
1
Fifth stage
♪Medicine♪
Lec
د.خالد نافع
1/11/2016
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia CLL
• CLL is the most common leukemia in Westren countries, accounting for one-third of
cases.
• The disease is rare in Asians; 90% of patients are older than 50, median age at
presentation is between 65 and 70 years
• Men are affected more often than women by a ratio of 2:1.
Pathology and natural history :-
Pathology
CLL results from suppression of programmed cell death (apoptosis) of mature B-cell.
Surface membrane antigens include the B dell antigens CD 19 , CD 20 , CD 23 , CD 5
is always present on CLL cells.
CD 38 has been associated with unfavorable prognosis.
Natural history
1. Immunological abnrmalities;
Advanced disease is associated with hypogammaglobulinemia and decreased humoral
respnses to antigens.
Avariety of in vitro lymphocyte function test are abnormal.
Coomb`s postive warm antibody hemolytic anemia occurs in 10% & immune
thrombocytopenia in about 5%.
2. Clinical course :
Survival is closely correlated with the stage of disease at time of diagnosis.Because most of
patients are elderly at time of diagnosis ; more than 30% die of diseases untrelated to
leukemia.
Manifestation :-
In 70% of patients CLL is first recognized at routine physical exam.or by routine
CBC.
Clinical manifestation develop as the leukemic cell acumalate on lymph nodes ,liver
,spleen & bone marrow
.
Presenting problems may be anaemia, infections,painless lymphadenopathy, and
systemic symptoms such as night sweats or weight loss. However, these more often
occur later in the course of the disease.
Transformation in to a diffuse large B-cell lymphoma(Richter`s syndrome) or
prolymphocytic leukemia occurs in less than 5% of patients.
2
. progressive disease :
Death is usually due to infection , bleeding or other complication of the disease.
HERPES ZOSTER is the cause of 10% infection in CLL
Bacterial pathogens associated with hypogammoglobuliemia include Streptococus
pneumoniae Staphylococcus auerus and Hemophilus influenzae
.
Pneumocystis jirovecii
Laboratory studies :-
1. Hemogram
