
1
Fifth stage
Pediatric
Lec. 5
د. بسام
7/12/2016
Prematurity
-Prematurity
-Small for gestational age
-Large for gestational age
Premature (preterm) baby
Birth before 37 completed weeks gestation. 8% of all births. Most problems seen in with
infants born <32 completed weeks.
Predisposing factors
1. Idiopathic (40%).
2. Previous preterm birth.
3. Multiple pregnancy.
4. Maternal illness, e.g. chorioamnionitis, polyhydramnios, pre-eclampsia,
5. diabetes mellitus.
6. Premature rupture of membranes.
7. Uterine malformation or cervical incompetence.
8. Placental disease, e.g. dysfunction, antepartum haemorrhage.
9. Poor maternal health or socio-economic status
Complications of prematurity
1. Respiratory: surfactant deficiency causing respiratory distress syndrome, apnoea of
prematurity, chronic lung disease / bronchopulmonary dysplasia.
2. CNS: intraventricular haemorrhage, periventricular leucomalacia; retinopathy of
prematurity.
3. GIT: necrotizing enterocolitis ,inability to suck, and poor milk tolerance.
2
4. Hypothermia.
5. Immuno-compromise: resulting in recurrent infections.
6. Impaired fluid/electrolyte homeostasis: skin water loss, poor renal function.
7. Patent ductus arteriosus.
8. Hypoglycemia.
9. Anaemia of prematurity.
10. Jaundice liver enzyme immaturity.
11. Birth trauma.
12. Perinatal hypoxia.
13. Later: increased risk of adverse neurodevelopmental outcome,
14. behavioral problems and sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS).
Signs of prematurity
1. Thin gelatinous skin and dark red in color .
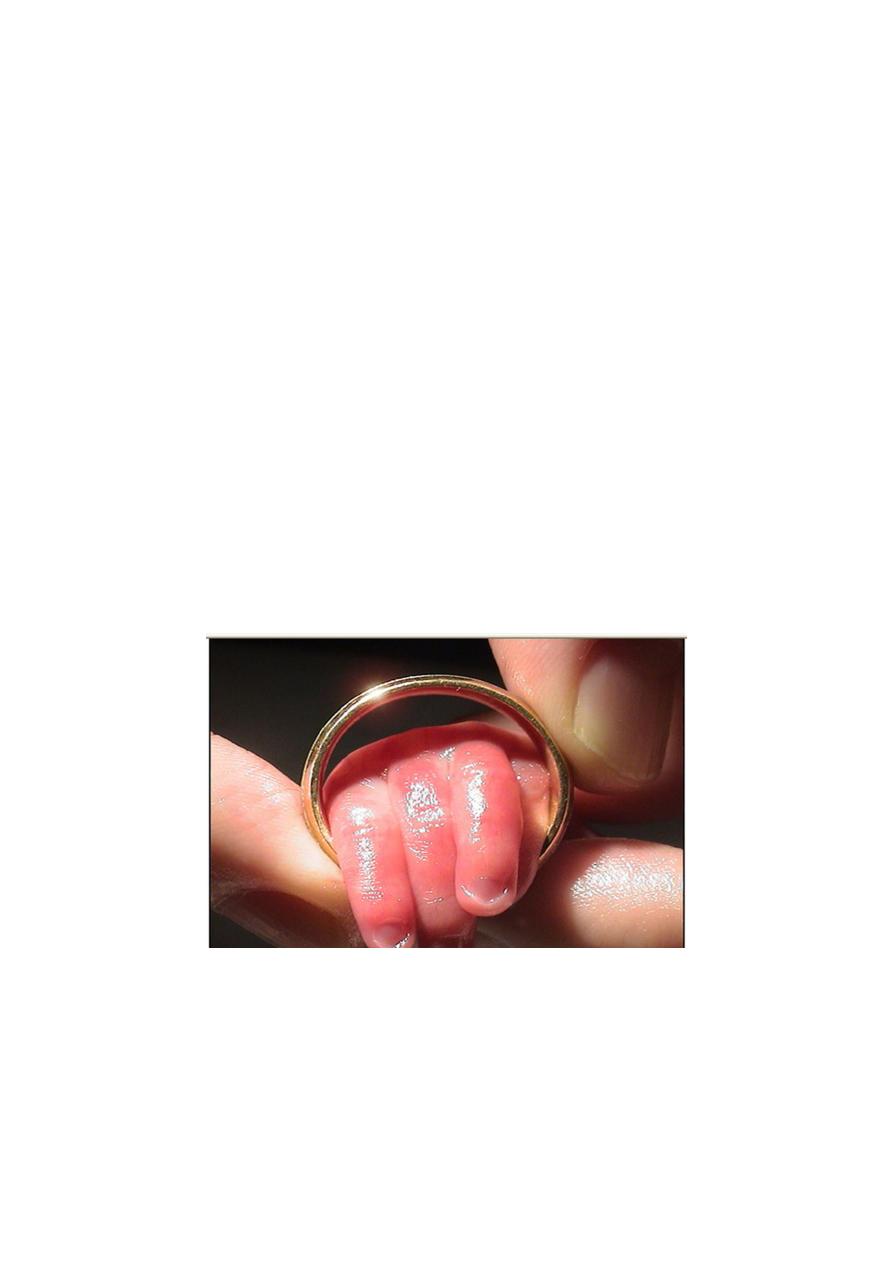
2. Poorly developed breast tissue, no palpable breast tissue or it is flat and less than
1cm in diameter.
