1
Fifth stage
radiology
Lec-4
د.هديل
19/12/2016
What it could be
The sign & findings
Wide zone of transition is being
Benign or malignant ????
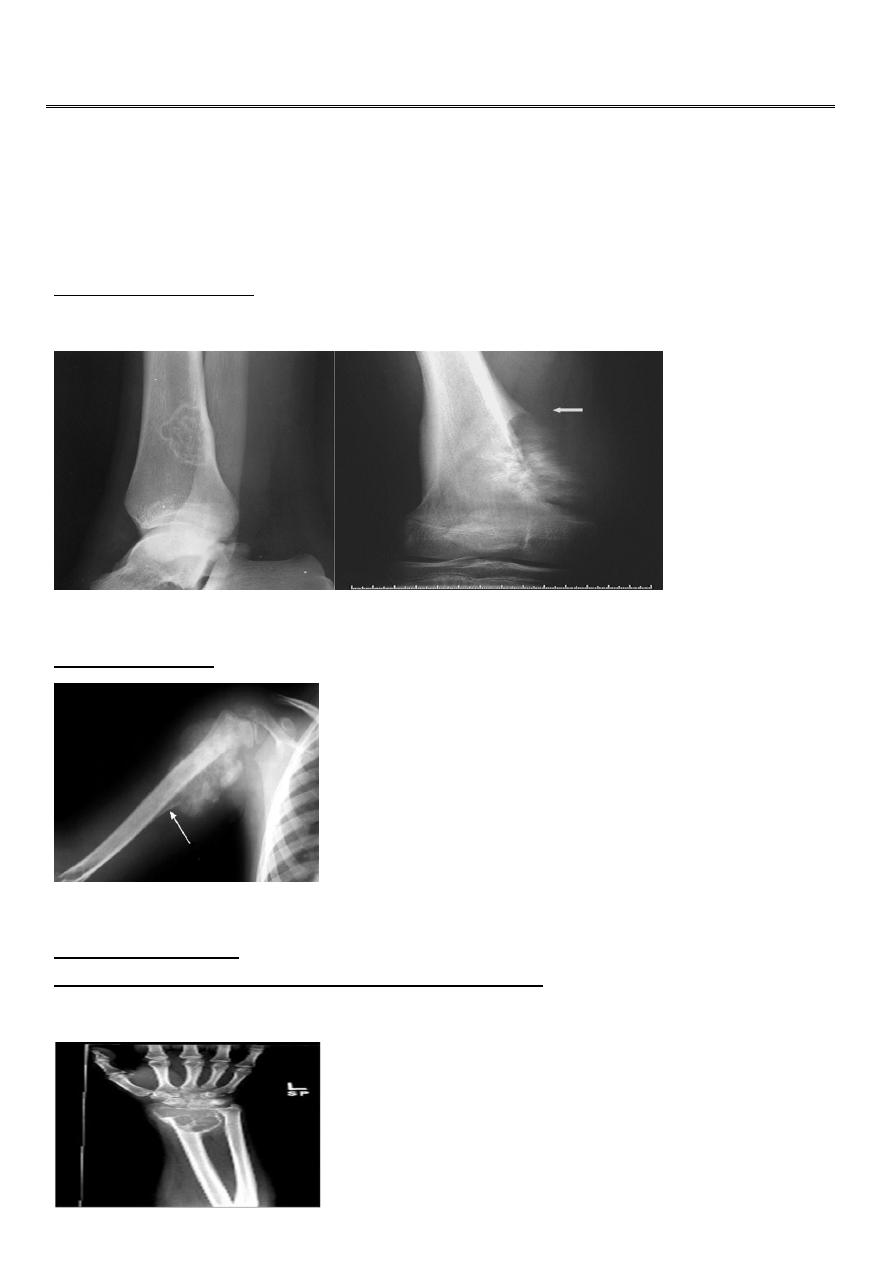
Codman's triangle:
Elevation of the periosteum at the side of the tumor margin
lytic, expansile lesion,
Sub articular in location give the soap bubble appearance
Giant cell tumor
2
onion peal periosteal reaction
Characteristic of ewings sarcoma
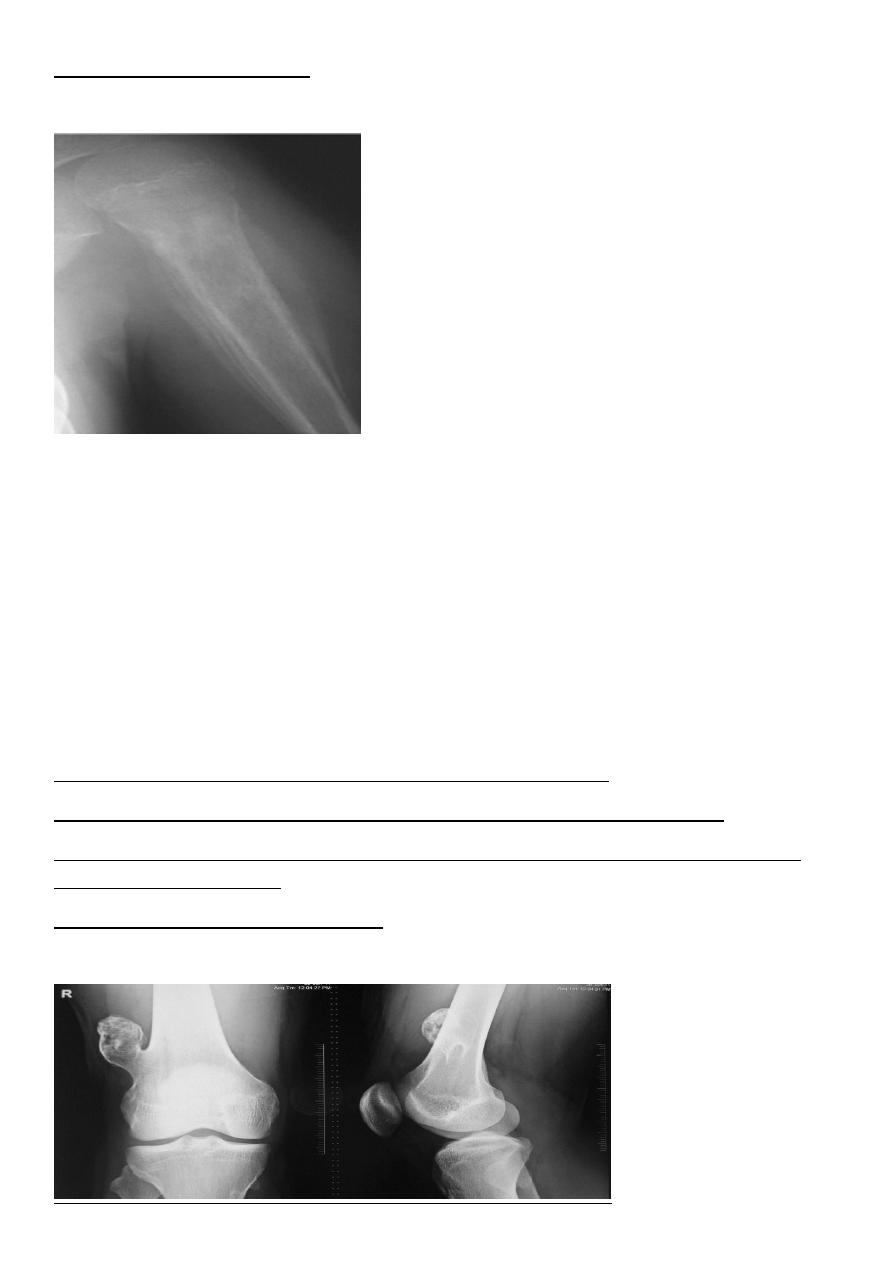
Tumor have slender pedicle directed from growth plate ,,, what it could be
???
Is the direction of pedicle toward joint or away
?????
What is being have at upper aspect
???
What is their significance ???
Answer
:Osteochondroma Most common benign bone lesion which have their own growth
plate).
Pedunculated: slender pedicle directed away from growth plate.
The thickness of the cartilage cap above the bony projection is very important
if the thickness > 1 cm of cartilaginous cap by CT, > 2 cm by MRI give high possibility of
Malignant transformation
Also Dispersed calcifications in the cap

3
(Ollier's disease) means multiple enchondromatosis
Diaphyseal acalsia means multiple exostosis
Multiple ivory osteoma associated with Gardner's syndrum
*shepherd crook deformity seen in fibrous dysplasia
*Codmans triangle seen in malignant bone tumor (OS)
*Soap bubble appearance (giant cell tumor )
