Assis.Prof.Radhwan Himmadi HasanB.D.S , M.Sc. , Ph.D. Prosthodontics2016
Principles of Removable Partial Dentures design with special emphasis on support and periodontal consideration of remaining teethPRINCIPLES OF DESIGN
1.Dentist should have thorough knowledge2.Treatment plan must be based on complete examination and diagnosis of individual patient.
3.Dentist must correlate the pertinent factors and determine a proper treatment plan
4.RPD should restore the function without injury to remaining oral strutures
5.It is a form of treatment and not a cure.Sunday, December 18, 2016
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan2
STRESS CONSIDERATION IN A PARTIAL DENTURE
The stresses can be divided as:
Vertical
HorizontalTorsional
Displacing stressesDislodging stresses
Sunday, December 18, 2016
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan3
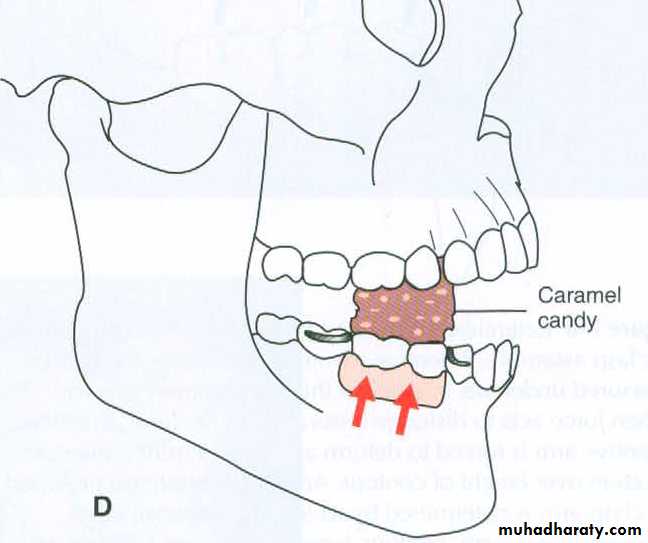
• VERTICAL STRESS
• Displacing stresses :•
• These are the least harmful and are borne well if within physiologic limits
• Those forces which are the result of downward
• stresses along
• the long axis of
• the teeth in a crown
• to apex direction and
• the relatively vertical
• stresses on the ridge
• mucosa.
Sunday, December 18, 2016
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
4
DISLODGING STRESSES :
These are the forces which tend to lift the partial denture from it’s rest position
Sunday, December 18, 2016Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
5
