Opportunistic mycoses
By
Dr. Mohammed H. Mushrif
Lecturer of Medical Mycology

Cryptococcus neoformans
Morphology
Yeast cells surrounded by gelatinous capsule.
Virulence factors
Capsule interferes with phagocytosis.
Phenol oxidase enzyme
o It acts on diphenolic substrate producing melanin
in the fungal cell wall.
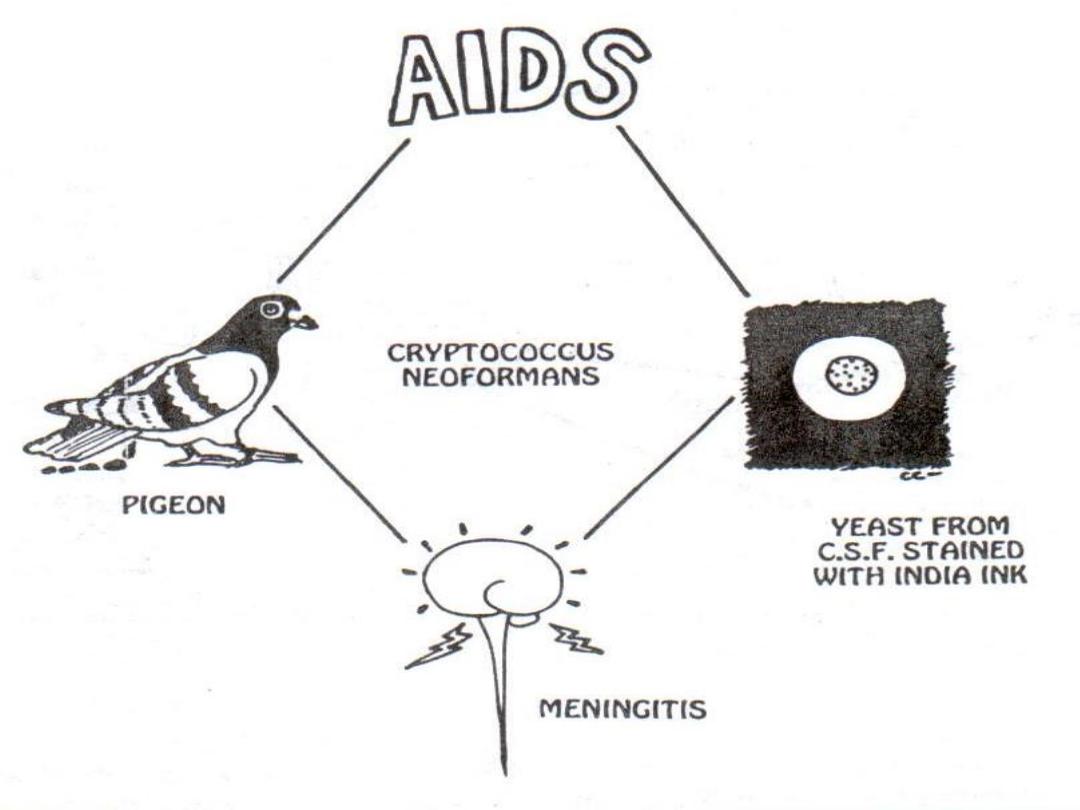
Pathogenesis
It lives in soil contaminated with excreta of
birds especially pigeons.
Infection occurs by inhalation.
It affects immunocompromised patients
especially those with AIDS.
Diseases
Pneumonia
It may spread systemically to meninges
causing
meningitis
.
