
Pediatric : Rickets
د.فاضل
ال
عمار
Rickets:
is a childhood disorder involving softening and weakening of the bones.
It is primarily caused by lack of vitamin D, calcium, or phosphate.
It s a disease of growing bones , specific for children , before closure of
epiphyseal palates , du to poor mineralization .
Etiology :
- The main causes of rickets is vitamin D deficiency .. mainly is VD
- The hypophosphetemic rickets most of them is congenital so ..
early manifestation
- Which are a group of diseases with normal V.D
Normal ca ions
But .. low P ions
- All genetic disorders is X-linked recessive except “
hypophosphoemic rickets “ which is Dominant
- They already have low level of p ions ,, but it is rare
Calcipaenic Rickets phoshopaenic Rickets
VD Related Rickets Hypophosphotemic Rickets
1. Vitamin D Deficiency 1.
X-linked Dominant (PHEX
2. impaired Hepatic gene mutation)
23-hydroxylation 2.
Autosomal Dominant
3. Impaired RenaI 3.
Autosomal Recessive Type 1
1a-hydfoxylation of I 25(OH)D 4.
Autosomal Recessive Type 2
End organ resistance to 1 ;25(OH)2 •Associated with:
(a)McCune-Albright syndrome
Rickets due to Dietary (b)Tumor induced
Calcium Deficiency osteomalacia
(c)Linear nevus sebaceous sync
Raised in PTH
Renal Phosphate Wastage
Hypophosphetemia
Impaired Apoptosis of Terminally Differentiated chondrocytes in the
Growth plate

Reasons of vitamin D deficiency
•
Environmental conditions where sunlight exposure is limited
•
Dark Pigmentation
•
nutritional causes of rickets, a lack of vitamin D in the diet,
