Baghdad College of Medicine / 5
th
grade
Student’s Name :
Dr. Ahmed Khalaf
Lec. 2
Hand Examination &
Infection
Wed. 4 / 10 / 2016
DONE BY : Ali Kareem
مكتب اشور لالستنساخ
2016 – 2017

Hand Ex. & Inf. Dr. Ahmed Khalaf
4-10-2016
2
©Ali Kareem 2016-2017
Hand Examination & Infection
Hand :
Mechanical device with receptors that can produce powerful, delicate and fine movements. The
requirement for the hand function:
1- Good skin coverage with intact sensation.
2- Supple joints and mobile fingers.
3- Pain free movements and with good tendon excursion.
4- Coordination
Functions of hand :
1- Fine pinch, e.g. picking up a small object .
2- Power grip, e.g. holding a hammer .
3- Key grip, e.g. holding a key .
4- Chuck grip, holding a pen .
5- Hook grip, e.g. carrying a suitcase .
History:
The patient age, hand dominance, occupation and history of prior upper extremities problem are
obtained.
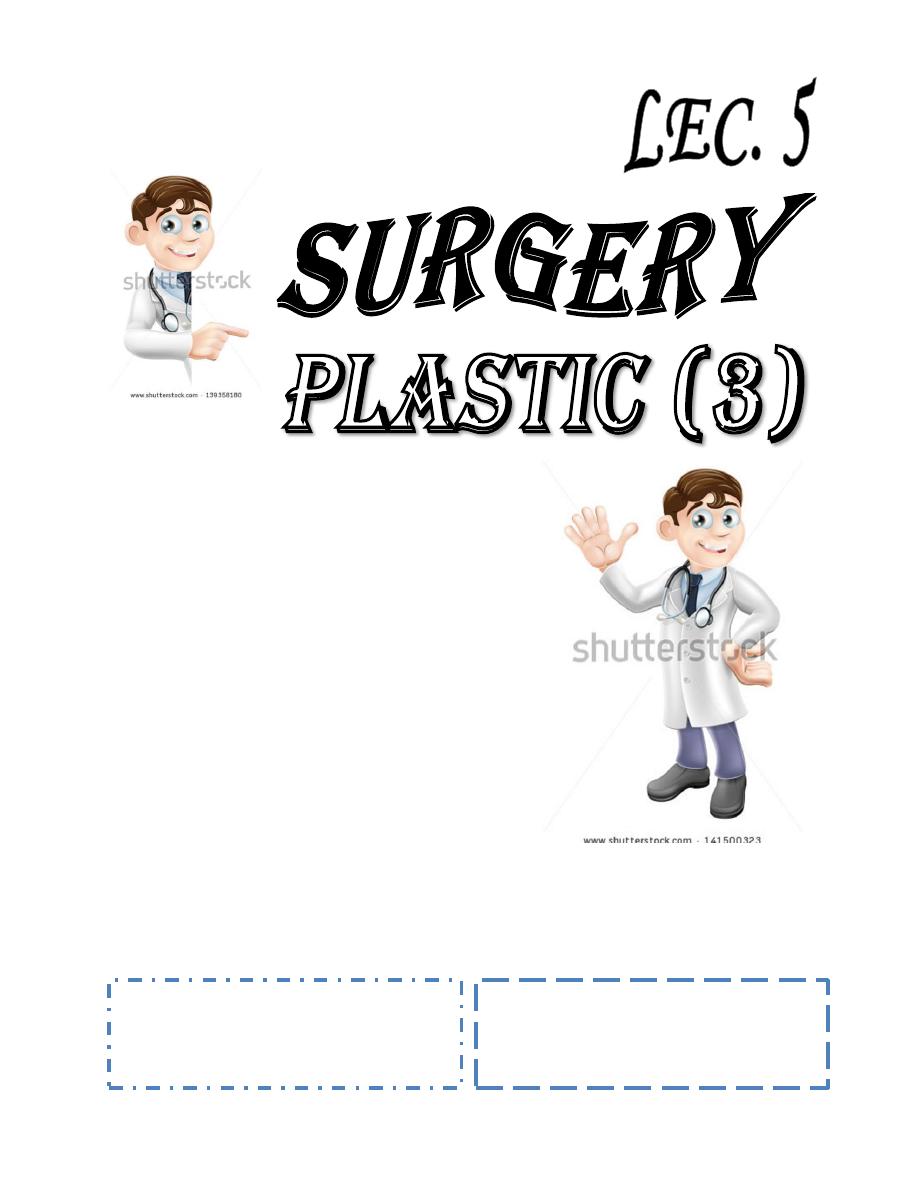
For traumatic injury ask about the following :
1- When? How much time has elapsed since injury?
Contamination usually low in 1
st
6 hours after injury.
2- Where? What was the environment at site of injury?
Whether clean or dirty environment.
3- How?
Mechanism of injury whether clear cut or crushing injury.
Position of hand or finger at time of injury (fall on outstretch hand or whether hand was open or
grasping)
Hand Ex. & Inf. Dr. Ahmed Khalaf
4-10-2016
3
©Ali Kareem 2016-2017
4- Previuos treatment which was given and tetanus immunization status?
5- Any associated injury?
Physical examination:
Look:
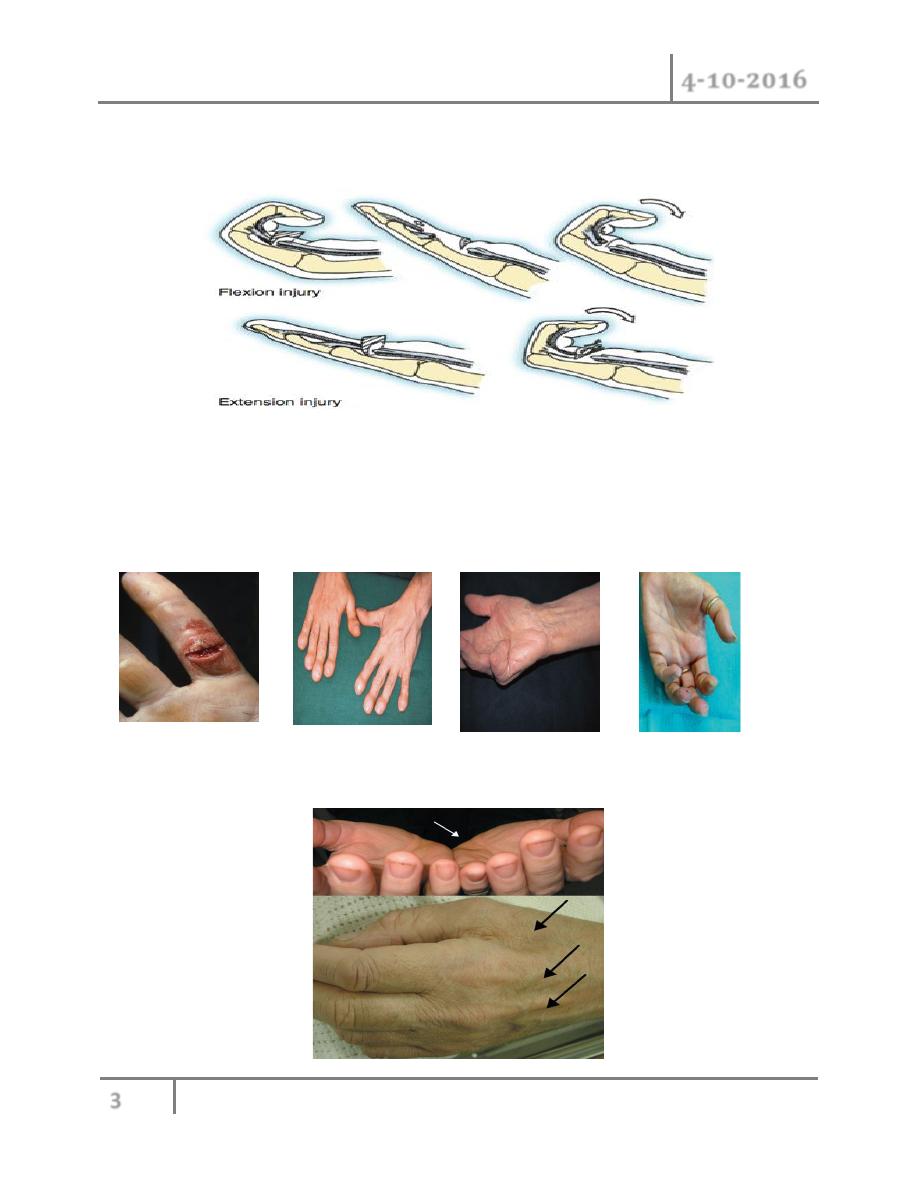
Skin: For any cuts, haematoma, swelling, bruise, nail, also look for tight Bands in palm leading
up to fingers (Duputyren contracture).
