
1
Fifth stage
Surgery-Ortho
Lec-2
.د
مثنى
11/10/2015
Complications of fractures
General complications:
Blood loss.
Shock.
diffuse coagulopathy .
respiratory dysfunction.
metabolic response.
tetanus.
gas gangrene.
fat embolism.
Crush syndrome. (if bulk muscle is crushed it is reflected on the kidney function ,end
with renal failure.)
Venous thrombosis &pulmonary embolism.
In veins of the calf and less in the thigh.
II Local complications:
A:early .
( bone ,soft tissue).
B:late.
(bone ,soft tissue,joint).
Early complications bone : Infection particularly in compound fracture.
Early complications Soft tissue :
Vascular injury: Brachial artery and Popliteal artery.
Nerve injury. (neuropraxia, neurotemesis, axonotemesis).
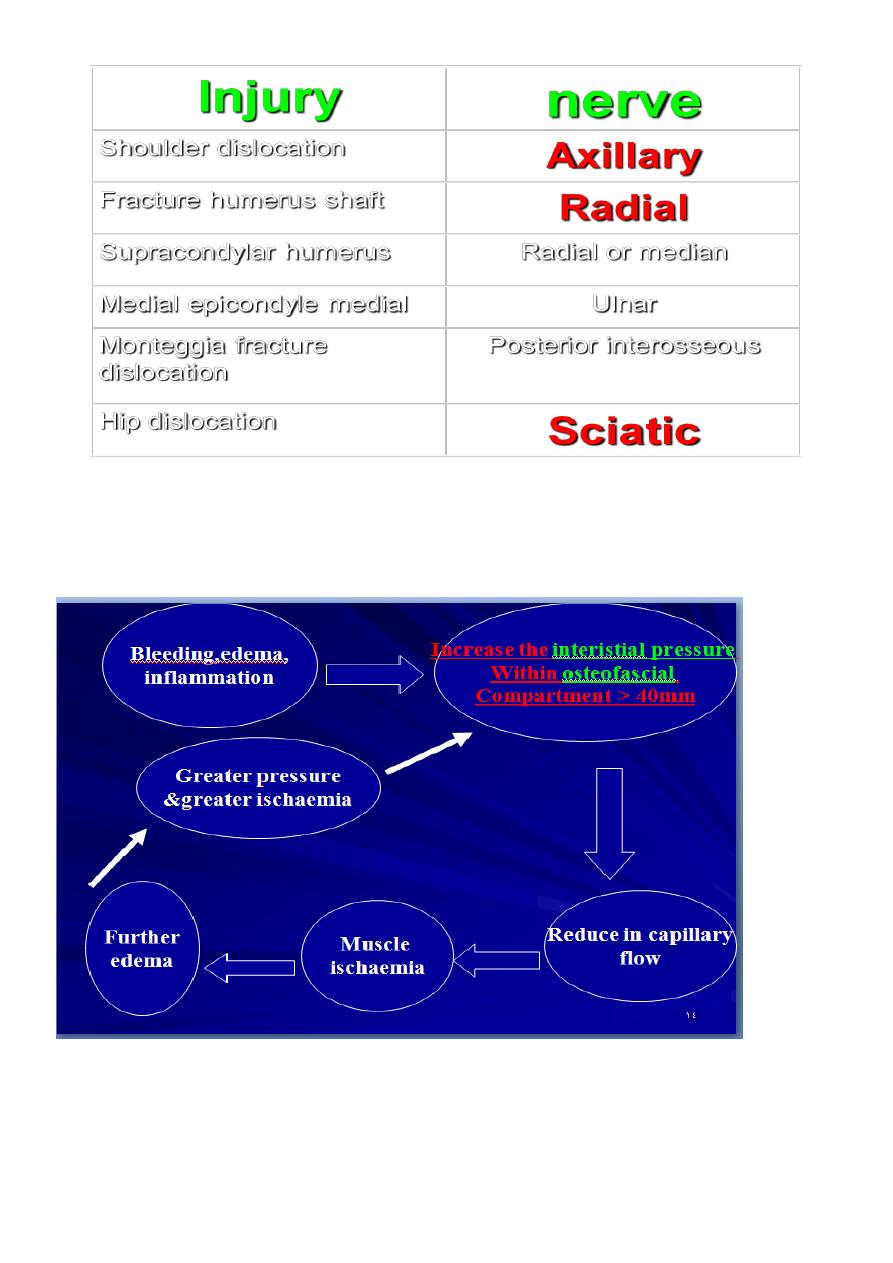
2
Visceral injury diaphragm (in fracture pelvis).
Compartment syndrome : Fracture of the arm or the leg can give rise to severe
ischaemia even if there is no damage to a major vessel. this lead to reduce in the
capillary flow.
