Physiology of the Cell
The basic living unit of the body is the cell. Each organ is an aggregate of many different cells held together by intercellular supporting structures. A typical cell contains nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm by a nuclear membrane, and the cytoplasm is separated from the surrounding fluids by a cell membrane.The cell membrane (also called the plasma membrane)
Envelops the cell, is a thin, elastic structure. The approximate composition is:
proteins, 55 %
phospholipids, 25 %
cholesterol, 13 %
other lipids, 4 %
and carbohydrates, 3 %
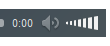
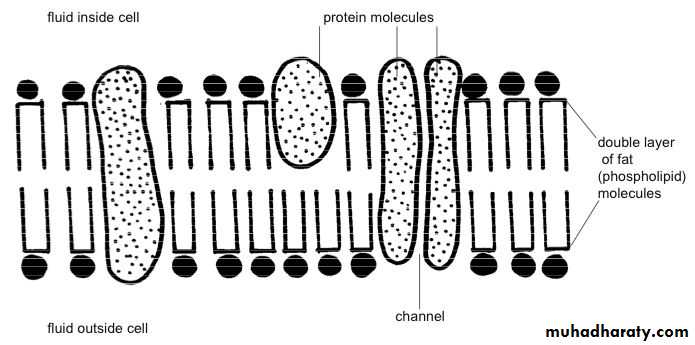
The lipid is bilayer is of phospholipid molecules. One end of each phospholipid molecule is soluble in water; that is, it is hydrophilic. The other end is soluble only in fats; that is, it is hydrophobic. The hydrophilic portions constitute the two surfaces of the complete cell membrane. The lipid layer is impermeable to the water-soluble substances. Conversely, fat-soluble substances, such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, and alcohol, can penetrate this portion of the membrane.
Cell Membrane Proteins. Globular masses floating in the lipid bilayer usually are glycoproteins.
Two types of proteins occur:
A-Integral proteins that protrude all the way through the membrane, form channels (or pores) through which water molecules and water-soluble substances, can diffuse.
Other integral proteins act as carrier proteins for transporting substances that otherwise could not penetrate the lipid bilayer
Integral membrane proteins can also serve as receptors for water-soluble chemicals, such as hormones,
B-Peripheral protein is often attached to the integral proteins. These peripheral proteins function as enzymes.Fig (1 and 2)
fig 1 and 2
Membrane Carbohydrates
The entire outside surface of the cell often has a loose carbohydrate coat called the glycocalyx have several important functions
1-Many of them have a negative electrical charge that repels other negative objects.
2- The glycocalyx of some cells attaches to the glycocalyx of other cells, thus attaching cells to one another.
3-Many of the carbohydrates act as receptor substances for binding hormones, such as insulin;
4- Some enter into immune reactions
Cytoplasm and Its Organelles
The different substances that make up the cell are collectively called protoplasm
Protoplasm is composed mainly of five basic substances: water, electrolytes, proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates
Water. The principal fluid medium of the cell, which is present in most cells (except for fat cells) in a concentration of 70 to 85 %. Many cellular chemicals are dissolved in the water.
Ions. The most important ions in the cell are potassium, magnesium, phosphate, sulfate, bicarbonate, and smaller quantities of sodium, chloride.
Proteins. normally constitute 10 to 20 % of the cell mass. These can be divided into two types: structural proteins and functional proteins
Structural proteins are present in the cell mainly in the cilia, nerve axons.The functional proteins are mainly the enzymes of the cell
Lipids. The important lipids are phospholipids and cholesterol, which together constitute only about 2 % of the total cell mass. In the fat cells, lipids often account for as much as 95 % of the cell mass. They represents the body’s main storehouse of energy.
Carbohydrates. Carbohydrates play a major role in nutrition of the cell. total amount about 1 %of their total mass ,However, carbohydrate in the form of dissolved glucose is always present in the surrounding extracellular fluid so that it is readily available to the cell.
The cytoplasmic organelles.
Five especially important organelles: the endoplasmic reticulum, the Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, lysosomes and peroxisomes(contain oxidase enzyme).
Endoplasmic Reticulum
network of tubular and flat vesicular structures. Their walls similar to the cell membrane.
a-Granular Endoplasmic Reticulum
Part of the endoplasmic reticulum has an Attachment of granular particles called ribosomes. They function to synthesize new protein molecules in the cell
b-Agranular(or smooth) Endoplasmic Reticulum. Part of the endoplasmic reticulum has no attached ribosomes. The agranular reticulum functions for the synthesis of lipid substances
Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus functions in association with the endoplasmic reticulum. small “transport vesicles” (also called endoplasmic reticulum vesicles, or ER vesicles) continually pinch off from the endoplasmic reticulum and fuse with the Golgi apparatus they processed in the Golgi apparatus to form lysosomes, secretory vesicles.