Soft tissues : Check for thenar and hypothenar wasting, also check for wasting in cleft between
fingers dorsally (damage to ulnar nerve or T1)
Hand Ex. & Inf. Dr. Ahmed Khalaf
4-10-2016
4
©Ali Kareem 2016-2017
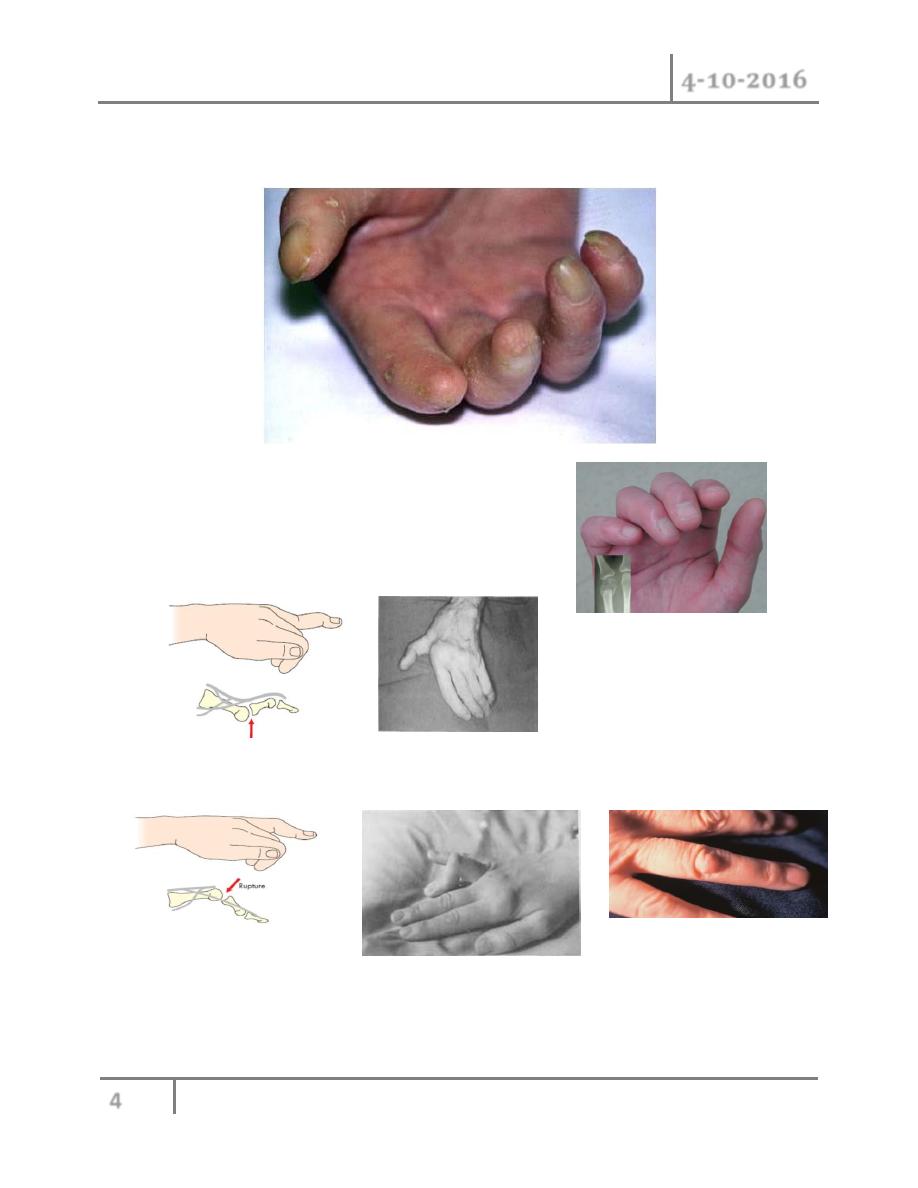
Circulation : pallor of finger indicate arterial insufficiency or anaemia. ischaemic atrophy of the
pulp of fingers make the finger thin and pointed.
Bone : Look for any bone malialigmant.
for swan neck deformity (hyperextension in middle IP joint
With flexion of distal IP joint).
Look for Boutonniere deformity (hyperextension at distal IP joint With flexion at middle IP
joint).
Also look for Heberden nodule over the DIP joint dorsally which associated with osteoarthritis,
or Garrod knuckle pad over PIP dorsally.
Hand Ex. & Inf. Dr. Ahmed Khalaf
4-10-2016
5
©Ali Kareem 2016-2017
Feel :
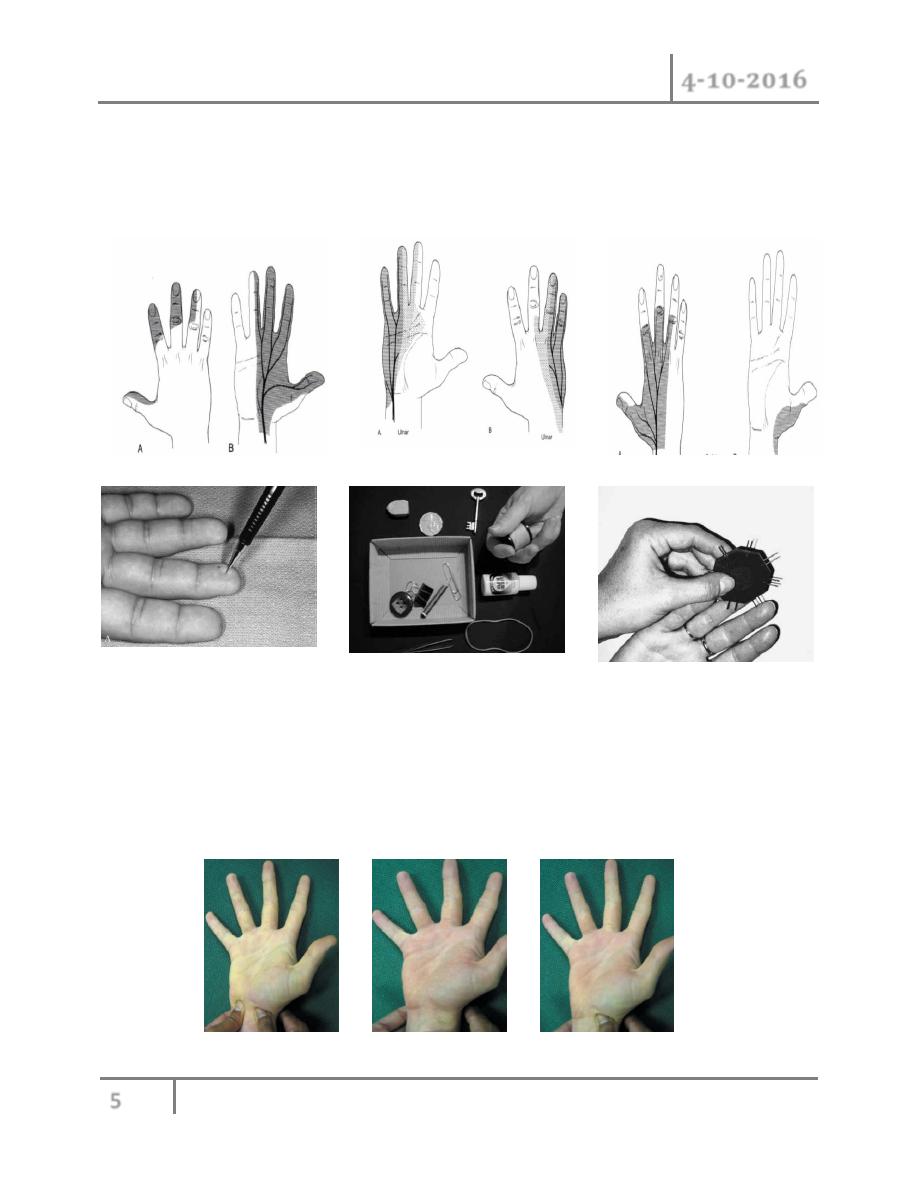
Skin: feel for loss sensation or altered sensation by (cotton wick, pin Test, 2 point
discrimination) along median, ulnar, radial nerve distribution
Soft tissues: feel for wasting of thenar and hypothenar muscles.
