
1
Fifth stage
Surgery (Pedo)
Lec
د.عبدالرحمن
23/10/2016
Hirschsprung’s Disease
♪
♪
(
Congenital or Aganglionic Megacolon
)
In 1887 Hirschsprung described two infants who died with gross abdominal distension and
(
hugely dilated colon containing masses of feces (Hirschsprung syndrome
In 1948 Zuelzer and Wilson noted that in some children with this syndrome the myenteric
plexuses were absent with no ganglion cells in the affected part of the bowel
(Hirschsprung’s disease).After these steps in the diagnosis ,several surgical techniques were
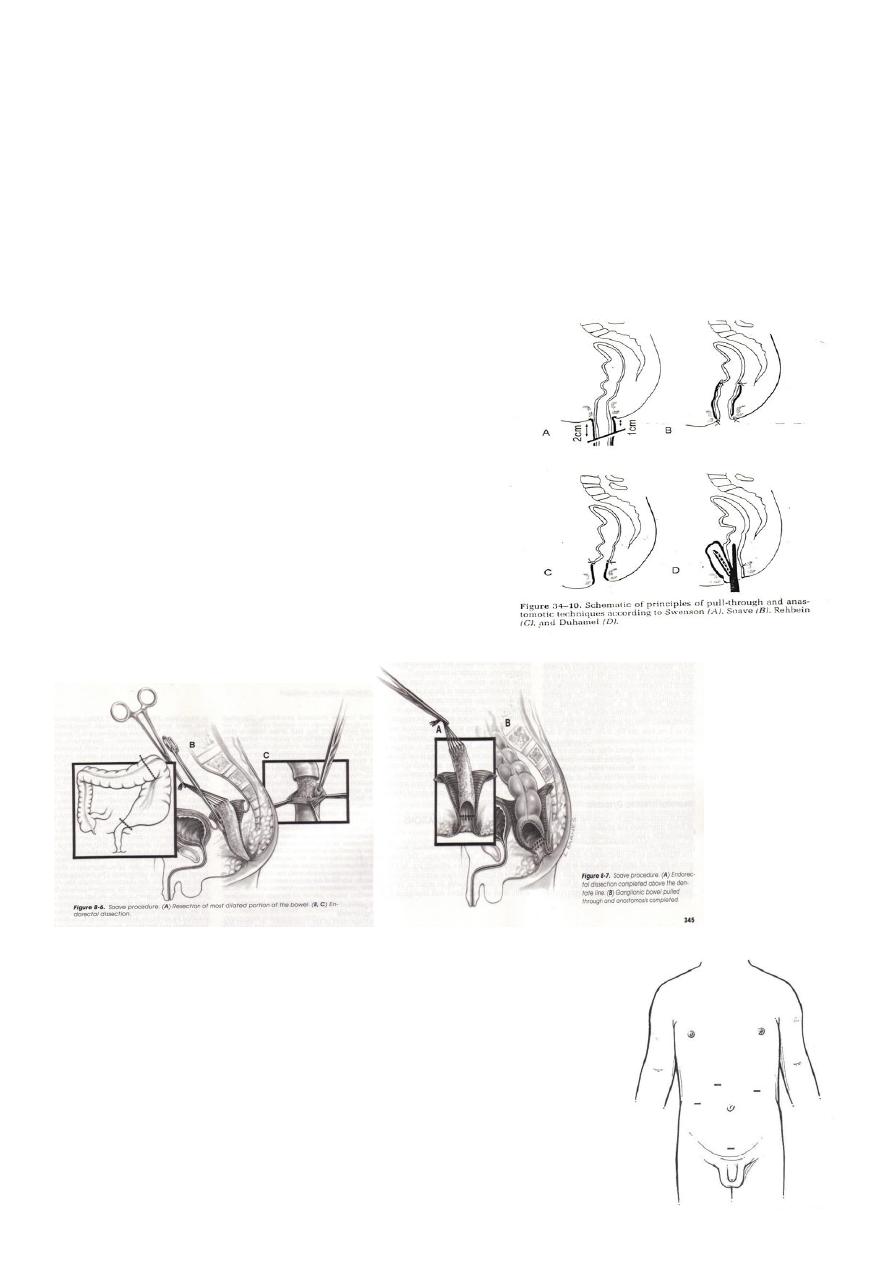
adopted to treat such problems (Swanson,Duhamel,Soave).
