Glass sporozoa
Genus plasmodiumThere are 4 species of plasmodium responsible for human malaria
P.vivax-benign tertian malaria.P.malariae-quartan malaria.
P.falciparum-malignant tertian or sub tertian malaria.
P. ovale-tertian or benign tertian malaria
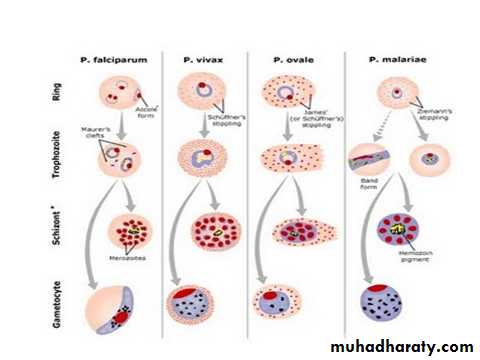
Morphology
The earliest form after the invasion of the R.B.C by the malarial parasite. is the trophozoite stage.
The early trophozoite form rings usually with a single nucleus .As the troph.grows It will metabolize the haemoglobin of the R.B.C. and produce a darkly staining malarial pigment-hemozoin.
The nucleus of the trophozoite divides and it is now called immature schizont then each nuclear division surrounded by piece of cytoplasm forming mature schizont.Merozoits form&ruptures RBCs,then it infect other RBCs.
Some merozoites develops into gametocytes or sexual stage which have compact cytoplasm and no nuclear division.
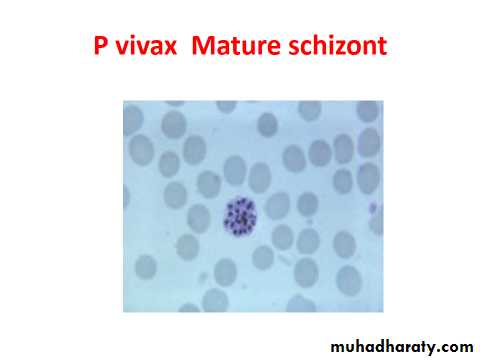
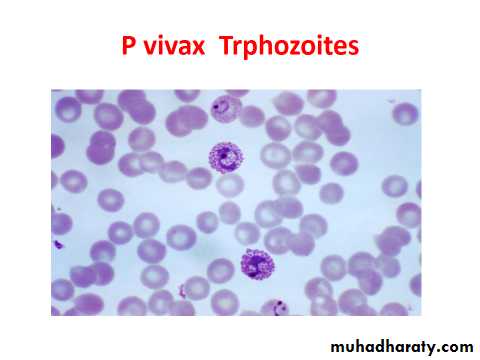
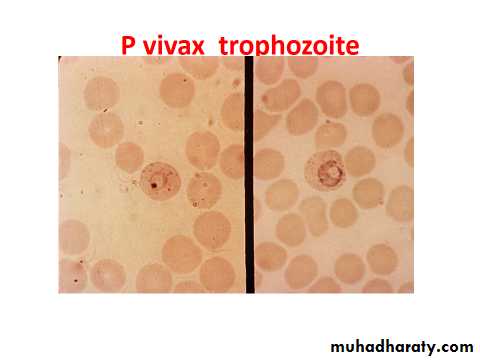
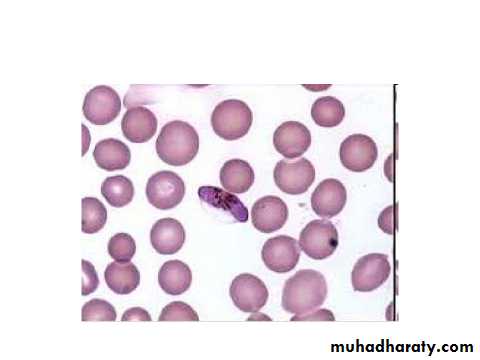
P. vivax
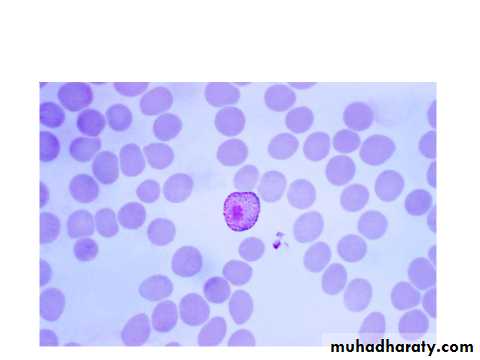
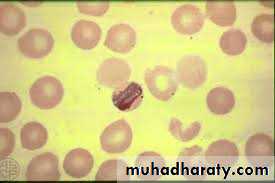
The infected R.B.C. is enlarged because the parasite invade the reticulocytes –immature R.B.C. which is larger than other R.B.C. as the trophozoite grows, it form ring stage then the cytoplasm become irregular in shape with amaeboid extention forming amaeboid stage .Fine pink or reddish granules appear all over the infected R.B.C. these are schuffners dotes-believe to be an allergic reaction from the host to the presence of the parasite.Malarial pigment in the cytoplasm of the parasite is fine light brown in colour
In immature schizointes nucleus start division then.