Circulation: feel the temperature of skin. Feel radail and ulnar pulses at the wrist. Also feel for
capillary refilling.
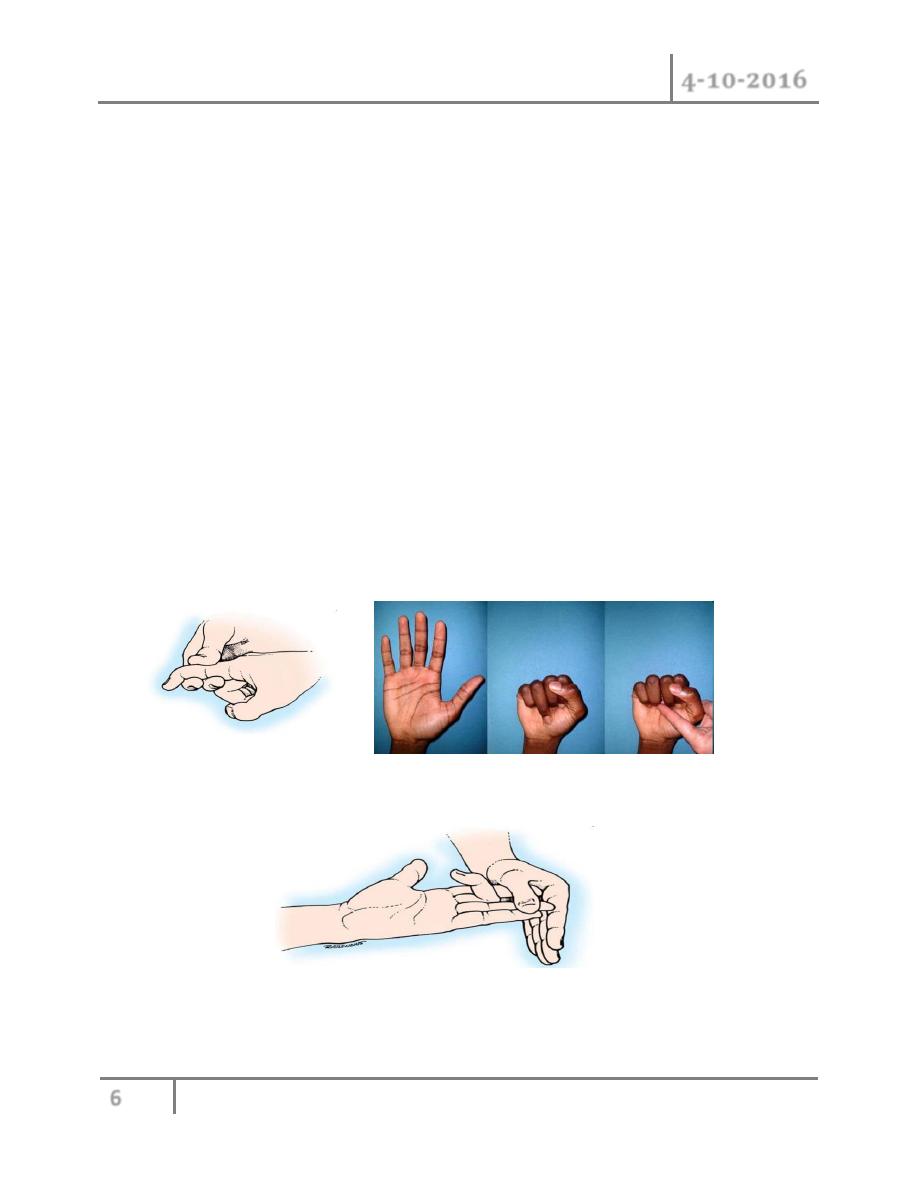
Allen`s test: ask the patient to clench one fist tightly and then compress the ulnar and radial
arteries at wrist with your thumb. After 10 seconds, ask the patient to open hand. The palm will
be white. Reales the compression on the radial artery and watch the bloood flow into the hand,
repeated the procedure on the ulnar artery.
Allen test
Hand Ex. & Inf. Dr. Ahmed Khalaf
4-10-2016
6
©Ali Kareem 2016-2017
Bone: feel for any swelling, tenderness.
Move:
Active: ask patient to roll finger from full extension to full flexion .test Flexion of MCP joint in
isolation while keeping PIP joint and DIP joint extended. this test patient ability to intrinsic
muscles movement. Also test abduction and adduction of fingers.
Passive: Passively move the joints to see the range of movement, Pain in movement, and
unstable joints
Flexor tendon examination:
There are 4 methods for examination:
1- active motion:
o by blocking all joints in single digit and allow only distal interphalangeal (DIP) flexion,
one can examine flexor digitorum profundus (FDP).
o by holding all digit in extension except in digit to be examine, and ask patient to flex
proxiaml interphalangeal joint (PIP), one can examine flexor digitorum supeficialis
(FDS)
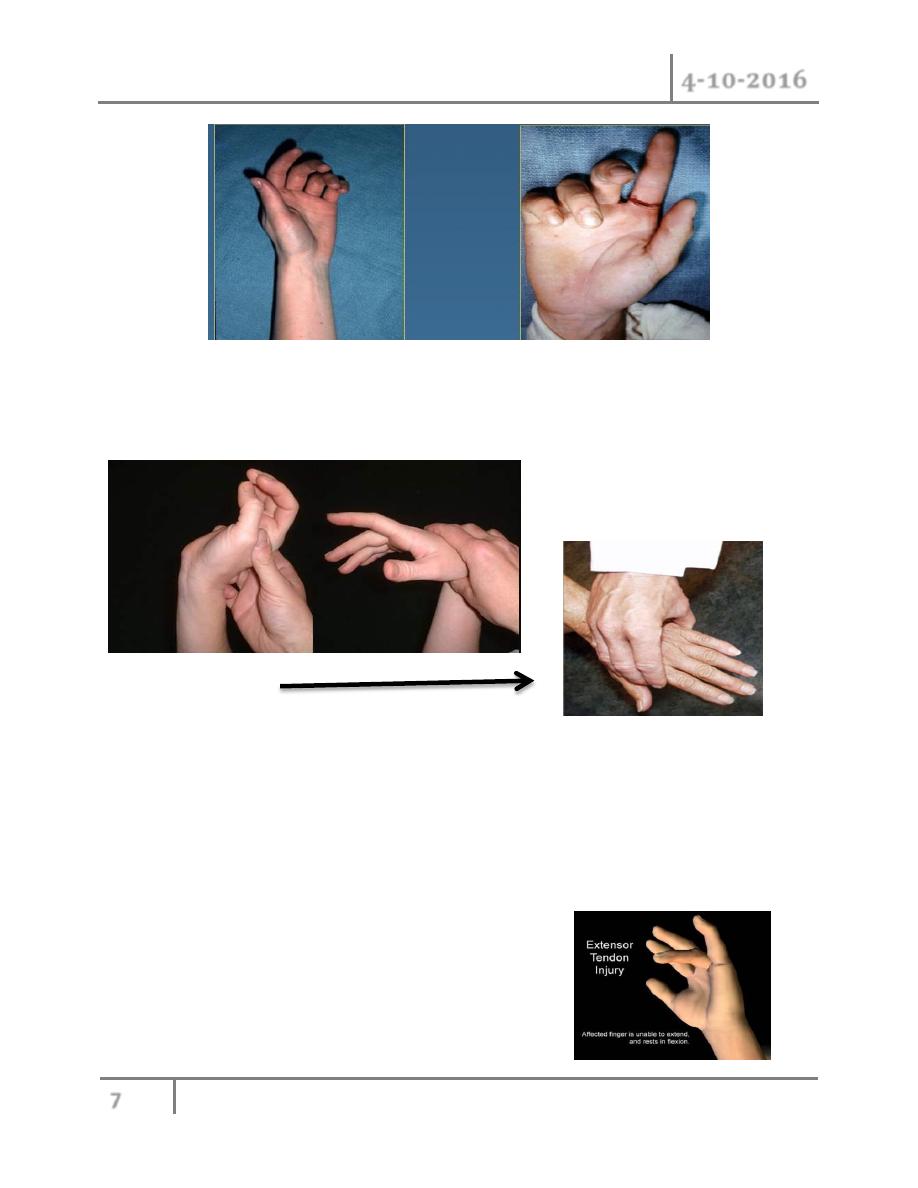
2- observation at rest:
See the cascade of digit at rest ,normally there is progression of increasing flexion from index to
little finger. Extended position of digit mean suspected flexor tendon injury.