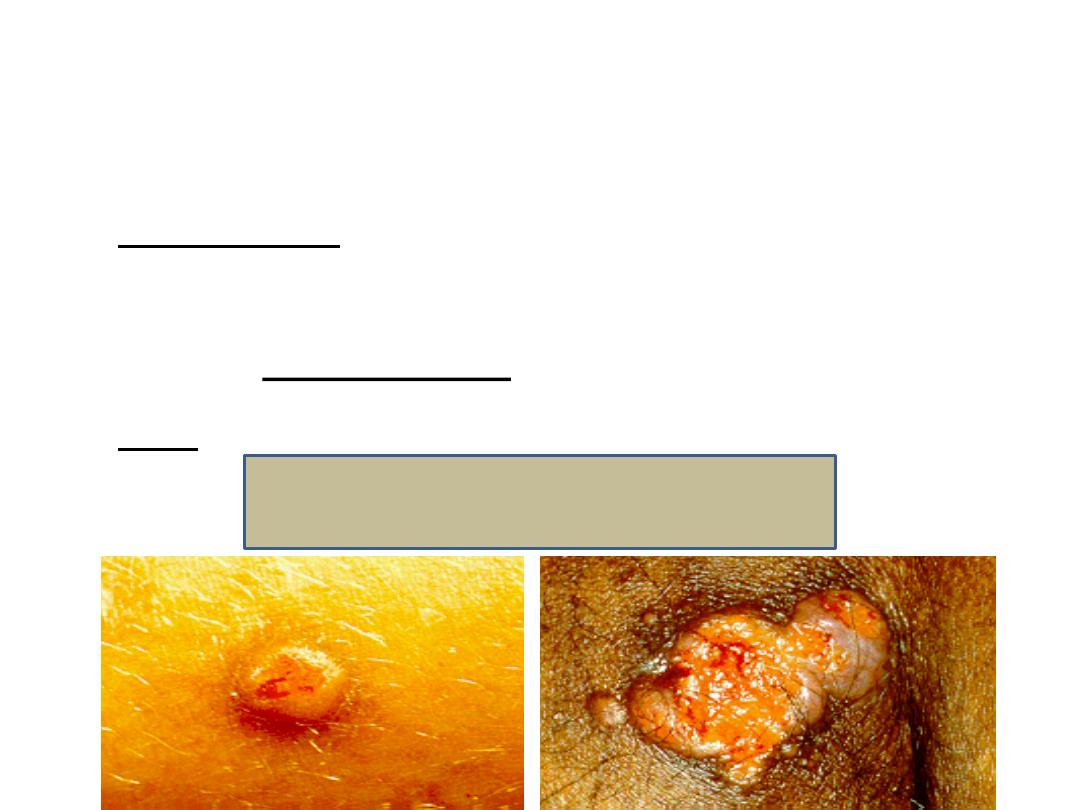
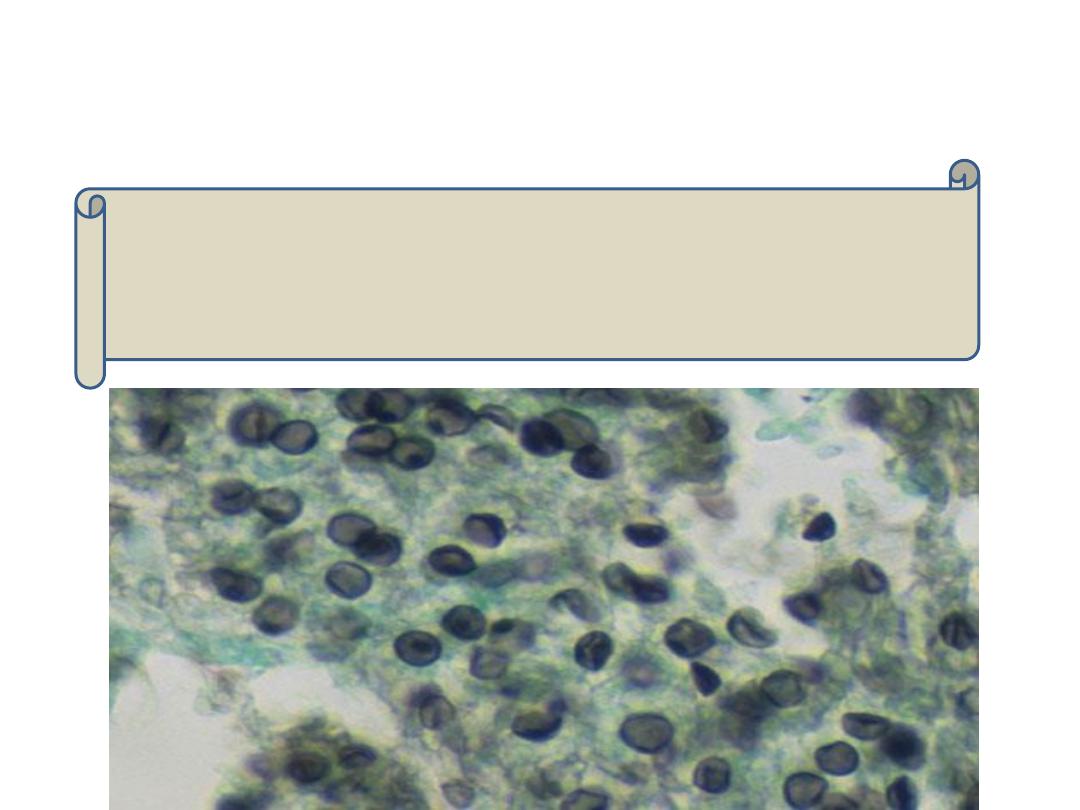
Skin lesions
Cryptococcal Skin lesions
Laboratory diagnosis
Specimen:
