Congenital anomalies of renal tract
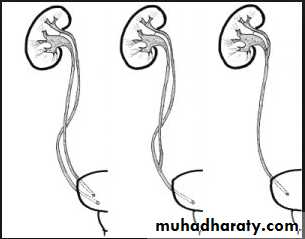
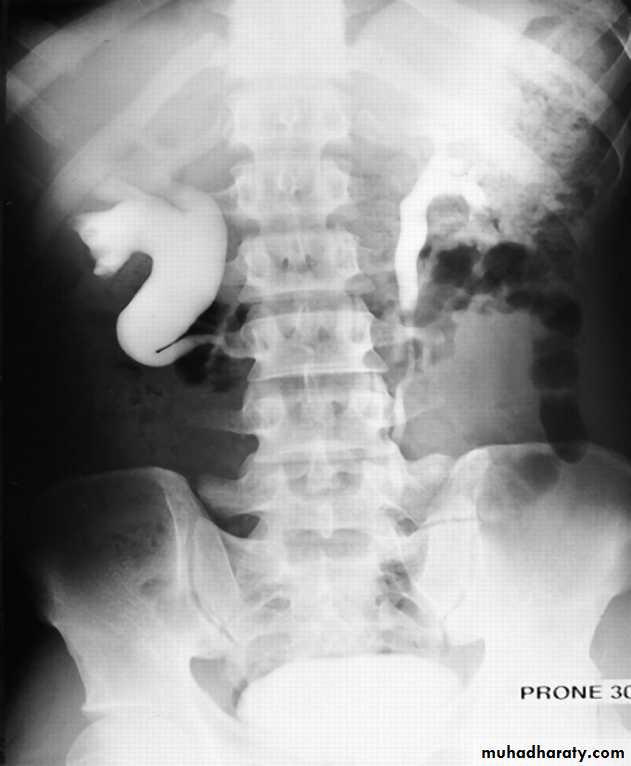
Bifid collecting system :- Most frequent.
- Unilateral or bilateral.
- Incomplete ; sometimes only pelvis is bifid , 10 %o f population, (not significant)
- Complete ; (1-2 % of population),
two ureters may be separate down to their insertion into the bladder.
Upper moiety ureter inserts inferior and medial to its normal site , or ectopically to vagina or urethra leading to urine incontinence if beyond urethral sphincter, may associate with obstruction or uretrocele.
- Lower moiety ureter inserts into normal anatomical position, usually associated with reflux.
Renal agenesis :
- Incidental finding.
The opposite kidney shows compensatory
hypertrophy .
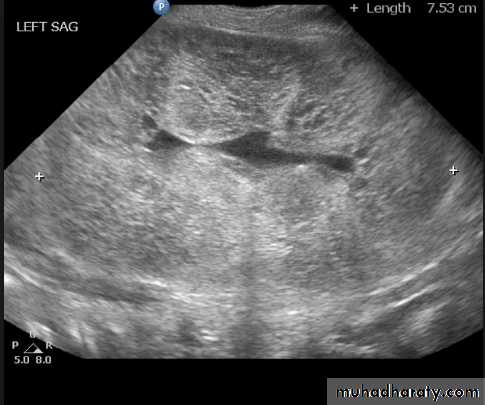
- Can be diagnosed as absent kidney on ultrasound or CT.
- IVU will show a single kidney with active contrast excretion .
Ectopic kidney:
- Result from halted ascend of kidneys during fetal development .- Often are incidental findings during routine ultrasound , usually located in the lower abdomen and rotated, short ureter.
- Chronic pyelonephritis, calculi and hydronephrosis are more common in ectopic kid. .