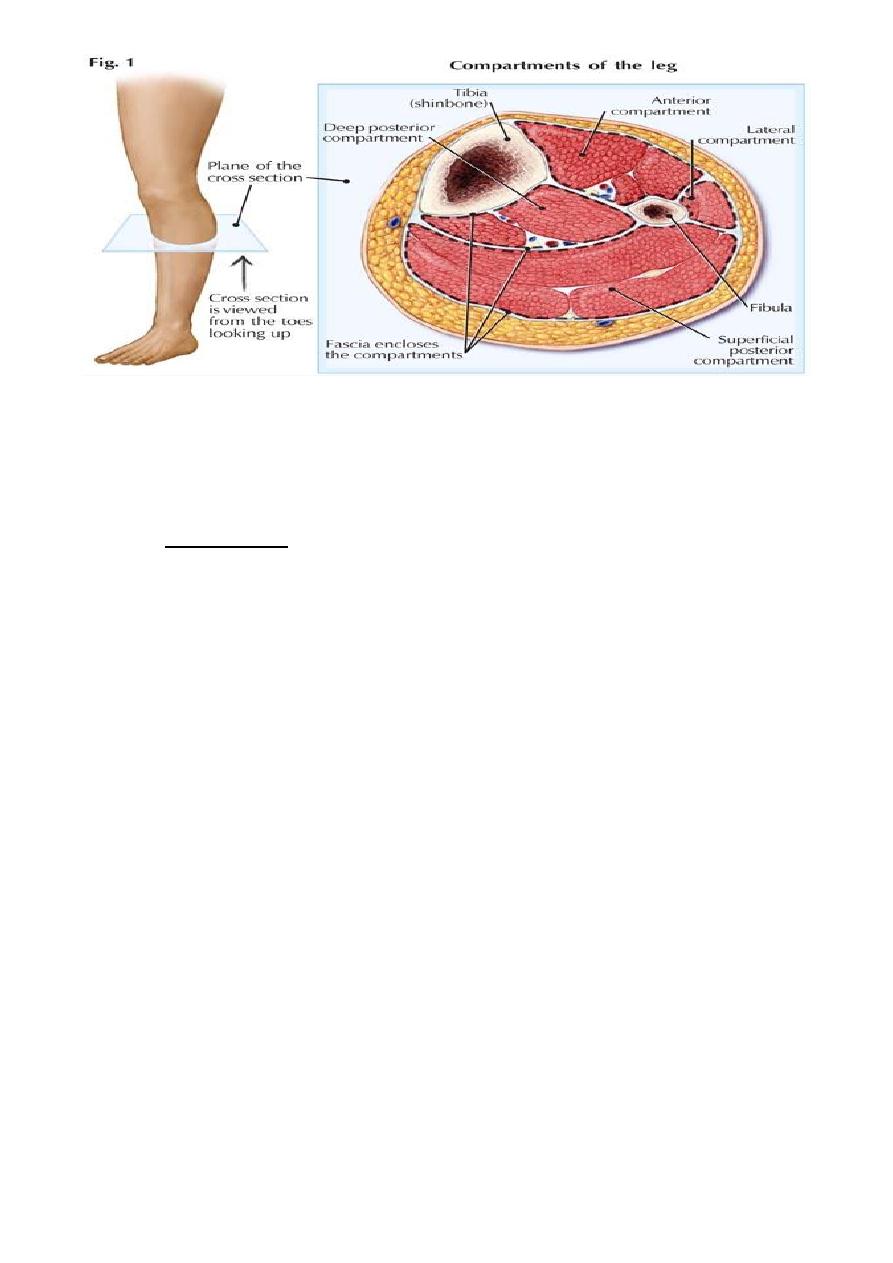
3
After 12 hours or less necrosis of the nerve,which is capable for regeneration. But muscle
once infract can never recovers and is replaced by inelastic fibrous tissue (VOLKMANNS’
ischaemia contractures)
Clinical features of Compartment syndrome : Five Ps.
1. Pain with sever swelling .
2. Parasthesia.
3. Pallor.
4. Paralysis.
5. Pulse less.
Treatment :
1. Removal cast bandage.
2. Fasciotomy >40 mm Hg.
3. <40 mmHg close observation.
4. The wound should be left open and inspected 5 days late to be suture or skin graft.
Fracture blisters occurred by edema.
Plaster sores.
Torn muscle fibers.
Haemarthrosis.
Gas gangrene with clostridium M.O. in a dirty wound

4
Late complications bone :
avascular necrosis: Due to ischaemia after injury as fracture neck femur.
Delayed union:
1.inadequate blood supply.
2.infection.
3.incorrect splint age.
4.intact fellow bone (as in fracture tibia and fibula).
Non union:
1.too large gap.
2.Soft tissue interposition.
3.Intra articular fractures.
Mal union: When the fragments join in an unsatisfactory position.
Growth disturbance: damage to the physis may lead to abnormal or arrested growth.
Late soft tissue complications :
Myositis ossificans (heterotopic ossification in muscle as after elbow injury ).
Bed sores
Tendinitis: (tibilalis posterior in ankle fracture).
Tendon rupture: (extensor pollicis longus in colles).
Nerve compression: as in radial palsy followed faulty use of crutches.
Nerve entrapment: ( median nerve following injuries around wrist).
Volkmann's’ contracture
Late joints complication :
Sudecks’ atrophy: (painful osteoporosis of the hand , reflex sympathetic dystrophy ).
Osteoarthritis : (fracture involving a joint may severely damage the articular cartilage).
Instability : (muscle weakness, gun shot with bone loss, recurrent dislocation)
Joint stiffness: due to oedema and fibrosis of the capsule.
Pathological fractur :
1. Osteogesis imperfecta.
2. Pagets’ disease.

5
3. Chronic infection.
4. Solitary bone cyst.
5. Aneurysmal bone cyst.
6. Osteosarcoma.
7. Ewing's sarcoma.
8. Metastatic tumors
Clinical features of pathological :
Fracture develop spontaneously or after trivial injury.
Examinations:
general &Local.
Investigations:
1. x-r,
2. blood,
3. urine,
4. scanning,
5. biopsy.
Treatment :
Underlying pathology , and fixation with bone cement and internal fixation.
https://www.muhadharaty.com/lecture/13300/Complications-of-
fractures/%D8%AF-%D9%85%D8%AB%D9%86%D9%89
