Working length determination
WORKING LENGTHWorking length is defined as the distance from a coronal reference point to the point at which canal preparation and obturation should terminate
Anatomical considerations
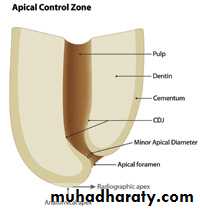
Anatomic apex: it is defined as the tip or end of the root determined morphologically.Radiographic apex: it is defined as the tip or end of the root determined radiographicaly.
Apical foramen (Major diameter): it is the main apical opening of the root canal.it is frequently eccentrically located away from the anatomic or radiographic apex.
Apical constriction (Minor diameter):
it is the apical portion of the root canal having the narrowest diameterCementodentinal Junction: it is the region where the dentin and cementum are united. It is a histological landmark and cannot be located clinically or radiographically. The CDJ does not always coincide with apical constriction and is located 0.5 -3mmshort of anatomic apex
METHODS OF WORKING LENGTH DETERMINATION
RADIOGRAPHICAL METHOD
1.Grossman’s formula
2. Ingles method
3.Weine’s method
4.Radiovisiography
5.Xeroradiography
NON RADIOGRAPHICAL METHOD
1.Digital tactile sense
2.Apical periodontal sensitivity
3.Paper point method
4.Electonic apex locator
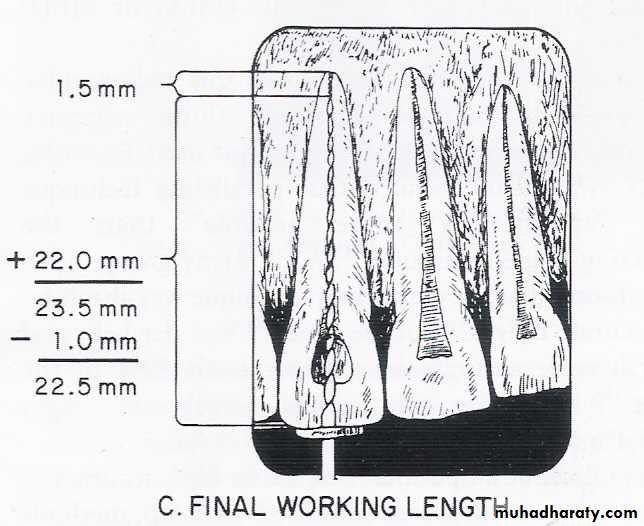
Radiographic Length
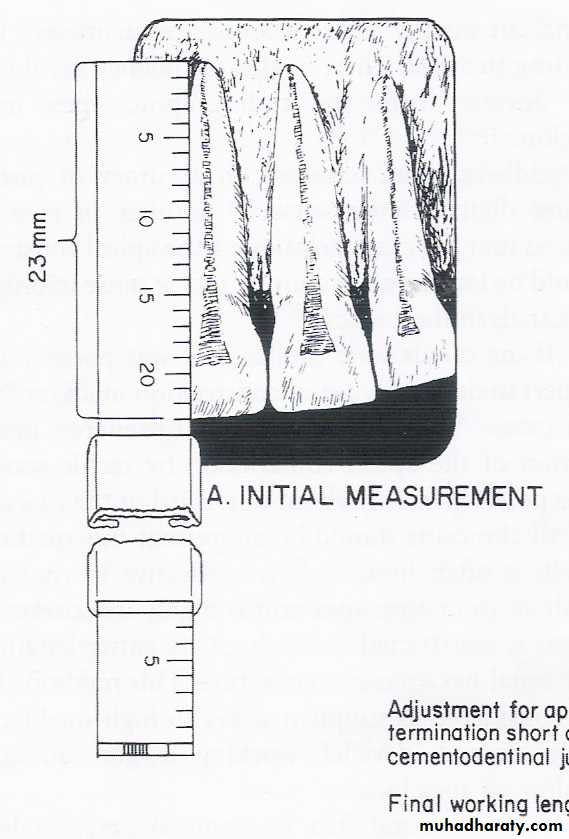
The length of the tooth as it appears on the radiograph.Estimated Working Length
Radiographic length minus 1mm.Final Working Length
is determined to be -1 mm from the anatomical apex as measured from the working length (WL) radiograph.THIS IS THE LENGTH TO WHICH THE CANAL WILL BE CLEANED & SHAPED AND OBTURATED.