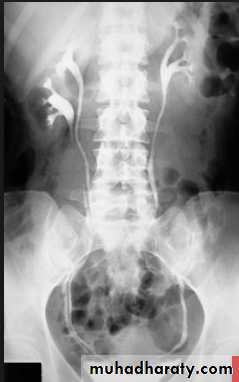
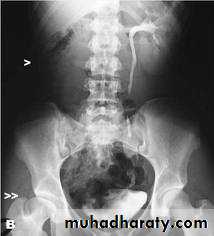
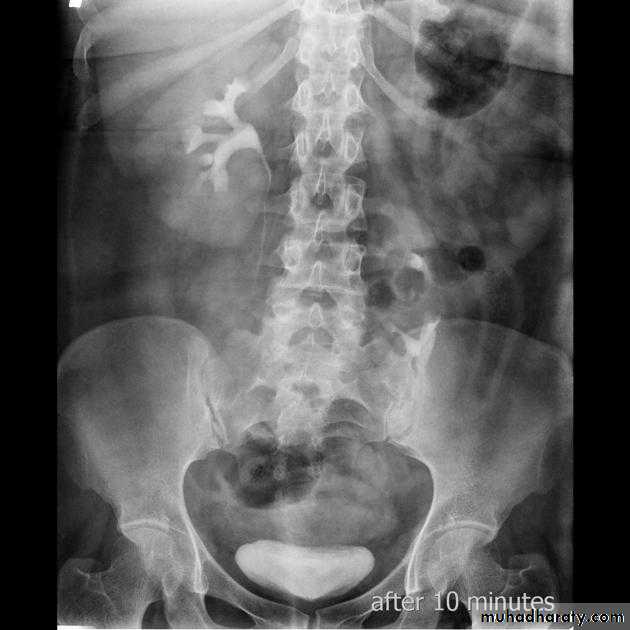
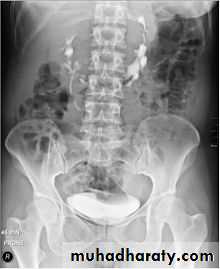
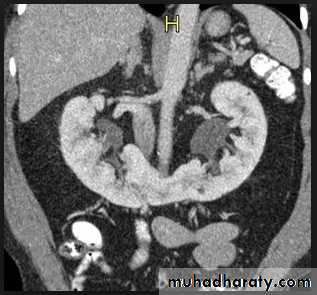
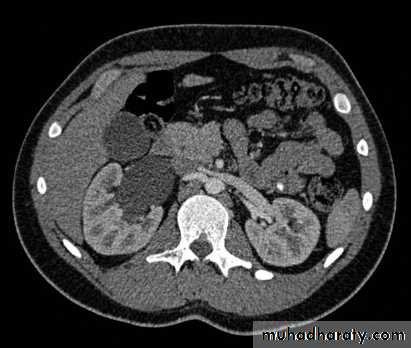
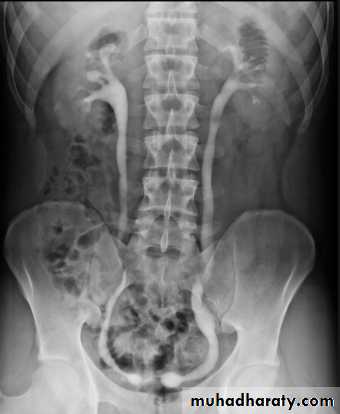
Horse shoe kidney -Kidneys may fail to separate.
-Almost invariably the lower poles remain fused.
-The kidneys axes are more parallel to the spine and malrotated.
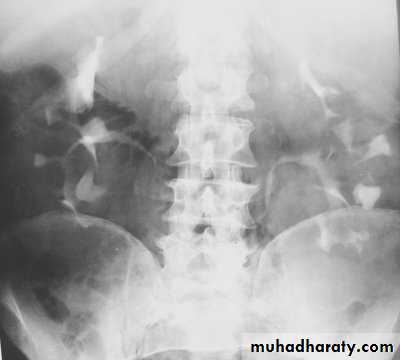
-Diagnosis can be made by plain x-ray in some cases.
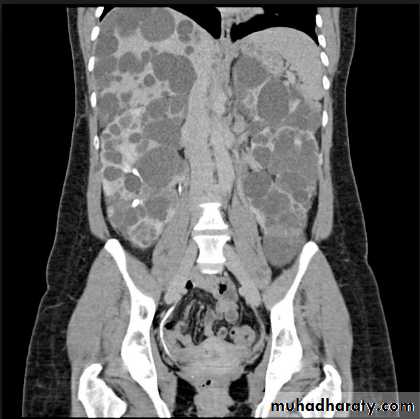
-US, CT scan and MRI can better demonstrate the anatomy and morphology hence the diagnosis.
-May be an incidental finding.
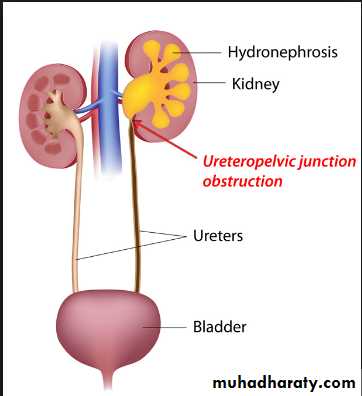
-PUJ obstruction and calculi formation are common .
IVU shows
1. The kidneys at low position .
2.Close to the spine with long axis parallel to the spine .
3. Malrotation manifested by medially directed calyces.
4- The renal pelvis and ureters are anterior and lateral in position .
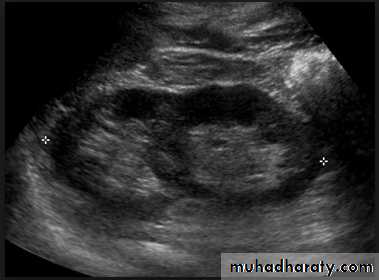
Poly cystic disease
Adult typePresent after the third decade of life , Familial.
Renal parenchyma is replaced by numerous cysts containing fluid , The cysts are of variable size ,
Clinically renal colic, loin mass , heamaturia and hypertension, Renal tissue interposed between the cysts after time dssimcted ended with renal failure
Almost bilateral.
IVU
Large kidney .Lobulated out-line.
Distortion of pelvi- calyceal system depend on cyst size, number and position.
In advanced cases there is elongation and stretching of minor and major calyces ( spider leg).
