
pg. 1
Fifth stage
Pediatric
Lec2
.د
رياض
9/11/2016
Neonatal respiratory distress syndrome
(RDS)
Hyaline membrane disease
(HMD)
DEFINITION:
• Respiratory problem in premature babies <32 wks gestation due
to lack of surfactant as a result of immaturity of the lung and its
incidence increases with decrease in gestational age.
• Surfactant is phospholipid formed in the fetal lung after 34wk
gestation and completed within the last trimester.
• Its function is to reduce surface tension of the alveolar wall help
aeration of the alveoli and prevent alveolar collapse.
• Hypoxia and meconium aspiration prevent its formation and
function.
• Its absence causes collapse and atelectasis of alveolar spaces.
Risk factors:
• Premature babies <32 wks gestation
• Cesarean section
• Maternal diabetes
• Birth asphyxia
pg. 2
Clinical features
• Premature babies developed tachypnea and respiratory distress
soon after birth within first hour of birth, with grunting,
intercostal recession and subcostal retraction, and even cyanosis
and apneic attacks. Difficult feeding and less crying.
• Pulse oximetry <90% and BGA show low O2 and CO2 retention.
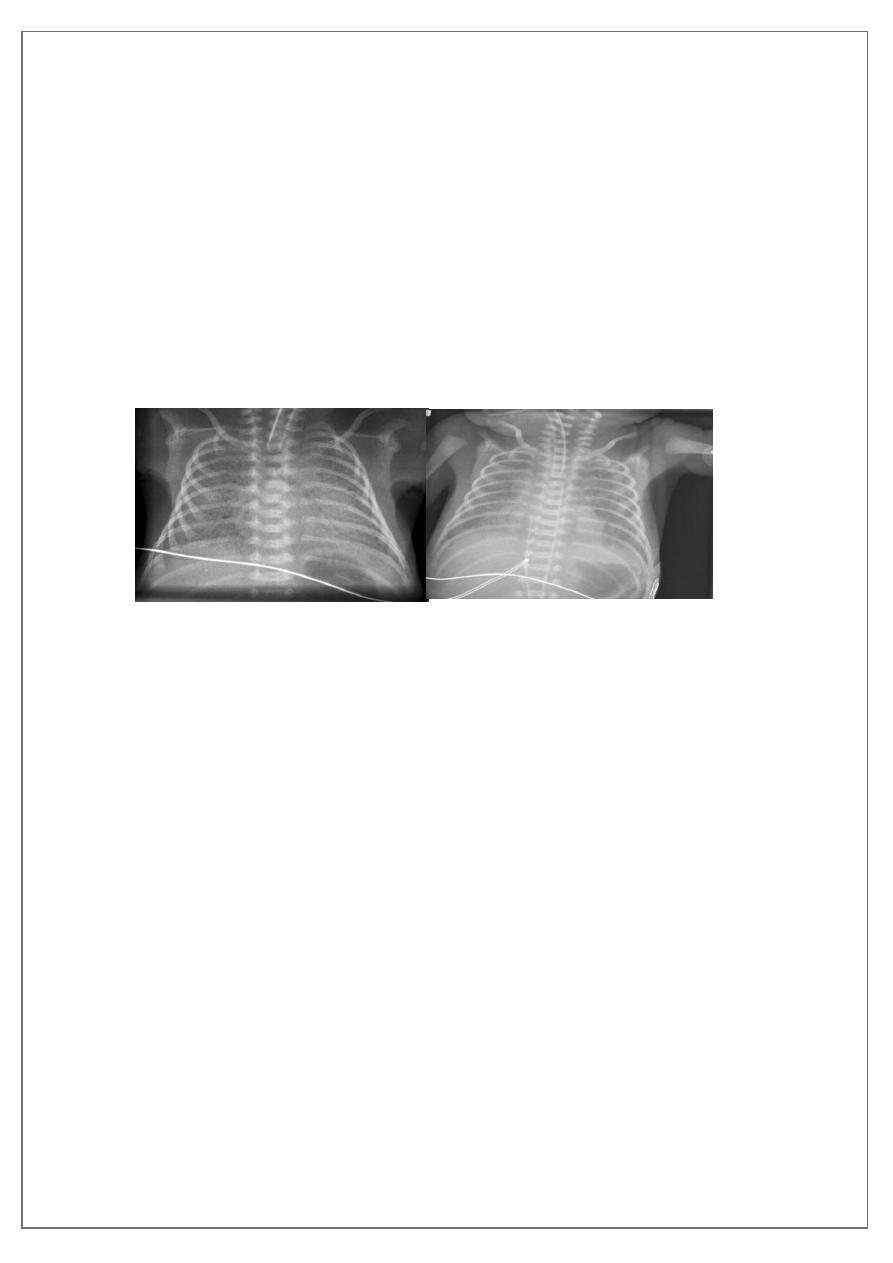
• CXR shows whitening of lung with less aeration and reticular
feature with ground glass appearance due to atelectases.
Differential diagnosis:
• TTN; tansient tachypnea of newborn has mild course and its CXR
shows hyperinflation and aeration and Gestational age >35+wks
• Neonatal pneumonia
• Meconium aspiration
• Congenital heart disease

pg. 3
Complications:
• Pneumothorax and pneumomediastinum,
• Apnea due to hypoxia
• PDA due to prematurity and hypoxia
• Infection ;lung or sepsis
• Intraventricular hemorrhage IVH due to prematurity with swinging
of vascular pressure at periventricular subepindymal vessels.
Treatment:
Usually RDS is severe condition and it needs respiratory
support:
• Oxygen by head box; in mild cases .
• Surfactant therapy given in 1-3 doses through ETT endotracheal
tube intubation; followed by connection to CPAP(continuous
positive air way pressure) system; or even connection to
mechanical ventilator machine for 1-3 days .
• Antibiotics ampicillin and aminoglycosides like amikacin or
gentamicin given because difficult to exclude neonatal
pneumonia .
Prevention
• Can be prevented in suspected premature delivery by steroids to
enhance the fetal lung maturation by giving dexamethasone to
the mother for 2-4 doses for the 24-48 hrs before delivery.