digesting milk products, lactose intolerant;
•
Liver Failure
•
Renal failure & RTA
•
Malabsorption & Steatorrhea
•
Drugs, antiepileptic, cs, antacid
1. Lack of sunshine due to:
1)
Lack of outdoor activities
2)
Lack of ultraviolet light in fall and winter
3)
Too much cloud, dust, vapour and smoke
2. Improper feeding:
1) Inadequate intake of Vitamin D
•
Breast milk 0-10IU/100ml
•
Cow’s milk 0.3-4IU/100ml
Egg yolk 25IU/average yolk
Herring
1500IU/1OO g
2)
Improper Ca and P ratio : normal ca:P is 2:1 .
Increase PTH means decrease in V.D.
*The level of V.D is low but the bioavailability is high .. so each child
after 2 months must given V.D 400 IU/Day
PTH > increase absorption of Ca .. decrease P
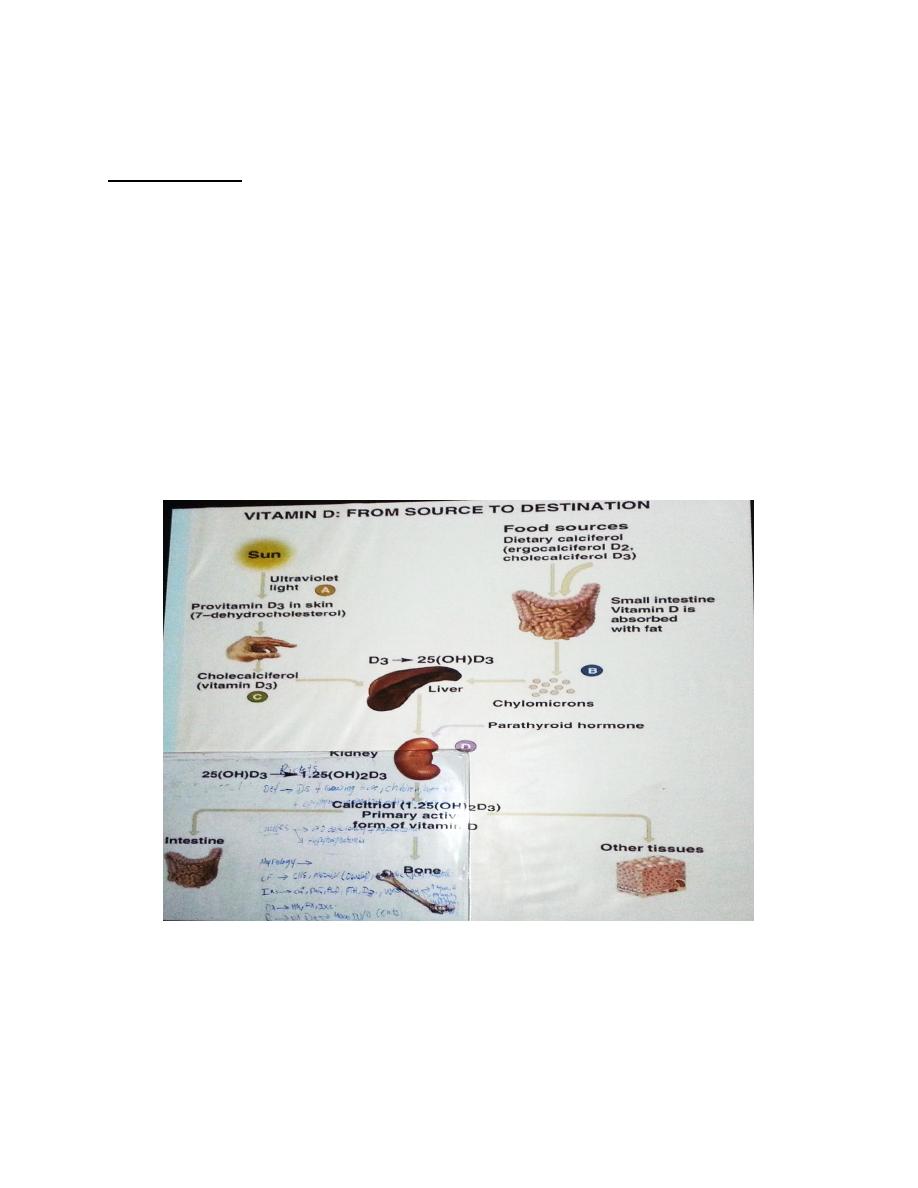
Physiology :
The sun light “ UV” convert 7-dihydrocholestrol found in skin into
Cholecaiciferol which enter blood .. go to liver .. 25(OH)D3 .. to the
kidney .. other enzymes “ 1,25(OH)2D3 “ “Called 1alpha “
.. 1,25(OH)2D3 the primary active form of V.D
PTH act on kidney very important .. it have positive effect on
hydroxylation (stimulate of hydroxylation at the level of kidney )
The active form act on the intestine >> increase the absorption of Ca &
P …. On bone >> liberation of Ca .
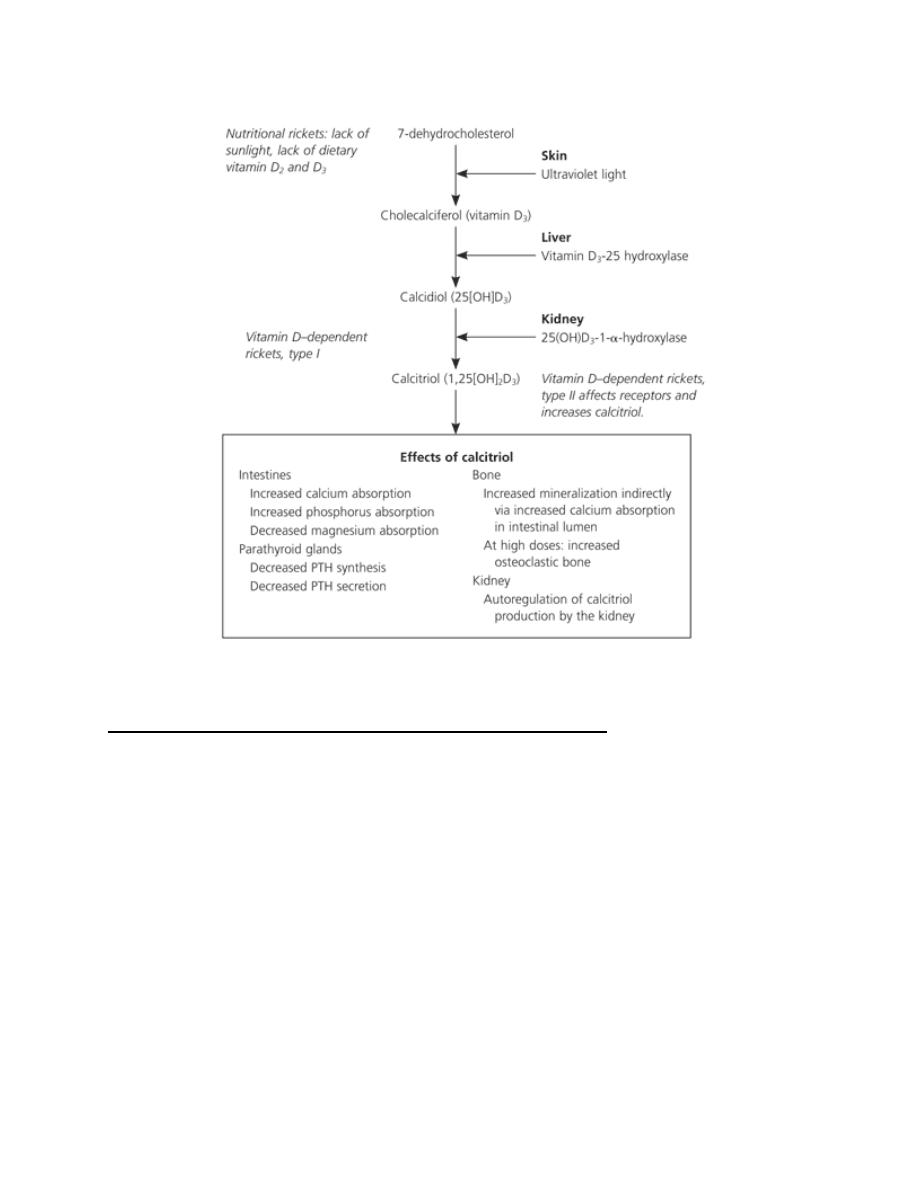
Calcitriol acts on regulation of calcium metabolism:
Calcitriol promotes absorption of calcium and phosphorus from the
intestine,
increases reabsorption of phosphate in the kidney,
acts on bone to release calcium and phosphate; 3KH
