
1
Fifth stage
Radiology
Lec-4
.د
محمد ميسر
28/10/2015
Introduction to ultrasound Imaging
HISTORY
The potential of ultrasound as an imaging modality was realized as early as the late 1940s
when, utilizing sonar and radar technology developed during World War II, Although pulse–
echo ultrasound had been used to diagnose a variety of medical problems since the 1950s,
it did not become a widely accepted diagnostic tool until the early 1970s when gray-scale
ultrasound mapping was introduced . Continuous wave (CW) and pulsed wave Doppler
(PW) ultrasound devices for measuring blood flow also became available during that time.
Duplex ultrasound scanners that combined both functions , thus allowing the imaging of
natomy and the measurement of blood flow with one single instrument, soon followed .
Today, ultrasound is the second most utilized diagnostic imaging modality in medicine,
second only to conventional x-ray, and is a critically important diagnostic tool of any
medical facility.
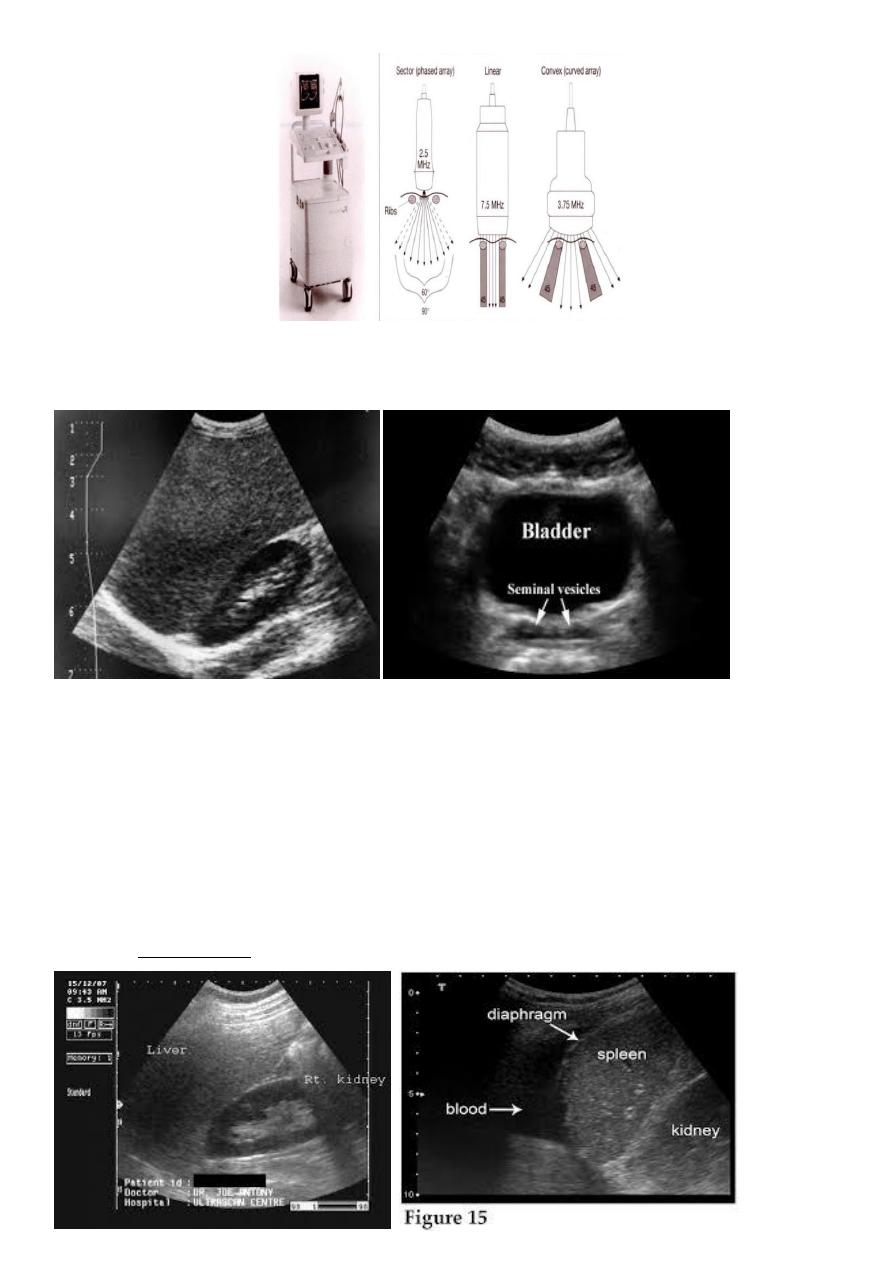
Physics of US imaging
The audible range of human ear is from 20 Hz to 20 kHz. Ultrasound sound waves in the 2-
to 10-MHz frequency range are used for imaging the body by detecting the intensity of the
reflected waves from various organs and displaying this reflected intensity as a gray-scale
(or color) image .
Because ultrasound is a wave, it transmits energy just like an
electromagnetic wave or radiation, but unlike an
electromagnetic wave, sound requires a medium in which to
travel and thus cannot propagate in a vacuum.
The sound waves are generated by applying an electrical pulse to
a piezoelectric crystal.
This crystal also acts as a receiver of the reflected waves after the
transmitter pulse is terminated.
The higher the frequency the less the penetration .
2
Ultrasonic descriptive terms
Typically, a cyst containing a clear fluid has few if any echoes (anechoic =black ) ,
Tissues such as liver and spleen give a picture with rather homogeneous small echoes due
to the fibrous interstitial tissue (hypo echoic , isoechoic or hyper echoic = gray scale
spectrum ) ,
Metals or Calcium in the bone and stones ( echogenic = white ) .
