
Fifth stage
Psychiatry
Lec-13
د.الهام
الجماس
17/12/2016
Neuroleptics
Antipsychotics used to treat schizophrenia.
Schizophrenia is a severe chronic disorder
Positive symptoms: hallucinations, and delusions
Negative symptoms: amotivation, poverty of speech, flat affect
Disorganized symptoms: speech, thought, and behavior
Now being used to treat Bipolar as well
Antipsychotics
Indications for use:
schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder, bipolar disorder- for mood
stabilization and/or when psychotic features are present, delirium,
psychotic depression,
dementia,
trichotillomania, augmenting agent in treatment resistant anxiety
disorders.
Pathways affected by DA in the Brain
مكتب الجامعه للطباعه
واالستنساخ
عدد االوراق
7
السعر
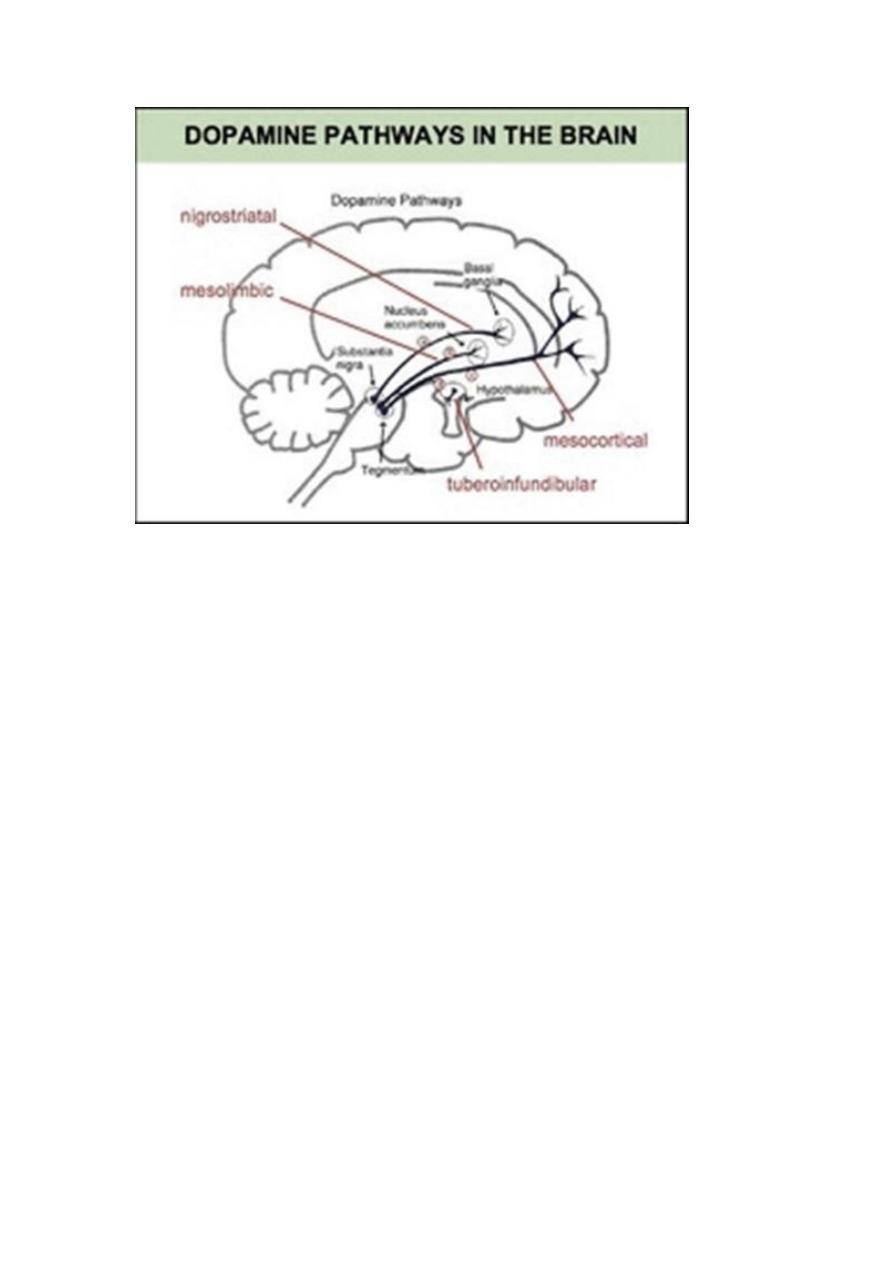
Antagonize dopamine – block a specific receptor
The Atypical Antipsychotics
- atypical agents are serotonin-dopamine 2 antagonists (SDAs)
They are considered atypical in the way they affect dopamine and
serotonin neurotransmission in the four key dopamine pathways in the
brain.