sputum, CSF
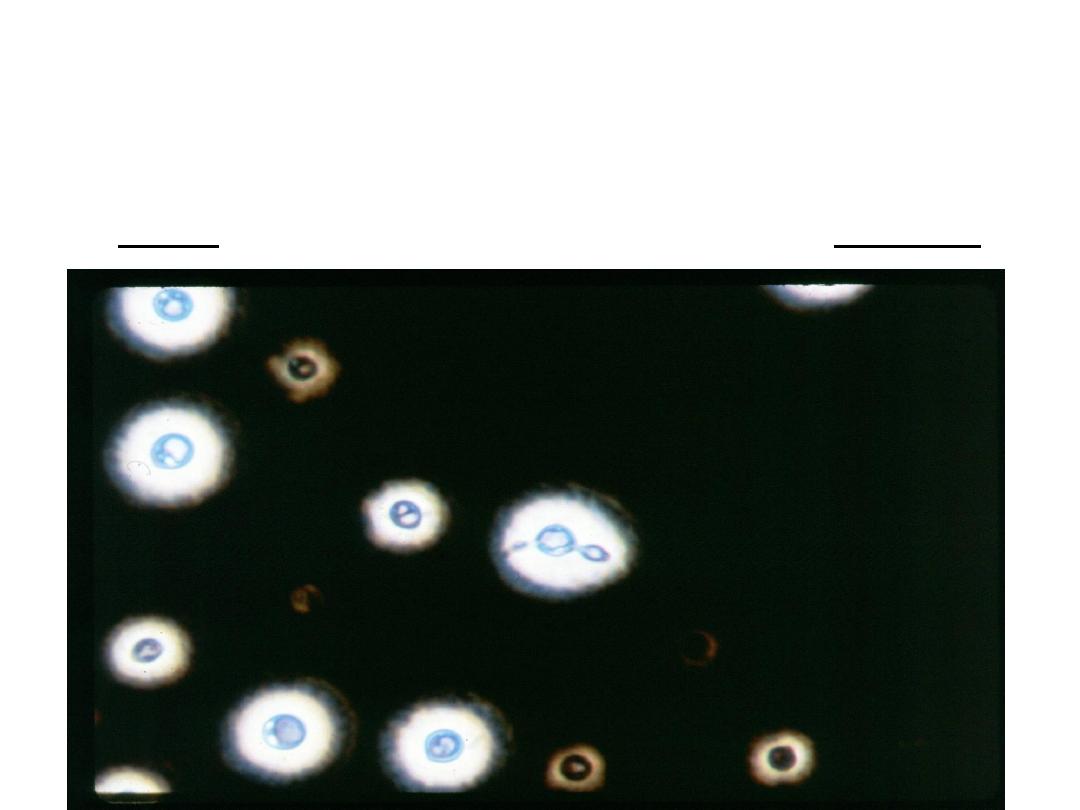
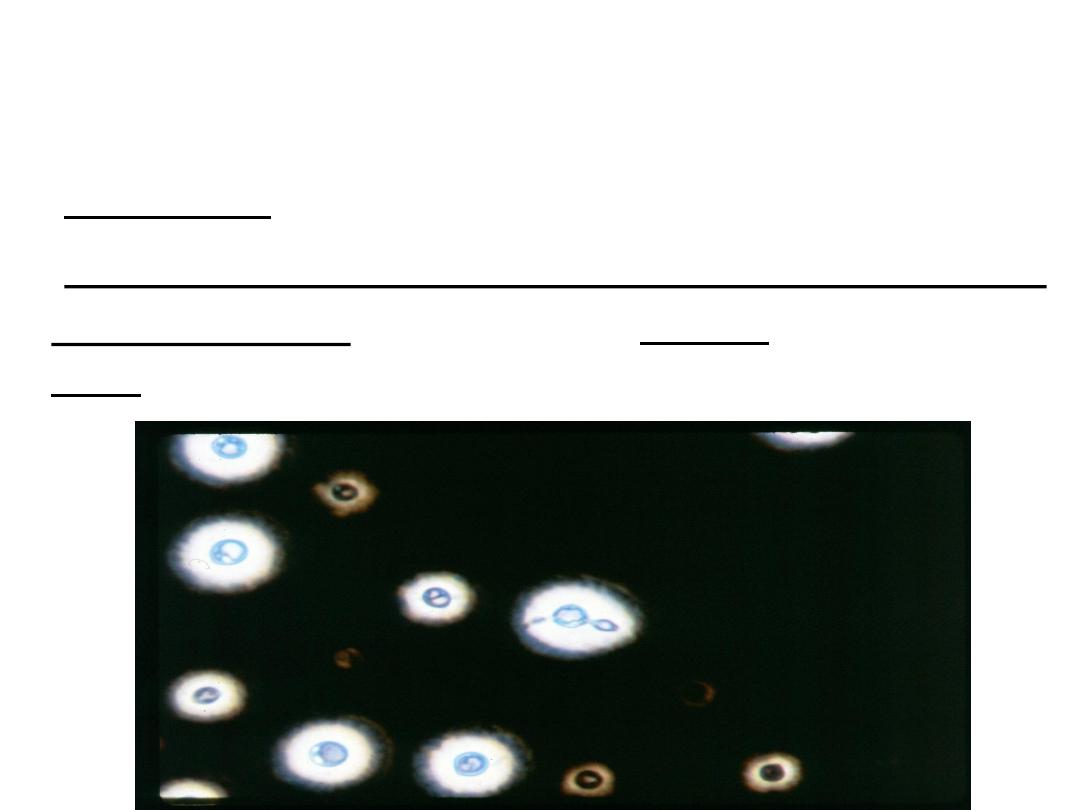
Direct examination of the specimen after staining
using india ink:
large gelatinous capsule around budding
yeast cells.
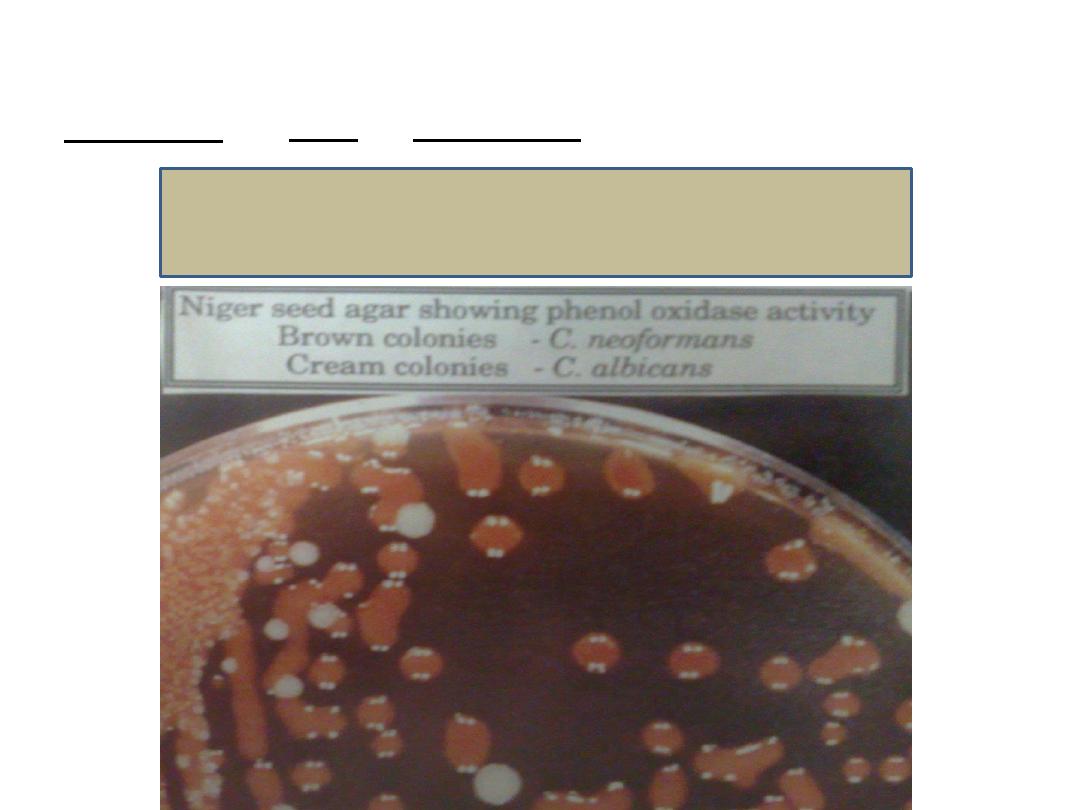
Culture:
on SDA or bird seed agar at 25 – 37 degree.