Biologecal effects :
Because ultrasound radiation is nonionizing, no adverse biologic effects have been
observed at diagnostic power levels

3
ROLE OF ULTRASOUND IN MEDICAL IMAGING
The many advantages that ultrasound can offer have enabled it to become a valuable
diagnostic tool in many medical disciplines such as
obstetrics and gynecology,
Abdominal ultrasound
Superficial structures such as breast, scrotal , thyroid , musculoskeletal ….ext
pediatrics, and pediatrics neurology.
Vascular ultrasound (Doppler)
Interventional radiology
Cardiology (echocardiography )
The advantages of ultrasound
Ultrasound is a form of nonionizing radiation and is considered safe to the best of
present knowledge.
It is less expensive than imaging modalities of similar capabilities.
It produces images in real time, un attainable at the present time by any other
methods.
It has a resolution in the millimeter range for the frequencies being clinically used
today, which may be improved if the frequency is increased.
It is portable and thus can be easily transported to the bedside of a patient.
It can yield blood flow information by applying the Doppler principle .
** Ultrasound is the tool of choice in obstetrics primarily because of no adverse
biologic effects , noninvasive nature, its cost-effectiveness, and its real-time imaging
capability. This role will not change in the foreseeable future.
Ultrasound also has several drawbacks.
Chief among them are :
Organs containing gases and bony structures cannot be adequately imaged without
introducing specialized procedures.
Only a limited window is available for ultrasonic examination of certain organs, such
as heart and neonatal brain.
It depends on operator skill.
It is sometimes impossible to obtain good images from certain types of patients,
including obese patients (penetration limitations ) .
4
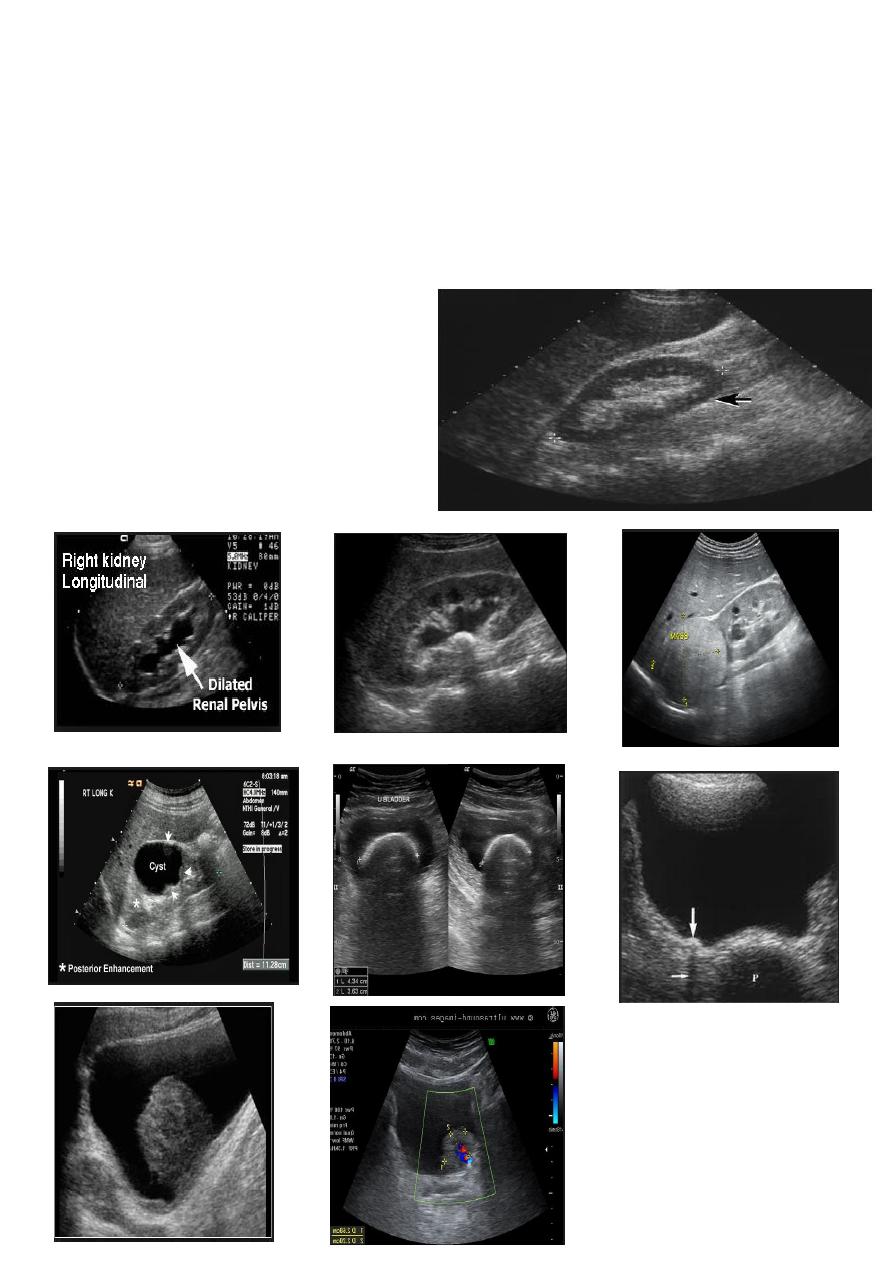
Urinary tract US
Renal ultrasound is a simple noninvasive examination .
The kidney is bean shaped and has bright central echoes because of the fat
surrounding the collecting system.
Ultrasound is typically ordered to exclude , stones , hydronephrosis or to evaluate
renal size or suspected renal cysts .
Normal renal ultrasound.
A longitudinal view of the right kidney was
obtained by passing the sound beam
through the right lobe of the liver. The
kidney is seen behind this, outlined by the
markers. The central bright echoes in the
kidney are due to fat around the collecting
system.