Grossman’s method
CLT = KLI × ALT / ALI Where, CLT= correct length of the toothKLI= known length of the instrument in the tooth
ALT= apparent length of the tooth on radiograph
ALI= apparent length of the instrument on radiograph
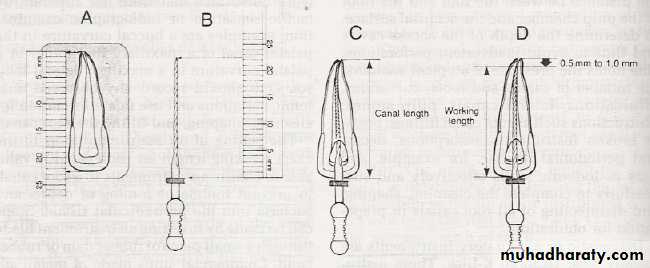
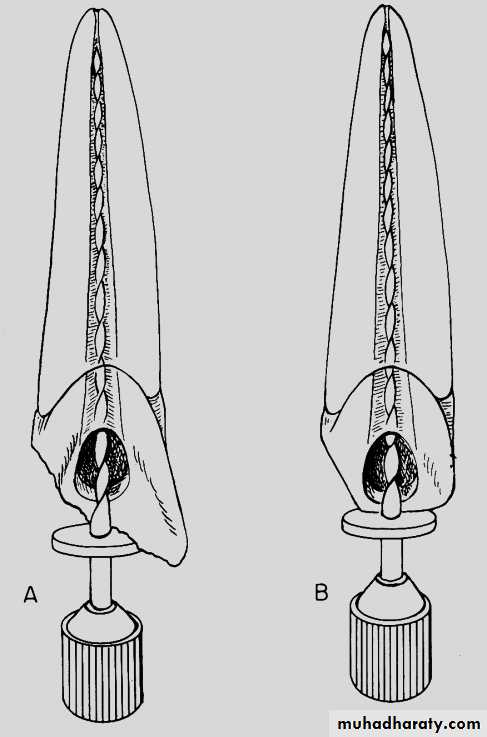
• A,The length of the tooth is measured on the diagnostic radiograph (schematic view).
• B, This measurement is transferred to a diagnostic instrument prepared with a silicone stop, the instrument is placed in the root canal, and a radiograph is made.• C and D, The root canal and working lengths are determined from the radiograph.
Ingle’s method
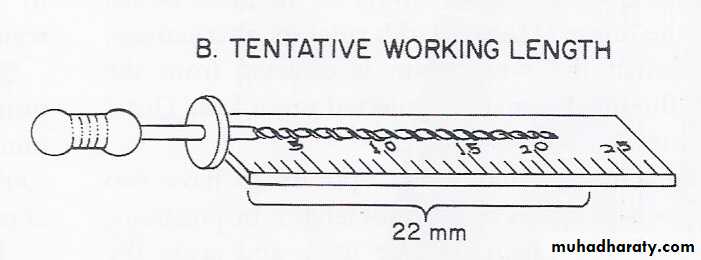
Tooth length is measured in the pre operative radiograph1 mm “safety allowance” is subtracted for possible image distortion
the endodontic file is set at this tentative working length, and the instrument is inserted in the canal
on the radiograph the difference between the end of file and root end is measured and this value is either subtracted or added to the initial working length measurement depending on weather the file is shortof apex or extended beyond apex
From this adjusted working length 1mm “ safety allowance” is subtracted again to confirm with the apical termination of instrument
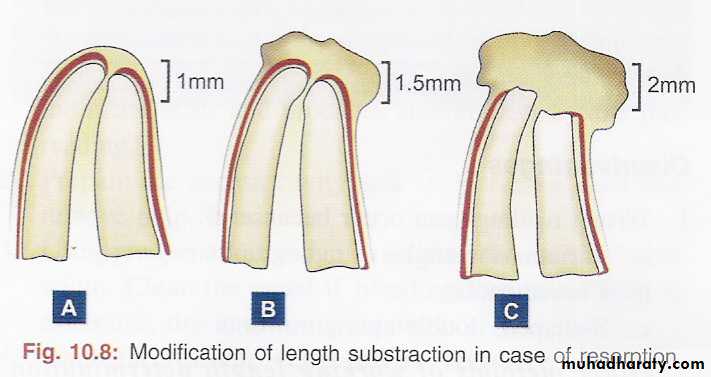
Weine’s modification
• A .If, radiographically, there is no resorption of the root end or bone, shorten the length by the standard 1.0 mm.• B. If periapical bone resorption is apparent, shorten by 1.5 mm, and
• C. if both root and bone resorption are apparent, shorten by 2.0 mm
•
Electronic method of determining working length:electronic apex locators
With a apex locator the working length is determined by comparing the electrical resistance of the periodontal membrane with that of gingiva surrounding the tooth, both of which should be similar
A probe , such as a file, is attached to an electronic instrument with an electric cord and is inserted through the root canal until it contacts the surrounding PDL.