Hand Ex. & Inf. Dr. Ahmed Khalaf
4-10-2016
7
©Ali Kareem 2016-2017
3- tenodesis effect:
The wrist moved from flexion to extension passively, normal function is demonstrated by the
finger curling into flexion with wrist extension and should be extended (open) with wrist flexion
4- squeeze test:
Can result in flexion of intact tendon.
Extensor tendon examination:
1- active motion:
Placing hand flat on table and ask patient to lift each finger from table. Test is done against light
resistance from examiner hand.
2- observation at rest:
With extensor tendon injury we see the finger slightly more
flexed than other normal digit.
3- tenodesis effect.

Hand Ex. & Inf. Dr. Ahmed Khalaf
4-10-2016
8
©Ali Kareem 2016-2017
Investigation:
o Plain x-ray
o E.M.G
o Ultrasound
o Doppler ultrasound
o Angiography
o Radioistope study
o Arthroscope.
o CT/SCAN
o MRI
General principles of management of hand infection:
If hand infection are not treated promptly, tendon adhesion, necrosis and even repture, stiffness,
and loss of function will ensue.
In summery:
Trauma ,Infection →swelling →ligament adhesion and contracture →loss of function
1- Rest: resting an infecting part minimizes the opening of tissue plane along which it can
spread and the breaking down of barriers which is important for wall off the infection.
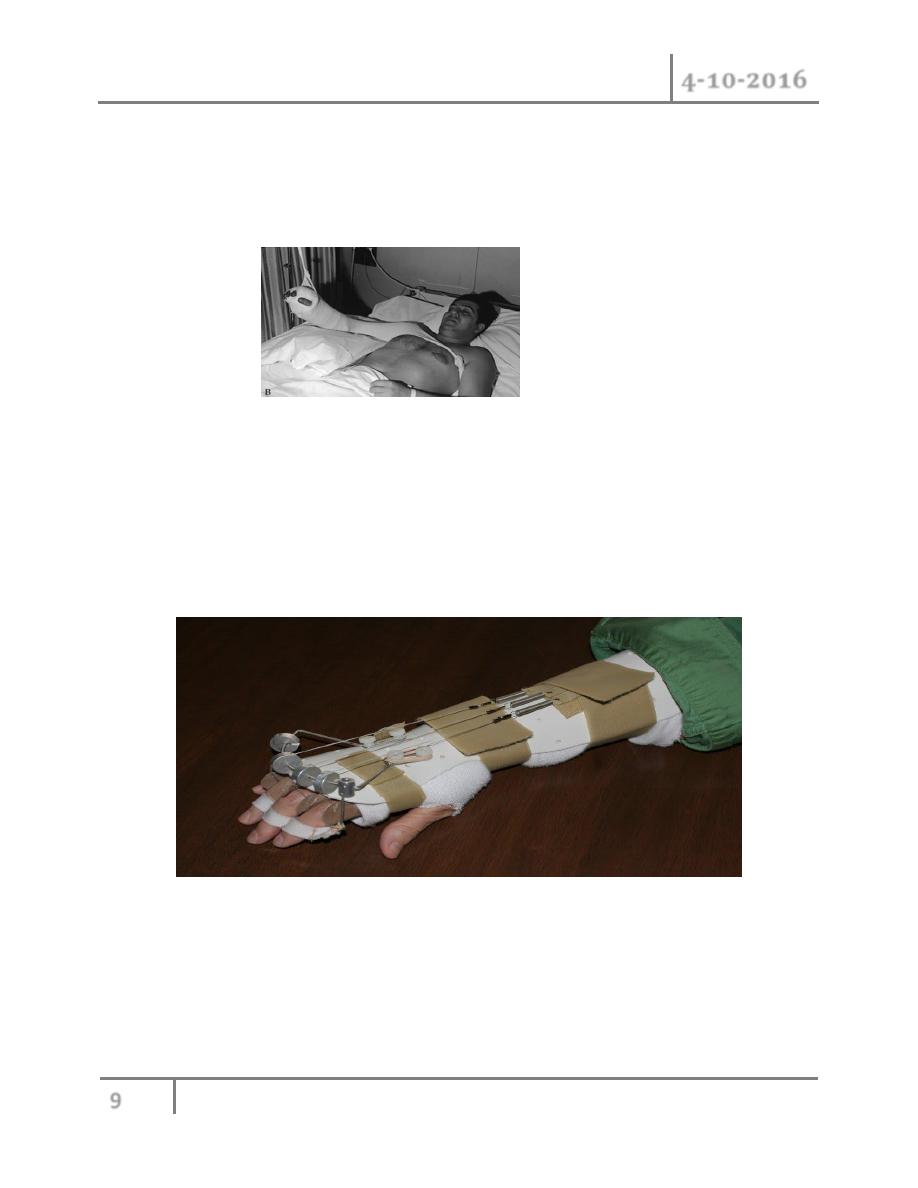
2- Splinting : when we need to immobilize hand it should be putting in (safe position) this
keep ligament under maximum stretch to prevent their shortening and subsequent
restriction of joint mobility.
Safe position: IP joint extension, MCP joint flexion and
Palmer abduction of thumb and slight wrist extension.
Hand Ex. & Inf. Dr. Ahmed Khalaf
4-10-2016
9
©Ali Kareem 2016-2017
3- Elevation: of hand above the level of the heart so encouraging venous and lymphatic
return , which is minimizes edema due to the inflammatory reaction and poor muscular
activity which is due to pain and therapeutic rest.
The point of reference for elevation of the part is its relation to right atrium of heart.
4- heat application: the application of heat increase the delivery of inflammatory cells to
affected area by vasodiltation, and laso improve patient comfort. Moist heat more
effective than dry heat. Frequent seperated application are recommended rather than
attempting to do it continuously.
5- movement and rehabilitation : because prolonged immobilization can lead to stiffness of
small joints, immobilization should be maintained where essential for minimal time while
continued movement of other parts is encourages.
6- antibiotics: in all cases , initial antibiotic selection has to be on a (best guess). The
majority of hand infection are due to staphylococcal and streptococcal bacteria, with
anaerobic bacteria being relatively rare. Therefore, it is recommended that for ordinary
caese , a penicillinase resistance antibiotic such as 1
st
generation cephalosporin, which
may combined with antistaph penicillin, be used. Antibiotic change later according to
result of culture and sensivity test.
Hand Ex. & Inf. Dr. Ahmed Khalaf
4-10-2016
10
©Ali Kareem 2016-2017
7- surgical drainage: any abscess or necrotic tissues that can be positively identified, it
should be surgically drained and specimen for bacterial studies should be taken.
Hand infection:
may involved skin, subcutaneous tissue, tendon sheath, joints and bone and may be caused by
wide of vraiety of pathogens, including viruses,bacterai,mycobacteria and fungi.