The schizont matures in about 48 hrs. after the invasion of the R.B.C. and becomes segmented into12- 16 merozoites .Gametocytes are round and nearly filling the R.B.C. all these stages are seen in the peripheral blood.
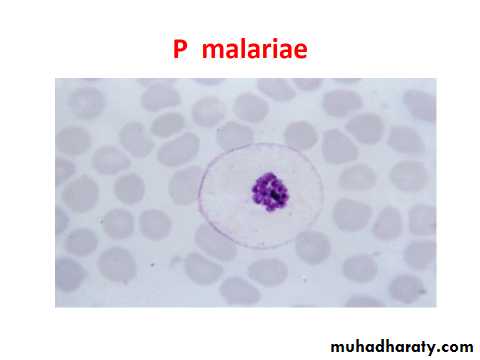
P.malariae
The infected R.B.C. is not enlarged because the parasite invade the old or mature R.B.C. ring are smaller than those of vivax and more compact, no schuffners dotes malarial pigments are coarse dark brown or black, trophozoite assume band shape across the infected R.B.C.mature schizont need 72 hrs.to develops contain 6-10 merozoits mostly 8 in No. which may be arranged in a rosette form with merozoits at the periphery and dark malarial pigments at the center,gametocytes are round, all these stages are seen in peripheral Bl.
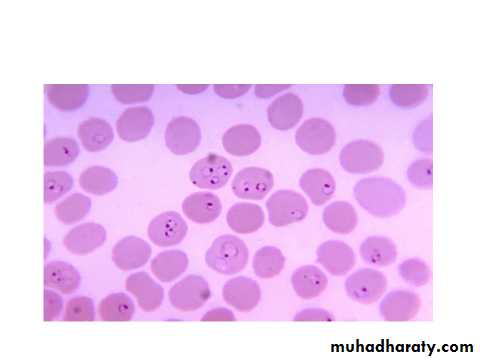
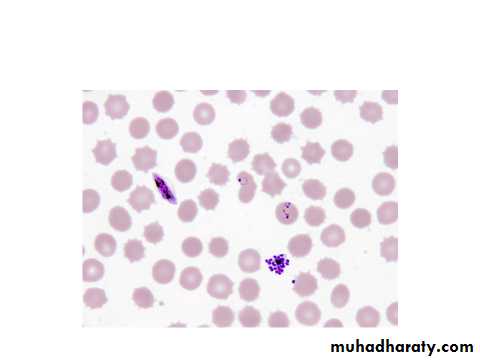
P.falciparum
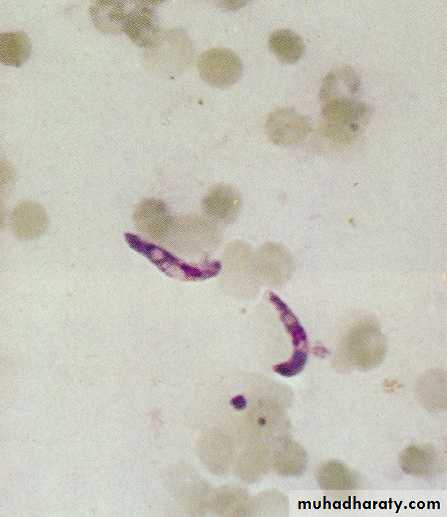
The parasites infect all ages of R.B.C.rings are small,multiple infection in one R.B.C.is common,ring may have double chromatin dots-2 N- Schizonts are rarly seen at the peripheral Bl. Except in sever infection with high parasitemia, schizogony take place in the capillaries of muscles and viscera,mature schizont has 8-32 merozoit .gametocytes are cresent in shape, only ring and gametocytes are ordinarily seen in the peripheral Bl.P. ovle
Commonly seen in west Africa.The infected R.B.C.is slightly enlarged and oval in shape and show schuffners dots,it has irregular or fimbriated appearace of the edges of the infected R.B.C. mature schiz.cotains 8 meroz.malarial pigments is coarse and brown.
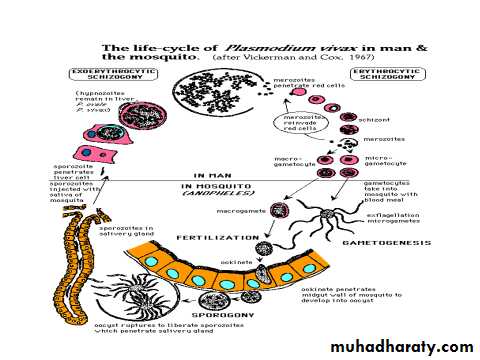
Life cycle
Vertebrate host-asexual cycle-schizogony.
Invertebrate host-sexual cycle-sporogony
Human infection result from the bite of an infected female anophyline mosquito in which sporozoites are injected into the human Bl. Stream during feeding Within 30 min.sporozoites move rapidly to the liver, invade hepatocytes and undergo exoerythrocytic development 8-15 days depend on the species leading to the formation of liver schizots.Rupture of each liver schizont releases thousands of meroz.into the peripheral Bl.where they invade the R.B.C.&the erythrocytic stages started.forming the erythrocytic cycle.