Calcitriol may also directly facilitate calcification.
Calcitriol (U5-DHC) - acts as a hormone rather than a vitamin, endocrine
and paracrine properties
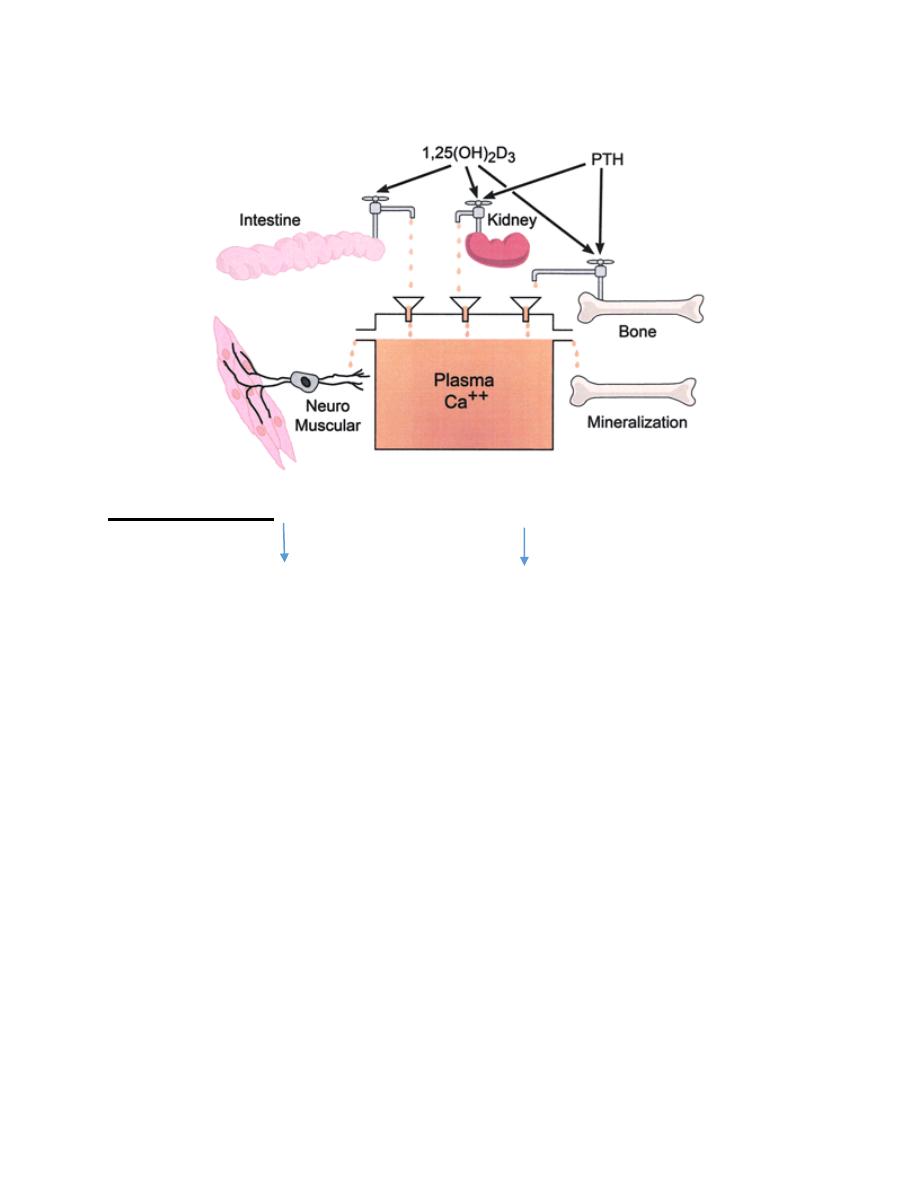
Plasma calcium homeostasis
Pathogenesis
V.D. deficiency … absorption of Ca & P .. serum Ca .. functioning of
PTH
•In the vitamin D deficiency state, hypocalcaemia develops, which
stimulates excess parathyroid hormone, which stimulates renal
phosphorus loss, further reducing deposition of calcium in the bone.
•Excess parathyroid hormone also produces changes in the bone
similar to those occurring in hyperparathyroidism.
• Early in the course of rickets, the calcium concentration in the serum
decreases.
•After the parathyroid response, the calcium concentration usually
returns to the reference range, though phosphorus levels remain low 0
•
Alkaline phosphatase, which is produced by overactive osteoblast
cells, leaks to the extracellular fluids so that its concentration rises to
anywhere from moderate elevation to very high levels.

So .. Ca in rickets .. at the beginning will decrease .. then will return to
normal because the effect of PTH
*ALP : is good indicator of Ca deficiency .. increase of ALP ? because the
liberation of Ca not only for it also for all tissues in the bones
Evaluation
The history in patients with rickets may include the following:
The infant's gestational age, diet and degree of sunlight exposure
should be noted.
A detailed dietary history should include specifics of vitamin D and
calcium intake.