*Fallen fragment sign (simple bone cyst with # )
* moth eaten appearance (rarifaction ) acute osteomylitis
*sequestrum dead bone
* involucrum new bone formation
*cloaca The cloaca is an opening
Gibbous deformity wedging of the vertebra (anterior loss of vertebral height)
Seen in TB infection of vertebra
*spina ventosa means TB Dactylitis
Rain drop appearance ( multiple lytic lesion in skull MM
*Rackety rosary of the ribs mean widening of the anterior end of the rib seen in (rickets)
* codfish appearance Vertebral collapse resulting in biconcave vertebra with widened disc
(osteomalasia )
*Triradiate pelvis in which pelvic side walls bend inward (sever cases of osteomalasia )
* Looser's zones these are thin short lucent lines with sclerotic margins running across the
cortex at right angle, best seen in the scapula , femoral neck , pubic rami (osteomalacia )
Subperiosteal bone resorption seen particularly in the radial aspect of the middle phalange
(hyper parathyriodism)
*Salt and pepper sign multiple tiny hyper lucent areas in the skull vault (hyper
parathyriodism )
*rugger jersey spine band of increased density within the vertebral body & across the
metaphysis of long bones in renal osteodystrophy.
*hair on end appearance Increase diploic space thickness with vertical striation I seen in
haemolytic anaemia (thalacimia).
