Lecture two
Cephalometric assessmentCephalometric lines of reference
1. True horizontal:Can be identified when the patient’s head is in the natural postural position, this line is differ from one person to other.
Cephalometric lines of reference
Cephalometric lines of reference2. Frankfort plane:
Po - Or
Cephalometric lines of reference
3. Sella - Nasion plane:S - N
Cephalometric lines of reference
4. De Coster’s line:The floor of the anterior
cranial base, from ethmoid
bone to sella turcica
Cephalometric lines of reference
5. Maxillary line:
ANS - PNS
Cephalometric lines of reference
6. Mandibular plane:Me - Go
Cephalometric lines of reference
7. Occlusal plane:Cusp tips of molars – tip of lower incisor
Cephalometric lines of reference
8. Functional occlusal plane (FOP):
Cusp tip of lower 1st molar –
cusp tip of lower 1st premolar
Cephalometric lines of reference
9. The facial plane:N - Pog
Cephalometric lines of reference
10. Line from point A to pogonion:A - Pog
Antero-posterior skeletal relations
Antero-posterior skeletal relations
SNA angle (82 + 3)
Indicates antero-posterior position of maxillary apical base in relation to the cranial base: Large angle = Prognathic maxilla
Normal angle = Orthognathic maxilla Small angle = Retrognathic maxilla
82
Antero-posterior skeletal relations
SNB angle (79 + 3)Indicates antero-posterior position of mandibular apical base in relation to the cranial base
Large angle = Prognathic mandible
Normal angle = Orthognathic mandible
Small angle = Retrognathic mandible
80
Antero-posterior skeletal relations
ANB angle (3 + 1)Indicates the skeletal relationship between maxilla and mandible:
Large angle = postnormal relation (skeletal class II)
Normal angle = Normal relation
(skeletal class I)
Small angle (reverse) = Prenormal relation (skeletal calss III)
Antero-posterior skeletal relations
A-B / FOP angle (90 + 5):
Indicates the skeletal relationship between maxilla and mandible with reference to FOP :
Large angle = postnormal relation (skeletal class II)
Normal angle = Normal relation
(skeletal class I)
Small angle = Prenormal relation
(skeletal calss III)
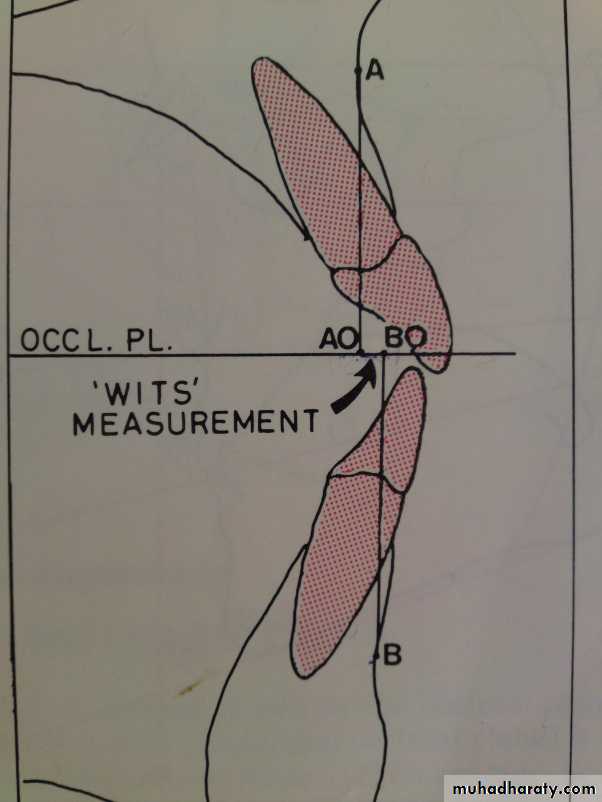
-1 mm
BO anterior to AOSkeletal AssessmentWits (AO-BO)
Antero-posterior skeletal relations
(wits= University of Witwatersrand)Facial angle
87° + 3
Indicate the anteropost
Position of the chin
Antero-posterior skeletal relations
N-S-Gn (Y-Axis) = 66⁰This angle determine the position of the mandible relative to the cranial base
N
S
Gn
Antero-posterior skeletal relations
Vertical skeletal relations
Vertical skeletal relations
MM angle (27 + 5)Large angle = Skeletal open bite
Normal angle = NormalSmall angle = Skeletal deep bite
Vertical skeletal relations
Frankfort-mandibular angle (27 + 5)Large angle = Skeletal open bite
Normal angle = NormalSmall angle = Skeletal deep bite
Vertical skeletal relations
Frankfort-SN angle (6 + 5)32
Vertical Skeletal Assessment
Skeletal Vertical AssessmentNS(SN plane)-GoGn
Dentoskeletal relationsUI / Mx plane angle (108 + 5)
LI / Mn plane angle (90 + 3)
Interincisal angle (133 + 10)LI / A-Pog distance (0 + 2 mm)
UI / Mx plane angle (108 + 5)
Dental Assessment
108
90
Incisor Angulation Assessment
Dental AssessmentL1-GoGn (Man 1 - GoGn)0 mm ± 2
Dental AssessmentAPog - Man 1130