HORIZONTAL STRESS
They originate as a component of rhythmic chewing stroke. These forces are effective in mesio-distal and buccolingual direction.
These lateral stresses are most damaging.
Sunday, December 18, 2016
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
6
TORSIONAL STRESS
It is a twisting rotational type of force. It’s a combination of vertical and horizontal force
Sunday, December 18, 2016
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
7
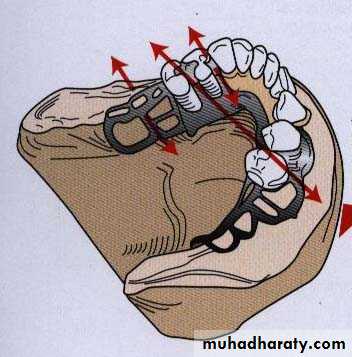
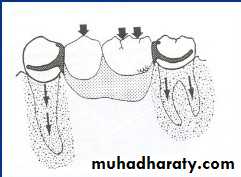
FORCES ACTING ON PARTIAL DENTURE
Sunday, December 18, 2016Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
8
McCracken’s Removable Partial Prosthodontics 11th edition
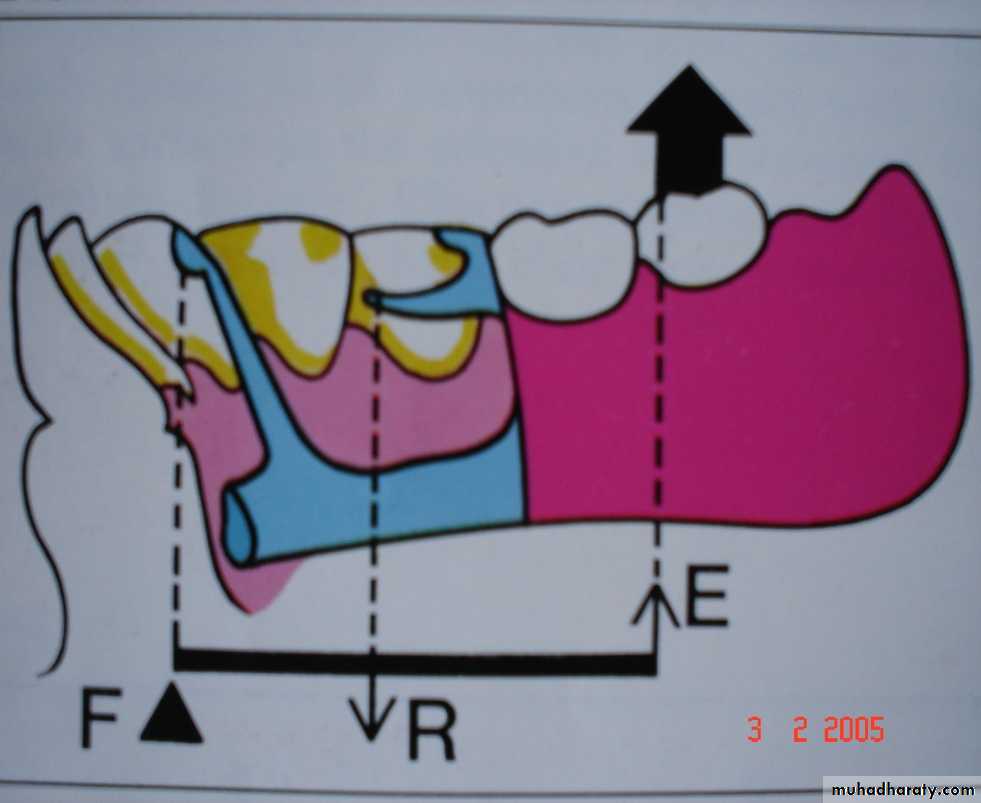
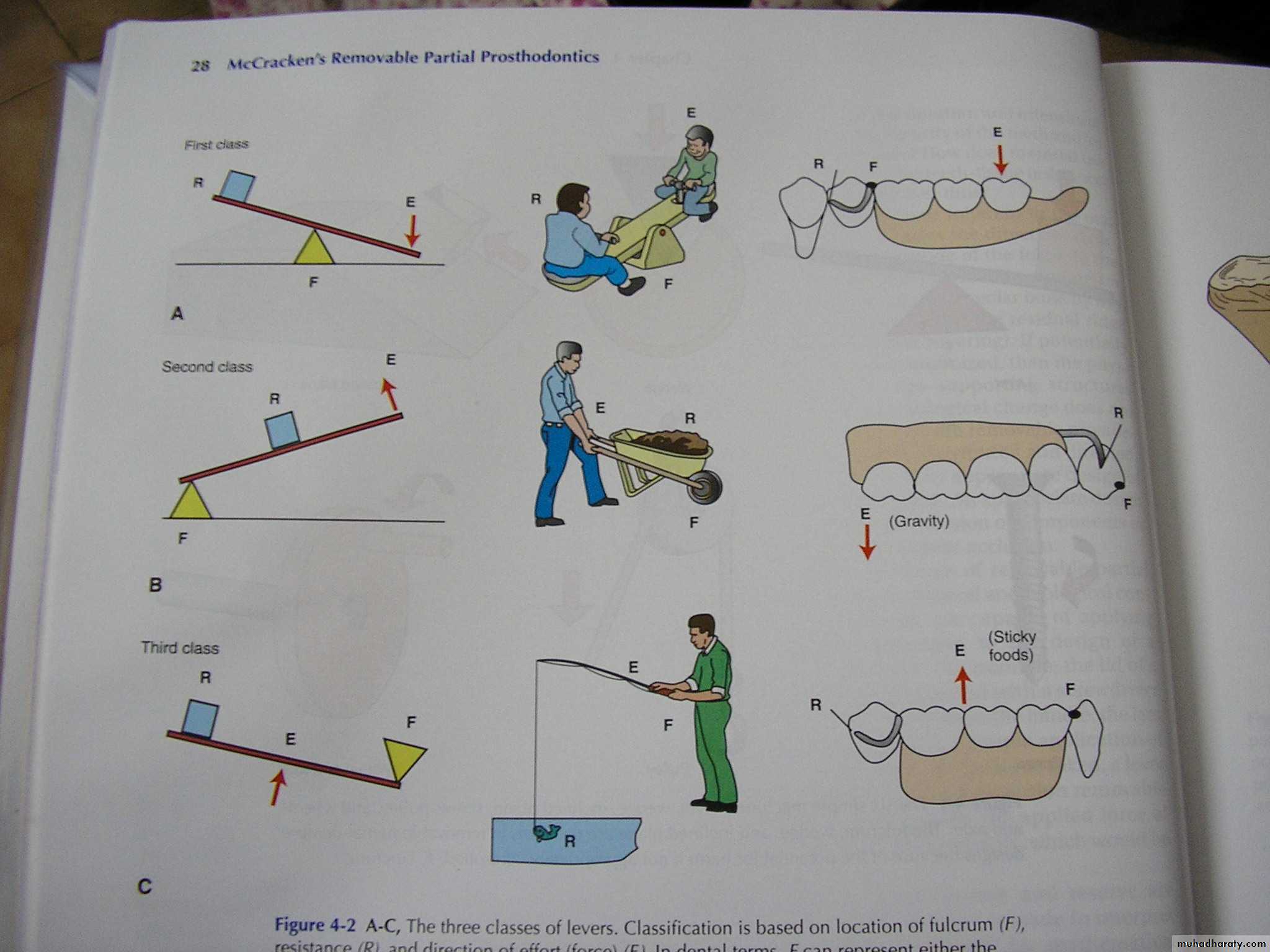
Is a rigid bar supported somewhere along its length..The point where the bar is supported is called the fulcrum
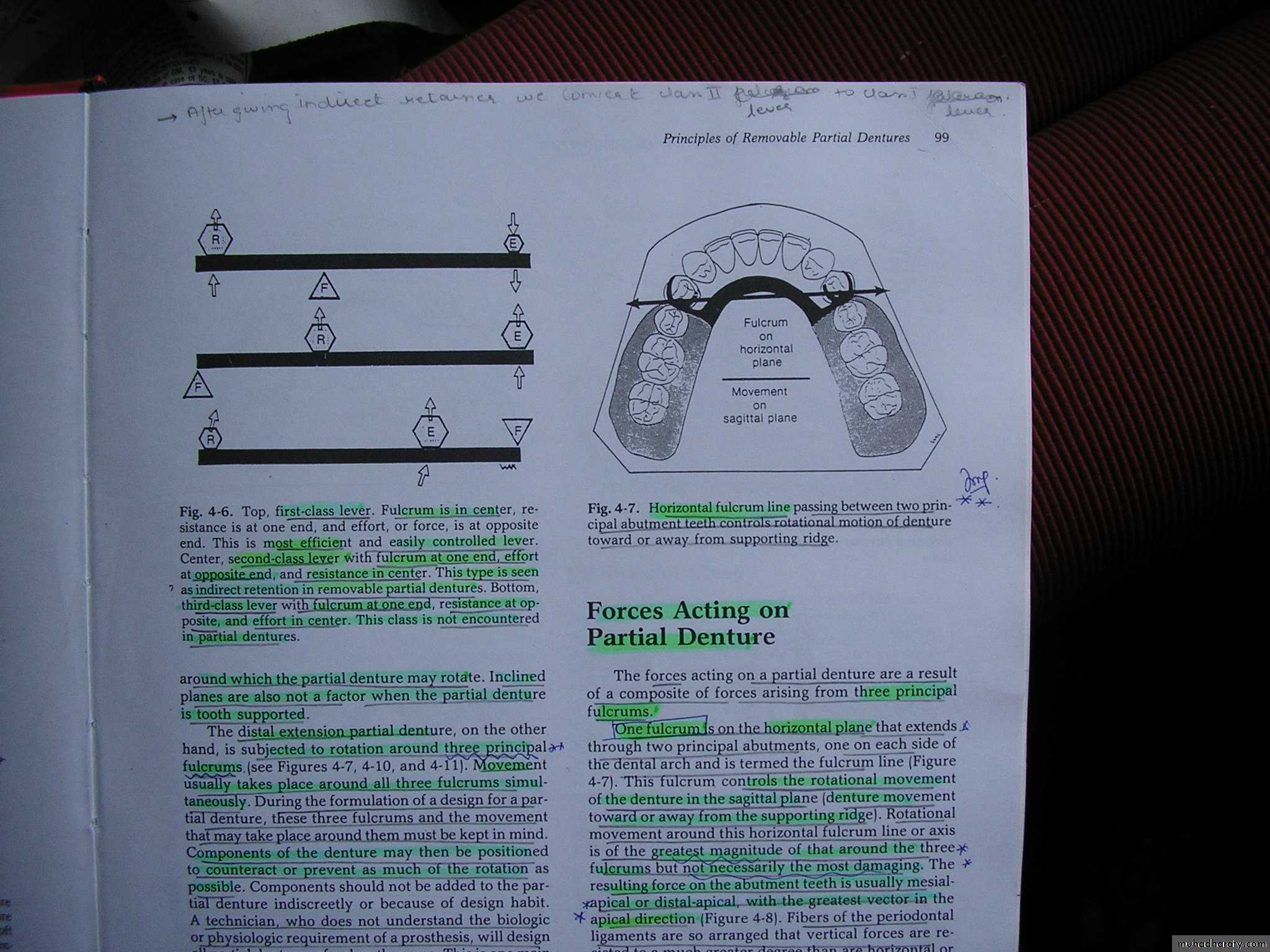
Three classes of levers (based on location of fulcrum, resistance and direction of effort (force).Class I
Class II
Class III
LEVER
Sunday, December 18, 2016
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan9
CLASS I LEVER
Fulcrum lies in the centre,
Resistance is at oneend and force at the other.
McCracken’s Removable Partial Prosthodontics 11th edition
Sunday, December 18, 2016Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
10
CLASS II LEVER
Fulcrum is at one end effort
at the opposite end andresistance in the centre.