Typical
Chlorpromazine
Trifluperazine Thorazine
Haloperidol – (Haldol)
Atypical
Risperdal - Risperidone
Olanzepine - Zyprexia
Quetiapine - Seroquel
Ziprasidone – Geodon
Aripiprazole – Abilify
Paliperidone – Invega
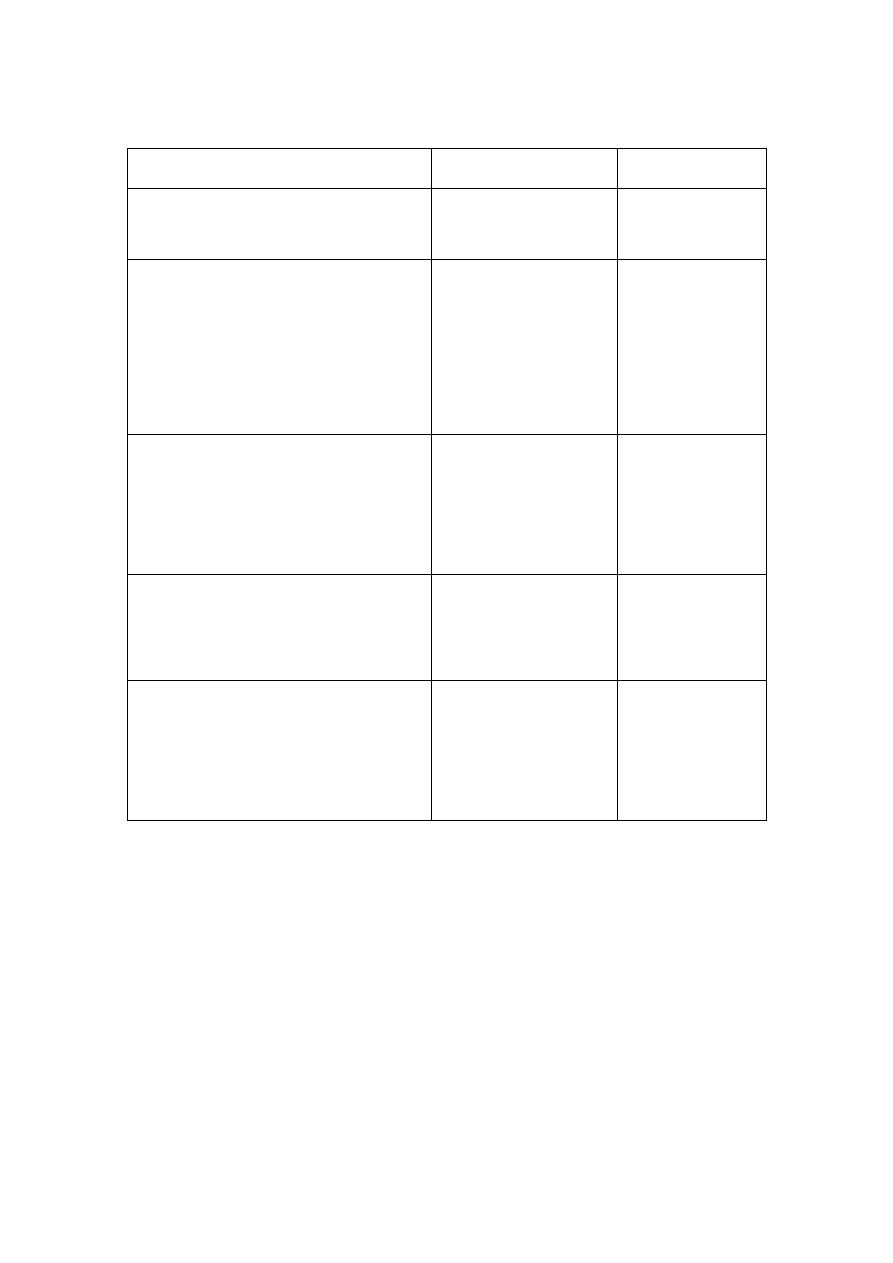
Antipsychotics drugs (typical)
Group
drug
Usual dose
Phenothiazines
chlorpromazine
100-1500mg
daily
Butyrophenones
haloperidol
5-30mg daily
50-100mg IMI
monthly
5mg IMI o
rIVI
on need
Thioxanthenes
flupentixol
40-200mg
fortnight
Short & long
acting
Diphenylbutylpiperidines
Trifluperazine
Pimozide
stelazine
4-30mg daily
1,5,10mg
orally
Substituated benzamides
Fluphenazine decanoate
Sulpiride
Modecate
600-1800mg
daily
25 mg IMI
monthly
Neuroleptics
. The traditional or typical neuroleptic drugs (also called conventional or
first-generation antipsychotics) are competitive inhibitors at a variety of
receptors, but their antipsychotic effects reflect competitive blocking of
dopamine receptors. These drugs vary in potency. For example,
chlorpromazine is a low-potency drug, and fluphenazine is a high-
potency agent No one drug is clinically more effective than another.
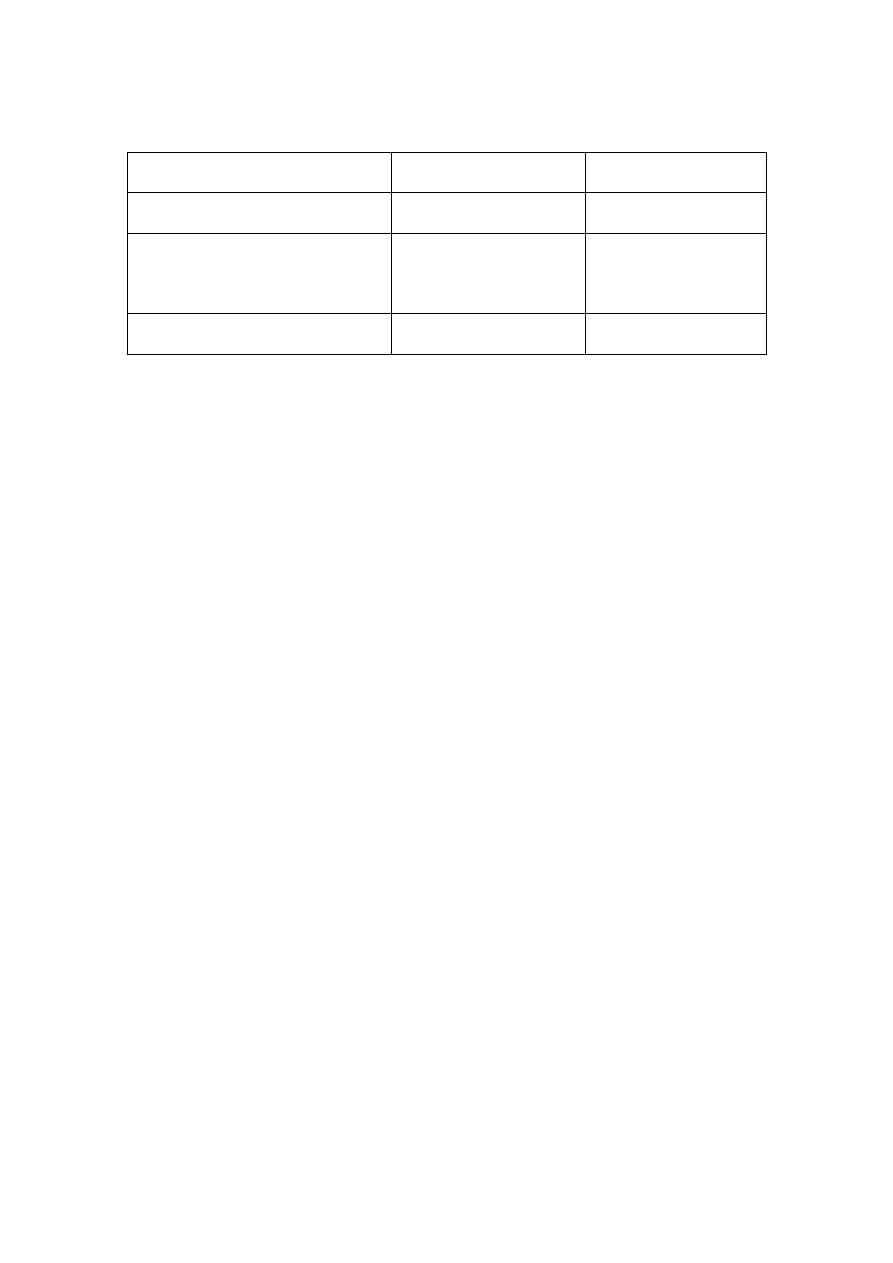
Atypical antipsychotic agent
Group
drugs
Usual dose
Dibenzodiazepine
clozapine