*Bullets vertebrae anterior vertebral beaking ( achondroplasia )
*Ballooning of the sella ( acromegaly )
4
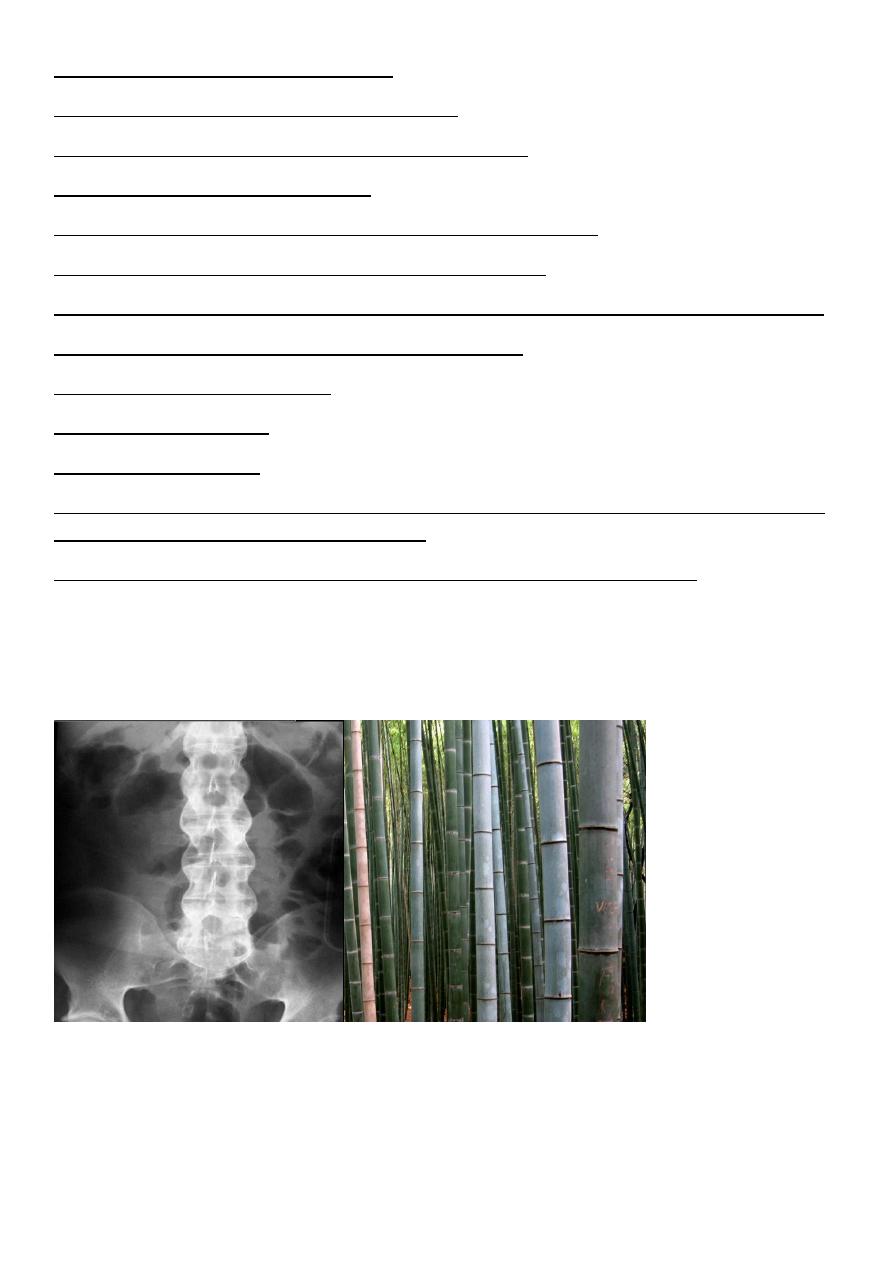
*Bamboo spine (ankylosing spondylitis )
*square shape vertebra (ankylosing spondylits )
*punched out peri articuler erosion of the bone (Gout )
*charcot joint (nueropathic arthritis )
*Legg-Calve-Perthes disease osteochodrosis of the femur head
*Mushroom deformity of femoral Neck (perthes diseade )
*Scheuermann's disease : (adolecent Kyphosis) osteochodrosis of the vertebral end plates
*Osgood-Schlatter osteochodrosis of the tibial tubercle
*Blount's disease tibial epiphysis
*Kohler's Navicular bone
*Kienbock's lunate bone
*Osteochondritis dissecans separation of the affected part in to the joint space resulting in
intra-articular loose body seen in large joint
* Psueodoarthrosis of the femoral head with iliac bone (old neglected CDH)
