
Systemic Mycoses
Dr. Mohammed H.Mushrif

These infections result from inhalation of the spores of dimorphic
fungi that have their mold forms in the soil.
Within the lungs, the spores differentiate into yeasts or other
specialized forms.
Most lung infections are asymptomatic and self-limited.
However, in some persons, disseminated disease develops in which
the organisms grow in other organs, cause destructive lesions, and
may result in death.
Infected persons do not communicate these diseases to others.
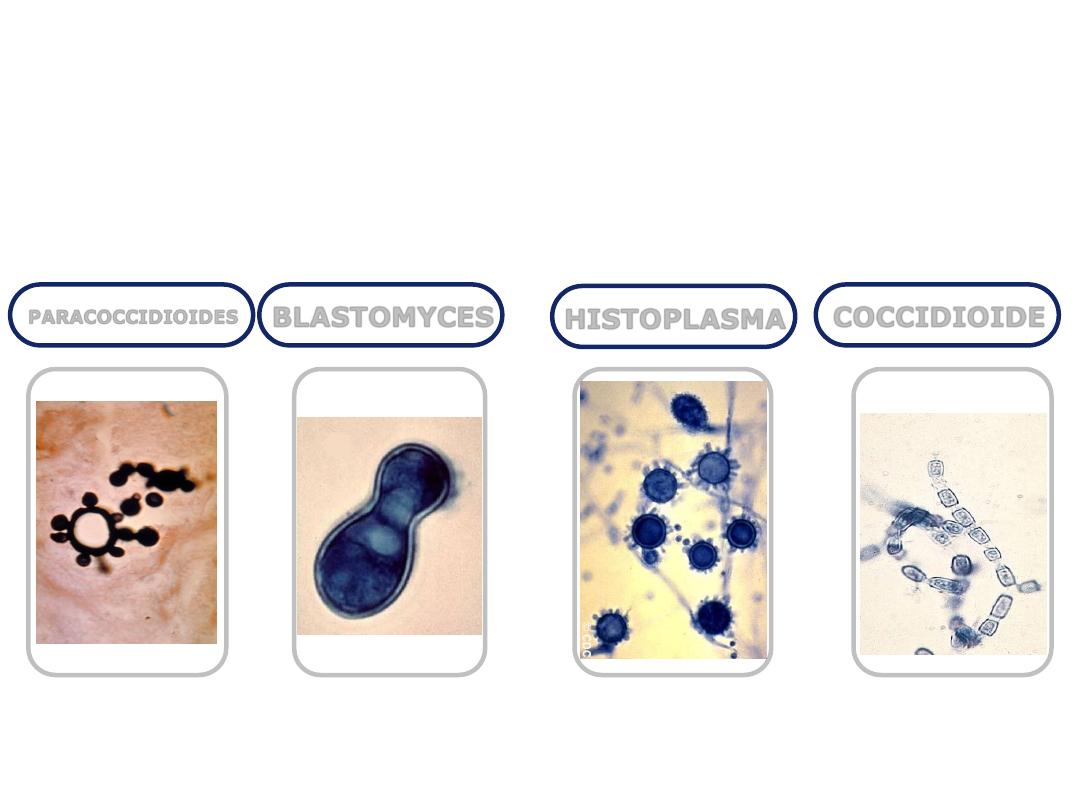
COCCIDIOIDE
HISTOPLASMA
BLASTOMYCES
PARACOCCIDIOIDES
Systemic Mycoses

COCCIDIOIDE
COCCIDIOIDE
Disease
Coccidioides immitis causes coccidioidomycosis.
Properties
C. immitis is a dimorphic fungus that exists as a
mold in soil and as a spherule in tissue

