Phenylalanine
• A• m
• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M
phenylalanine (Phe), one of the essential amino acids that cannot be manufactured by the body and must therefore be consumed in protein rich foods
Phenylalanine
• A
• m
• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M
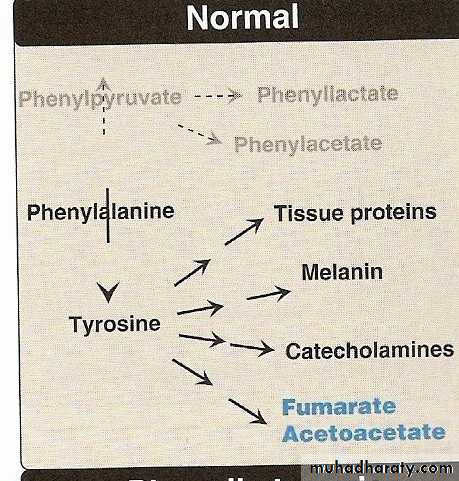
Metabolism of Phenylalanine:
*It is one of the essential Aromatic Amino Acid.
*Can not be synthesized in the body.
*It is metabolized mainly in the liver in to two pathway:
1.Major pathway (Hydroxylation pathway) Tyrosine pathway) 90%
2.Minor pathway (Transamination pathway) 10%
Phenylalanine
• A
• m
• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M
Major pathway
PhenylalanineTyrosine
• A
• m
• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M
Phenylalanine
• A
• m
• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M
This reaction need O2 and at the
same time need a cofactor (molecule
of tetrahydrobiopterine which is
converted to dihydrobiopterine by the
effect of biopterine reductase enzyme
which need molecule of NADH to
convert back to tetrahydrobiopterine
α-
Phenylalaninephenylpyruvate
Phenyl lactate
phenyl acetate
phenylaetylglutamine
• A
• m
• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M
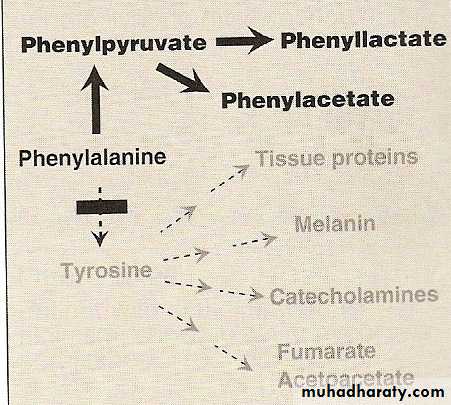
Inborn Error of Metabolism Of Phenylalanine
Phenylketonuria:
*autosomal recessive 1/10000.
*Treatable disease with early diagnosis.
Late diagnosis lead to mental retardation. if diagnose after 2 weeks
Classification:
Hyperphenylalaninemia I (classical) Defect: Phenylalanine hydroxylase.
Hyperphenylalaninemia II ,III (minority) Defect:Dihydrobiopterine reductase enzyme.
Hyperphenylalaninemia IV,V Defect: Synthesis of biopterine cofactor
Deficiency of Ph. Hydroxylase enzyme
• A• m
• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
A disorder of the metabolism of phenylalanine, a substance present in milk and also in products containing aspartame (NutraSweet).
Phenylalanine is not metabolized by the body it accumulates in the blood and reaches toxic levels, damaging various body structures, including the brain.
PKU is largely preventable, and testing for PKU
in newborns is required.• A
• m
• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M
PHENYLALANINE HYDROXYLASE
PHENYLALANINE
Dietry sources, particularly plant proteins
BODY PROTEINS
BREAKDOWN
(b)
(a)
The normal metabolism of phenylalanine
(pathways a and b)
TYROSINE
© 2008 Paul Billiet ODWS
• A
• m
• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M
HYDROXYPHENYLACETIC ACID
PHENYLACETIC ACID*
(c)
(c)
The abnormal metabolism in phenylketonuric
(pathway c) subjects
Hydroxyphenylacetic Acid
• A• m
• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
• A
• m
• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M
The PKU gene is found on the chromosome 12, locus 24.1 in the phenylalanine hydroxylase gene
Punnett Square
Carriers of Phenylketonuria. Both Gg.G
g
G
g
GG
Gg
Gg
gg
The punnet square below shows the results of when two parents, both carriers of PKU produce offspring.
• A
• m
• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
• A
• m
• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M
Clinical Features:
**Irritability, feeding problem,vomiting.fits during the first week of life
**Mental retardation developing between 4-6 months.
**Generalized Eczema.
**Tendency to reduce melanin formation because of reduced production of tyrosine . Blue eyes.
** Deficiency of pigmentation (,fair hair,light skin colour) .
Biochemical Effects
• Accumulation of substrate of blocked reaction. Phenylalanine
• Reduced formation of the product . Tyrosine
• Alternative pathways of metabolism of the precursor,( formation & excretion of phenylpyruvate, phenyllactate & phenylacetate).
• The mental retardation of PKU can be prevented by a diet containing low level of phenylalanine up to six year
• A
• m• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
• A
• m
• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M
Neonatal Screening
Early diagnosis of PKU is important because the disease is treatable by diet. However the infant has normal blood level of phenylalanine at birth because the mother clears increased blood phenylalanine in her affected fetus through the placenta,
Normal level of phenylalanine my persist until the new born is exposed to 24-48 hr protein feeding.
Screenig should be done after this time to avoid false negative.
Positive rsult by quantitatve measurement of phenylalanine.
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
• A• m
• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M
• Diagnosis:Measurement of phenylalanine in blood taken from a heel prick.
• Amino Acid Analysis High peak level of Phenylalanine and Low level of Tyrosine.
• Guthrie Test:
• Ferric Chloride Test:
• Urine Chromatography.
Amino Acid analysis in the blood is the most important method
which give high peak of phenylalanine& low peak of Tyrosine.
The advantage of this method is the early diagnosis.
• A• m
• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M
It is only suitable for mass screening.
** Should be performed about 4 days after birth.
False positive……. Premature infantFerric Chloride Test:
Pink or green ring……• A
• m• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M
• Management:
• To lower plasma phenylalanine ,give low phenylalanine diet special milk formula).
• Supplementation with tyrosine.
• Diet may be terminated at age of 6 years.
• The earlier treatment is started ,the more completely neurological damage can be prevented
• Tyrosine can not be synthesized from phenylalanine and it becomes an essential amio acid and should be supplied in the diet.
• A
• m
• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M
PKU Treatment
Meat, fish, eggs, cheese, milk products,, and bread are all foods that have high levels of phenylalanine
• A
• m• I
• n
• o
• A
• c
• I
• d
• S
• M
• E
• T
• A
• B
• O
• L
• I
• S
• M