A family history of short stature, orthopedic abnormalities, poor
dentition, alopecia, parental consanguinity may signify inherited rickets.
Why alopecia ?! because Hypophosphetemic rickets 70% of them birth
with it !
*_* >> Hypophosphormic rickets is rare !
The Clinical Signs
Affect all systems ..
CNS: Irritability, hidrosis, sleeplessness, sweating, crying.
Muscular: Generalized muscular hypotonia is observed in the most
patients with clinical signs of rickets.
Metabolic : decrease Ca >> tetanus

Skeletal : dividing from head to feet
Head :
Craniotabes manifests early in infant although this feature may be
normal in premature
if rickets occurs at a later J I age, thickening of the skull develops,
frontal Bossing , &delays the closure of the anterior fontanel.
Delay dentation
Protruding forehead , asymmetrical or box shape skull
Chest :
Pigeon chest “ pectus carinatum “
Funnel chest “ pectus excavetum “
Bumps in ribs cage called “ rachitic rosary “
In the chest, knobby deformities results in the rachitic rosary
along the costochondral junctions.
The weakened ribs pulled by muscles also produce flaring over
the diaphragm, which is known as Harrison groove.
The sternum may be -m pulled into a pigeon-breast deformity.
Hands : thickening ( widening of wrist and all long bones )
Legs :
Knock knee deformity (genu valgum)
Bowleg deformity ( genu varum )
Wind swip deformity
Increased tendency toward bone fractures. Because the softened
long bones may bend, they may fracture one side of the cortex
(greenstick fracture).