Three major factors contribute to development of infection in hand:
1- the infecting organism
2- the anatomic location of the infected space.
3- systemic and local host defense factors.
Specific infection:
1- Cellulitis and lymphangitis: all hand infection is begin as cellulitis. cellulitis is non-
supporative superficial infection of skin. there is poor localization in addition to the
cardinal sign of inflammation i.e. redness,hotness,swollen,pain and tendrness.usaully
caused by B hemolytic streptococci, staphylococci and c.perfringens.tissue
destruction,gangene and ulceration may follow ,which are caused by release of protease.
Systemic sign and symptoms like fever,chill,tachycardia follow the realese of exotoxine
and cytokines into circulation.
Cellulitis is usually located at the point of injury and subsequent tissue infection.
Lymphangitis is part of a similar process and present in painful red streak in affected lymphatic
usually accompanied by painful lymph node groups in the related drainage area.

Hand Ex. & Inf. Dr. Ahmed Khalaf
4-10-2016
11
©Ali Kareem 2016-2017
The vast majority of cases will respond to oral antibiotics, rest, warm soaks and elevation.
Because gram positive organism are typically responsible, first generation cephalosporin or
antistaph penicillin is appropriate e.g. flucloxacillin.
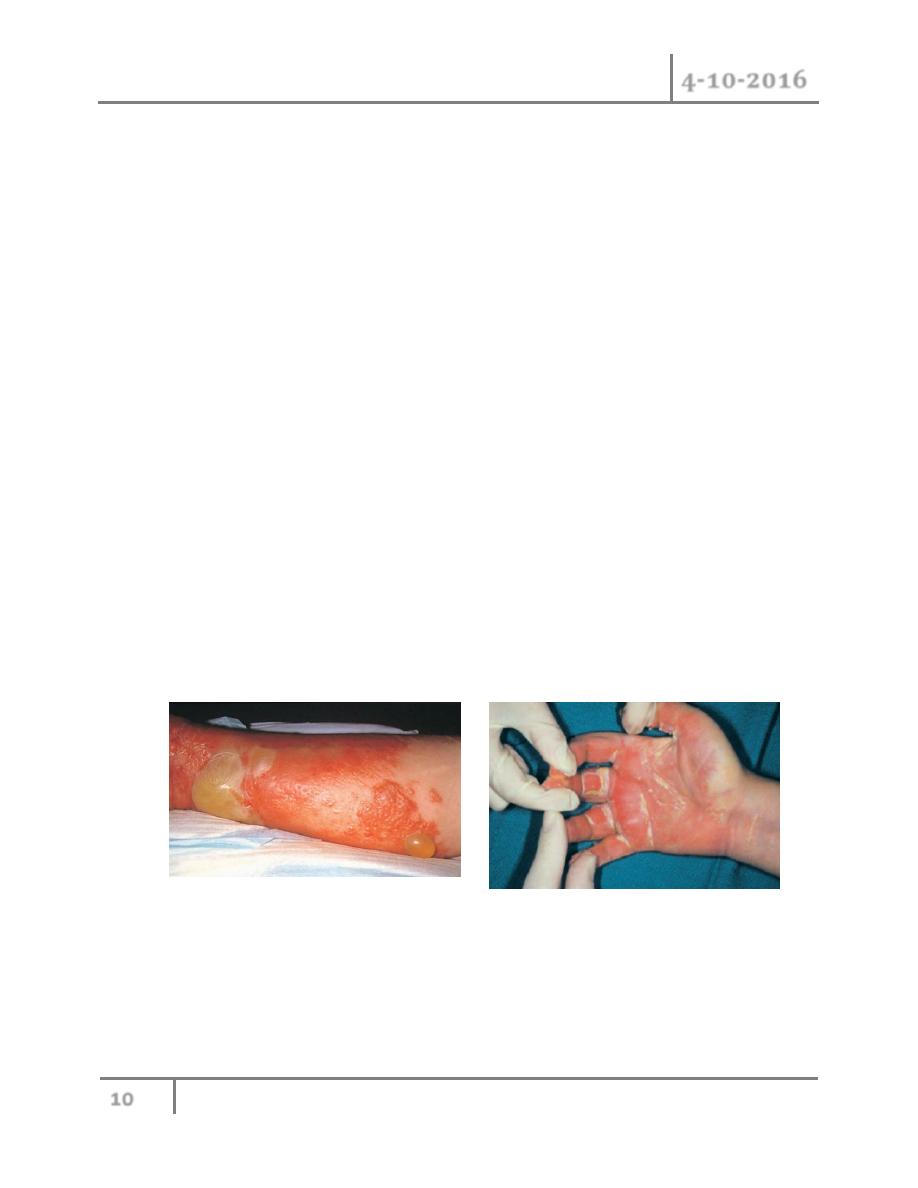
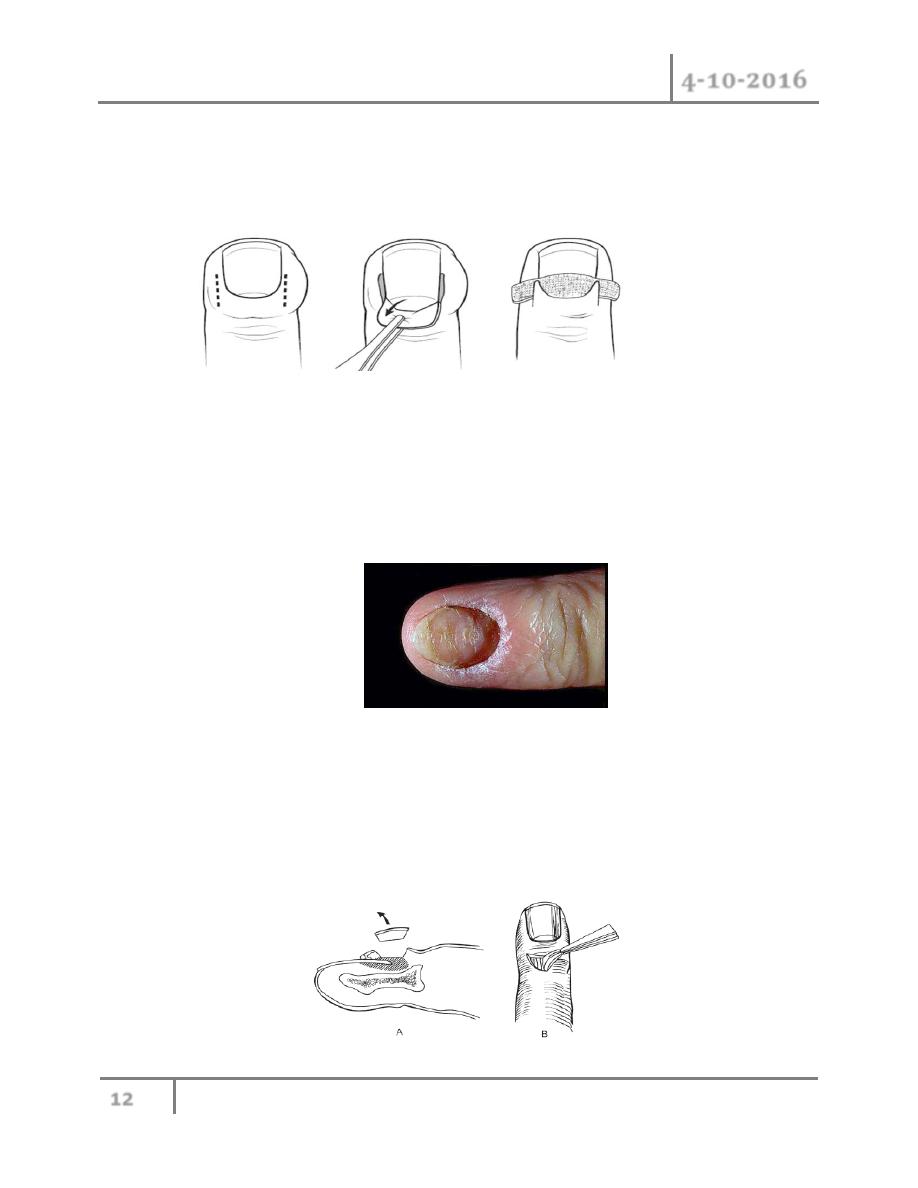
2- Acute paronychia: this is the most common infection of the hand, it is infection of the soft
tissues alongside the nail plate. this is typically result from inoculation of bacterium
between the nail and surrounding tissues, often as consequence of relative minor trauma
such as nail biting, hangnail, puncture wound, foreign body and manicure.