25-900mg daily
Bezisoxazole
Quetiapine -
Risperidone
Seroquel
2-16mg daily
100-200mg/d
Thienobenzodiazepine
olanzapine
5-20mg daily
Atypical
atypical agents are serotonin-dopamine 2 antagonists (SDAs)
They are considered atypical in the way they affect dopamine and
serotonin neurotransmission in the four key dopamine pathways in the
brain.
Mechanism of action
Dopamine receptor blocking activity in the brain:. D
1
and D
5
receptors
activate adenylyl cyclase, often exciting neurons, whereas D
2
, D
3
and D
4
receptors inhibit adenylyl cyclase, or mediate membrane K
+
channel
opening leading to neuronal hyperpolarization. The neuroleptic drugs
bind to these receptors to varying degrees. However, the clinical
efficacy of the typical neuroleptic drugs correlates closely with their
relative ability to block D
2
receptors in the mesolimbic system of the
brain. atypical drug clozapine has higher affinity for the D
4
receptor and
lower affinity for the D
2
receptor, which may partially explain its
minimal ability to cause extrapyramidal side effects (EPS).
Serotonin receptor blocking activity in the brain: Most of the newer
atypical agents appear to exert part of their unique action through
inhibition of serotonin receptors (5-HT), particularly 5-HT
2A
receptors.
(clozapine ,olanzapine,aripiprazole , Quetiapine ).
The undesirable side effects of these agents, however, are often a
result of actions at these other receptors:

Antipsychotic actions: All of the neuroleptic drugs can reduce the
hallucinations and delusions associated with schizophrenia
by blocking dopamine receptors in the mesolimbic system of the brain.
The antipsychotic effects usually take several days to weeks to occur,
suggesting that the therapeutic effects are related to secondary changes
in the corticostriatal pathways.
Extrapyramidal effects: Dystonias (sustained contraction of muscles
leading to twisting distorted postures), parkinson-like symptoms,
akathisia (motor restlessness), and tardive dyskinesia (involuntary
movements of the tongue, lips, neck, trunk, and limbs) occur with
chronic treatment. Blocking of dopamine receptors in the nigrostriatal
pathway probably causes these unwanted movement symptoms. The
atypical neuroleptics exhibit a lower incidence of these symptoms.
Antiemetic effects: With the exceptions of aripiprazole and thioridazine ,
most of the neuroleptic drugs have antiemetic effects that are mediated
by blocking D
2
-dopaminergic receptors of the chemoreceptor trigger
zone of the medulla.