Transmission & Epidemiology Coccidioide
The fungus is endemic in arid regions of the
southwestern United States and Latin America.
People who live in Central and Southern California,
Arizona, New Mexico, Western Texas, and Northern
Mexico, a geographic region called the Lower
Sonoran Life Zone, are often infected.
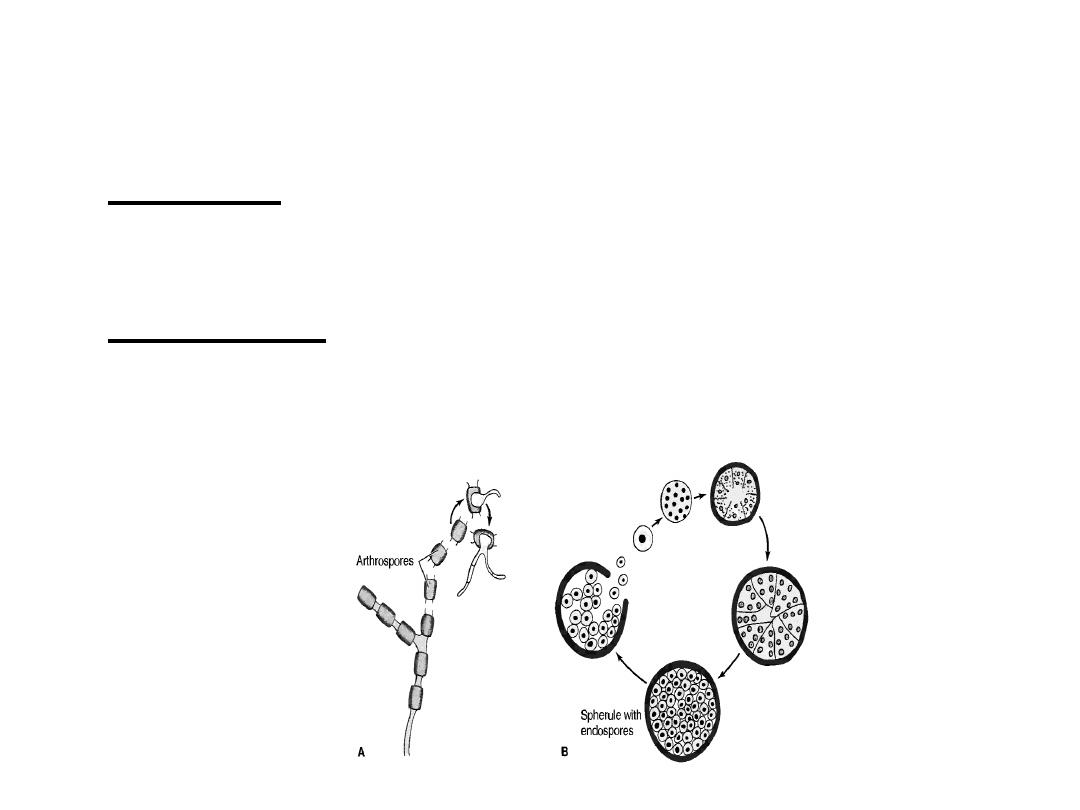
In soil, it forms hyphae with alternating arthrospores
and empty cells.
Arthrospores are very light and are carried by the
wind.
They can be inhaled and infect the lungs.

Pathogenesis of Coccidioide
In the lungs, arthrospores form spherules that are large,
have a thick, doubly refractive wall, and are filled with
endospores.
Upon rupture of the wall, endospores are released
and differentiate to form new spherules.
The organism can spread within a person by direct
extension or via the bloodstream.
Granulomatous lesions can occur in virtually any organ
but are found primarily in bones and the central nervous
system (meningitis)
Dissemination from the lungs to other organs occurs in
people who have a defect in cell-mediated immunity.

Pathogenesis of Coccidioide
Most people who are infected by C. immitis
develop a cell-mediated (delayed
hypersensitivity) immune response that restricts
the growth of the organism.
One way to determine whether a person has
produced adequate cell-mediated immunity to
the organism is to do a skin test (see below).
In general, a person who has a positive skin test
reaction has developed sufficient immunity to
prevent disseminated disease from occurring.
If, at a later time, a person's cellular immunity is
suppressed by drugs or disease, disseminated
disease can occur.

Clinical Findings of Coccidioide
Infection of the lungs is often asymptomatic and is
evident only by a positive skin test and the presence of
antibodies.
Some infected persons have an influenza like illness with
fever and cough.
About. 50% have changes in the lungs (infiltrates,
adenopathy, or effusions) as seen on chest x-ray.
10% develop erythema nodosum (see below) or
arthralgias.
This syndrome is called "valley fever" or "desert
rheumatism"; it tends to subside spontaneously.
Disseminated disease can occur in almost any organ;
the meninges, bone, and skin are important sites.