Bamboo spine … Ankylosing spondylits
Mushroom Deformity of the femoral neck in perthes disease
being flattened femoral head with a contiguous broad neck, accompanied by awidened
articular space .
5
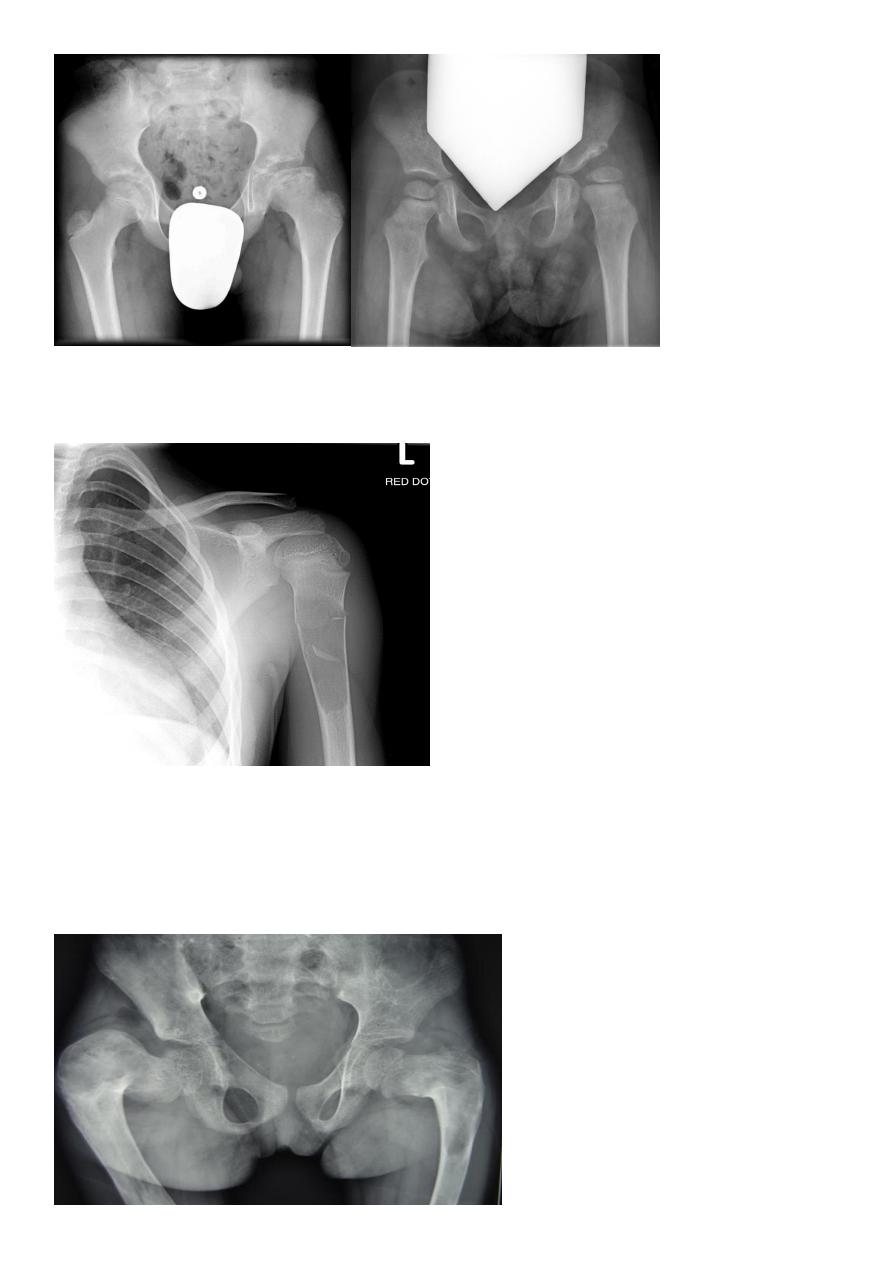
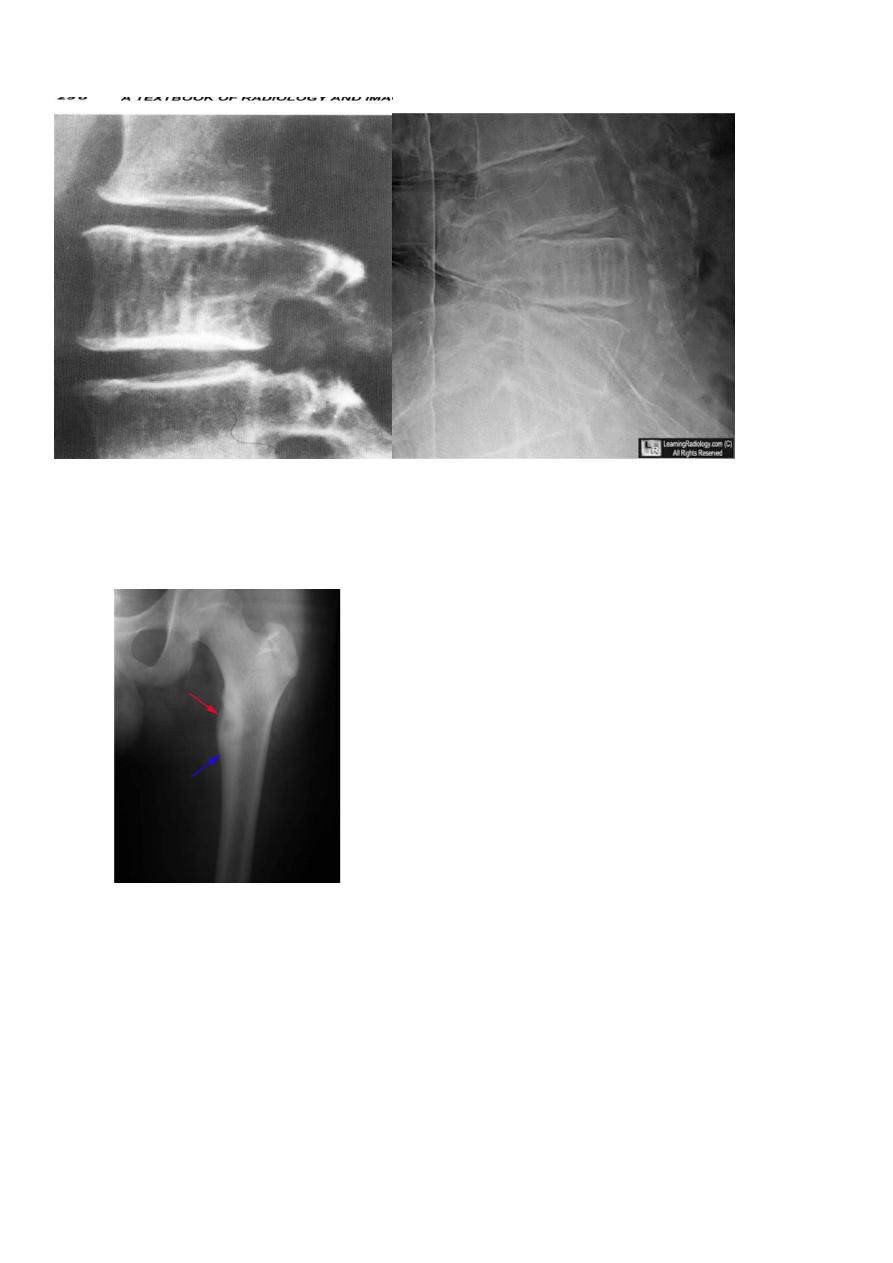
Fallen fragment sign
shepherd crook deformity seen in fibrous dysplasia
A shepherd crook deformity refers to a coxa varus angulation of the proximal femur,
classically seen in femoral involvement by fibrous dysplasia .
6
The whole vertebral body marked by vertical striation … being Haemangioma
Osteoid osteoma:
lucent area surrounded by calcification
nidus surrounded by sclerotic rim with or without periosteal reaction
Both secondary metastasis & MM being cause multiple lytic lesion within the skeletal
system who can you differentiated secondary from MM if each one of them affecting
vertebra
????