Cryptococcus on bird seed agar
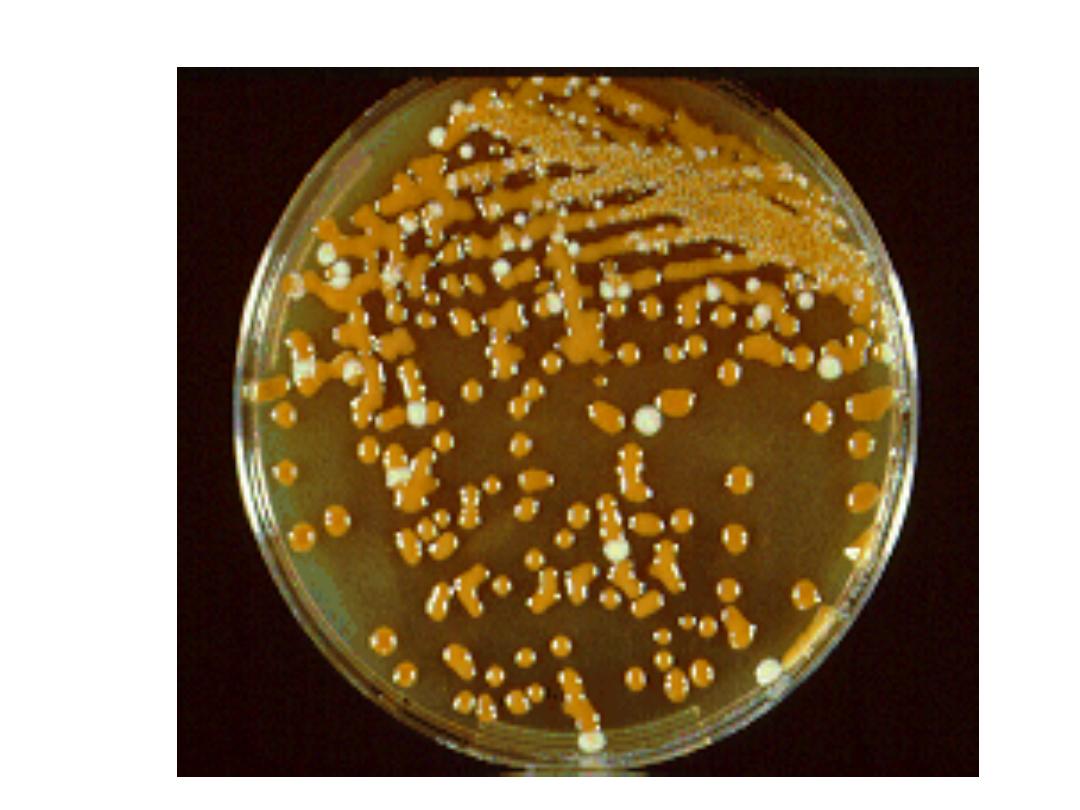
Identification of cryptococcus on the plate is
done by:
1. Morphology:
mucoid colonies. It appears brown to
black on bird seed agar.
2. India ink staining
3. Biochemical reactions:
urease positive + phenol
oxidase positive.