Clinical Findings of Coccidioide
The overall incidence of dissemination in
persons infected with C. imrnitis is 1%, although
the incidence in Filipinos and African Americans
is 10 times higher.
Women in the third trimester of pregnancy also
have a markedly increased incidence of
dissemination.
Erythema nodosum (EN) manifests as red,
tender nodules ("desert bumps") on extensor
surfaces such as the shins.
It is a delayed (cell-mediated) hypersensitivity
response to fungal antigens and thus is an
indicator of a good prognosis.

Clinical Findings of Coccidioide
There are no organisms in these lesions; they
are not a sign of disseminated disease. EN is
not specific for coccidioidomycosis; it occurs in
other granulomatous diseases, eg,
histoplasmosis, tuberculosis, and leprosy.
In infected persons, skin tests with fungal
extracts cause at least a 5mm induration 48
hours after injection (delayed hypersensitivity
reaction).
Skin tests become positive within 2-4 weeks of
infection and remain so for years but are often
negative in patients with disseminated disease.
Laboratory Diagnosis of Coccidioide
In tissue specimens, spherules are seen
microscopically.
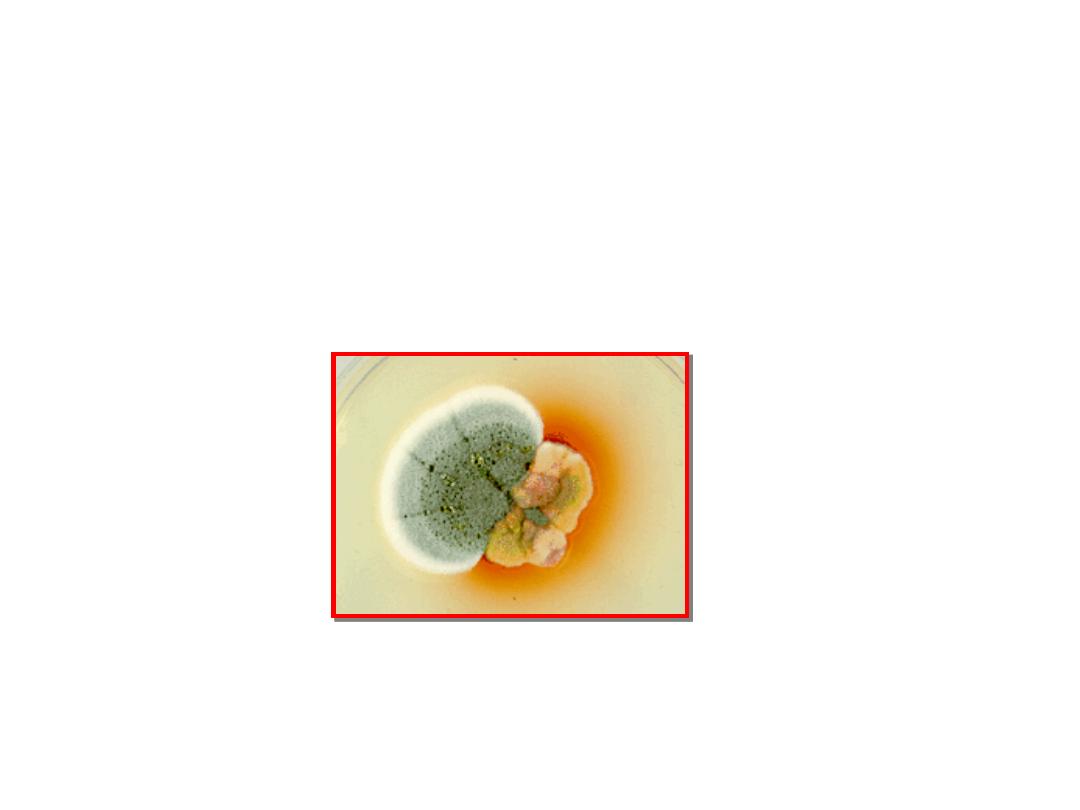
Cultures on Sabouraud's agar incubated at 25
°C
show hyphae with arthrospores
(Caution: Cultures are highly infectious;
precautions against inhaling arthrospores must
be taken.)