*secondary M primarily affecting & have predilection to pedicle
*MM spares vertebral pedicle.
7
causes of reduced bone density:
Metastatic carcinoma.
Multiple myeloma.
Hyperparathyroidism.
Osteomalacia.
Osteoporosis .
Causes of generalized increase in the density of the bone:
1.Sclerotic metastases.
2.Osteopetrosis (Marble bone disease)
3.renal osteodystrophy
4.Fluorosis
5.Myelosclerosis
Who can you do Von Rosen view
At 3-6 months
:
abduction of the thigh 45 degree and internal rotation
Define the following:
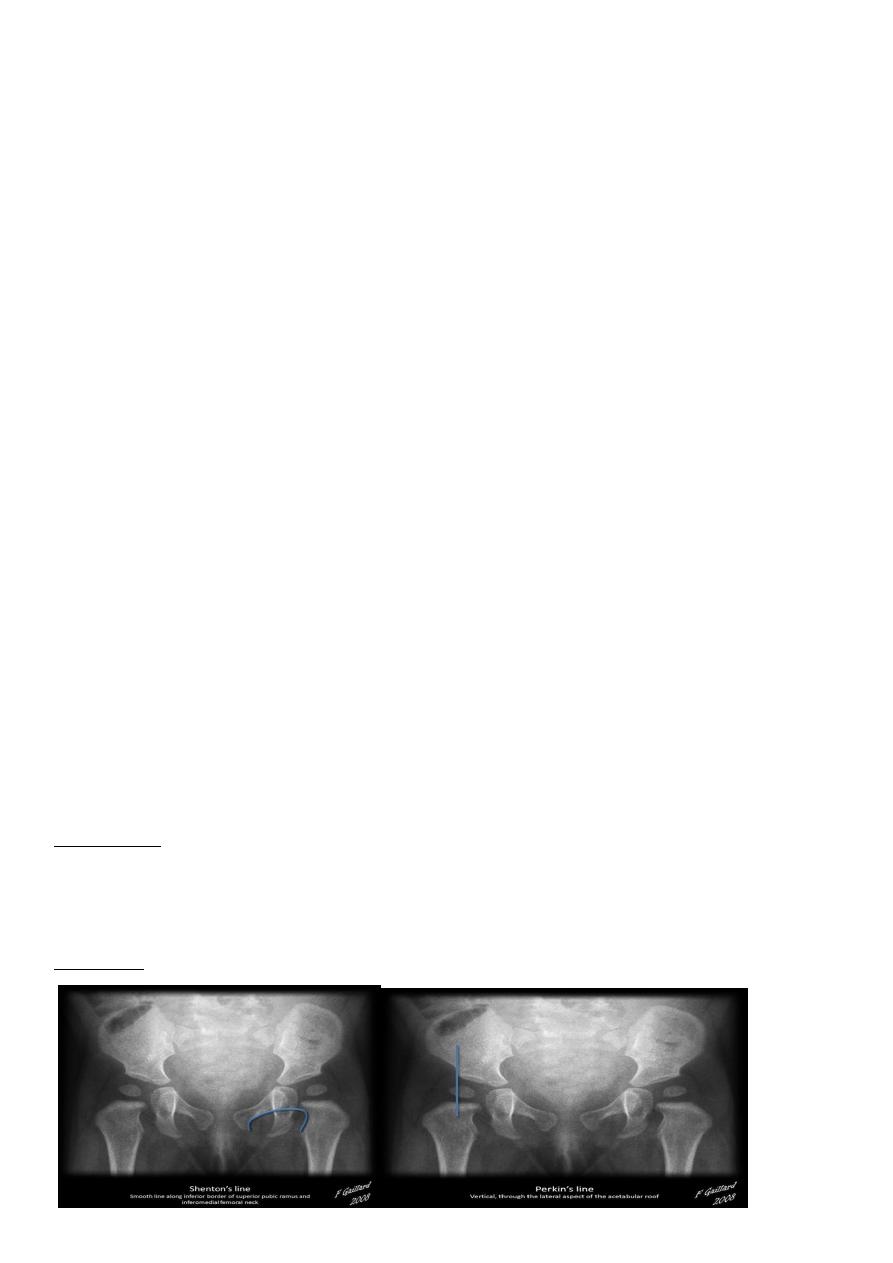
Shenton line is drawn along the inferior border of the superior pubic ramus and should
continue laterally along the infero medial aspect of the proximal femur as a smooth line. If
there is supero lateral migration of the proximal femur due to DDH then this line will be
discontinuous
Perkin line is drawn intersecting the lateral most aspect of the acetabuler roof & iliac creast

8
Periosteal reaction is a non specific radiographic finding that occurs with periosteal
irritation .
Codman's triangle is a type of periosteal reaction seen with aggressive bone lesions could
be singlelayer and mulitlayered periosteal reaction), only the edge of the raised periosteum
will ossify .
Brodies abscess is an intraosseous abscess infavouer of subacute pyogenic osteomyelitis
Gary's osteomylitis is a specific type of chronic osteomyelitis. It mainly affects children and
young adults . It typically affectes the mandible
Potts disease also known as tuberculous spondylitis, refers to vertebral body and
intervertebral disc involvement with tuberculosis (TB)
Gibbus deformity is a short-segment thoracolumbar kyphosis causing sharp angulation.
