Medical Statistic
What is a statisticA statistic is a field of study concerned with methods of Collectionتجميع ,Organizationتنظيم, Summarizingتلخيص ,
It makes presentation عرض, Classificationوصف, and analyzing تحليل the data. This analysis may lead to conclusions نتائجand decision قرارات .
A statistician(الاحصائي) is someone who is versed متمكنin the successful ways application of statistical analysis.
Medical Statistics
deals with applications of statistics to medicine and the health sciences, includingepidemiology(علم الاوبئة),
public health(الصحة العامة),
forensic medicine(الطب العدلي),
clinical research(البحوث السريرية) .
Types of Statistics Science: statistic may be: (i) Descriptive ; (ii) Inferential
When we first collect data for some project, it will usually be in a ‘rawخام ’ form . That is, not organized غير منظمهin any way, making it difficult to see what’s going on. Descriptive statistics is a series of procedures designed to illuminateالقاء الضوء the data, This may mean sorting the data by size; perhaps putting it into a table, maybe presenting it in an appropriate chart, or summarizing it numerically; and so on.An important consideration in this process is the type of variable concerned. The data from some variables are best described with a table, some with a chart, some, perhaps, with both. Other variables, a numeric summary is more appropriate.
When we want to discoverاكتشاف things that interest us about a population, we take a sample. We then hope to generalize our sample findings, Statisticians call this process, of generalizing from a sample to a population, statistical inference .
It is include two main parts:
Estimation التقدير
Test of Hypothesis اختبار الفرضيات
Population & Sample
Population: This is a much larger group that containing all the values & observations about which we wish to make inference.Sample: This is a part of population generally selected so as to be representative of the population in the variable(s) under study.
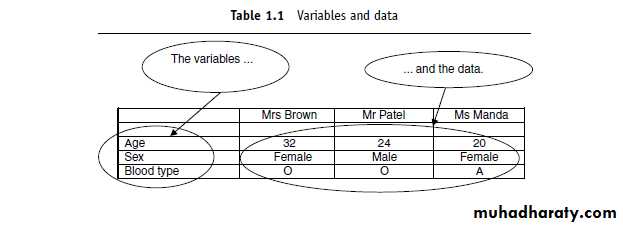
Variables and data
A variable is something whose value can vary. For example, age, sex and blood type are variables.Data are the values you get when you measure a variable. For example, 32 years(for the variable age), or female (for the variable sex).
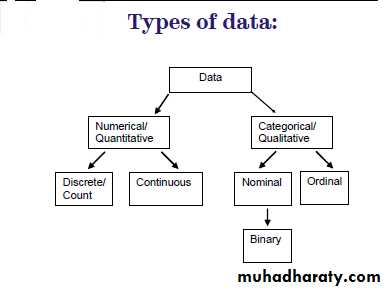
Types of Data
Categorical (Qualitative)Nominal (no natural ordering)
Blood groups: A,B,O,AB, Sex :m/f
Ordered categorical (ordinal)
Pain severity - mild, moderate, severe
Grade of breast cancer, Social Class: I to V
Numerical (Quantitative)
Discrete
Number of children in a family, Number of attacks of asthma نوبات الربوper week
Continuous
Age (in years, days, hours, seconds….)
Height in cm , Weight in kg
Statistical Notations
The information in statistic may be a number of variables (say X, Y, Z…etc.) and each variable is a number observation (say Xi, Yi, Zi… etc.), then:Rules of the Summation:
∑c = n.c (c is a constant)
∑(c yi) = c ∑yi
∑(xi±yi) = ∑xi±∑yi
∑ (xi± c) = ∑xi±n.c
∑(xi)2 ≠(∑xi)2
∑(xi / yi) ≠∑xi / ∑yi
∑(xiyi) ≠∑xi ∑yi
Example:
Calculate 1to 7 above if:
C=6 , Xi: 3, 5, 1 , Yi: 4, 2, 10