Antimuscarinic effects: Some of the neuroleptics, particularly
thioridazine, chlorpromazine, clozapine, and olanzapine ,produce
anticholinergic effects, including
blurred vision dry mouth (exception: clozapine increase salivation),
confusion, and inhibition of gastrointestinal and urinary tract smooth
muscle, leading to constipation and urinary retention. This
anticholinergic property may actually assist in reducing the risk of EPS
with these agents.
Important side effects to be considered when choosing
antipsychotic drugs
1-Extrapyramidial side effects:
Atypical antipsychotic has less extrapyramidal effect.
2-hyperprolactinaemia: Lead to menstrual disturbances,increased risk
of malignancy,increased galactorrhea,& increased osteoporosis.
Prolactine sparingis aripiprazole
3-sedation Increased sedation with high affinity to histamine&
muscarinic receptors
CPZ,olanzapine,clozapine
Helpful in acute state
4-weight gain:
Histamine & 5HT R block
(>olanzapine)less with resperidone,amisulpride,&aripipraz 5.Type 11
DM
>clozapine &olanzapine
Should be monitored by Bd sugar,lipid profile& weight.
6-CV& 6erebrovascular events ,
through their effect on the lipid profile ,Wt,& insulin
resistance. Some produce prolonge QT interval.
Olanzapine& resperidone
7-postural hypotension
8-sexual dysfunction
9-photosensitivity
10-agranulocytosis
11-constipation
12-reduction of fit threshold
Other effects: Blockade of -adrenergic receptors causes orthostatic
hypotension and light-headedness. The neuroleptics also alter
temperature-regulating mechanisms and can produce poikilothermia
(body temperature varies with the environment). In the pituitary,
Photosensitivity

neuroleptics block D
2
receptors, leading to an increase in prolactin
release. Atypical neuroleptics are less likely to produce prolactin
elevations. Sedation occurs with those drugs that are potent antagonists
of the H
1
-histamine receptor, including chlorpromazine, olanzapine,
quetiapine, and clozapine. Sexual dysfunction may also occur with the
antipsychotics due to various receptor-binding characteristics.
Therapeutic uses
Treatment of schizophrenia:
The neuroleptics are considered to be the only efficacious treatment for
schizophrenia.
Prevention of severe nausea and vomiting: The older neuroleptics
(most commonly prochlorperazine) are useful in the treatment of
drug-induced nausea
Other uses: The neuroleptic drugs can be used as tranquilizers to
manage agitated and disruptive behavior secondary to other
disorders.
Neuroleptics are used in combination with narcotic analgesics for
treatment of chronic pain with severe anxiety
Chlorpromazine is used to treat intractable hiccups.
Promethazine, this agent is used in treating pruritus .
Pimozide is primarily indicated for treatment of the motor and
phonic tics of Tourette's disorder. risperidone and haloperidol are
also commonly prescribed for this tic disorder.
Also, risperidone is now approved for the management of
disruptive behavior and irritability secondary to autism

Antipsychotic adverse effect
Tardive Dyskinesia (TD)-involuntary muscle movements that may
not resolve with drug discontinuation- risk approx. 5% per year
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS): Characterized by severe
muscle rigidity, fever, altered mental status, autonomic instability,
elevated WBC, CPK and lfts. Potentially fatal.
Extrapyramidal side effects (EPS): Acute dystonia, Parkinson
syndrome, Akathisia
Parkinson-like symptoms of bradykinesia, rigidity, and tremor
usually occur within weeks to months of initiating treatment.
Clozapine can produce bone marrow suppression, seizures, and
cardiovascular side effects. The risk of severe agranulocytosis
necessitates frequent monitoring of white-blood-cell counts
The neuroleptics depress the hypothalamus, affecting
thermoregulation, and causing amenorrhea, galactorrhea,
gynecomastia, infertility, and impotence. Significant weight gain is
often a reason for noncompliance. It is also recommended that
glucose and lipid profiles be monitored in patients taking
antipsychotics
The choice of medication &dose :depend on
1-sevirety of the problems.
2-degree of sedation required.
3-side effect profile.
4-preferance of individual clinician.

Study Questions
Choose the ONE best answer.
13.1 An adolescent male is newly diagnosed with schizophrenia. Which
of the following neuroleptic agents may improve his apathy and blunted
affect?