Lysosomes
A membrane-bound organelle found in most cells. They are spherical vesicles which contain hydrolytic enzymes (hydrolase),So its provide an intracellular digestive system
lysosom digest:
(1) damaged cellular structures
(2) food particles
(3) bacteria.
Mitochondria
The mitochondria, are called the “powerhouses” of the cell. Without them cells would be unable to extract enough energy from the nutrients, and essentially all cellular functions would cease. The liberated energy is used to synthesize a “high-energy” substance called adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Nucleus
The nucleus is the control center of the cell. Briefly, the nucleus contains large quantities of DNA, which are the genes.
Ingestion by the Cell—Endocytosis
Very large particles enter the cell by endocytosis. The principal forms of endocytosis are pinocytosis and phagocytosis.
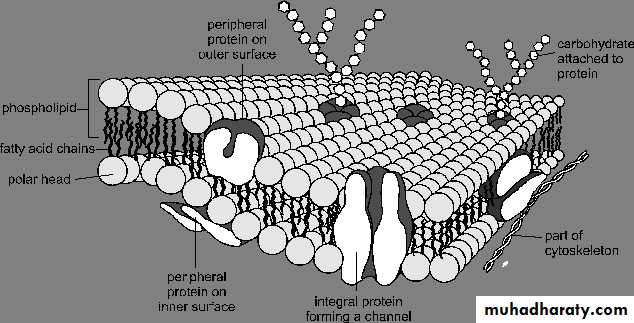
Pinocytosis :Means cell drinking is the invagination of the cell membrane to form a pocket, which then pinches off into the cell to form a vesicle filled with a large volume of extracellular fluid and molecules within it.Fig 3
Fig 3
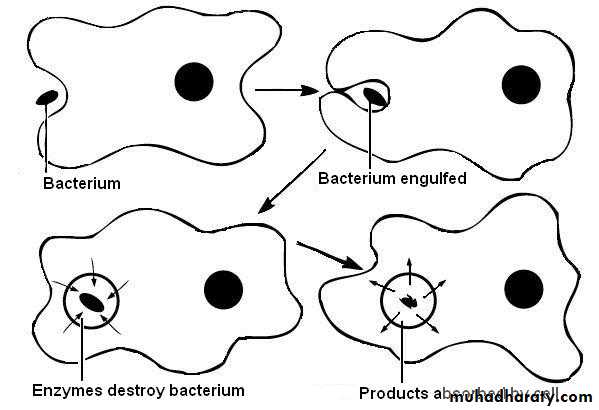
Phagocytosis Means cell eating :The edges of the membrane around the points of attachment evaginate outward to surround the entire particle; to form a closed phagocytic vesicle.
Actin surround the phagocytic vesicle and contract around its outer edge, pinch the vesicle and pushing the vesicle to the interior of the cell. ingestion of large particles, such as bacteria is by phagocytosis. Only certain cells have the capability of phagocytosis, like the white blood cells. Fig 4
.Fig 4
Digestion of Pinocytotic and Phagocytic Foreign Substances Inside the Cell
Almost immediately after a pinocytotic or phagocytic vesicle appears inside a cell, one or more lysosomes become attached to the vesicle and empty their acid hydrolases to the inside of the vesicle, Thus, a digestive vesicle is formed inside the cell cytoplasm in which the vesicular hydrolases begin hydrolyzing the proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and other substances in the vesicle. The products of digestion are small molecules of amino acids, glucose,phosphates, and so forth that can diffuse through the membrane of the vesicle into the cytoplasm. What is left of the digestive vesicle, called the residual body represents indigestible substances. this is finally excreted through the cell membrane by a process called exocytosis
Regression of Tissues and Autolysis of Cells.
Tissues of the body often regress to a smaller size. For instance, this occurs in the uterus after pregnancy, in muscles during long periods of inactivity, and in mammary glands at the end of lactation. Lysosomes are responsible for much of this regression.
Exocytosis. In a highly secretory cell, the vesicles formed by the Golgi apparatus are mainly secretory vesicles containing protein substances that are to be secreted through the surface of the cell membrane .These secretory vesicles first diffuse to the cell membrane, then fuse with it and empty their substances to the exterior by the mechanism called exocytosis
Uses of ATP for Cellular Function.
Energy from ATP is used to :
(1) to supply energy for the transport of substance through the cell membrane
(2) to promote protein synthesis by the ribosomes
(3) to supply the energy needed during muscle contraction