3
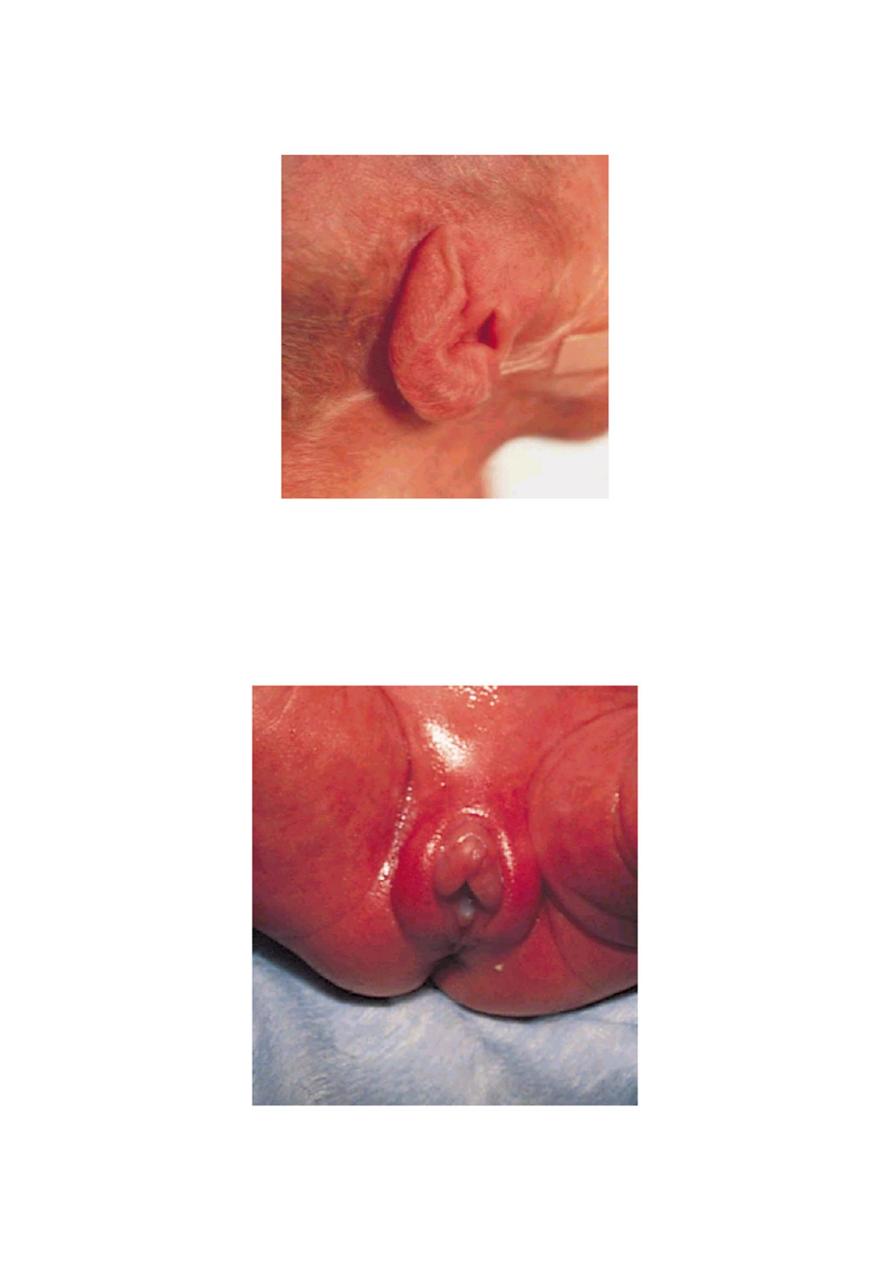
3. The ear auricle is soft, no cartilage and there is slow or no recoil.
4. Genitalia:
male: the testes are not descended in the scrotum and no creases on the scrotum
Female: labia majora are not covering completely labia minora .
