Dr. Hicham Nuaimi
BDS, PGDip in RestorativePGDip in Implantology
Mclin in Operative and Esthetic
Pulp protection
Outlines
Pulpal IrritantsEffect of Dental Caries on Pulp
Effect of Tooth Preparation on Pulp
Effect of Chemical Irritants on Pulp
Pulp Protection Procedures
Materials Used for Pulp Protection
Methods of Pulp Protection Under Different Restorations
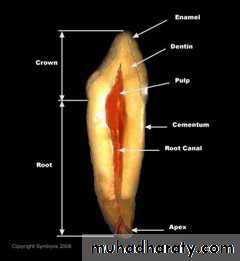
What is the PULP???
is a soft tissue of mesenchymal origin in both Crown (pulp chamber )and Roots (root canals) of teeth
It compose of:
Nerves.
Vessels.
Lymph channels.
PULPAL IRRITANTS
Bacterial irritantsTraumatic
Iatrogenic:
Bacterial irritants:
cause for pulpal irritation by their products :Caries
pathological exposure
Extension of infection from gingival sulcus
Periodontal pocket and abscess
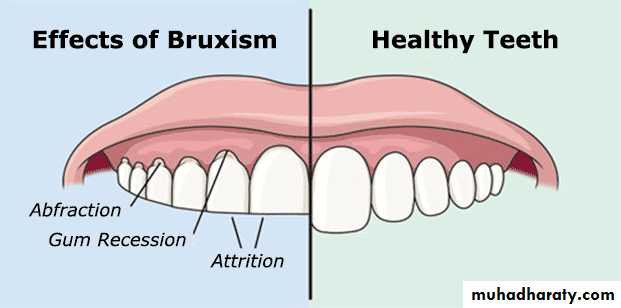
Traumatic
Acute trauma like fracture, luxation or avulsion of Pulp Protection toothChronic trauma including Para-functional habits like bruxism.
Iatrogenic:
Thermal changes generated by :cutting procedures.
bleaching of enamel.
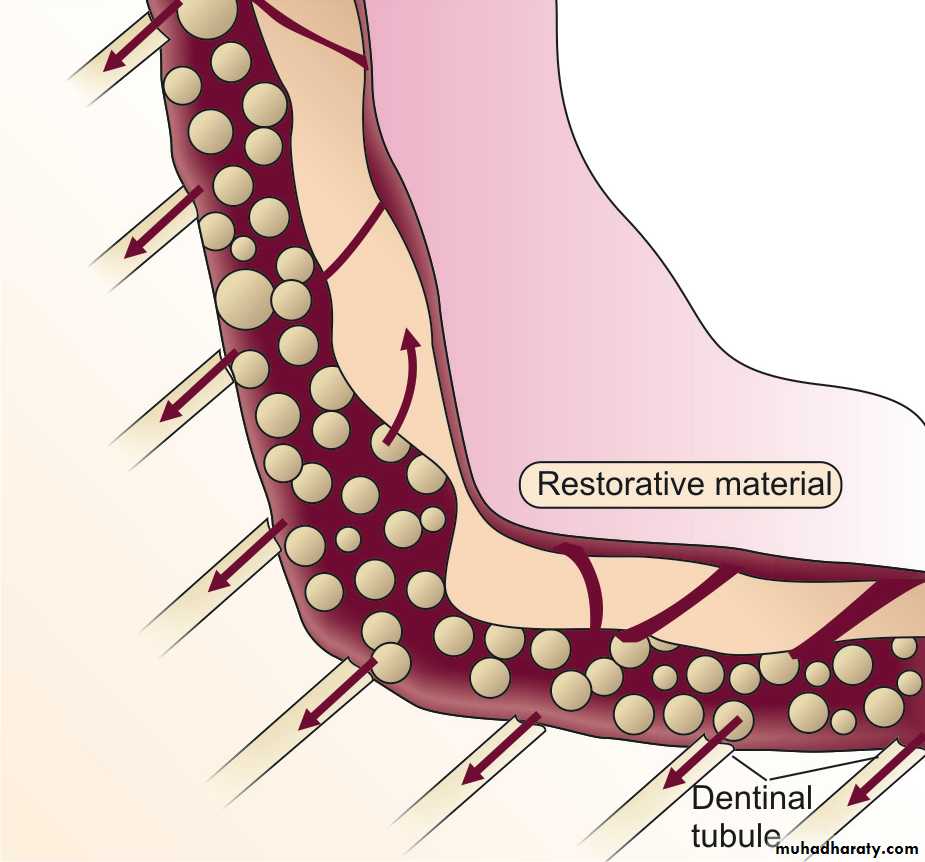
Micro-leakage occurring along the restorations.
Electrosurgical procedures.
Orthodontic Treatment.
Periodontal Curettage.
Periapical Curettage.