When the probe touches the soft tissues of the PDL, the electrical resistance gauges for both gingiva and PDL would have similar readings.
By measuring the depth of insertion of the probe, one may determine the exact working length of root canal
New advancement electronic apex locators
Integration of the apex locators with the battery powered endodontic slow speed hand piece.File start to automatically rotate the moment the instruments is introduced in to the canal.
If the preset torque level for the instruments is exceeded then the hand piece automatically stops and reverse rotation.
The integrated apex locators stops the file rotation and reverse the moment the file tip extends beyond the apical constriction.
Advantages of apex locator
Devices are mobile, light weight and easy to useMuch less time required
Additional radiation to the patient can be reduced (particularly useful in cases of pregnancy)
80 - 97 % accuracy observed
Disadvantages OF APEX LOCATORS
Accuracy limited to mature root apicesExtensive periapical lesion can give faulty readings
Weak batteries can affect accuracy
Can interfere with functioning of artificial cardiac pacemakers – cuatious use in such patientsDigital tactile sense
Although it may appear to be very simple, its accuracy depends on sufficient experience.Confirmation may be done either by the radiographic or electronic method.
If the coronal portion of the canal is not constricted, an experienced clinician may detect an increase in resistance as the file approaches the apical 2 to 3 mm.Tactile sensation, although useful in experienced hands, has many limitations.
The anatomical variations in apical constriction, location of apical constriction, tooth size, tooth type, age make working length assessment unreliable.In some cases the canal is sclerosed or the constriction has been destroyed by inflammatory resorption
Apical periodontal sensitivity
• Based on patient’s pain perception• Any method of working length determination, based on the patient’s response to pain, does not meet the ideal method of determining WL
Paper point method
• In a root canal with an immature (wide open) apex, the most reliable means of determining WL is to gently pass the blunt end of a paper point into the canal after profound anesthesia
• The moisture or blood on the portion of the paper point that passes beyond the apex - an estimation of WL or the junction between the root apex and the bone.
• This method, however, may give unreliable data
• If the pulp not completely removed
• If the tooth – pulpless but a periapical
• lesion rich in blood supply present
• If paper point – left in canal for a long time
REFERENCE POINT
The reference point is the site on the occlusal or incisal surface from which measurements are made. This point is used throughout canal preparation and obturation.Select a Reference Point
Take a Preoperative Radiograph
Preoperative Radiograph
Measure the radiographic length.Reference pt.
ApexSELECTION
A reference point is chosen that is stable and easily visualized during preparation. Usually this is the highest point on the incisal edge on anterior teeth and a buccal cusp tip on posterior teeth. The same reference point is best used for all canals in multirooted teeth. The mesiobuccal cusp tip is preferred in molars.STABILITY
A reference point that will not change during or between appointments is selected. If it is necessary to use an undermined cusp, it should be reduced considerably before access preparation. Areas other than cusp tips, such as marginal ridges or the floor of the chamber, are unreliable or difficult to visualize.Do not use weakened enamel walls or diagonal lines of fracture as a reference site for length-of-tooth measurement.
B, Weakened cusps or incisal edges are reduced to a well-supported tooth structure.
Diagonal surfaces should be flattened to give an accurate site of referenceDetermination of Working Length by Radiographic Methods
• Good, undistorted, preoperative radiographs showing the total length and all roots of the involved tooth.• Adequate coronal access to all canals.
• An endodontic millimeter ruler.
• Working knowledge of the average length of all of the teeth.
• A definite, repeatable plane of reference to an anatomic landmark on the tooth, a fact that should be noted on the patient’s record.
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION
• The cementodentinal junction or minor diameter is a practical and anatomic termination point for the preparation and obturation of the root canal – and this cannot be determined radiographicaly.• Modern apex locators can determine this position with accuracies greater than 90% but with some limitations.
• No individual method is truly satisfactory in determining endodontic working length.
• Therefore, combination of methods should be used to assess the accurate working length determination