
Fifth stage
Psychiatry
Lec-1
د
.
الهام
الجماس
9/10/2016
Introduction to Psychiatry
History Concepts
How were mentally ill treated prior to1790’s?
• Banishment
• Confinement
• What were attitudes toward them?
• Possessed by the devil
• Lacked basic human qualities
• Period of Enlightenment begins in 1790’s
• Concept of “Asylum” (sanctuary):
If we treat patients humanely and
respectfully, they will improve.
Mental illness worsens with stress
• First mental hospitals (“asylums”) in US in 1820’s
Era of Psychotropic Drugs
Medications first available in 1950s, i.e. chlorpromazine (Thorazine) for
Schizophrenia, Lithium for Mania
Hope for previously “incurable” mental illnesses and enhanced quality
of life.

WHAT IS HEALTH
World Health Organization's Definition
"A state of complete physical, mental, social and spiritual well-being and
not merely the absence of disease or infirmity'
WHAT IS MENTAL HEALTH?
DIVERSE OPINIONS EXIST
The most acceptable concept nowadays
person who is:
Able to cope/function normal
Meets the responsibilities.
Expressed balanced attitude towards day to day challenges/problems.
MENTAL HEALTH IN THE WORLD
1. MORE THAN TWO FIFTHS OF THE TOTAL DISABILITIES ARE DUE TO MENTAL ILLNESSES
(WORLD HEALTH REPORT, 2001)
2. EXISTING DATA SUGGEST:
Schizophrenia 45million
(above the age of 18).
Depression. 340million
Both disorders cause 60% of Suicide across the globe.

MENTAL HEALTH IN THE WORLD
Mental Retardation 4.6%
(total psychiatric diagnoses)
Alcohol Dependence 140 million
(Nations for Mental WHO.2001)
Alzheimer's disease 11 million
Epilepsy 45 million
(Murray L and Lopes A 1996)
DISEASES IN 2020
Ischemic Heart Disease
Depression
Road Traffic Accident
Cerebrovascular diseases
Chest diseases
(Murray L and Lopes A 1996)
MYTHS
Violent
Aggressive
Irrational
Untreatable
Unreliable
Dependent
Chronic
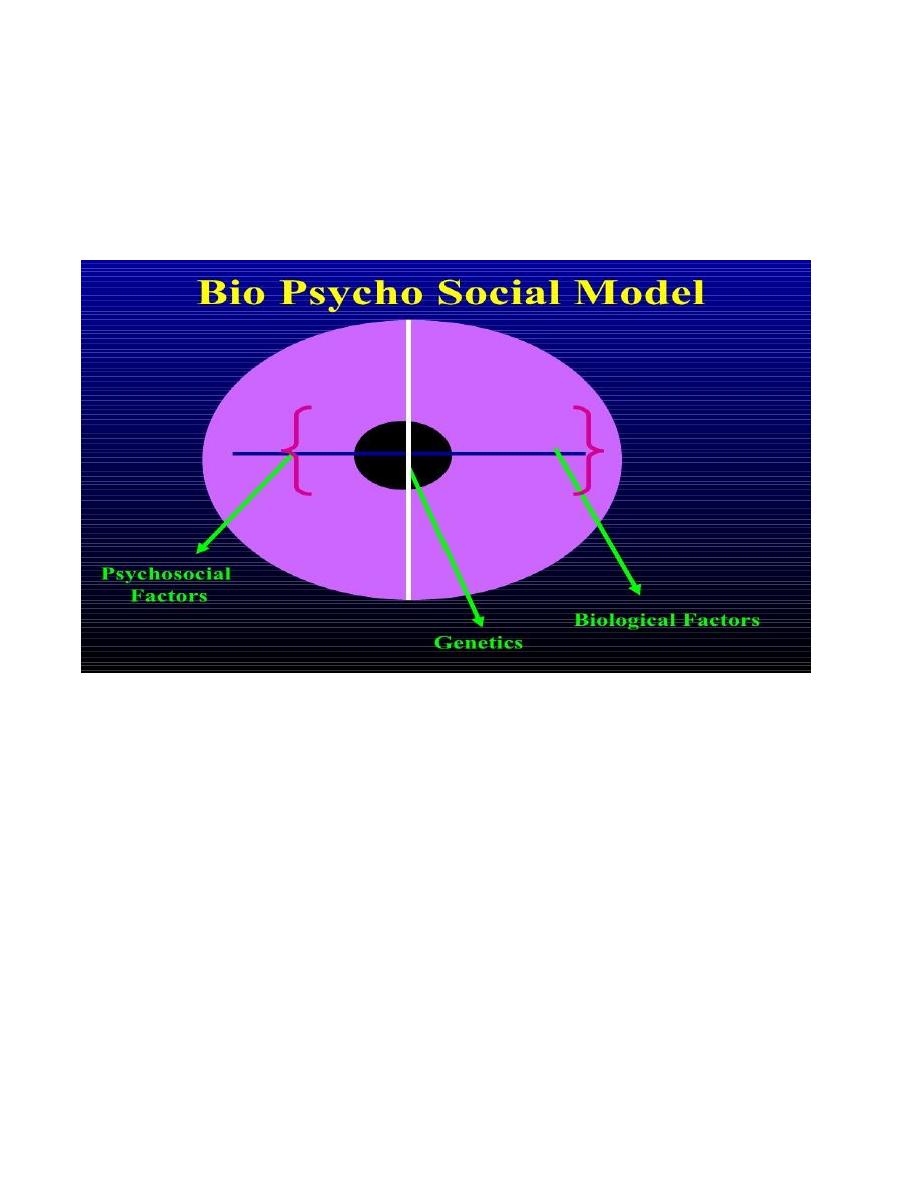
AETIOLOGY
Genetics
Biological Factors
Psychological Factors
Social Factors
GENETIC
Twins Studies
Family Studies
Adoptions Studies
Mode of Inheritance
Molecular Genetics
BIOCHEMICAL
Postmortem Studies
Brain Biochemistry & Imaging
Peripheral Measures