Erythrcytes; anemia may be caused by :-
1.bone marrow infiltration.
2.hypersplenism
3.autoimmune hemolysis
Lymphocytes; the absolute count ranges from 10x10
9
/l - 200x10
9
/l but may exceed
500x10
9
/l.
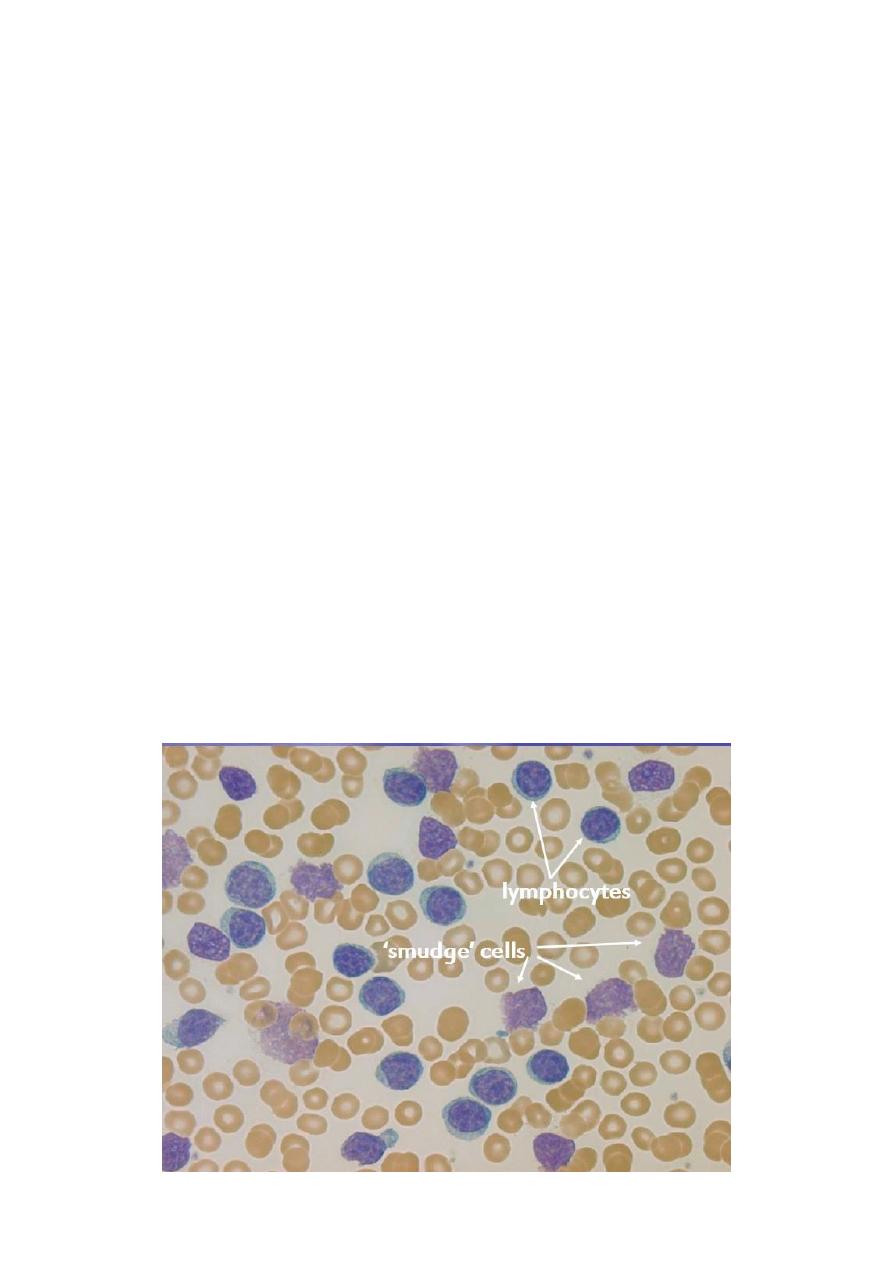
When blood smears are made , the cells are easily ruptured producing typical “basket”
or “smudge” cells.
Granulocyte; absolute counts are normal or increased until late in the disease.
Platelets; thrombocytopenia may prodused by bone marrow infiltration , hypersplenism,
immune thrombocytopenia

3
DIAGNOSIS :-
1. Lymphocytes ( x10
9
/L) > 5; > 1 B-cell marker (CD 19, CD20 , CD 23) + CD5
2. Atypical cells (prolymphocyte) (%) < 55
3. Bone marrow lymphocytes ( %) >30
Binet Staging System :-
Area of involvement considered for staging.
1- Head & neck , including the Waldeyer ring ( this counts as one area even if more than
one group of nodes are enlarged
2- Axillae ( involvement of both axillae count as one area)
3- Groins, including superficial femorals counts as one area.
Stage A
Hb > 100 g /L
platelets > 100 x109/L
up to two of the above lymph node involved
Stage B
Hb > 100 g / L
platelets > 100 x109 / L
three or more areas of nodal or organ enlargement
Stage
C
All
patients
,
irrespective
of
organomegaly
in
whom
Hb < 100 g / L & or platelets < 100 x 109 / L.
Indications for Therapy in B cell- CLL :-
• Anemia
• Thrombocytopenia
• Disease- related symptoms
• Markedly enlarged or painful spleen
• symptomatic lymphadenopathy
• Blood lymphocyte count doubling time < 6 months
• Prolymphocytic transformation
• Richter`s transformation

4
RESPONSE CRITERIA
Complete remission(CR) PARTIAL REMISSION(PR)
Treatment :-
1- Watch and wait
2- GLUCOCORTICOIDs
3- ALKYLATING AGENTS
Chlorambcil (leukeran); alkylating agents.*Daily oral dose or Intermittently
total oral dose every 2-4 weeks
CYCLOPHOSPHAMIDE
4- FLUDARABINE; Inhibit adenosine deaminase IV infusion 25- 30 mg/ m² daily for 5
days repeated 5-6 times every 3 - 4 weeks.
5- Anti-CD20 Rituximab.
• Rituximab+Fludarabine+cyclophosphamide
Prolymphocytic leukaemia
Hairy cell leukaemia
SH.Jღ