In P. vivax and P . ovale some parasites remain dormant in the liver cells as hepatic sch. which are later released as merozoites.such parasites persisting in the liver cells and called hypnozoites which responsible for late relapses.
In P.falciparum and P.malariae true relapse does not occur and hepatic sch.survive only a short time.
There is no return of merozoit from R.B.C.to the liver cells.
In the infected R.B.C.the early trophozoits form –ring stage-develop into late troph.with an enlarged cytoplasm and accumulation of hemozoin pigment. Mature sch .ruptures releasing meroz.There are reinvasion of R.B.C.by meroz.and repeat the schizogony cycle
Some meroz.that invades R.B.C.does not go into schizogony but goes into gametogony cycle forming male and female gametocytes.
Without treatment,falciparum infection ordinarly will terminate spontaneously in less than than 1 year unless it ends fatally.In P.vivax and P.Ovale some parasite will stay in the liver cells after the initial Bl.stream invasion,these are known as hypnozoites which later will develop into mature liver schiz.then invade the R.B.C.later causing parasitemia and relapse after original infection.
Relapses in P.vivax is up to 3-4 years.
Relapses in P.ovale is up to 4-5 years.
Sporogony
Is the sexual stage take place in the mosquito, the gametocytes ingested with the Bl. Meal of the mosquito not digested, they are;Male microgametocyte-its chromatin dots [nucleus] divided into 6-8 divisions that migrate to the periphery with cytoplasmic projections forming whip like actively motile filaments [microgamets] detached from the parent cell, this process called exflagellation which lasts 10-20 min. occur in the stomach of mosquito.
Female macrogametocyte become mature into macrogamete its nucleus shift to the periphery .
Fertilization occurs in the stomach of mosq. Results in the formation of zygote, which will change into worm like body after 12-24 h.of the Bl. Meal and now it is called ookinete which penetrates the wall of the gut and develops into oocyst between the epithelium and the basement membrane. Oocyst increase in size become rounded, projects into the body cavity of the mosq. And will develop thousands of sporpzoites inside it.after rupture of the oocyst,sporozoites are librated into the body cavity and migrate to the salivary gland.the cycle in the mosq. Lasts 10-17 days,when mosq.feeds sporoz.are injected to the host T.
stages of different malaria species(erythrocytic cycle)
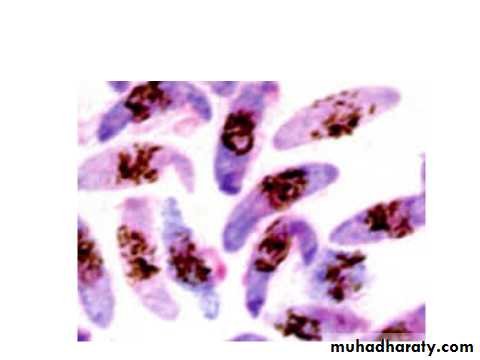
P.falciparum ring,gametocyte&mature schizote.
Thick blood film showing susage shape gametocyte of P. falciparum.
Thin blood of P.vivax showing gametocyte notice enlarged RBC.the gamete is rounded with compact Nu.on one side.
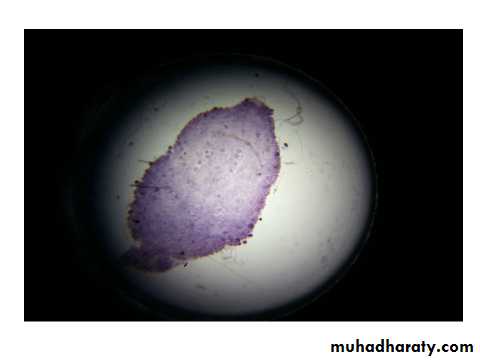
Stomach of mosquito showing the oocyst in its tissue.
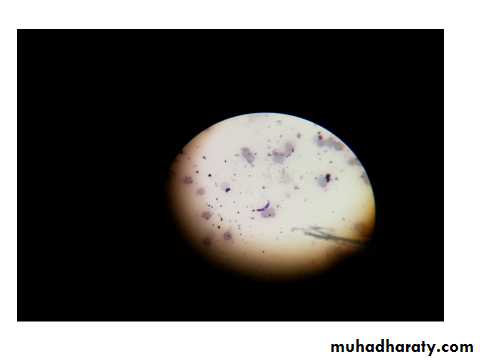
Cotent of the stomach of the mosquito showing ookinete stage of P. species it has one round end &the other end is poited with one Nu.¢ral vacuole.
Band stage of P.malariae.
Ookinete of P .species in stomach of mosquito.
Diagnosis:
Clinical picture.
Blood film to detect malaria parasite.
Identification of asexual erythrocytic parasites in the blood. ,if only gametocytes in the blood. ,it is not sufficient because gamt. May be present for long period after cure .
Blood films are of 2 types:
Thick film for detecting parasites.here the border of RBCs.not seen only the parasite are seen.it just diagnose malaria.
Thin film to differentiate the species.here the borders of RBCs.are seen that is why we can defferentiat the species this film is needed to start treatment.
Serodiagnosis.as PCR.