A sequestrum is usually a complication of osteomyelitis and represents devascularisation of
a portion of bone with necrosis and resorption of surrounding bone leaving a 'floating'
piece
An involucrum is a complication of osteomyelitis and represents a thick sheath of
periosteal new bone surrounding a sequestrum
A cloaca is an opening in a involucrum which allows drainage of purulent and necrotic
material out of the dead bone.
Osteomalacia (OM) is bone softening due to insufficient mineralisation of the osteoid
secondary to any process results in vitamin D deficiency
Looser zone are wide transverse lucencies traversing part way through a bone, usually at
right angles to the involved cortex and are associated most frequently
with osteomalacia and rickets
Code fish vertebra fish vertebra (or codfish vertebra) describes the biconcave appearance
of vertebrae (espaically lumbar vertebrae) .
Rachitic rosary refers to expansion of the anterior rib ends at the costochondral junctions
and is most frequently seen in rickets as nodularity at the costochondral junctions.
Brown tumor more common in the primary type seen as lytic expansile lesion in any bone
particularly the mandible & pelvis.
Rugger-jersey spine describes the prominent subendplate densities at multiple contiguous
levels to produce an alternating dense-lucent-dense appearance .
Wormian bone are a subset of the small intra sutural bones that lie between the cranial
sutures mainly seen around the lambdiod sutures
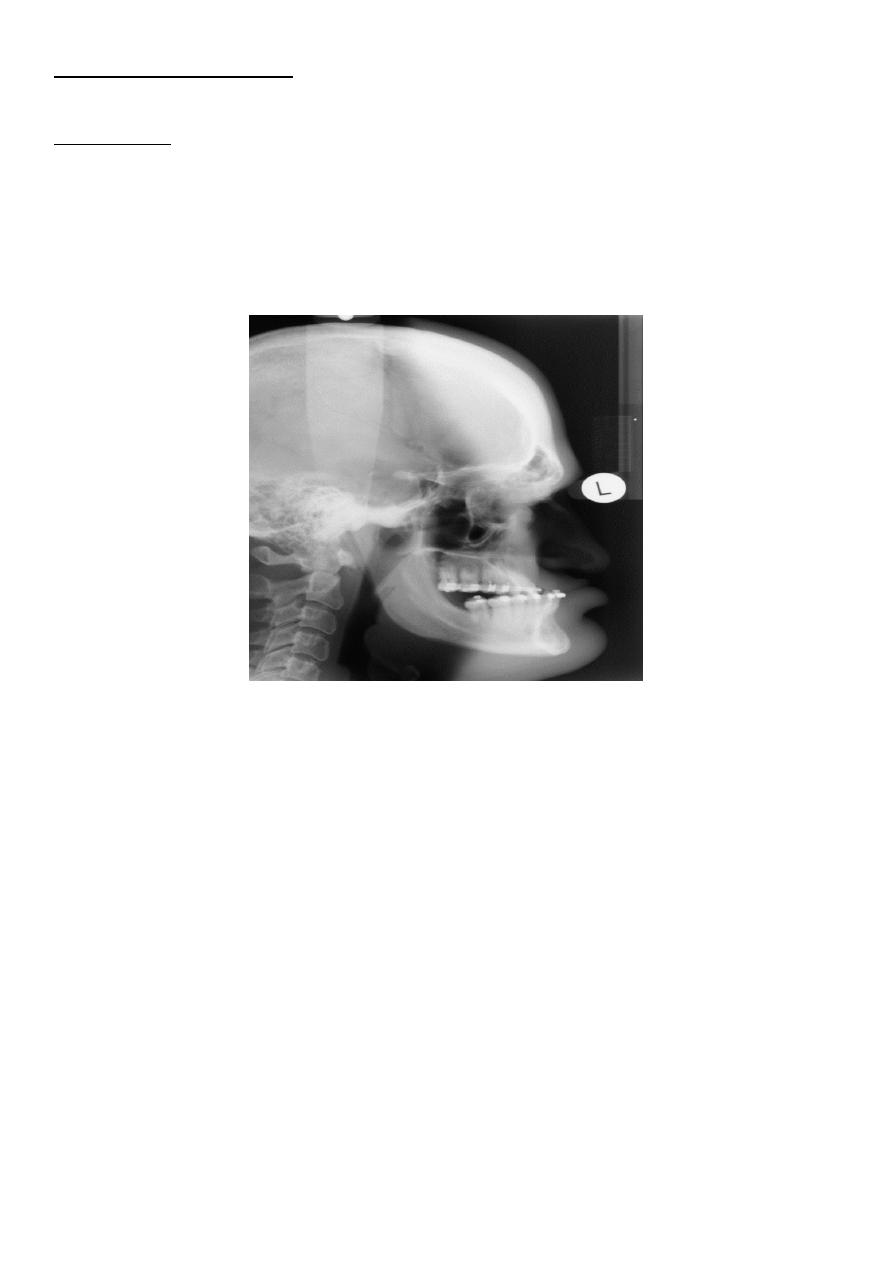
Prognathism widening of angle between the body and ramus of the mandible .
9
A shepherd crook deformity refers to a coxa varus angulation of the proximal femur,
classically seen in femoral involvement by fibrous dysplasia
Osteo porosis is metabolic skeletal disease defined as a reduction of bone mineral density
(BMD) below a defined lower limit of normal.