Laboratory Diagnosis of Coccidioide
In serologic tests, [gM and IgG precipitins appear
within 2-4 weeks of infection and then decline in
subsequent months.
Complement-fixing antibodies occur at low titer
initially, but the titer rises greatly if dissemination
occurs

Treatment & Prevention of Coccidioide
No treatment is needed in asymptomatic or mild
primary infection.
Amphotericin B (Fungizone) or itraconazole is
used for persisting lung lesions or disseminated
disease.
Ketoconazole is also effective in lung disease.
Fluconazole is the drug of choice for meningitis.
Intrathecal amphotericin B may be required and
may induce remission, but long-term results are
often poor.
There are no means of prevention
except avoiding travel to endemic areas.

HISTOPLASMA

Disease of Histoplasma
Histoplasma capsulatum causes histoplasmosis.

Properties of Histoplasma
H. capsulatum is a dimorphic fungus that
exists as a mold in soil and as a yeast in
tissue.
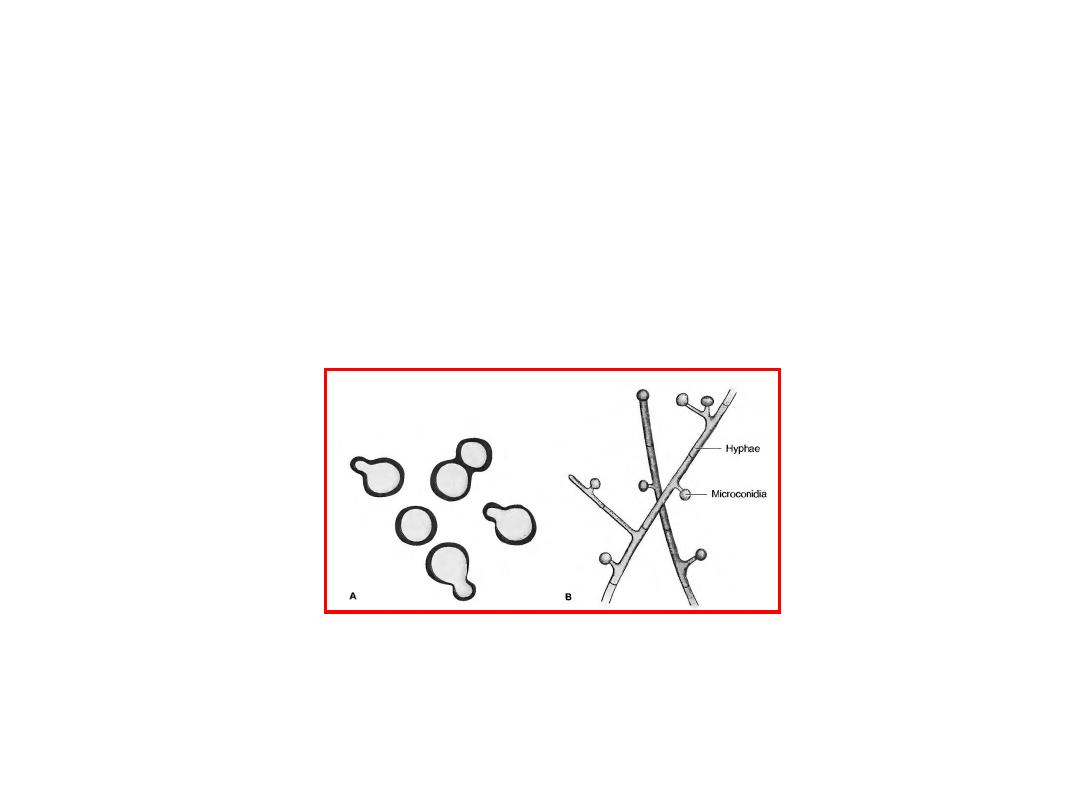
It forms two types of asexual spores
(1) tuberculate macroconidia, with typical thick
walls and fingerlike projections that are
important in laboratory identification,
(2) microconidia, which are smaller, thin,
smoothwalled spores that, if inhaled, transmit
the infection.