S.aureus is the most common isolate bacteria, but anaerobes are frequently present and
attributed to contamination of the wound with oral secretion. Usually presented with
pain, erythema and oedema of tissues surrounding the nail, later on if no treated abscess
may be formed.
An infection that involves the proximal nail and one lateral fold known as eponychia
When the abscess dissects under the nail sulcus to the opposite lateral fold know as run around
abscess. Confined collection of pus can place presure on germinal matrix, resulting in nail
deformity.
Treatment: if the paronychia diagnosed at an early stage before abscess formed, oral
antibiotics, warm soak, rest, and elevation may be sufficient treatment.
For abscess localized to one lateral fold , the fold can be elevated bluntly by Freer elevator or
blade can be used.
Hand Ex. & Inf. Dr. Ahmed Khalaf
4-10-2016
12
©Ali Kareem 2016-2017
For treatment of eponychia : two incision are made at the edge of nail fold, the proximal nail is
excised , and the fold is elevated and packed with guaze.
Rarely, the pus collection will elevated entire nail plate, which need at that time removal of nail
plate.
3- Chronic paronychia: A paronychia may present as a chronic process, with an indurated,
erythematous eponychium (proximal nail fold)and occasional drainage from the nail fold
and longitudenal grrove in the nail plate. This occurs more frequently in diabetic patients
and in those with frequent occupational exposure to a moist environment, such as food
service handlers with frequent immersion of the hands in water. Candida albicans is the
most common pathogen responsible.
Treatment: it may resolve if the hands are kept dry and the nail fold are regularly
dressed with topical antifungal e.g. clotrimazole and steroid.
Removal of a thickened , deformed nail plate may be improve the result.
If all are failed , eponychial marsupialization is done, where a crescent-shaped portion of the
skin overlying the proximal nail bed is excised , with removal of all granulation tissues down to
germinal matrix. The wound is leave to healed by secondary intention.
Hand Ex. & Inf. Dr. Ahmed Khalaf
4-10-2016
13
©Ali Kareem 2016-2017
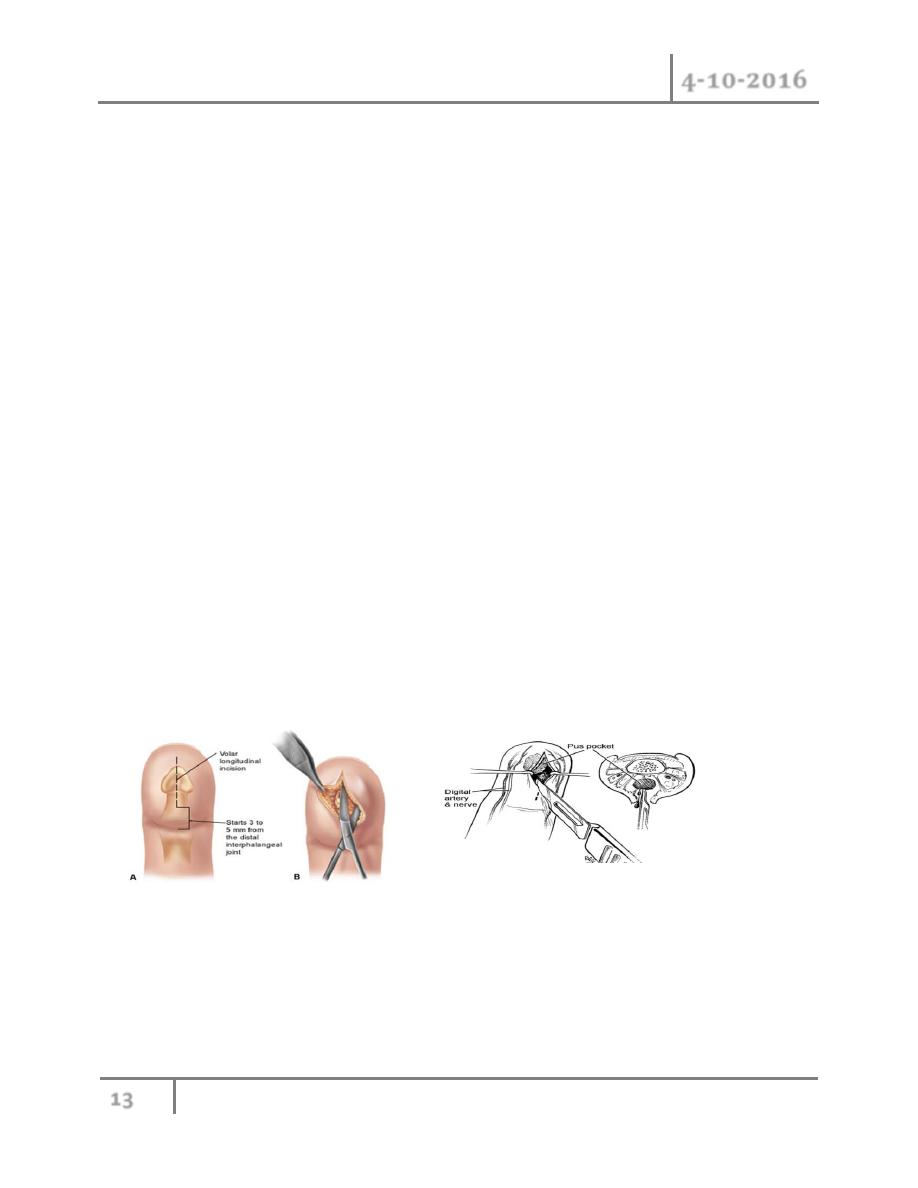
4- Flon : A felon is an abscess of the distal pulp of the thumb or finger. Because of the
unique anatomy of the pulp, with 15 to 20 longitudinal septa anchoring the skin to the
distal phalanx, the pulp is divided into multiple closed compartments. Abscess formation
within these small closed compartments results in rapid development of swelling and
throbbing pain. The pain is usually worsened by dependency, and may keep the patient
from sleeping at night.
Felons typically present after a history of a puncture wound, thus radiographs should be
examined carefully for evidence of retained foreign body.
The most common pathogen involved is S. aureus
Complications of untreated or inappropriately treated felon:
1- painful , unstable , insensate , unaesthetic scar.
2- acute flexor tenosynovitis
3- septic arthritis.
4- osteomylitites.
5- deep space infection.
6- amputation.
Treatment: Early felons may resolve with oral antibiotics, warm soaks, rest, and elevation;
however, any sign of fluctuance requires surgical drainage. A variety of incisions have been
described for the drainage of felons.
If the abscess is pointing, the preferred approach is a longitudinal volar incision through the tip
of the abscess, and should not cross the DIP crease.
Alternatively, a longitudinal incision is made just dorsal to the midlateral line, and may be
extended around the tip of the finger in a “hockey stick” fashion for extensive felons

Hand Ex. & Inf. Dr. Ahmed Khalaf
4-10-2016
14
©Ali Kareem 2016-2017
5- Bacterial flexor tenosynovitis: synovial sheath that surrounding index , middle and ring
finger extended from DIP to MCP. In thumb has a sheath from IPJ through a radial
bursa into the distal forearm. The little finger synovial sheath extended from DIP to large
ulnar bursa which surronded the FDS and FDP tendons of all four digits from midpalm
proximally to proximal margin of pronator quadratus. In 80% there is interconnection
between radial and ulnar bursa in palm.