Pathology:-
genetically there are two types
1- Large group where males affected 4-5 times more than females , And there is a
short aganglionic segment involving the rectum or sigmoid
.
2- Smaller group with long aganglionic segment affecting both sexes equally. Usually
there is higher degree of penetrance i.e. may affect more than one member of the family. The
affected segment begins at the anus and extend proximally for a variable distance .As far as
the sigmoid colon in most of the cases In some cases it may extend to involve the whole
colon or even the small bowel.
in Rare instances the entire alimentary canal is devoid of ganglion.
Clinical presentation:
varies from patient to patient depending on the length of the involved segment.
Delayed passage of meconium .
Chronic Constipation
Abdominal distension .
Vomiting .
Bouts of diarrhea(enterocolitis) .
On examination: there is abdominal distension .We may feel palpable loaded colon .
P-R: tight anal canal .some times fecal impaction .
2
Investigations:
1. X-ray:
in neonate :multiple air-fluid levels.
In infants distended colon loaded with feces.
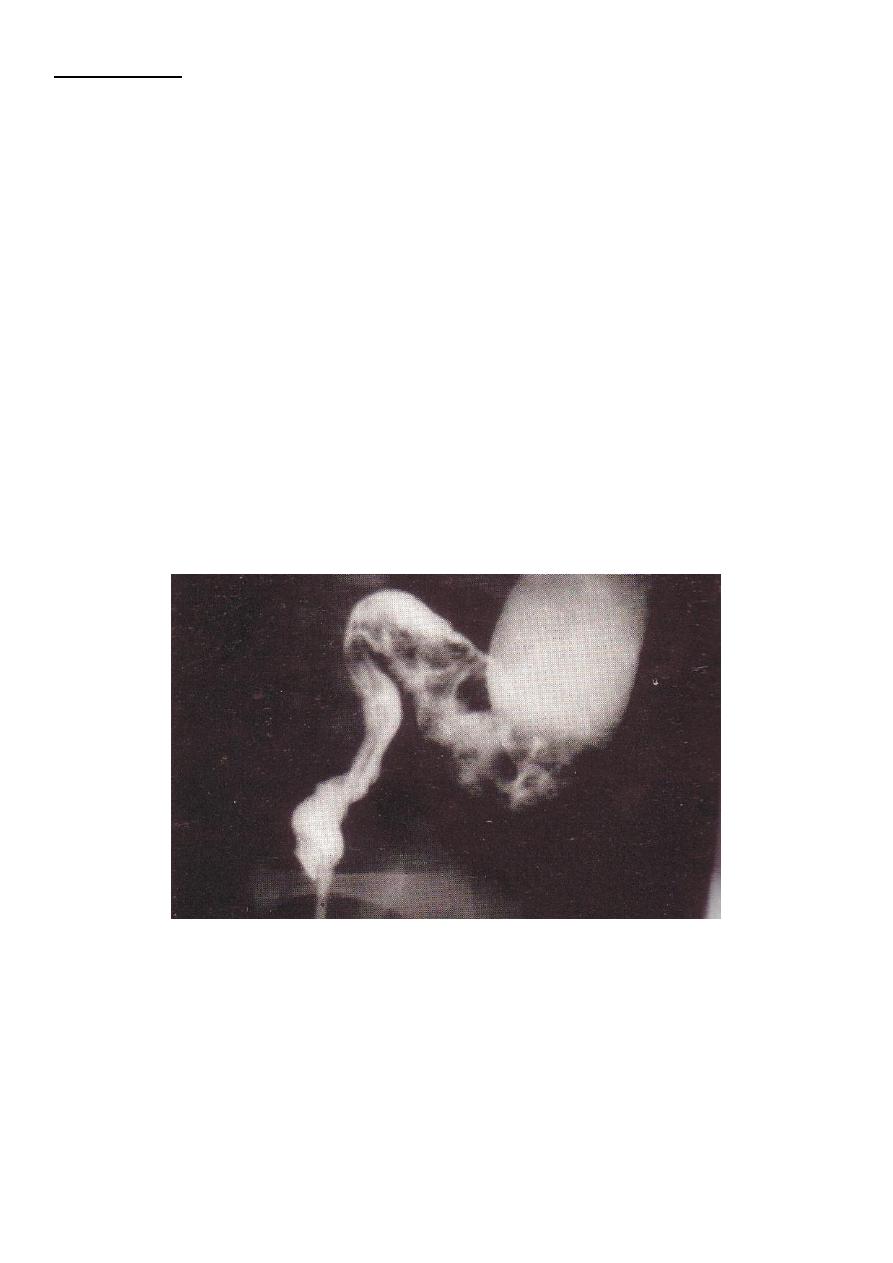
2. Barium enema :
it’s diagnostic :Ice cream cone
(transitional cone).