Transmission & Epidemiology of Histoplasma
This fungus occurs in many parts of the world.
In the United States it is endemic in central and
eastern states, especially in the Ohio and
Mississippi River valleys.
It grows in soil, particularly if the soil is heavily
contaminated with bird droppings, especially
from starlings.
Although the birds are not infected, bats can be
infected and can excrete the organism in their
guano.

Transmission & Epidemiology of Histoplasma
In areas of endemic infection, excavation of the
soil during construction or exploration of bat-
infested caves has resulted in a significant
number of infected individuals.
In several tropical African countries,
histoplasmosis is caused by Histoplasrna
duboisii.
The clinical picture is different from that
caused by H. capsulatum.
A description of the differences between African
histoplasmosis and that seen in the United
States is beyond the scope of this book.
Pathogenesis & Clinical Findings of Histoplasma
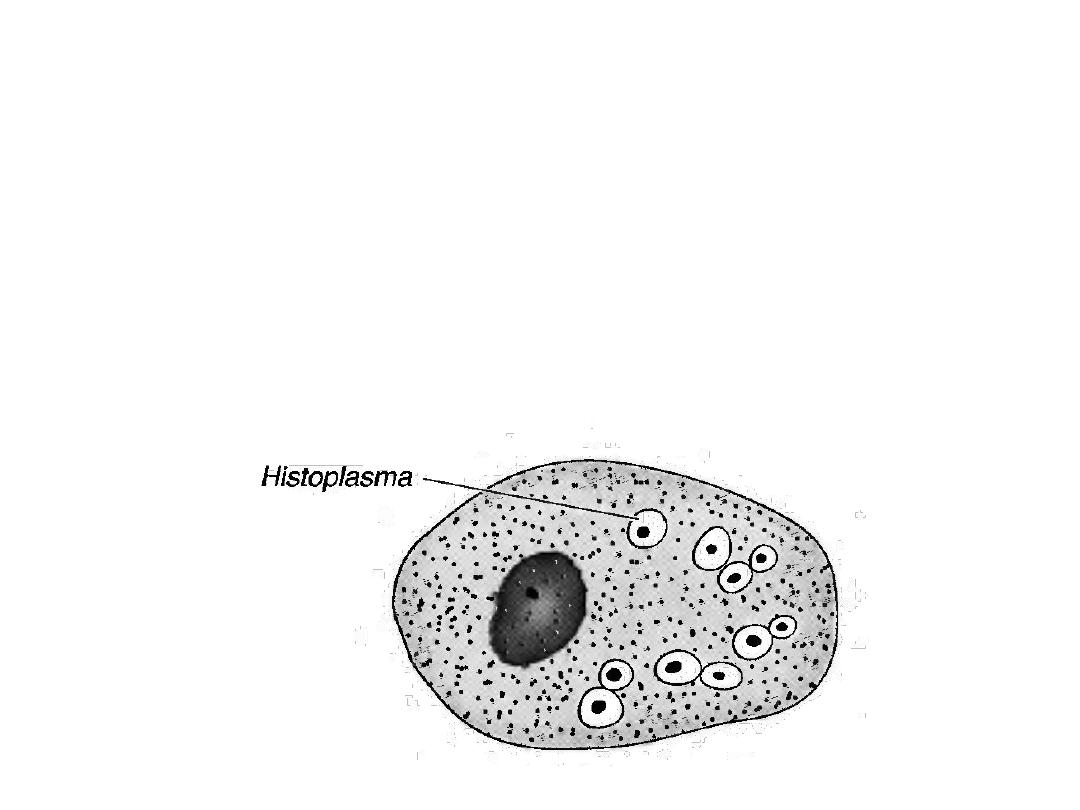
Inhaled spores are engulfed by macrophages
and develop into yeast forms.
In tissues, H. capsulatum occurs as an oval
budding yeast inside macrophages

Pathogenesis & Clinical Findings of Histoplasma
The yeasts survive within the phagolysosome of
the macrophage by producing alkaline
substances, such as bicarbonate and ammonia,
that raise the pH and thereby inactivate the
degradative enzymes of the phagolysosome
The organisms spread widely throughout the
body; especially to the liver and spleen, but most
infections remain asymptomaric, and the small
grantdomatous foci heal by calcification.