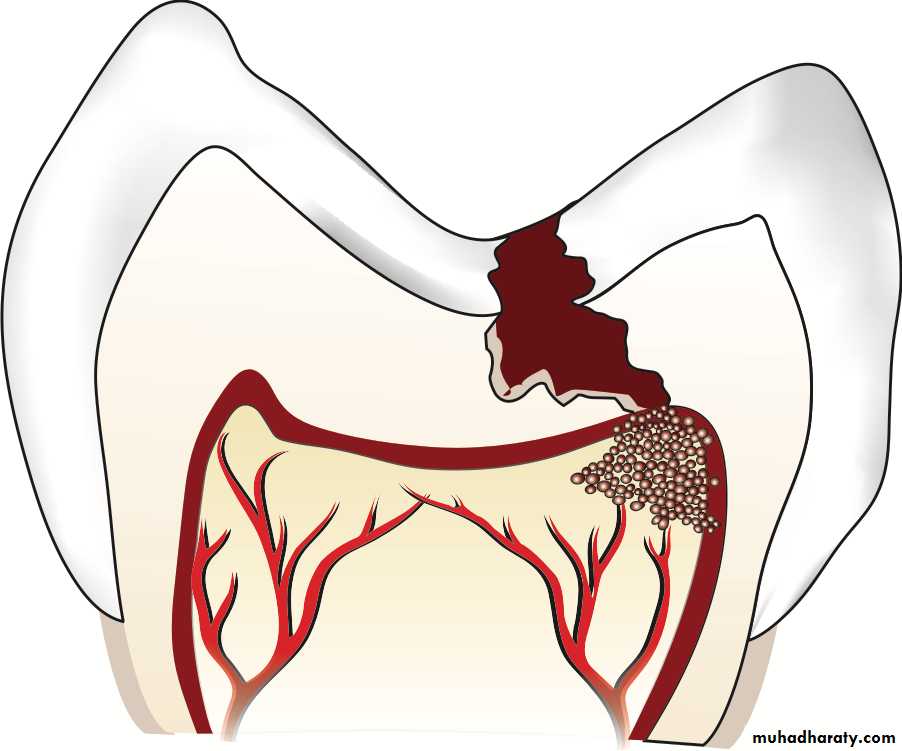
EFFECT OF DENTAL CARIES ON PULP
Caused by demineralization of the tooth surface by:
organic acids >>> produced by Bacteria.
• acids and other toxic substances
• penetrate through the
• dentinal tubules to reach the pulp.
Reparative dentin formation is related to rate of carious attack.
Acute Caries < Chronic CariesDentin Sclerosis presents in vital odontoblasts to obstacle partially or fully tubules>>> reduce the permeability of dentin.
Be as barrier for the ingress of bacteria and their product
EFFECT OF TOOTH PREPARATION ON PULP
PressureHeat
Vibration
Remaining dentin thickness
Pressure
During instrumentation on exposed dentin causes the aspiration of the nuclei of the odontoblasts or the odontoblasts themselves in the dentinal tubules.
This will disturb their metabolism and may lead to degeneration.
excessive pressure by hand than for rotary instruments
Deep cavities have more pressure effect than shallow.
Heat Production
Destructive of pulp occur when temperature is elevated by 11°C.more the RPM more is the heat production specially with minimum coolants
during preparation in deep cavity must pressure decrease to decrease heat generation
in vital dentin, desiccation can cause aspiration of the odontoblasts into the tubules.
Coolant sprays should be used even in nonvital or devitalized tooth structures, since the heat may burn the tooth structures.
Vibrations
Vibrations are an indication of eccentricity in rotary instruments.Higher the amplitude, more destructive is the pulp response.
Create micro-cracks in enamel and dentin.Remaining Dentin Thickness RDT
Is distance between the floor of the tooth preparation and the pulp
dentin is approximately 3 mm thick
Dentin permeability > with < RDT
RDT =<2 mm effectively precludes restorative damage to the pulp
effects of bacterial invasion at 0.75mm RDT
Pulp Protection in Shallow and Moderate Carious Lesions
caries penetrates the enamel and involve one half of the dentin, but not to the extent of endangering the pulp.To protect the pulp, use liner to cover the axial or pulpal wall.
Then, base material ( ZOE, GIC) is placed over the liner.
Finally permanent restoration is placed
Pulp Protection in Deep Carious Lesions
Caries reaches very close to the pulp.so requires precautions because of postoperative pulpal response.
If hard dentin is present >> give protective cement base and complete the permanent restoration as a moderate lesion.
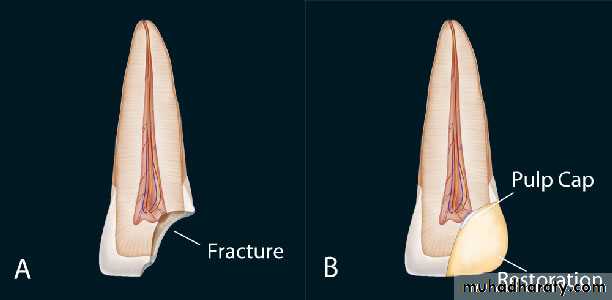
If a small mechanical exposure of pulp occurs during tooth preparation.
an appropriate protective base should be placed to maintain the vitality of the remaining pulp tissue.Materials that are used in PC
Insulate the pulp.Protect the pulp in case of deep carious lesion
Act as barriers to micro-leakage
Prevent bacteria and toxins from affecting the pulp.
Examples are (varnish, sealer, liner and base)