
pg. 1
Fifth stage
Pediatric
Lec3
.د
رياض
9/11/2016
Transient Tachypnea of newborn
Wet lung; RDSII
(TTN)
DEFINITION and causes:
• It is a respiratory problem that can be seen soon after birth within
first 3 hours mostly in full- term and sometime in preterm
neonates >35+ wks. The incidence is 1% of all newborns. It is mild
to moderate respiratory distress and self-limiting and mostly
improve within 1-2 days. Its cause is retained fluid in the lungs of
newborn at birth leading to reduced lung compliance and
respiratory difficulty. The rapid labor time or the cesarean section
that does not allow the squeezing process to milk out the fluid
from the fetal lung.
• Causes( aetiology) include cesarean section, and rapid labor
time for term or preterm babies >35+ wks getation due to
retained fluid in the fetal lung.
Risk factors:
1.cesarean section
2.baby of diabetic mother and macrosomia.
3.baby of asthmatic mother , cause unclear
4.baby small for gestational age or premature babies>35+ wks: due
to rapid delivery that not allowing time for clearing the fetal lung
from retained fluid.
pg. 2
Clinical features:
• Tachypnea developed within first few 3-6 hr hours of birth with
RR>60/min.
• Grunting
• Flaring of nostrils
• Intercostal recession and subcostal retraction
• rarely may in severe cases develop Cyanosis or low SPO2 (Hb
oxygen saturation) <90% by pulse-oximetry.
• Usually the respiratory distress is benign and improve within 3-4
days but if remain for more than 5 days other possibilities should
be considered, like RDS, congenital heart disease , neonatal
pneumonia, meconium aspiration syndrome.. So the diagnosis is
mainly by excluding other similar conditions like the later
problems.
pg. 3
Diagnosis and diff, diagnosis
History of full term delivered by C-section, or low birth WT baby born by
rapid precipitous labor or IDM baby develops tachypnea within first 3
hours of birth,
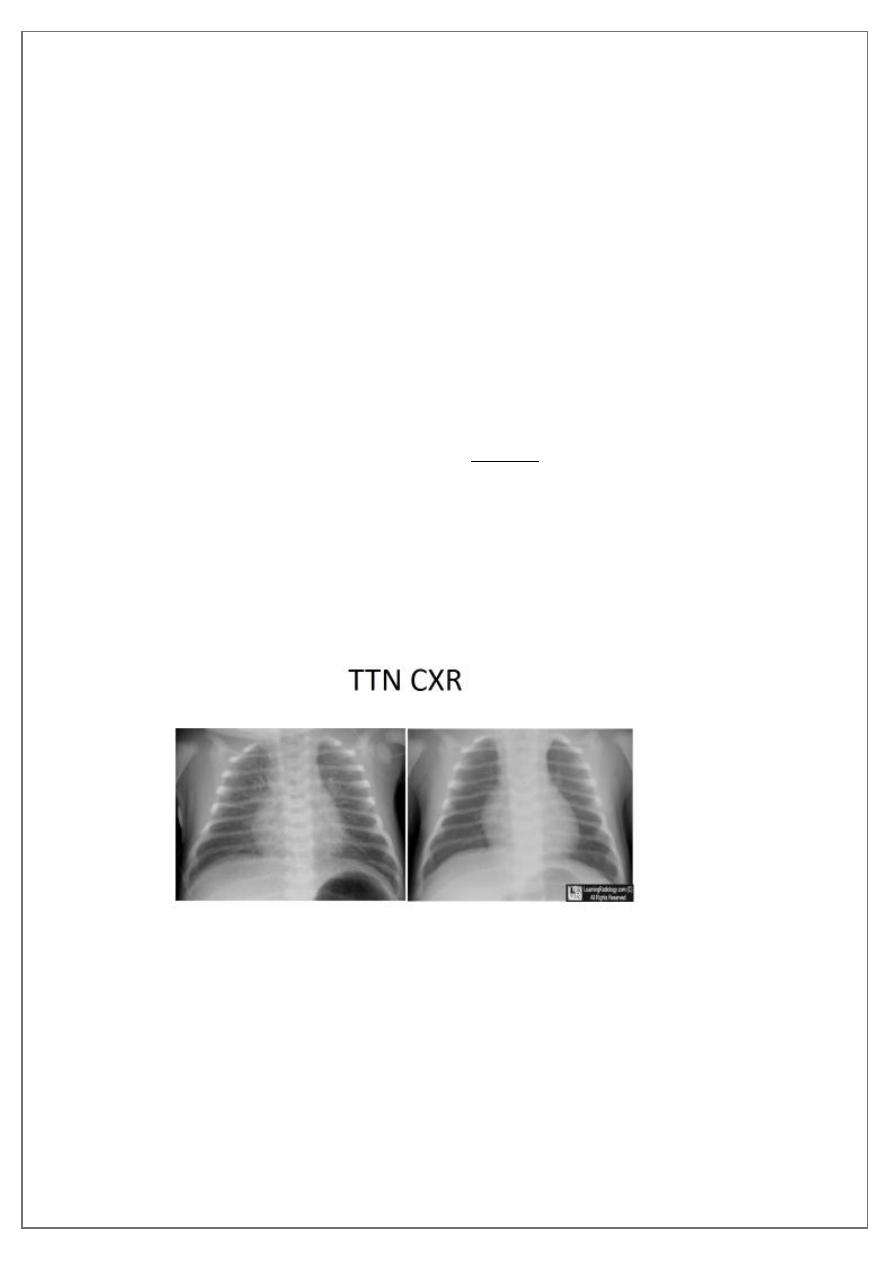
CXR showing; hyperinflation, more aerations , perihilar prominent
vascular lung marking, interstitial streaks of fluid and fissures shows fluid
lines, in addition to mild cardiomegaly, should suggest TTN. Low
Spo2<90%. -------------------------------------
To differentiate it from other causes like RDS is mainly by the exclusions;
by nature of delivery, the maturity of baby <32wks in RDS , and the
course of the tachypnea(severity and the duration in RDS more severe
and takes longer course up to 1 wk) x-ray in RDS; shows less aerations,
whitening of lung ,and presence of bronchogram .
Other diff. diagnoses: pneumonia, congenital heart disease, meconium
aspiration.

pg. 4
TREATMENT
• ADMISSION to NICU (neonatal intensive care unit) & put the baby
in incubator& give O2 by oxyhood box ( head box) with high O2
conc . 80-100%, for may hours or even for1-2days + IV fluid and
antibiotics, under monitor for Spo2 and RR, and follow up with no
oral feeding (NPO) till RR reaches<60/m and then can give milk by
nasogastric tube feeding NGF when the condition allow, rarely
CPAP may be used.(continuous positive air way pressure).
• the baby usually improves within 24-48 hours.
