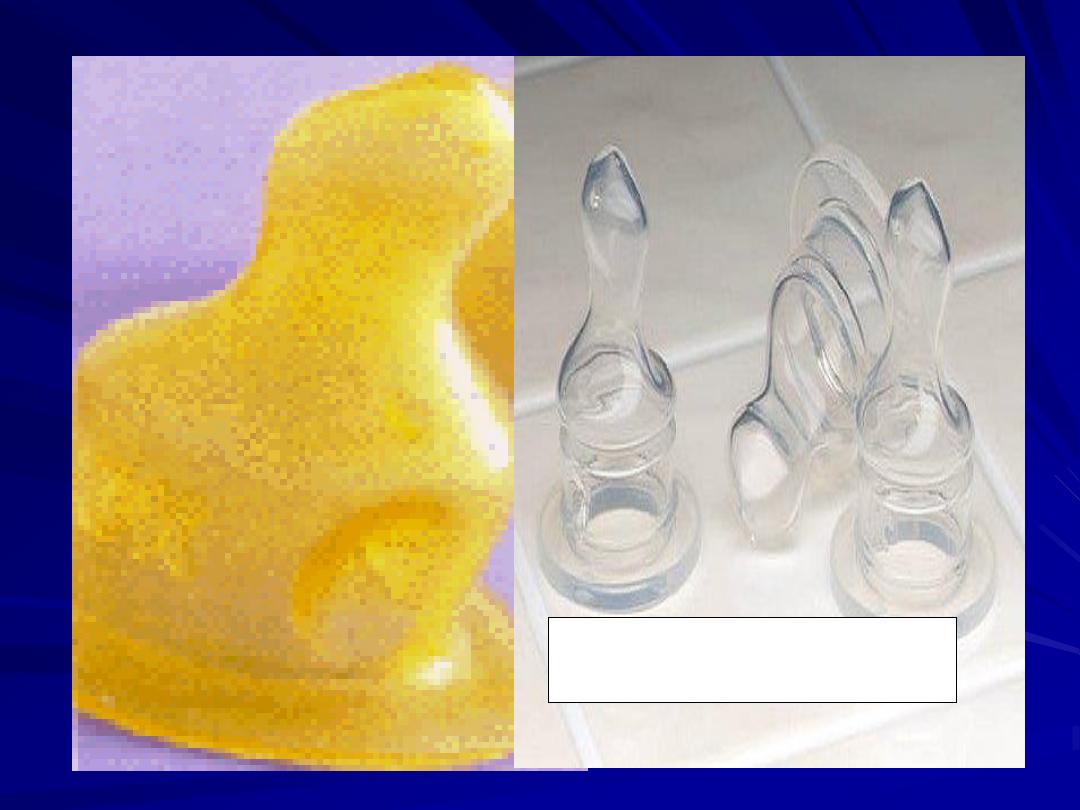
Silicone nipple
Latex nipple

Types of bottles:
Plastic or Glass
Glass for better sterilization

Basic principles of:
1-All equipment used must be sterile. Keep
the formula labeled.
2-Accuracy of measure.
3-(In hospital) wear gown & caps.(At home)
wear a clean dress or apron.
4-The flow of milk should be tested before the
nipple is used.(the chosen nipple should not
be very soft or too firm).

preparation the formula
According to daily caloric requirement(100-
120 cal\kg of body wt.):
* No. of cal. Required \ 24 hrs=
Total caloric requirement(p.d.) x baby's
body wt.
*No. of ounces infant needs\ 24 hrs =
( total cal. Requirement\24 hrs) \20
=(X )ounces.
*Volume of feeding in ml =
(X) x30\ no. of feeding.