3. Rectal biopsy
absence of ganglion cells .
4. Manometry.
Diagnosis :-
Radiological diagnosis
A plain supine and upright film of abdomen , The Ba enema
Management of Hirschsprung’s disease :-
1- Conservative management with dietary treatment and laxative or repeated enemas and it’s
not always effective
.
2- Surgical management :depends on the age and the length of the segment involved One
staged definitive operation without colostomy is possible ,but carries higher complication
rate than the 3 staged operation :
3
- Colostomy at the time of diagnosis
- Rectosigmoidectomy (pullthrough operation) Swanson,Duhamel,Soave.At 6-9
months
.
- Closure of colostomy 4-6 weeks later
Recently
Laparoscopic Approach
Trans-anal pullthrough without opening the abdomen
Management :
DECOMPRESION :
Rectal irrigation
Colostomy
DEFINITIVE SURGERY :
Swensen technique
Duhamel technique
Rehbein technique
soave procedure -modified soave (Boley’s)
LAPAROSCOPIC PULL THROUGH TECHNIQUES:
four ports
modified Swansons
Duhamel
Soave
4
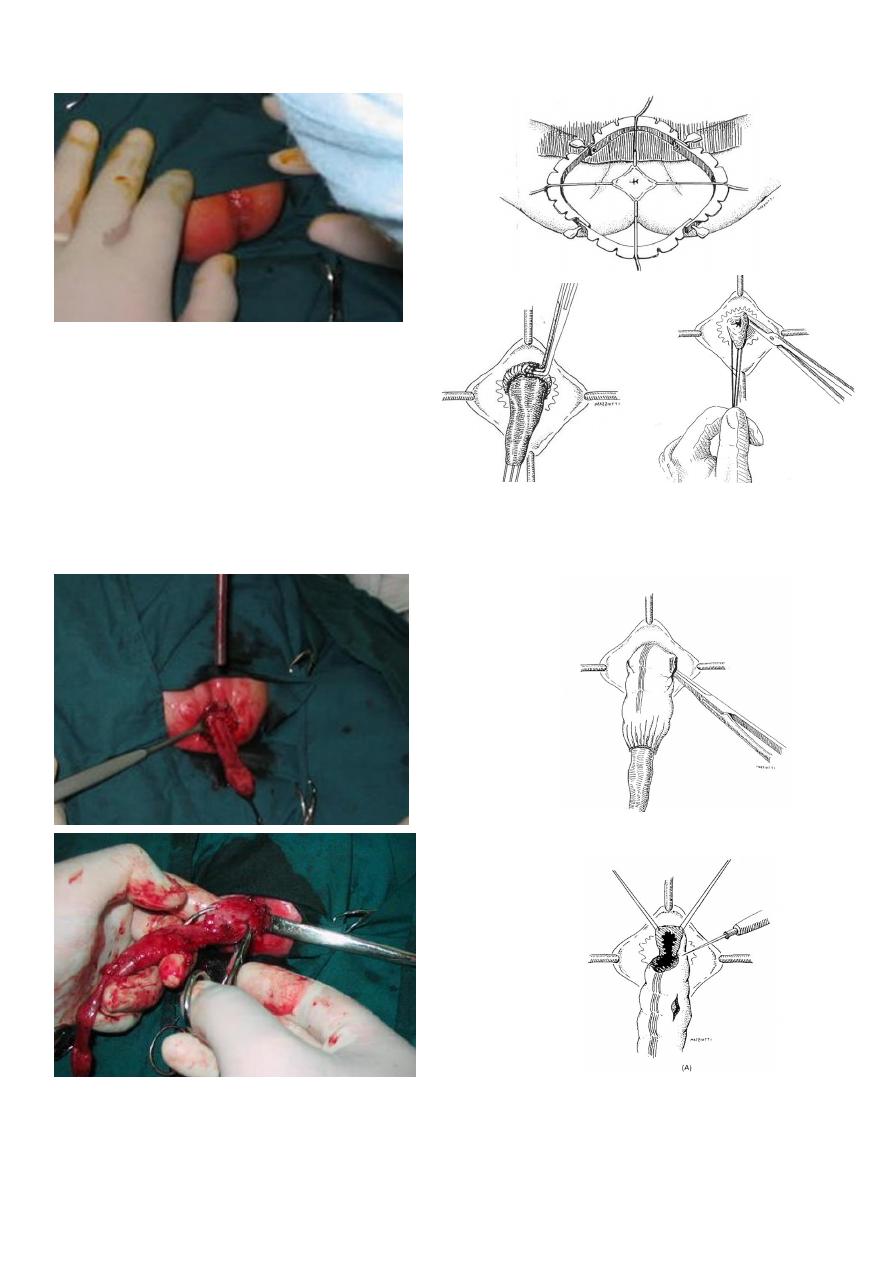
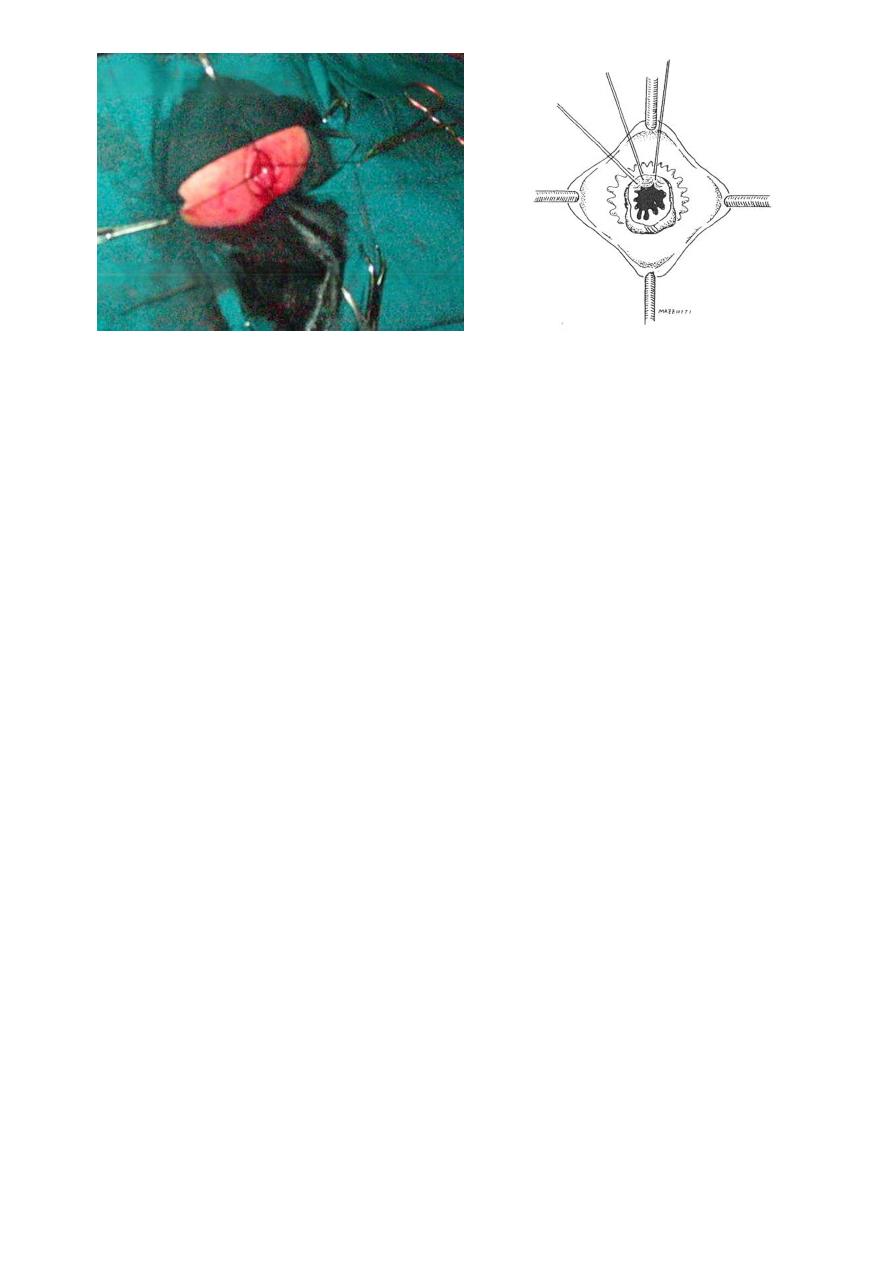
TRANSANAL ENDORECTAL PULL THROUGH:
5
SH.J
ღ