Flexor tenosynovitis is a surgical emergency as the pressure and pus in tendon sheath
cause ischaemic necrosis of the tendon, leading to rupture. In lesser state the tendon
rapidly adhere to its sheath result in permenant stiffness. The cause is penetrating injury
of flexor tendon at level of DIP and PIP. The injury may be not noted by patient.
The ring , middle, and index finger are the most commonly affected, and S. aureus is the
most common isolate.
Kanavel described the four cardinal signs of flexor tenosynovitis that bear his name:
A. fusiform swelling of the finger
B. partially flexed posture of the digit
C. tenderness over the entire flexor tendon sheath
D. disproportionate pain on passive extension
The latter sign is the most constant and typically the first present in early cases.
Treatment:
Early cases of flexor tenosynovitis (i.e., less than 48 hours ) may respond to conservative
management, including intravenous antibiotics, rest, heat, and elevation.
Failure to respond within 24 to 48 hours warrants immediate operative intervention.
Less severe cases of flexor tenosynovitis may be treated with a limited
incision and catheter irrigation technique (close method). A transverse incision is made
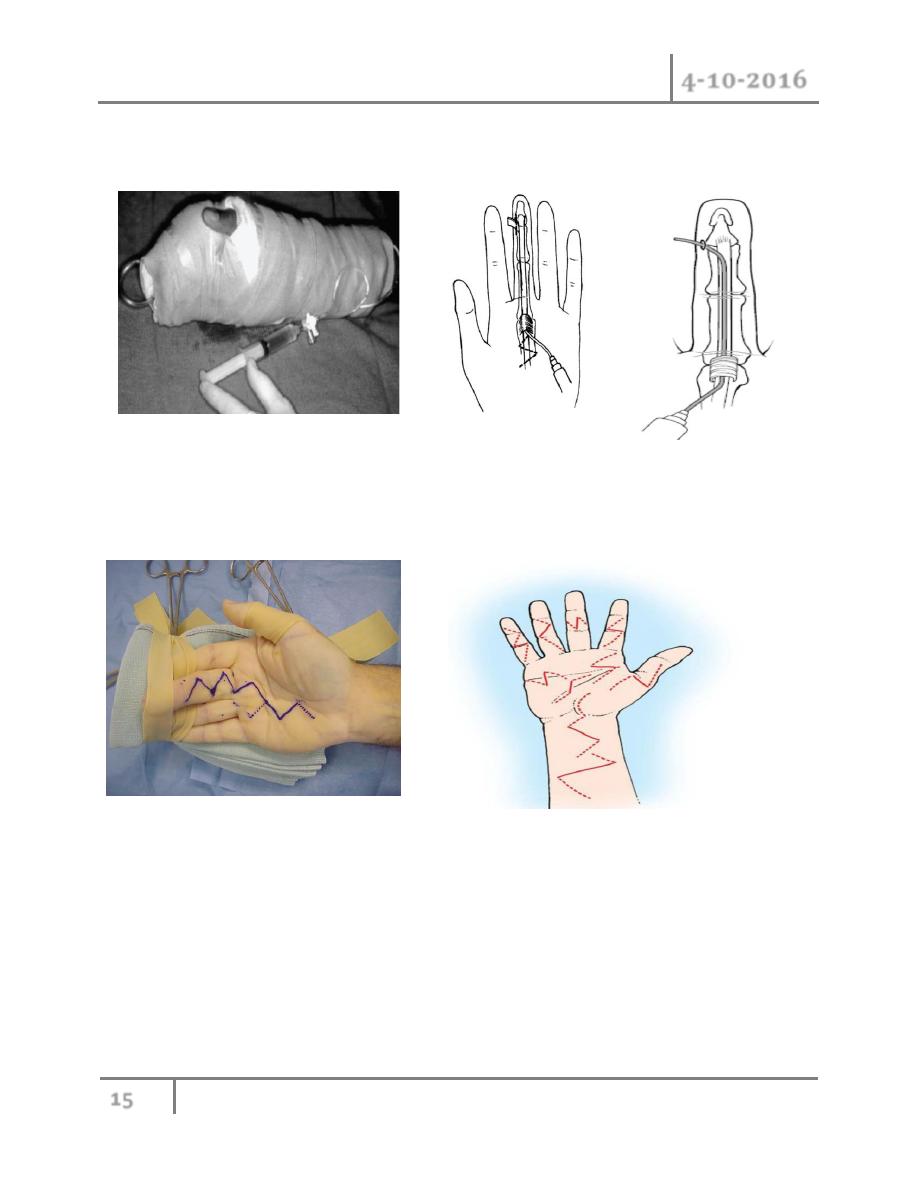
Hand Ex. & Inf. Dr. Ahmed Khalaf
4-10-2016
15
©Ali Kareem 2016-2017
just distal to the distal flexion crease. A similar incision is made in the palm over the proximal
edge of the A-1 pulley The sheath is copiously irrigated with sterile normal saline.
For severe cases, zigzag fashion incision is made over the entire course
of the flexor sheath (open method). The wound is packed open, and is loosely approximated
when the infection has subsided. Early and aggressive hand therapy is indicated for all cases.
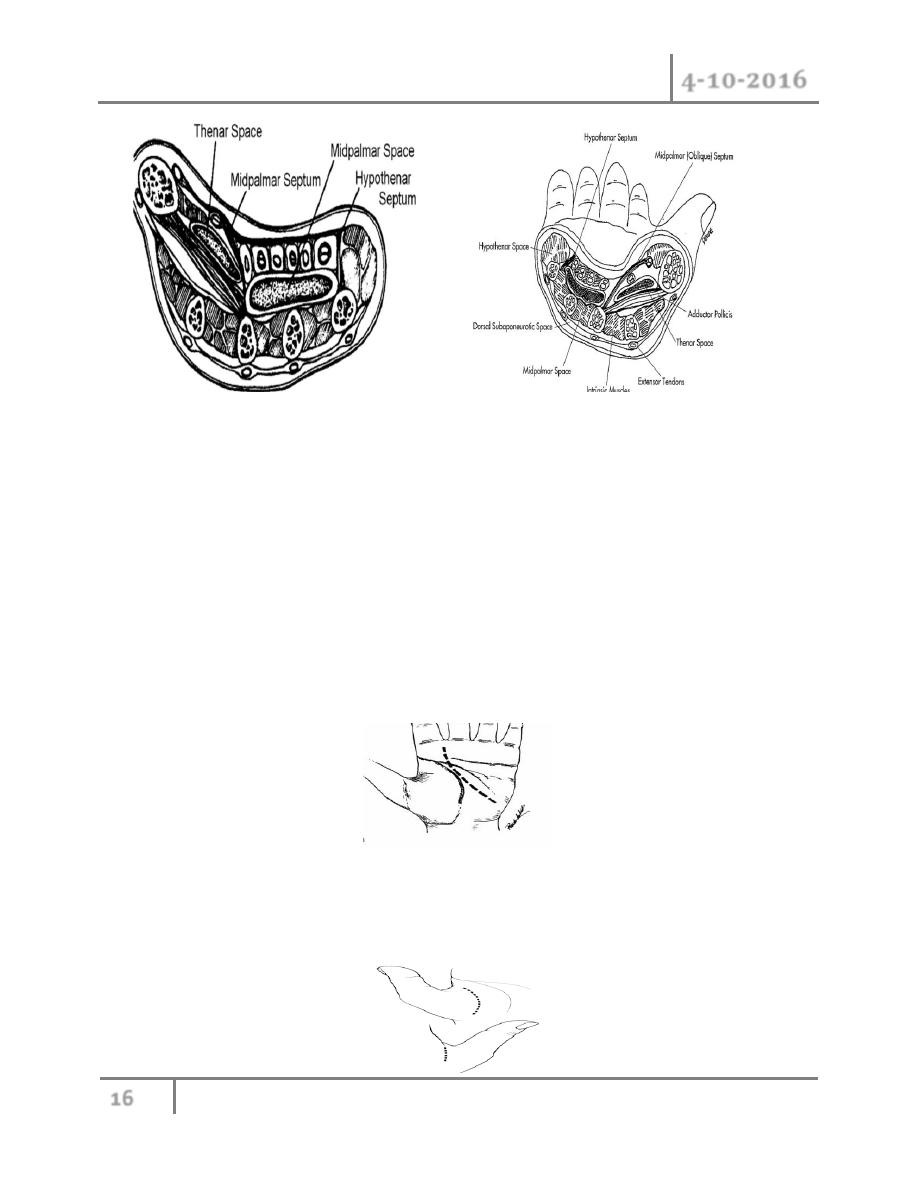
6- Deep space infection: there are 5 potential spaces between hand structures:
Thenar space:
Midpalmer space
Web space
dorsal subaponeurotic space
Hypothenar space
Hand Ex. & Inf. Dr. Ahmed Khalaf
4-10-2016
16
©Ali Kareem 2016-2017
Of these the thenar and midpalmer space are clinically the most important.