Pathogenesis & Clinical Findings of Histoplasma
With intense exposure (eg, in a chicken house or
batinfested cave), pneumonia may become clinically
manifest.
Severe disseminated histoplasmosis develops in a
small minority of infected persons, especially infants
and individuals with reduced cell-mediated immunity,
such as AIDS patients.
In AIDS patients, ulcerated lesions on the tongue are
typica] of disseminated histoplasmosis. In
immunocompetent people, EN can occur (see
description of EN in Coccidioides above).

Pathogenesis & Clinical Findings of Histoplasma
EN is a sign that cell-mediated immunity is
active and the organism will probably be
contained.
A skin test using histoplasmin (a mycelial
extract) becomes positive, ie, shows at least 5
mm of induration, within 2-3 weeks after
infection and remains positive for many years.
However, because there are many false-positive
reactions (due to cross-reactivity) and many
false-negative reactions (in disseminated
disease), the skin test is not useful for diagnosis.

Pathogenesis & Clinical Findings of Histoplasma
Furthermore, the skin test can stimulate an
antibody response and confuse the serologic
tests.
The skin test is useful for epidemiologic studies,
and up to 90% of individuals have positive
results in areas of endemic infection.

Laboratory Diagnosis of Histoplasma
In tissue biopsy specimens or bone marrow
aspirates, oval yeast cells within macrophages
are seen microscopically.
Cultures on Sabouraud's agar show hyphae with
tuberculate macroconidia when grown at low
temperature, eg, 25
°C and yeasts when grown
at 37
°C.
Tests that detect Histoplasma antigens by
radioimmunoassay and Histoplasma RNA with
DNA probes are also useful.

Laboratory Diagnosis of Histoplasma
An antibody titer of 1:32 in the CF test with yeast
phase antigens is considered to be diagnostic.
However, cross-reactions with other fungi,
especially Blastomyces, occur.
CF titers fall when the disease becomes inactive
and rise in disseminated disease.
The ID test detects precipitating antibodies
(precipitins) by forming two bands, M and H, in
an agar-gel diffusion assay.
The ID test is more specific but less sensitive
than the CF test.

Treatment & Prevention of Histoplasma
No therapy is needed in asymptomatic or mild
primary infections.
With progressive lung lesions, oral itraconazole
is beneficial.
In disseminated disease, arnphotericin B is the
treatment of choice.
In meningitis,fluconazole is often used because
it penetrates the spinal fluid well.

Treatment & Prevention of Histoplasma
Oral itraconazole is used to treat pulmonary or
disseminated disease, as well as for chronic
suppression in patients with AIDS.
There are no means of prevention except
avoiding exposure in areas of endemic infection.

BLASTOMYCES

Disease
of Blastomyces
Blastomyces dermatitidis causes blastomycosis,
known as North American blastomycosis.
Properties of Blastomyces
B. dermariridis is a dimorphic fungus that exists
as a mold in soil and as a yeast in tissue.
The yeast is round with a doubly refractive wall
and a single broad-based bud
Note that this organism forms a broad-based
bud, whereas Cryptococcus neoformans is a
yeast that forms a narrow-based bud.

Transmission & Epidemiology of Blastomyces
This fungus is endemic primarily in eastern North
America, especially in the region bordering the Ohio,
Mississippi, and St. Lawrence rivers, and the Great
Lakes region.
Less commonly, blastomycosis has also occurred
in Central and South America, Africa, and the
Middle East. It grows in moist soil rich in organic
material, forming hyphae with small pear-shaped
conidia.
Inhalation of the conidia causes human infection.

Pathogenesis & Clinical Findings of Blastomyces
Infection occurs mainly via the respiratory tract.
Asymptomatic or mild cases are rarely
recognized.
Dissemination may result in ulcerated
granulomas of skin, bone, or other sites.

Laboratory Diagnosis of Blastomyces
In tissue biopsy specimens, thick-walled yeast
cells with single broad-based buds are seen
microscopically.
Hyphae with small pear-shaped conidia are visible
on culture.
The skin test lacks specificity and has little value.
Serologic tests have little value.

Treatment & Prevention of Blastomyces
Itraconazole is the drug of choice for most
patients
Amphotericin B should be used to treat severe
disease.
Surgical excision may be helpful.
There are no means of prevention.