In the long bones, laying down of uncalcified osteoid at the
metaphases leads to J spreading of those areas, producing knobby
deformity (cupping and flaring of the metaphysis).
Back:
•Spine deformities (spine curves abnormally, including scoliosis or
kyphosis
•in more severe instances in children older than 2 years
Vertebral softening leads to kyphoscoliosis
Clinical signs
•
Pain in the bones of Arms, Legs, Spine, Pelvis.
*
Dental deformities
■ Delayed formation of teeth
* Defects in the structure of teeth
* Holes in the enamel
* Increased incidence of cavities in the teeth (dental caries )
•
Progressive weakness
•
Decreased muscle tone (loss of muscle strength)
•
Muscle cramps
•
Impaired growth
•
Short stature (adults less than 5 feet tall)
•
Fever or restlessness ,Specially at night

Laboratory findings
Laboratory investigation may include
*serum level of Ca (total & joined with albumin) = 2.2 mmo/l
* phosphorus 1.1 mmol/l
parathyroid hormone,
urea nitrogen
calcidiol
urine studies include urinalysis and levels of urinary calcium and
phosphorus.
The most common finding .. decrease VD and increase PTH
Classic radiographic findings include
widening of the distal epyphysis, fraying and cupping of the metaphysis,
and angular deformities of the arm and leg bones .
find : 1. Widening of the joint 2. Fraying 3. cupping
Clinical manifestation stages :
Early stage
Usually begin at 5 months old
Symptoms: mental psychiatric symptoms
Irritability, sleepless, hidrosis
Signs: occipital bald
Laboratory findings: Serum Ca, P normal or
decreased slightly. AKP normal or elevated slightly, 25(OH)D3 deceased
Roentgen-graphic changes: normal or slightly changed
Laboratory findings:
Serum Ca and P decreased Ca and P product decrease AKP elevated
HP
■Roentgen-graphic changes:
Wrist is the best site for watching the changes
Widening of the epiphyseal cartilage
Blurring of the cup-shape metaphyses of long bone
Types of Rickets :
Nutritional :
Result from inadequate sunlight exposure or inadequate intake of VD ..
Ca or P .
Vitamin D-dependent rickets:
type I is secondary to a defect in the gene that codes for the production
of renal 25(OH)D3
Vitamin D-dependent rickets, type II is a rare autosomal disorder
caused by mutations in the . Type II does not respond to vitamin D
treatment; elevated levels of circulating calcitriol differentiate this type
from type I.
hypophosphatemic rickets
|Rickets refractory to vitamin D treatment may be [caused by the most
common heritable form, known as vitamin D-resistant rickets or familial
hypophosphatemic rickets.

Because of mutations of the phosphate-regulating gene on the X
chromosome^ renal wasting of phosphorus at the proximal tubule level
results in hypophosphatemia. Normal levels of calcitriol are found in
this disorder
Treatment :
•
4000IU of oral vitamin D per day administered for approximately
one month.
•
Parents are instructed to take their infants outdoors for
approximately 20 minutes per day with their faces exposed. Children
should also be encouraged to play outside.
•
Foods that are good sources of vitamin D include cod liver oil, egg
yolks, butter and oily fish. Some foods, including milk and breakfast
cereals, are also fortified with synthetic vitamin D
1. Special therapy: Vitamin D therapy
A. General method: Vitamin 0 4000 IU/day for 2-4 weeks, then change
to preventive dosage - 400 IU.
6 Stoss therapy: A single large dose: For severe case, or Rickets with
complication, or those who can’t bear oral therapy
Vitamin D3 300000 IU, im.
preventive dosage will be used after 2-3 months.
Treatment of VD deficiency Recktes :
*
Improvement in symptoms (~ 3weeks)
*
I in serum PTH & alkaline phosphatase

*
i in serum phosphate, calcium & 25(OH)vitamin D ' .Radiological
heating (- 3 months)
Improvement of bow legs or knock-knees (- 3 years)
Prevention :
Vitamin D supplements
. Because of human milk contains only a small amount of vitamin D, the
American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends that all breast-fed
infants receive 400IU of oral vitamin D daily beginning during the first
two months of life and continuing until the daily consumption of
vitamin D-fortified formula or milk is two to three glasses, or 500IU.
AAP also recommends that all children and adolescents should receive
400IU a day of vitamin D.
Noor Rahman