In advanced cases IVU shows non-functioning kidney .
Infantile type :
Usually affect liver, spleen and pancreas , Incompatible with life .I.V.U.
Bilateral Large kidney due to numerous small cysts
(1-2 mm size ).
- The out-line is not lobulated as in adult.
- I.V.U, may be normal.
- Nephrogram shows minute filling defects.
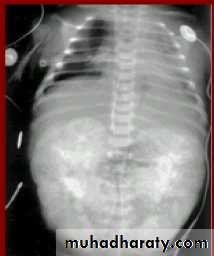
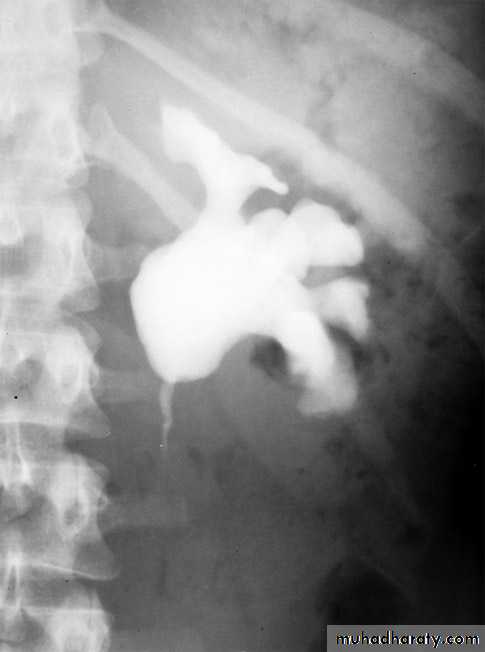
Infantile hydronephrosis
( PUJ OBSTRUCTION ):IVU shows :
Marked dilatation of pelvis and may be extra-renal.
Calyceal dilatation is late and in advanced cases form foot shape PCS
The ureter is not seen and when it is seen looksnormal .
Delayed film with I.V. diuretic produce gross dilatation .
Congenital anomalies of ureter
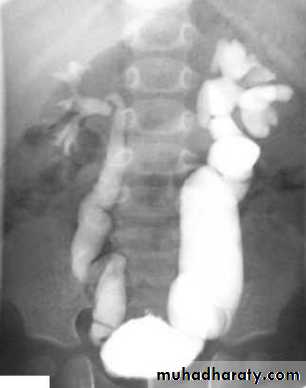
Mega ureter :- Unilateral or bilateral dilatation of the ureter with no evidence of organic obstruction.
Cause – unknown
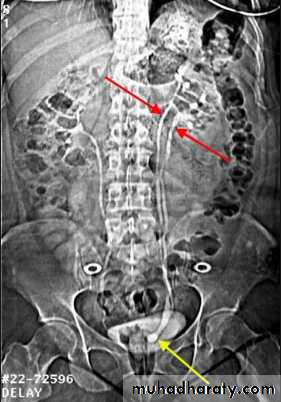
Retrocaval ureter :
The middle third of right ureter curve medially behind the IVC , then laterally to regain it’s normal position , this lead to obstruction of upper third of ureter.
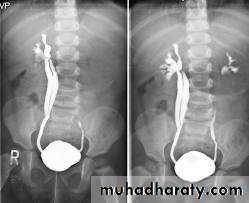
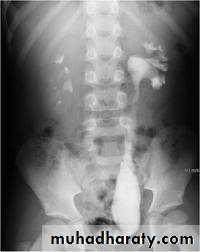
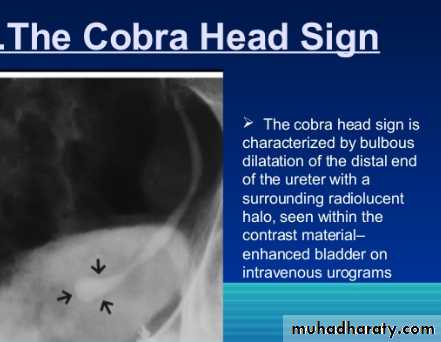
Ureterocele :
Congenital cystic dilatation of lower end of ureter ( intra-mural part) due to pin-hole meatus .May be simple or ectopic .
simple : the orifice is in proper position of bladder ,
Ectopic >> in bladder neck , urethra , uterus & vagina .
IVU :
- There is rounded or elliptical dilatation of lower end of ureter with thin linear filling defect around it , resembling (cobra head appearance),
- Proximal dilatation of rest of ureter .
- In advanced cases hydronephrosis .
- In obstructed ureterocele , filling defect in the bladder
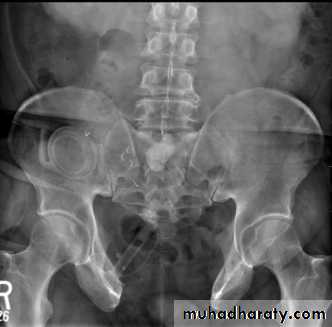
Ectopia vesica
(bladder extrophy) :bladder located at low position & plain x-ray shows separation of symphysis pubis .