Acromegaly & prognathism
Wormian bone :
What is it being ??? Wormian bone are a subset of the
small intra sutural bones that lie between the cranial sutures mainly seen
around the lambdiod sutures
Causes ?????
osteogenesis imperfecta
rickets
cleidocranial dysostosis
Hypothyroidism
Down syndrum
11
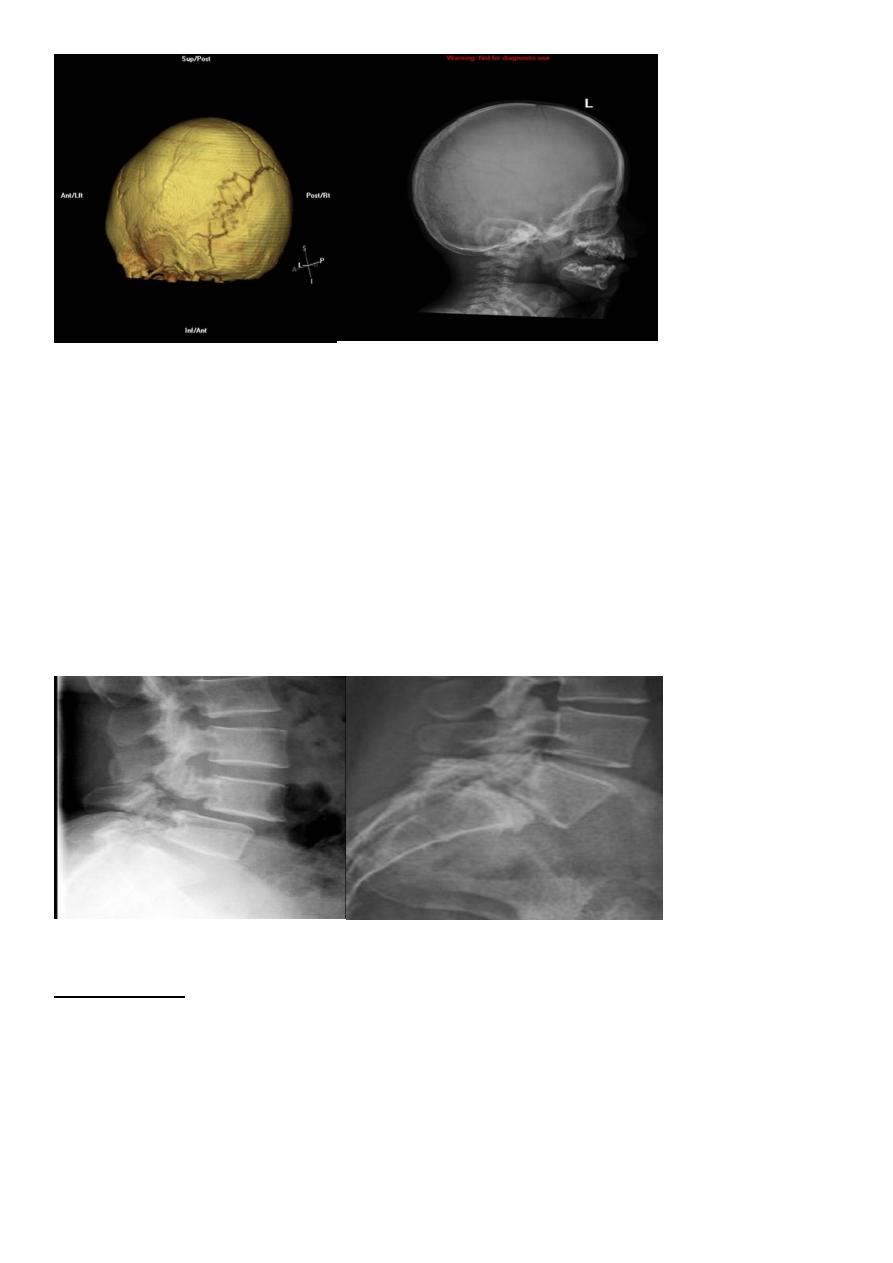
Spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis
Spondylolisthesis:
is a term denoting fore ward or backward movement of a vertebra
relative to the vertebral segment below, typically due to spondylolysis (pars interarticularis
defects) .
Spondylolysis:
Spondylolysis is a defect in the pars interarticularis of the neural arch, the
portion of the neural arch that connects the superior and inferior articular facet in which
cause defect in the neck of scotty dog .
scotty dog sign refers to the normal appearance of the lumbar spine when seen on oblique
radiographic projection. On oblique views, the posterior elements of vertebra form the
figure of a Scotty dog with:
the transverse process being the nose
the pedicle forming the eye
the inferior articular facet being the front leg
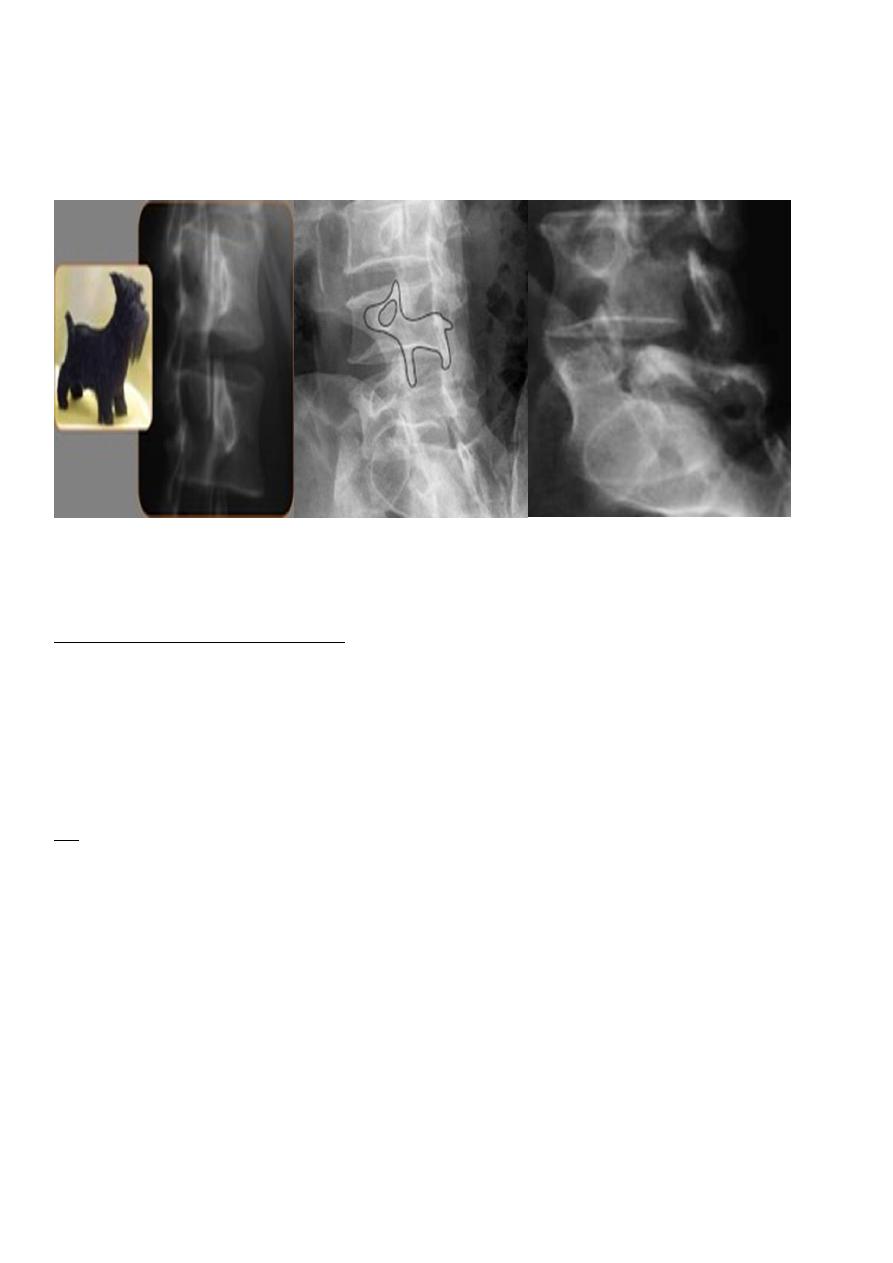
11
the superior articular facet representing the ear
the pars interarticularis (the portion of the lamina that lies between the facets) equivalent
to the neck of the dog.
question
sacroiliitis & facet joint ankylosis Being charct. Of which one of the following
???
*Ankylosing spondylitis
*DISH
Ans…. Ankylosing spondylitis ( is the true answer )
Q..What do you mean the symbol ( DISH )
????
Ans….DIFFUSE IDIOPATHIC SKELETAL HYPEROSTOSIS
MCQs:
*Erosive changes of DIP and PIP (osteoarthritis )
*Peri articuler erosive changes at 2nd and 3rd MCP joint( Rheumatoid arthritis )
*punched out peri articuler lytic lesion affecting 1st MTP joint (of the big toe ( Gout
Sub periosteal resorption at the radial aspect of the middle phalanges (hyper
parathyriodism ).

12
Types of metastasis:
Osteolytic (most common causes) : neuroblastoma (in children), breast (adult female),
bronchus (adult male), thyroid, kidney, colon The vertebral pedicles are often involved.
Osteoblastic : prostate, breast , carcinoid , TCC of bladder,, neuroblastoma.
Mixed: breast, prostate, lymphoma.