McCracken’s Removable Partial Prosthodontics 11th edition
Sunday, December 18, 2016Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
11
CLASS III LEVER
Fulcrum is at one end,
resistance at oppositeend and effort is in the centre.
McCracken’s Removable Partial Prosthodontics 11th edition
Sunday, December 18, 2016
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
12
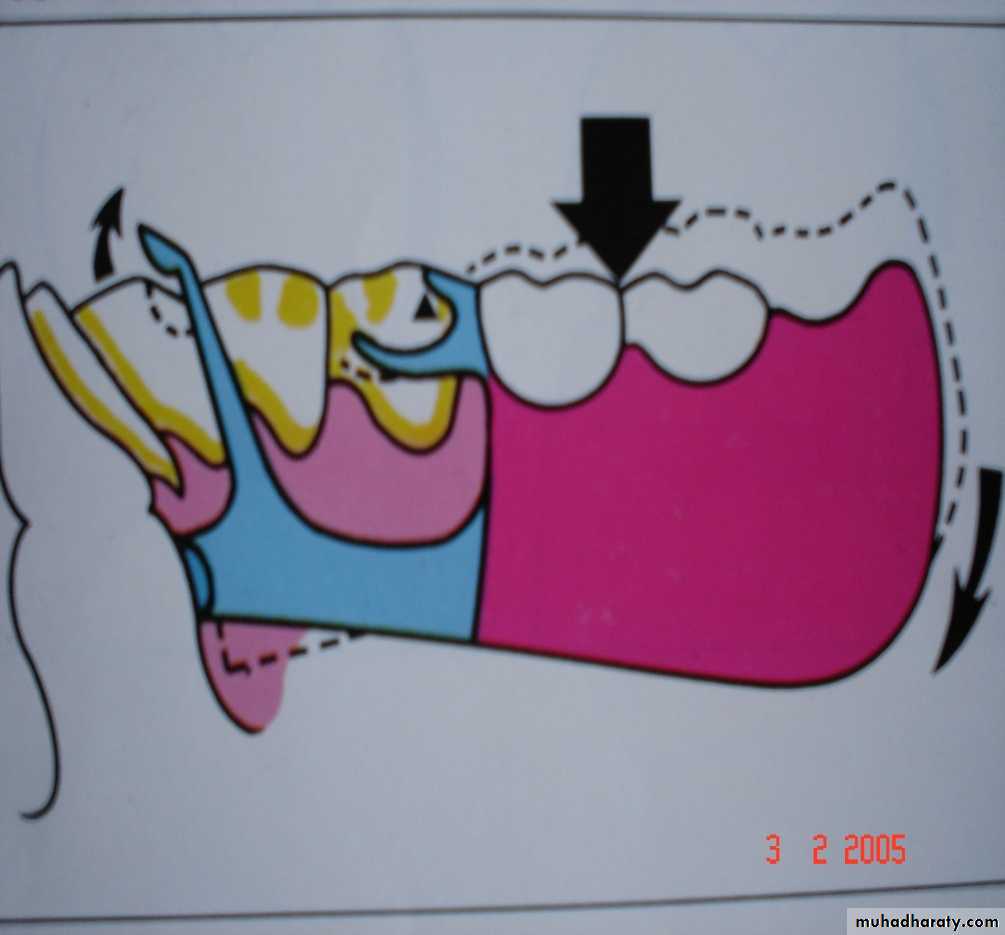
Possible movements of partial denture.
Tooth –tissue supported partialdenture:
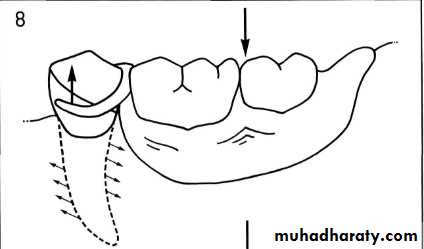
FULCRUM ON HORIZONTAL PLANE:
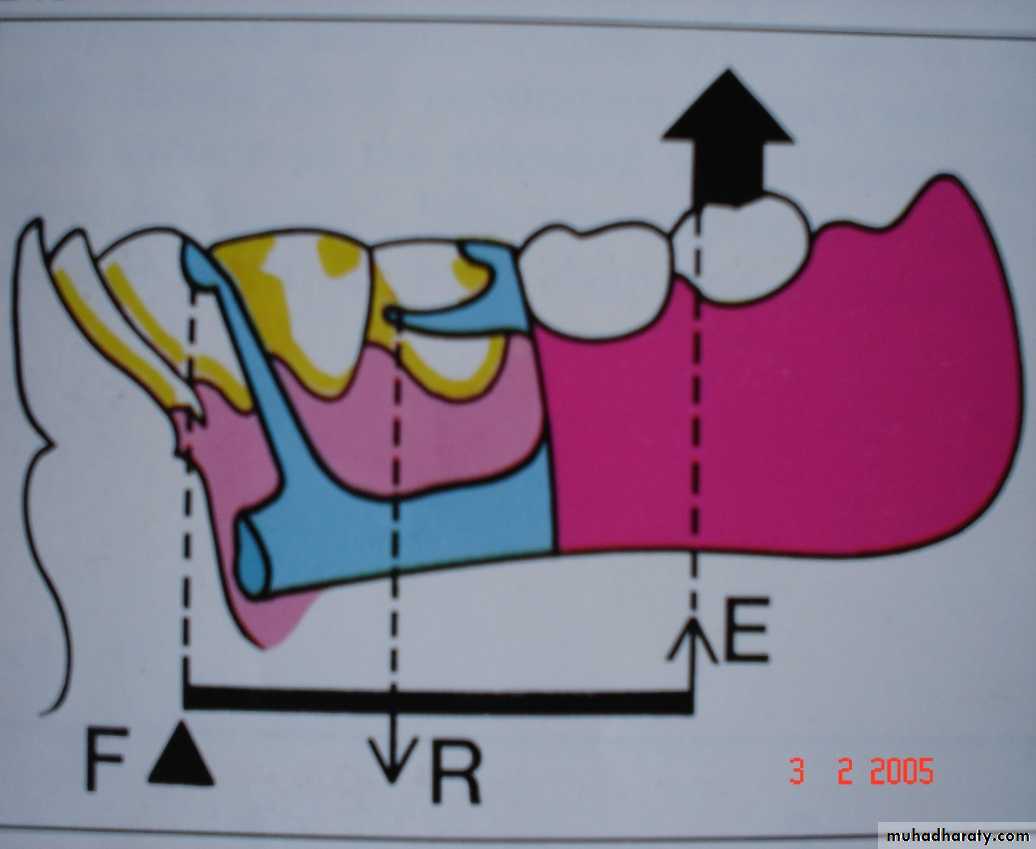
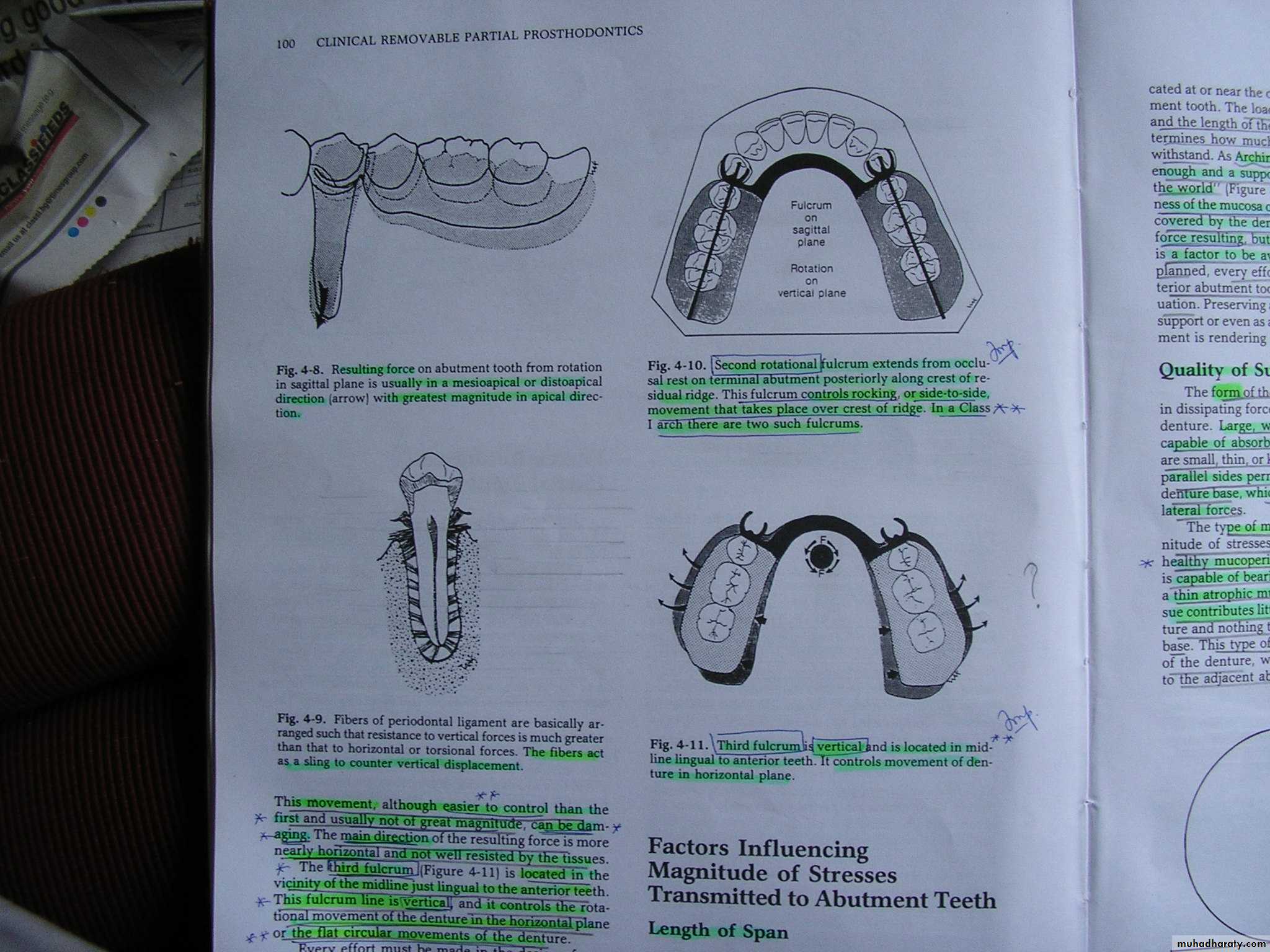
Extends through the rest of principle abutments.Rotational movement of the denture in the sagittal plane.
Stewart’s clinical Removable Posthodontics 4th edition