PSYCHOLOGICAL FACTORS
Parental Deprivation
Relationship with Parents
Life Events
Effect of Physical illness
High Express Emotion
SOCIAL FACTORS
Place of Residence
Occupation and Social Class
Culture
Migration
Social Isolation
CLASSIFICATIONS
1. International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10)
2. Diagnostic and Statistical manual (DSM-IV)
ORGANIC MENTAL DISORDERS
Delirium
Dementia
Amnestic Disorders
Personality and Behavioral disorders due to brain disease, damage and dysfunction
PSYCHIATRIC DISORDER
Psychotic Disorders
Non Psychotic Disorders
Personality Disorders

PSYCHIOTIC DISORDERS
Schizophrenia
Drug Induced Psychosis
Schizoaffective
Postnatal Psychosis
MOOD DISORDER
Bipolar Affective Disorder
Major Depression
Post Natal Depression
PERSONALITY DISORDERS
CLUSTER A
Paranoid Schizoid, Schizotypal
CLUSTER B
Antisocial, Border line, histrionic, narcissistic
CLUSTER C
Avoidant, Dependent, Obsessive Compulsive
ANXIETY DISORDERS
Generalized -Anxiety Disorder
Panic Disorder
Phobic Disorders
Obsessive compulsive disorder
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Hypochondrical Disorder

Substance Abuse Disorders
Intoxication
Abuse
Dependence
Withdrawal
Psychotic Disorders
Amnestic Disorders
Mood Disorders
Anxiety Disorders
Sexual dysfunction
Sleep Disorder
CLASSIFICATION OF SUBSTANCE ABUSE DRUGS
Alcohol
Caffeine
Opioids
inhalants
Nicotine
Cannabis
Sedatives / Hypnotics
Multiple drug use
PSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS WITH SOMATIC SYMPTOMS
Stress & Adjustment Disorders
Mood Disorders
Anxiety Disorders
Somatoform Disorder:
Dissociative / Conversion Disorders
Hypochondriacal syndrome
Pain syndrome
SEXUAL DYSFUNCTION
AROUSAL
RESPONSE
MALE
Erectile impotence
Premature ejaculation
Retarded ejaculation
FEMALE
Lubrication failure
Anorgasmia
PSYCHOSEXUAL DISORDER
CHILDHOOD PSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS
- Problems of Preschool Children
- Specific Developmental Disorders
- Pervasive Developmental Disorders
Gender identity Gender role
SEXUAL
PREFERENCE
DRIVE AND
RESPONSEVENESS
RELATIONSHIP
BEHAVIOR

Principal Psychiatric Disorders
• Hyperkinetic Disorders
• Conduct Disorders
• Juvenile Delinquency
• Anxiety Disorders
• Somatization Disorders
• Depressive Disorders
• School Refusal
• Functional Enuresis
• Stammering
• Schizophrenia
• Gender Identity Disorders
• Abuse
- Physical
- Sexual
- Emotional
SPECIFIC DEVELOPMENTAL DISORDER
• Specific Reading Disorder
• Mathematical Learning Disorders
• Communication Disorders
TYPES OF MENTAL RETARDATION
- Mild (IQ 50-70)
- Moderate (IQ 35-49)
- Severe (IQ 20-34)
- Profound (IQ below 20)

PSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS AMONG THE MENTAL RETARD
Schizophrenia
Mood Disorders
Emotional Disorders
Eating Disorders
Personality Disorders
Cognitive Psychiatric Disorders
Behavioral disorders.
EFFECTS OF MENTAL RETARDATION ON THE FAMILY
- Initially Shock
- Depression
- Guilt
- Sham
- Anger
- Inability to cope with practical and financial problems