A penetration injury such as a splinter is often the inciting event in palmer space infection and
S.auerus is the most common pathogen.
All present with swollen hand with losing of normal concavity on palmer aspect of hand and
edema may extended to dorsal aspect of the hand giving appearance of frog hand, very tender
areas, restriction of movement with generalized symptoms like malaise, fever.
Treatment: antibiotics, elevation, hot soack. if no response, drainage of abscess according to
site of infection, with special incision and irrigation.
For midpalmar space preferred to do curve longitudinal incision in the palm with care to avoid
injury to superficail palmar arch and digital vessels.
For thenar space infection combined dorsal and volar incision , slightly curve longitudinal
incision in dorsum of first web space, and separated incision on thenar eminence parallel to
thenar crease. Care to avoid injury to palamr cutaneaous nerve and motor branch of median
nerve
Hand Ex. & Inf. Dr. Ahmed Khalaf
4-10-2016
17
©Ali Kareem 2016-2017
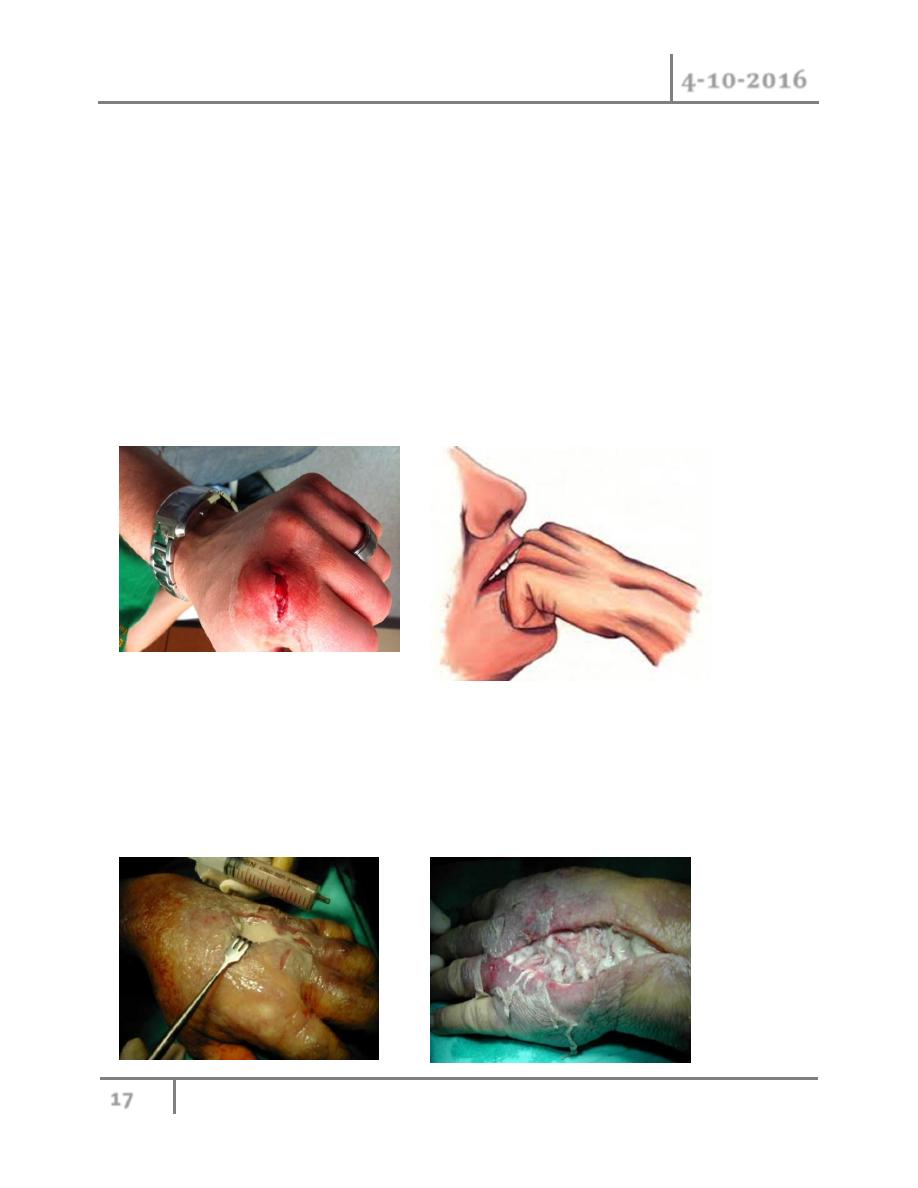
7- Bites: serious infection and subsequent loss of function can result from animals or human
bites. Human bite is potentially serious because of virulence organism comprising human
oral flora. Human saliva may contained as many as 100 millon microorganism per
milliliter, with over 42 species. S. aureus and Streptococcus viridans are the most
common pathogens, also contained anaerobic bacteria e.g. Bacteroides sp. and
Eikenella corrodens. The most common mechanism is striking a tooth with a clenched
fist.
The wound is most commonly over the metacarpophalangeal joints, putting the extensor
mechanism and joint surfaces at risk of injury
Radiographs are mandatory, and may reveal a tooth fragment, fracture of the metacarpal
head, or air in the joint..
Treatment:
All human bites to this region should be explored . The joint space should be irrigated and
wound edges debrided. Human bite wounds should not be closed primarily, but in selected cases,
large wounds may undergo secondary closure after 7 to 10 days of dressing changes and
antibiotics. Eikenella corrodens is sensitive to penicillin and to clindamycine.

Hand Ex. & Inf. Dr. Ahmed Khalaf
4-10-2016
18
©Ali Kareem 2016-2017
Animal bites: cause by domestic dog and cat ,these wound tend to be less infected than human
bite, but can cause substantial crush because of powerful jaw of dog. Cat bites are usually small
puncture wounds because cat teeth are long and sharp.
All animal bites should be thoroughly irrigated and joints explored when potentially violated.
The majority of acute dog bite wounds may be loosely approximated after debriding the edges
sharply.
Cat bites rarely require closing, but may be if needed.
Antibiotic coverage for animal bites should cover the mixed flora found in animal saliva. This
includes the gram-positive Staphylococcus and Streptococcus spp., anaerobes such as
Bacteroides sp., and Pasteurella multocida, a small, gram-negative
coccus
8- Viral infection: most commonly caused by herpes simplex virus and called herpetic
whitlow and commonly seen in dental and medical personnel, and in children .usually
presented with intense pain and erythema and small vesicular rash usually it self limited
resolve in 3-4 weeks.
The distinction from felon is made primarily from the history. Herpetic whitlow usually
presents with a prodromal phase of 24 to 72 hours of burning pain prior to the development of
skin changes. This is followed by erythema and swelling, then the formation of clear vesicles.
The vesicles may coalesce. The fluid within may become turbid, but not frankly purulent without
bacterial superinfection. The pulp of the affected digit is not tense as in a felon.
The diagnosis may be confirmed by viral culture .
This process occurs over approximately 2 weeks and then resolves over the next 7 to 10 days.
Treatment: supportive care,acyclovir oral or intavenous.
Incision and drainage of a whitlow will invariably lead to a worse outcome than conservative
management..
#END of this Lecture …

Hand Ex. & Inf. Dr. Ahmed Khalaf
4-10-2016
19
©Ali Kareem 2016-2017