Sunday, December 18, 2016
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
14
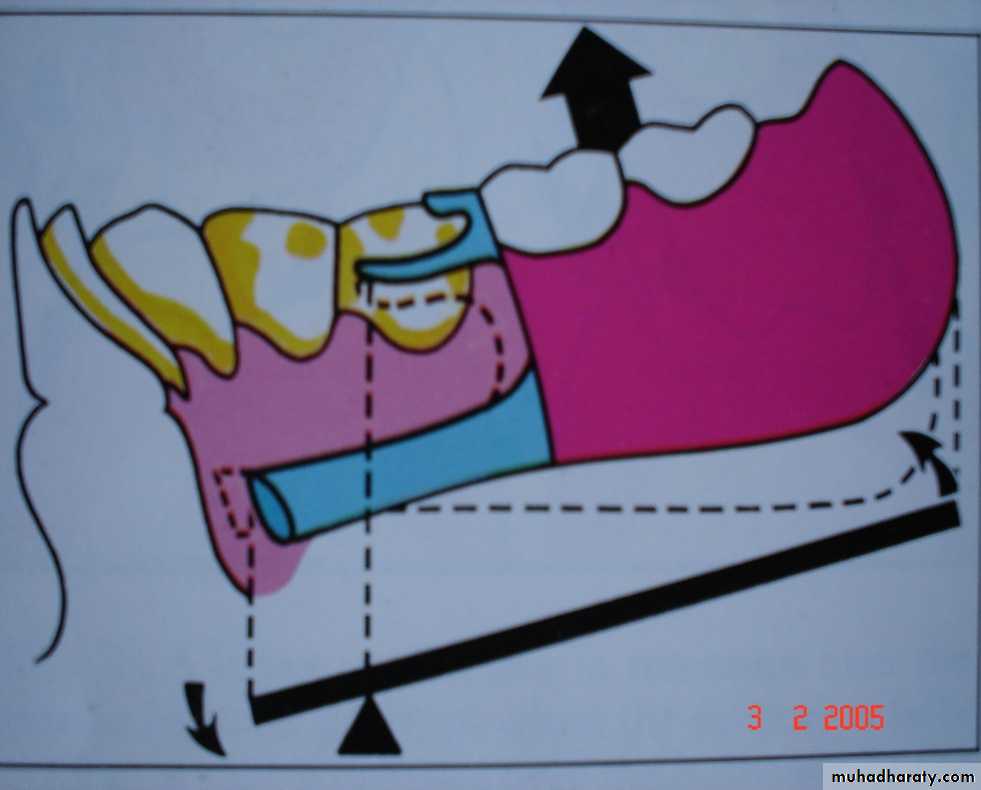
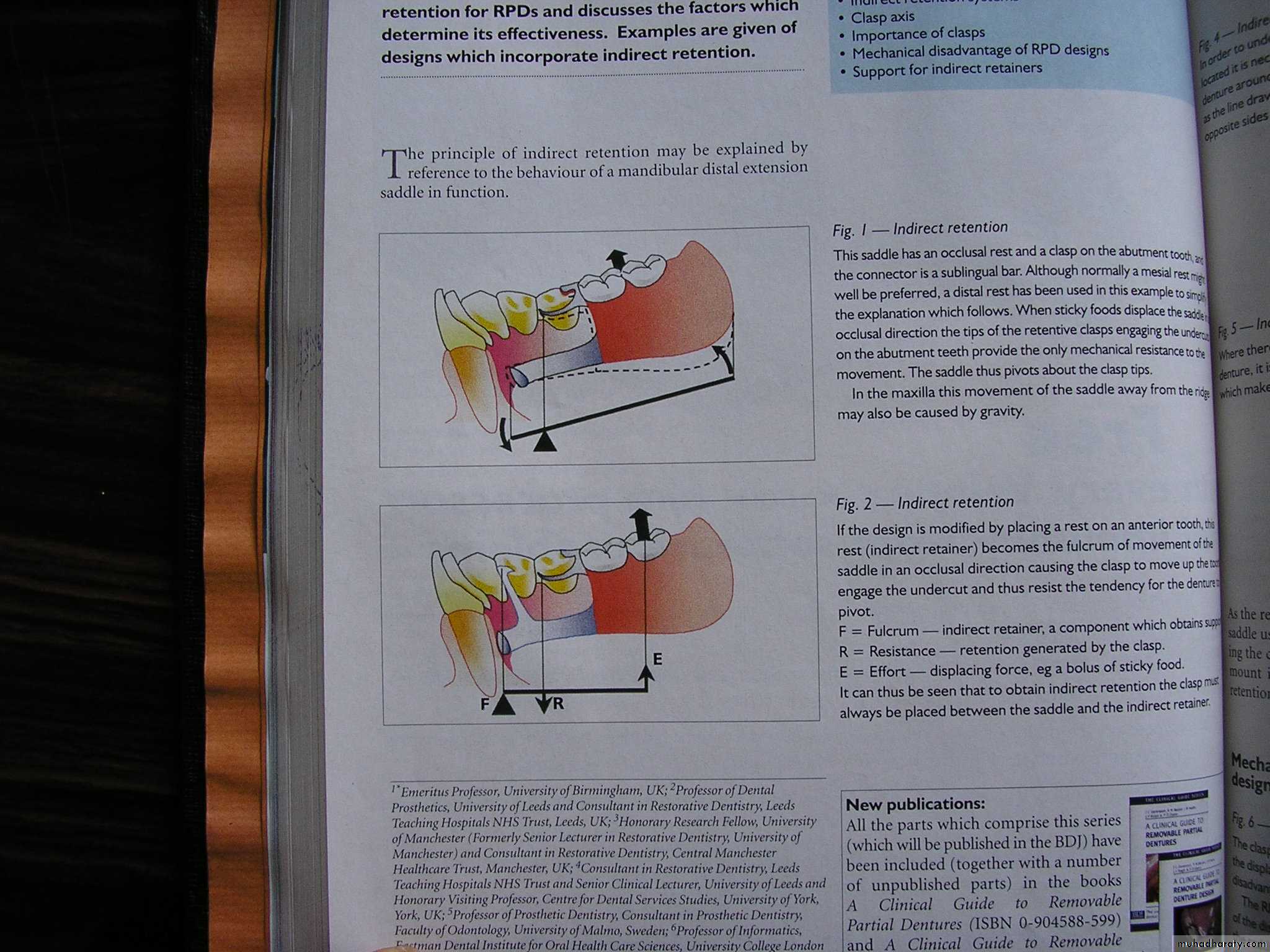
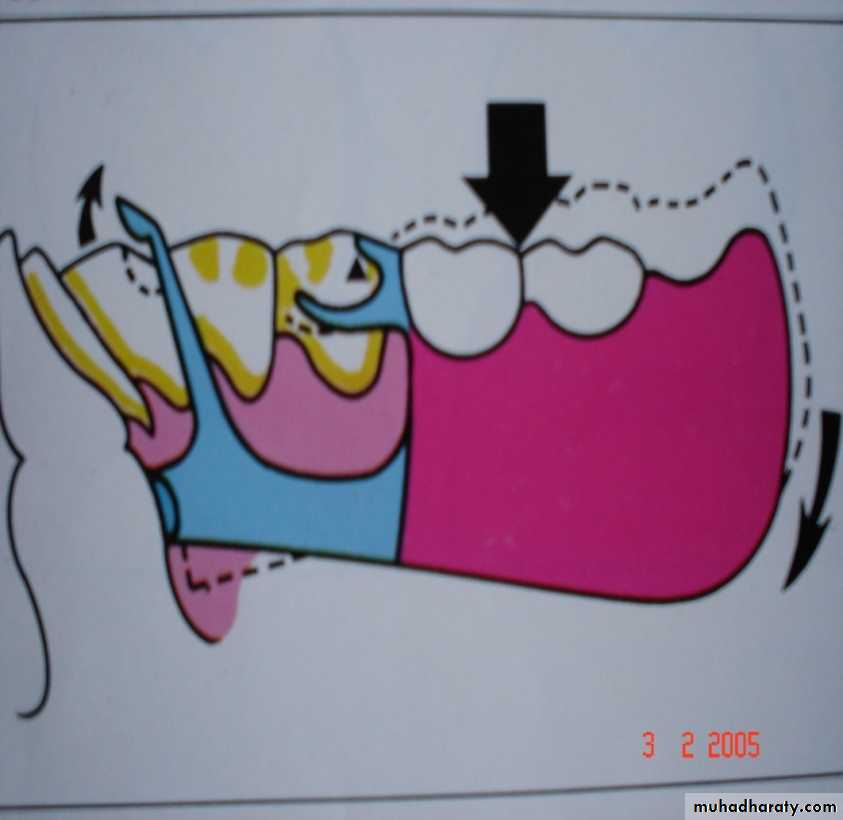
• DENTURE BASE MOVES AWAY FROM SUPPORTING TISSUES:
•Counteracted by:
Direct retainer andIndirect retainer
McCracken’s Removable Partial Prosthodontics 11th edition
Sunday, December 18, 2016
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
15
DENTURE BASE MOVES TOWARDS THE
SUPPORTING TISSUES:Counteracted by:
• Occlusal rest.
• Tissues of supporting ridge
McCracken’s Removable Partial Prosthodontics 11th edition
Sunday, December 18, 2016Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
16
resulting forces on abutment teeth less damaging as it is in apical direction fibers of the periodontal ligament are so arranged that vertical forces are resisted greatly than horizontal forces
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
17Sunday, December 18, 2016
FULCRUM ON THE SAGITTAL PLANEExtends through the occlusal rest on the terminal abutment and along the crest of the ridge.
Or Rotation about a longitudinal axis at the residual ridge
Movement is in the frontal plane
Stewart’s clinical Removable Posthodontics 4th edition
Sunday, December 18, 2016
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan18
Counteracted by:
Rigidity of major and minor connector and their ability to resist torque.Close adaptation of the denture base along the lateral slopes and the buccal slopes of the palate and ridge.