4. DNA probes
Direct detection of capsular antigen in CSF by
latex agglutination test.

Treatment
Amphotericin B and flucytosine are given for
6 months. Given for life with AIDS patients.
Pneumocystis jiroveci
Morphology
It was thought to be a protozoan but molecular
studies have proven that it is a fungus.
Pneumocystis jiroveci is the human species and the
more familiar Pneumocystis carinii is found only in
rats.
It has two distinct forms:
o Thick walled cyst which contain 4 – 8 nuclei. The cyst
wall is stained by silver.
o Thin walled trophozoites which are stained by Giemsa.
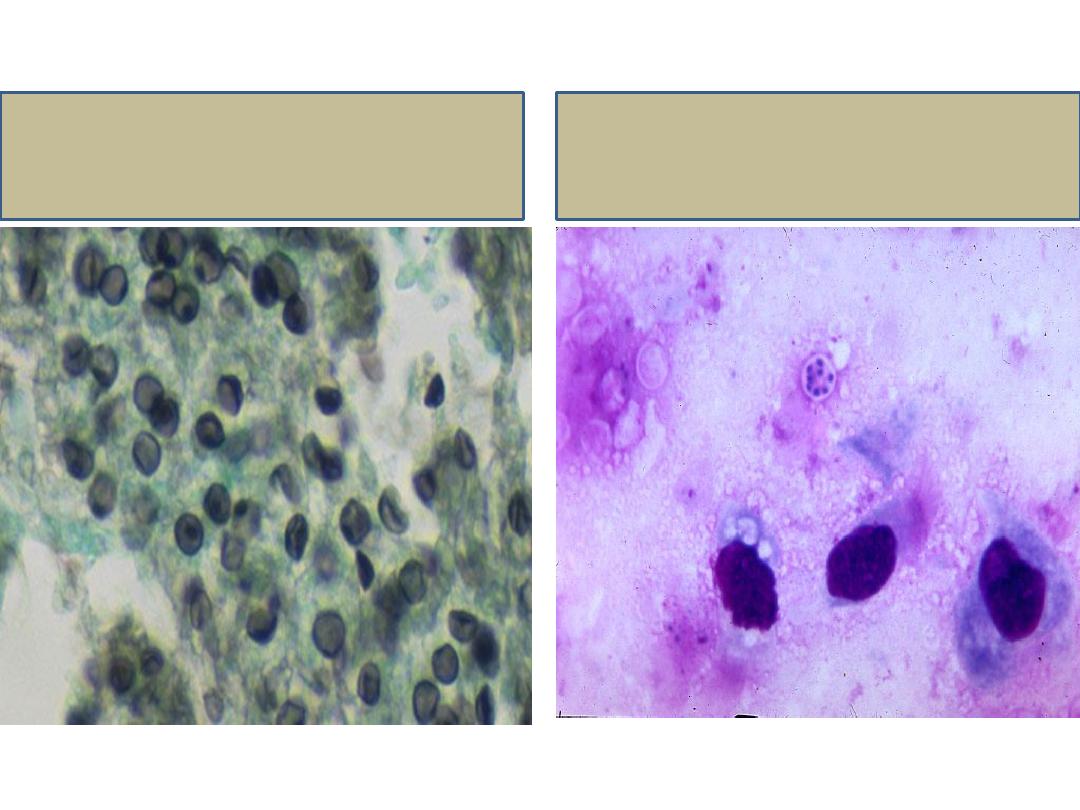
Cyst stained by silver
Trophozoites stained
by Giemsa
Pathogenesis
Infection occurs by inhalation.
It affects malnourished infants and
immunocompromised patients especially AIDS
patients.
Fungal growth is limited to above the alveolar
epithelium causing frothy exudate that blocks
oxygen exchange.

Diseases
Interstitial plasma cell pneumonia.
Death is 100% in untreated cases.
Extrapulmonary infections occur in late stages
of AIDS.
Laboratory diagnosis
Specimen:
bronchoalveolar lavage, induced sputum or
lung biopsy.
Direct examination of the specimen after staining
using:
o Silver to stain cyst wall
o Giemsa to stain trophozoites
Direct IF or PCR

Treatment
Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole is the drug of
choice.
Pentamidine and atovaquone are alternative
drugs.