Solitary expansile bubbly metastases with soft tissue involvement: thyroid, kidney.
Bone metastases with sun burst periosteal reactions: prostate, retinoblastoma and
neuroblastoma.
Very important note:
Myeloma resembles metastases in everything except
:
*it's more well defined ,
*cause bone expansion if solitory called plasmacytoma
*spares vertebral pedicle
Skull manifestation of the acromegaly
1.Thickening of the skull vault &diplioc space
2.Thickening of the posterior occipital tubercle
3.Prognathism
4.Froehead bossing with enlargement of the frontal sinuses also with enlargement of the
mastiod air cell
.
5.Balloning with Double floor appearance of the sella tursica .

13
Osteophytes ,
Subchondral sclerosis
Uneven loss of articular space
These signs being of which one of the following
???
1.Metabolic arthritis
2.Degenerative arthritis
3.Inflammtory arthritis
True answer is Degenerative arthritis
Q….What are the main 5 radiological sign of degenerative arthritis
???
Q….What sign in spine being pathgnomonic for degenerative spondylosis of the spine
???
Vacuum phenomenon: gas (N2),is pathognomonic of the degenerative process
Q…what are the types of inflammatory arthritis
Q… what are he early changes seen in Rheumatoid arthritis
??
Q…CDH occurs most commonly in
????
(
71
)%
in the left hip . Bilateral involvement is seen in 5%
Q…By simple diagram draw pelvis with lines (shenton’s & Perkins line)
Very important notes:
*Well defined clear cut with narrow zone of transition indicates benign or slowly growing
lesion.
*Ill-defined wide zone of transition indicates aggressive rapidly growing lesion as osteo
myelitis and malignant tumors.
* Metastases & myeloma lie in the middle of the spectrum (well defined lytic lesion with no
sclerotic margin).
*commonest malignant tumors affecting the
bone ??? secondary metastasis
*the commonest primary malignant bone tumor in young adults ?? Osteosarcoma

14
Q….lytic, expansile lesion, Sub articular in location, Not clearly defined margin with
thinning of the cortex
???
Giant cell tumor
What is the most conmen causative organism affecting the bone
???
staphylococcus aurous : 80-90% of all infections
vertebral metastases (94%) causing primerly affection of the
????
Pedicle