Direct retainer design
McCracken’s Removable Partial Prosthodontics 11th edition
Resulting forces more damaging as it is in horizontal directionSunday, December 18, 2016
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
19
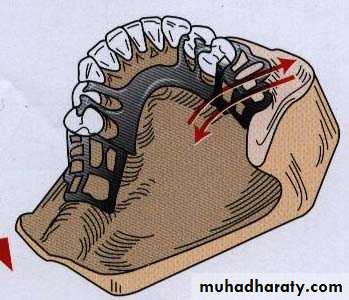
FULCRUM LOCATED IN MIDLINE JUST LINGUAL TO THE ANTERIOR TEETH (FULCRUM IS VERTICAL)
Rotational movement of denture in horizontal plane
orflat circular movements of the denture
Stewart’s clinical Removable Posthodontics 4th edition
Sunday, December 18, 2016
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
20
Counteracted by :
Stabilizing components (reciprocal arm and minor connector)Rigid major connector
Close adaptation of denture baseMcCracken’s Removable Partial Prosthodontics 11th edition
Resulting forces more damaging as it is in horizontal directionSunday, December 18, 2016
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
21
Tooth supported partial denture:
Movement :
Toward tissues resisted by rest on abutment teeth
Away from tissue resisted by retentive clasp arm
Horizontal movement resisted by stabilizing components
Rotation relatively non existent
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan22
Sunday, December 18, 2016
• FACTORS INFLUENCING MAGNITUDE OF STRESSES TRANSMITTED TO ABUTMENT TEETH
• 1. Quality of support of ridge• Form of residual ridge
• type of mucosal covering
• 2. Length of span
• 3. Clasp factor
• design
• length
• material
• amount of tooth contact
Stewart’s clinical Removable Posthodontics 4th edition
Sunday, December 18, 2016
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
23
4. Occlusion
Type of teeth
Harmony of occlusion
5. Areas of the base to which load is applied
Stewart’s clinical Removable Posthodontics 4th editionSunday, December 18, 2016
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
24
• QUALITY OF SUPPORT OF RIDGE
• Better support by ridge less stress on abutment teeth• Large well formed ridges absorb greater stress less stress on abutment
• Broad ridges with parallel
• sides longer flanges on
• the denture base stabilize
• the denture against lateral
• forces.
•
Stewart’s clinical Removable Posthodontics 4th edition
Sunday, December 18, 2016
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
25
b. TYPE OF MUCOSA
Influences magnitude of stresses transmitted to abutment teeth.Healthy mucosa capable
of bearing greater functionalloads than thin atrophic
mucosa
Soft, flabby, displaceable mucosa
Contribute little to vertical support of denture allows excessive movement of denture stress transmitted to abutment teethStewart’s clinical Removable Posthodontics 4th edition
Sunday, December 18, 2016Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
26
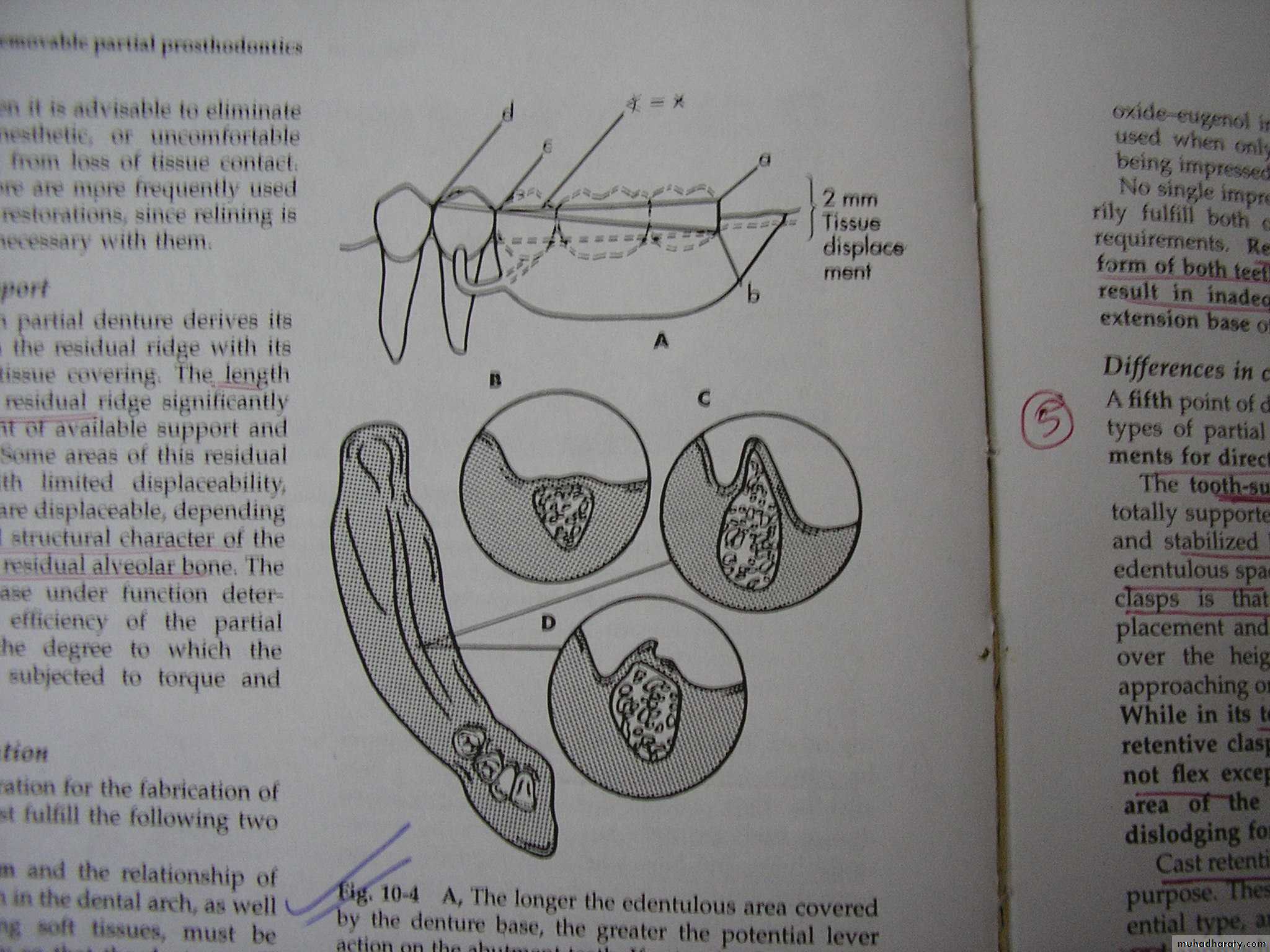
2. LENGTH OF SPAN
Longer edentulous span
longer denture basegreater force transmitted to
abutment teethEvery effort be made to retain a posterior abutment to avoid class I and class II situation.
Stewart’s clinical Removable Posthodontics 4th edition
Sunday, December 18, 2016Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
27
3. CLASP AS A FACTOR IN STRESS
More flexible the retentive arm of claspless stress to abutment toothBut, flexible clasp arm provides less stability against horizontal forces increase stress on residual ridge.
Decision should be made whether abutment or ridge requires more protection
Stewart’s clinical Removable Posthodontics 4th editionSunday, December 18, 2016
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
28
In examination phase decide whether ridge or abutment tooth require more protection
If periodontal support goodless flexible clasp like vertical projection clasp
If periodontal support weakuse more flexible clasp like
combination claspSunday, December 18, 2016
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan29
AMOUNT OF CLASP SURFACE IN CONTACT WITH TOOTH
Greater the area of tooth to metal contact between clasp and tooth
more will be stress exerted on the tooth.Stewart’s clinical Removable Posthodontics 4th edition
Sunday, December 18, 2016Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
30
OCCLUSION AS A FACTOR
Disharmonious occlusiongenerate horizontal stresses
when magnified by factor of leveragecan transmit destructive forces to both abutment teeth and residual ridge.