PARACOCCIDIOIDES

Disease of Paracoccidioides
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis causes
paracoccidioidomycosis, also known as
South American blastomycosis.
Properties of Paracoccidioides
P. brasiliensis is a dimorphic fungus that exists
as a mold in soil and as a yeast in tissue.
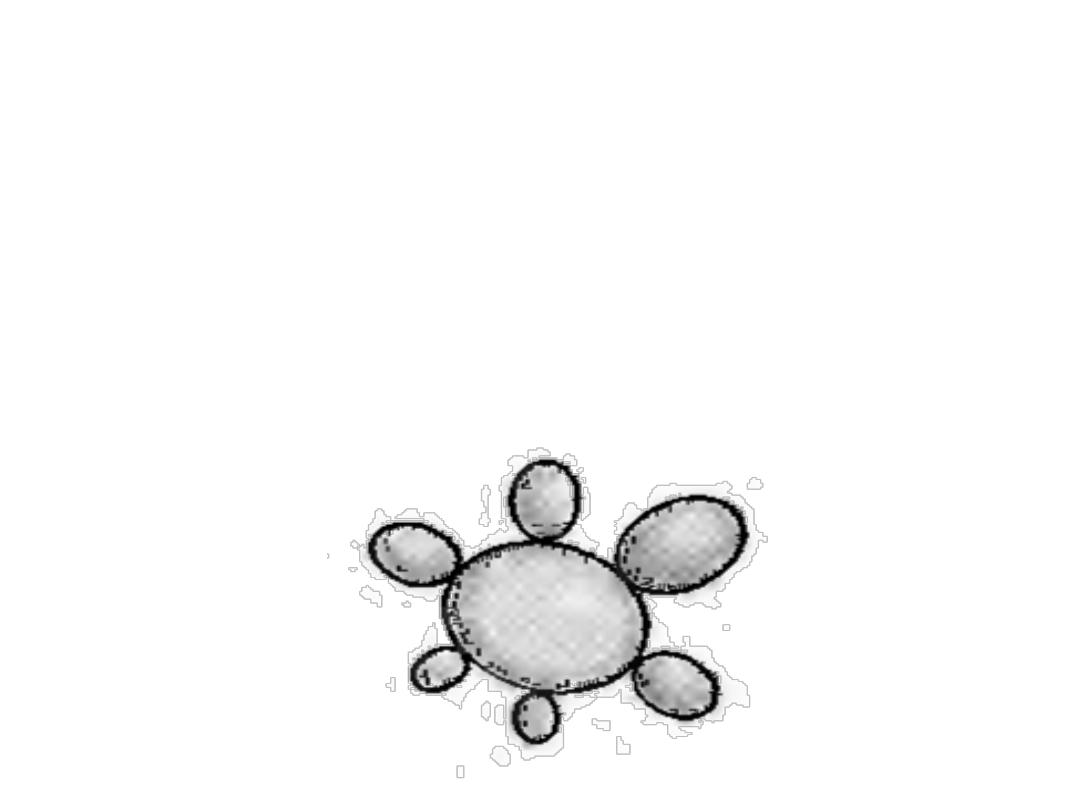
The yeast is thick walled with multiple buds, in
contrast to B. derrnatitidis, which has a single
bud .

Transmission & Epidemiology of Paracoccidioides
The spores are inhaled, and early lesions occur
in the lungs.
Asymptomatic infection is common.
Alternatively oral mucous membrane lesions,
lymph node enlargement, and sometimes
dissemination to many organs develop.

Laboratory Diagnosis of Paracoccidioides
In pus or tissues, yeast cells with multiple buds
are seen microscopically.
A specimen cultured for 2-4 weeks may grow
typical organisms.
Skin tests are rarely helpful.
Serologic testing shows that when significant
antibody titers (by immunodiffusion or
complement fixation) are found, active disease is
present.

Pathogenesis & Clinical Findings of Paracoccidioides
This fungus grows in the soil and is endemic in
rural Latin America. Disease occurs only in that
region.

Treatment & Prevention of Paracoccidioides
The drug of choice is itraconazole taken orally
for several months.
There are no means of prevention.