4
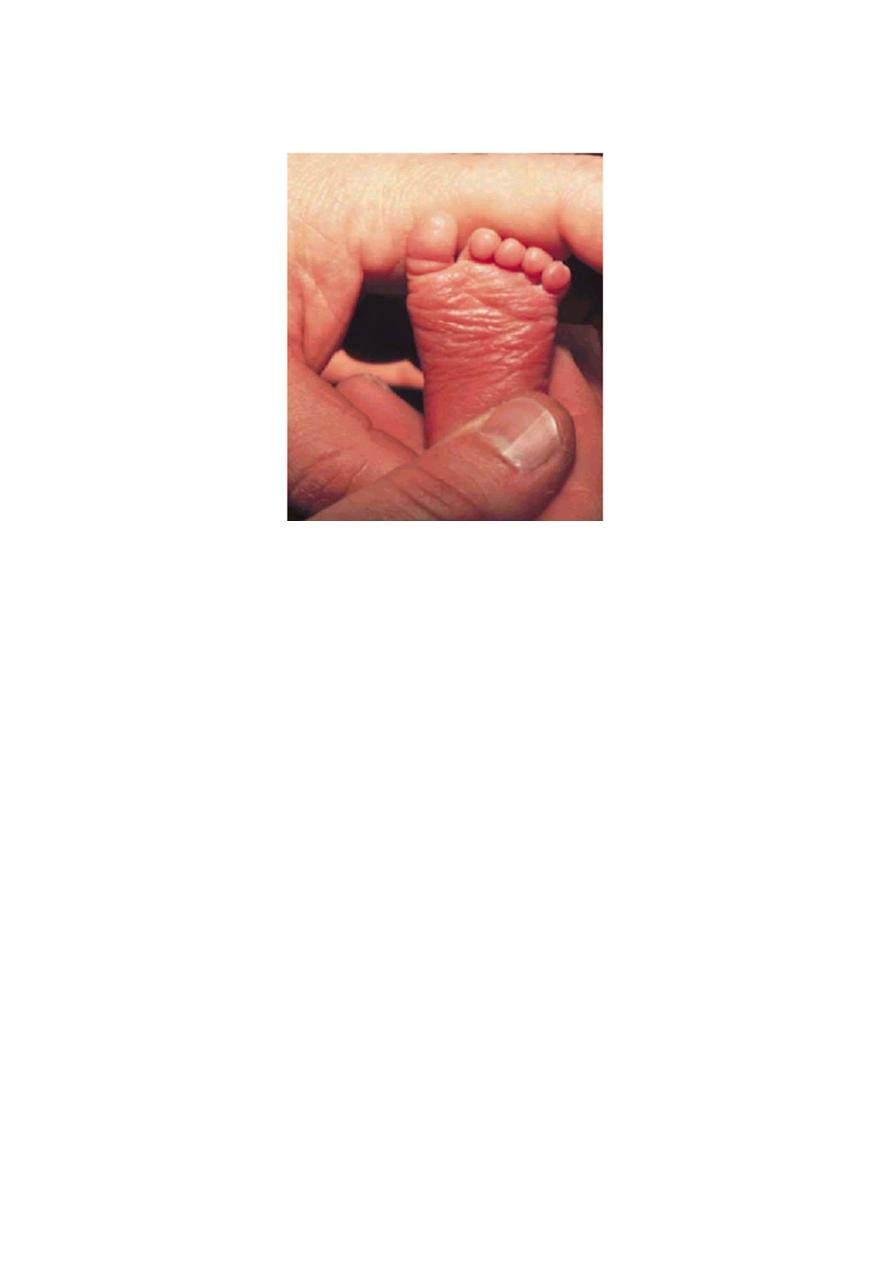
5. Plantar creases are absent or only seen on the anterior 2/3 of the sole:-
Small for gestational age (SGA)
SGA is birth weight < 10th centile for gestational age.
Causes
1. Constitutional: small parents (commonest).
2. Restricted fetal oxygen or glucose supply, e.g. placental dysfunction, maternal
hypertension, multiple pregnancy, maternal illness.
3. Fetal abnormality as chromosomal disorders, congenital anomalies and syndromes,
congenital infection.
4. Maternal substance exposure, e.g. alcohol, smoking, therapeutic or other drugs
Complications
1. Hypoglycaemia
2. Hypothermia
3. Polycythaemia
4. Necrotizing enterocolitis and/or intolerance of feeds .
5. Thrombocytopenia/neutropenia/coagulopathy .
6. Meconium aspiration syndrome.

5
Large for Gestational Age (LGA) :
Defined as birth weight > 90th centile for gestational age .
Causes
1. Most frequently constitutional, large parents .
2. Infant of diabetic mother .
3. Foetal hyperinsulinism, pancreatic islet cell hyperplasia .
4. Hydrops foetalis .
5. Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome .
Complication :
1. Perinatal asphyxia, nerve palsies, shoulder dystocia, fractures .
2. Hypoglycaemia, especially if due to maternal diabetes or in BWS .
3. Problems associated with the underlying cause LGA.