Stewart’s clinical Removable Posthodontics 4th edition
Sunday, December 18, 2016
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
31
TYPE OF OPPOSING OCCLUSION
Play important role in determining amount of stress generated by occlusionNatural teeth can exert closing force upto 300(136.078 kilograms) pounds/inch square, whereas, complete denture upto 30 (13.6. kilograms) pounds/inch square.
Therefore RPD constructed against removable prosthesis is subjected to much less occlusal stress than one opposed by natural dentition.
Stewart’s clinical Removable Posthodontics 4th edition
Sunday, December 18, 2016
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
32
AREA OF DENTURE BASE TO WHICH LOAD IS APPLIED
Less movement of base if load applied adjacent to the abutment tooth than if it is applied to the distal end of the base.movement may be 4 times greater at distal end of base than next to the clasp.
Sunday, December 18, 2016
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan33
STRATEGIC CLASP POSITIONING AS A MEANS OF STRESS CONTROL
Leverages can be controlled to a large extent by means of clasps, if there are sufficient abutment teeth and they are strategically distributed in the dental arch.If number and location of potential abutments is less than ideal harmful effects can be decreased by strategic placement of clasps.
Stewart’s Clinical removable partial Prosthodontics 4th edition
Sunday, December 18, 2016
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
34
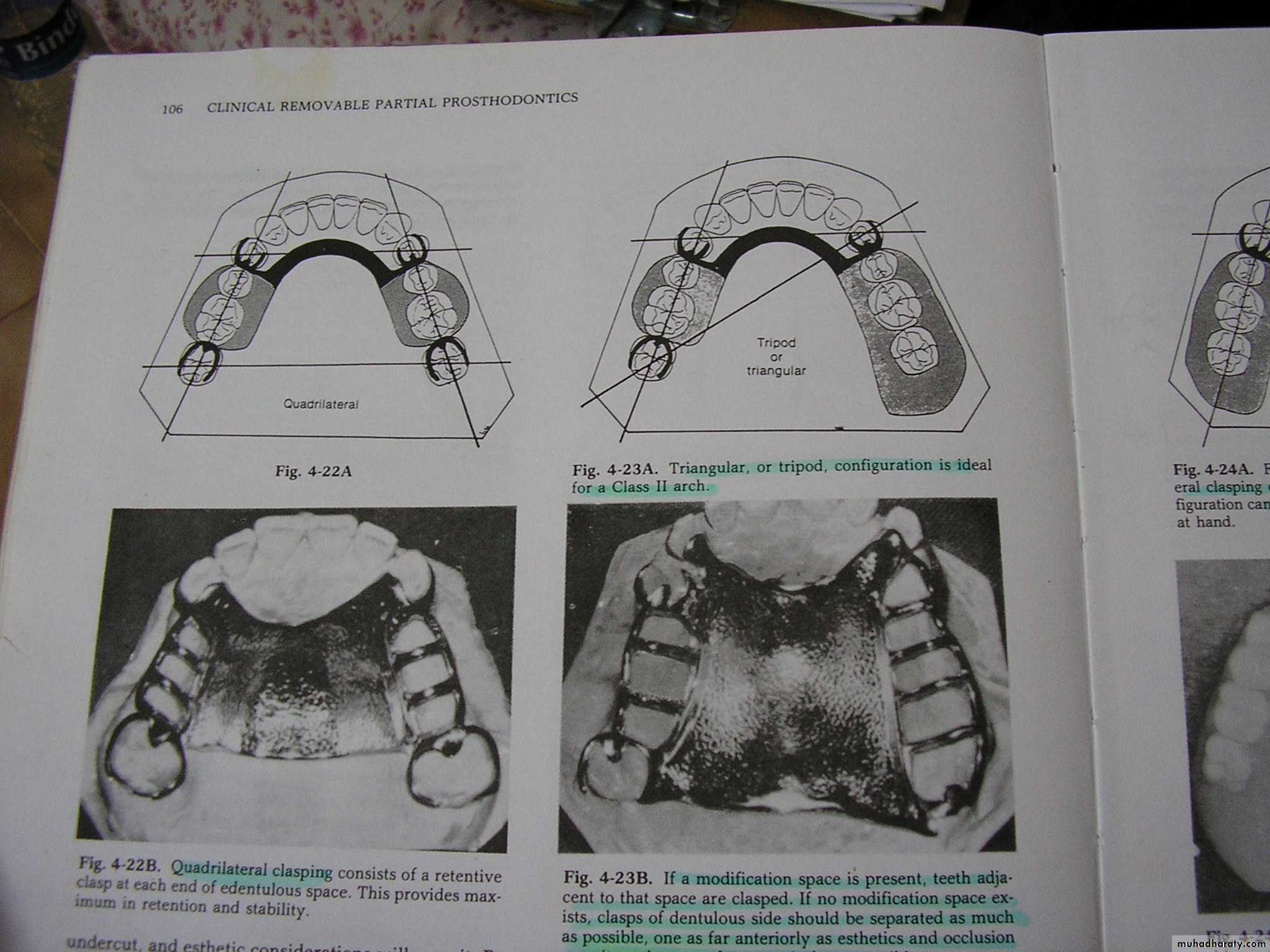
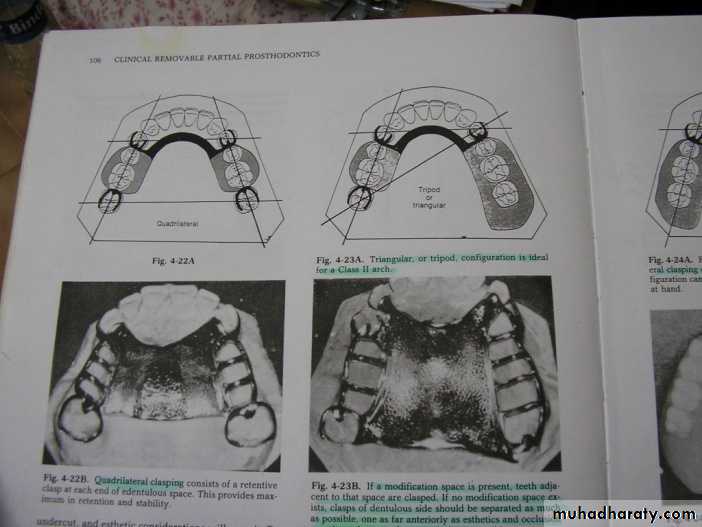
Indicated most often in class III arches (with modification space on opposite side)
QUADRILATERAL CONFIGURATION
McCracken’s Removable Partial Prosthodontics 11th editionSunday, December 18, 2016
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
35
TRIPOD CONFIGURATION
Class II situationsDistal abutment on one
side of arch missingleverage controlled to
some extent by creating
tripod configuration
of clasp placement.