A. Chlorpromazine.
B. Fluphenazine.
C. Haloperidol.
D. Risperidone.
E. Thioridazine
Correct answer = D. Risperidone is the only neuroleptic on the list that
has some benefit in improving the negative symptoms of
schizophrenia. All the agents have the potential to diminish the
hallucinations and delusional thought processes.
Which one of the following neuroleptics has been shown to be a partial
agonist at the D
2
receptor?
A. Aripiprazole.
B. Clozapine.
C. Haloperidol.
D. Risperidone.
E. Thioridazine.
Correct answer = A. Aripiprazole is the agent that acts as a partial
agonist at D
2
receptors. Theoretically, the drug would enhance action
at these receptors when there is a low concentration of dopamine and
would block the actions of high concentrations of dopamine. All the
other drugs are only antagonistic at D
2
receptors, with haloperidol
being particularly potent.

A 21-year-old male has recently begun pimozide therapy for Tourette's
disorder. He is brought to the emergency department by his parents.
They describe that he has been having “different-appearing tics―
than before, such as prolonged contraction of the facial muscles. While
being examined, he experiences opisthotonus (spasm of the body where
the head and heels are bent backward and the body is bowed forward. A
type of extrapyramidal effect). Which of the following drugs would be
beneficial in reducing these symptoms?
A. Benztropine.
B. Bromocriptine.
C. Lithium.
D. Prochlorperazine.
E. Risperidone
Correct answer = A. The patient is experiencing extrapyramidal
symptoms due to pimozide, and a muscarinic antagonist such as
benztropine would be effective in reducing the symptoms. The other
drugs would have no effect or, in the case of prochlorperazine, might
increase the symptoms.
A 28-year-old woman with schizoid affective disorder and difficulty
sleeping would be most benefited by which of the following drugs?
A. Aripiprazole.
B. Chlorpromazine.
C. Haloperidol.
D. Risperidone.
E. Ziprasidone.
Correct answer = B. Chlorpromazine has significant sedative activity as
well as antipsychotic properties. Of the choices, it is the drug most
likely to alleviate this patient's major complaints, including her
insomnia

Anxiolytic
Treat anxiety disorders
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Panic Disorder
PTSD
OCD
Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD)
Used to treat many diagnoses including panic disorder,
generalized Anxiety disorder,
substance-related disorders and their withdrawal,
insomnias and parasomnias.
In anxiety disorders often use anxiolytics in combination with SSRIS or
SNRIs for treatment.
Benzodiazepines
Used to treat insomnia, parasomnias and anxiety disorders.
Often used for CNS depressant
withdrawal protocols ex. ETOH
withdrawal.
Side effects/cons
Somnolence
Cognitive deficits
Amnesia
Disinhibition
Tolerance
Dependence
Monitor for efficacy and
tolerance and adjust as indicated.
If the patient does not improve step back, rethink your diagnosis
and treatment plan!
Keep an eye on drug-drug interactions

Benzodiazepines Facilitate GABA neurotransmission
Bind to a particular site on the GABA receptor
Xanax, Ativan, Valium, Serax, Librium
Beta-Blockers
Antagonize NE by blocking Beta receptor subtype
SSRIs
PTSD, OCD, SAD, and to some degree GAD
Others
Buspar
Non-sedating
Does not interact with alcohol
Not highly effective
ADD
Methylphenidate – Ritalin
DA reuptake inhibitor
So slowly it enters the brain that it is not addictive like cocaine
even though they have the same mechanism
Concerta (Immediate release combined with time release)
Adderal (mixed amphetamine salts)
Has extended release
Modafinil – Provigil
Vyvanse
An amphetamine pro-drug
Less abusable
Straterra

Mixing Med
.
Although classified as a certain type of drug most psych meds used for
many different disorders.
Antipsychotics in Bipolar Disorder
Abilify
Zyprexa
Mood stabilizers in alcoholism
Topiramate
Prescribing a medication for a disorder when it is known to work, but
there is no formal FDA indication is called “off-label prescribing”
It’s perfectly legal and quite common