McCracken’s Removable Partial Prosthodontics 11th edition
Sunday, December 18, 2016
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
36
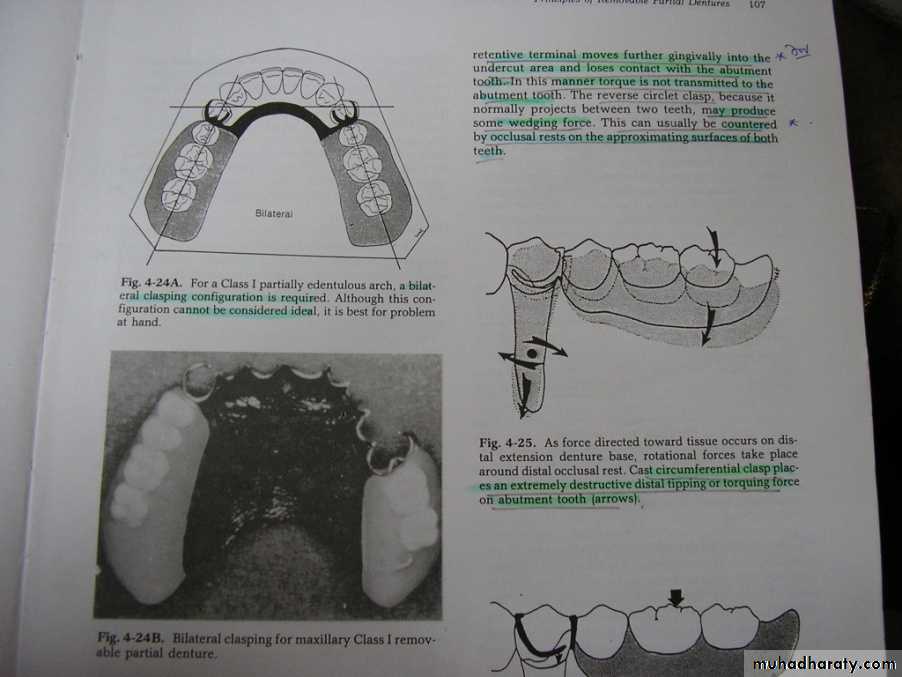
BILATERAL CONFIGURATION
For class I situations
Not considered ideal, but best option availableStress must be controlled by other means.
McCracken’s Removable Partial Prosthodontics 11th editionSunday, December 18, 2016
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
37
ESSENTIALS OF PARTIAL DENTURE DESIGN
Should be systematically developed on the diagnostic cast based on the following.• Where is the prosthesis supported.
• How the support is connected.
• How the prosthesis is retained.
• How the retention and support are connected.
• How the edentulous base support is connected
McCracken’s Removable Partial Prosthodontics 11th edition
Sunday, December 18, 2016
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
38
WHERE IS THE PROSTHESIS SUPPORTED.
Tooth supportedTooth - tissue supported:
Sunday, December 18, 2016Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
39
TOOTH SUPPORTED
• The most ideal support units are the RESTS.• The abutment selected for the support has to be evaluated for
Periodontal health.
Crown- root ratio.
Crown –root morphology
Location of the tooth in the arch
The opposing dentition
Sunday, December 18, 2016
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
40
TOOTH- TISSUE SUPPORTED
Depends on 6 factors:-• Quality of residual ridge
• The extent to which the ridge will be covered by mucosa• The accuracy and type of impression registration
• The design chracteristics
• The occlusal load applied
Sunday, December 18, 2016
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
41
Design of the removable partial denture
SimpleComfortable.
Harmless to the remaining tissues.
Sunday, December 18, 2016
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
42
Sunday, December 18, 2016
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan43
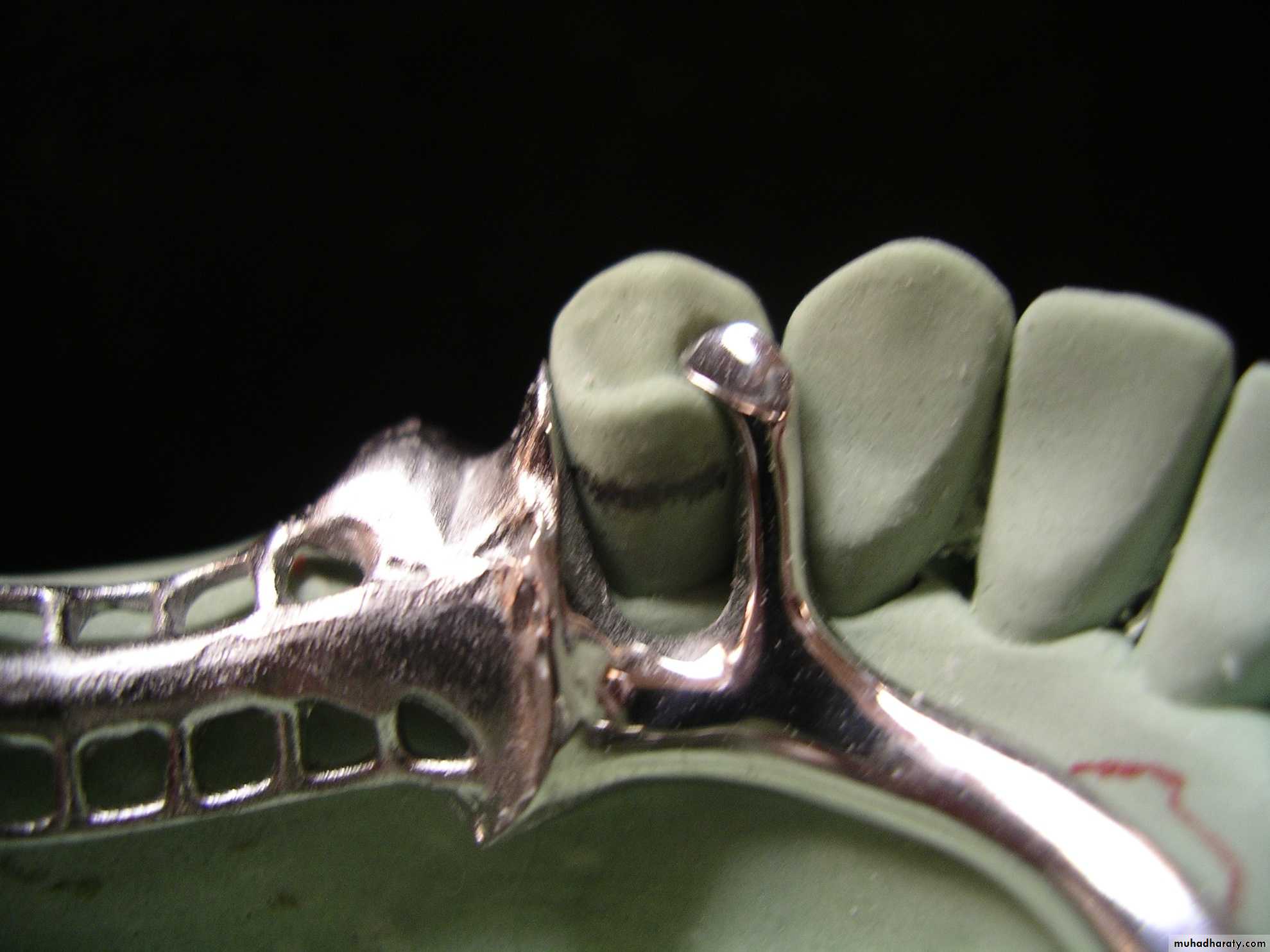
1-Name the minor connectors that appear in these case(6 marks)
2- What are the Methods of recording the degree of tilt(4 marks)
Sunday, December 18, 2016
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan44