Opportunistic mycoses
By
Dr. Mohammed H. Mushrif
Lecturer of Medical Mycology
Candida
Species
Candida is present as normal flora in the
mouth, GIT and vagina.
Species include:
o Candida albicans (the most important)
o Candida tropicalis
o Candida krusei
o Candida parapsilosis
o Candida glabrata
o Candida dubliniensis
Morphology
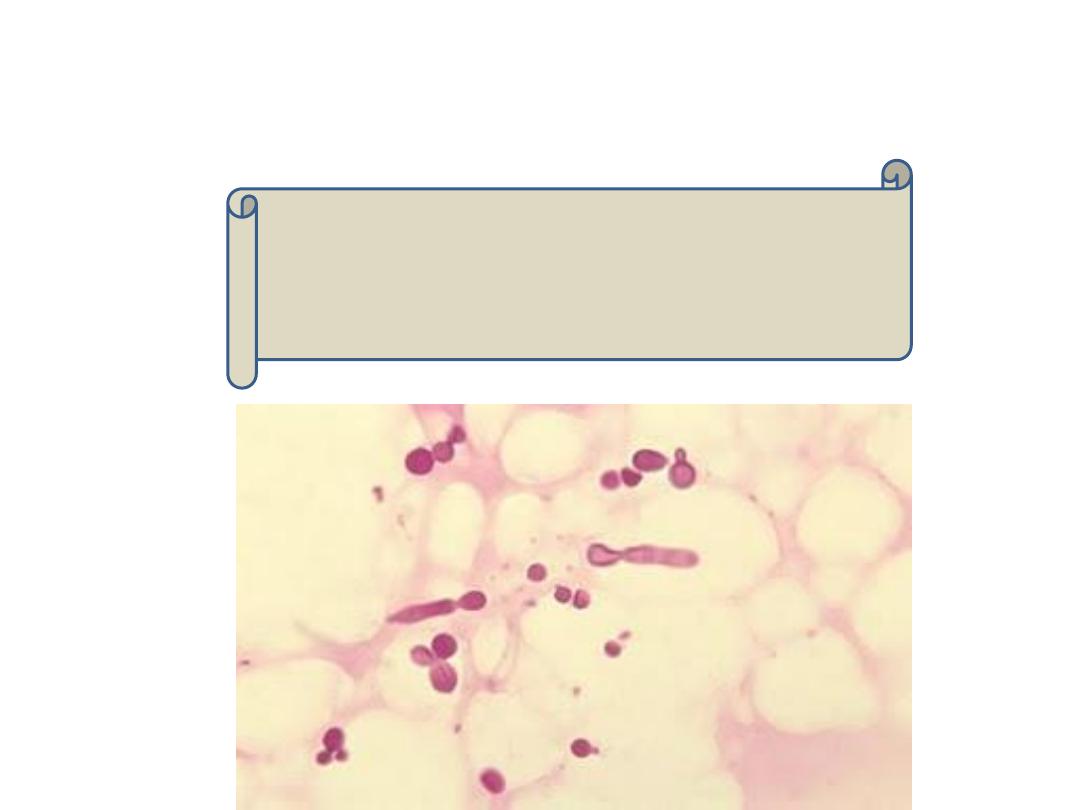
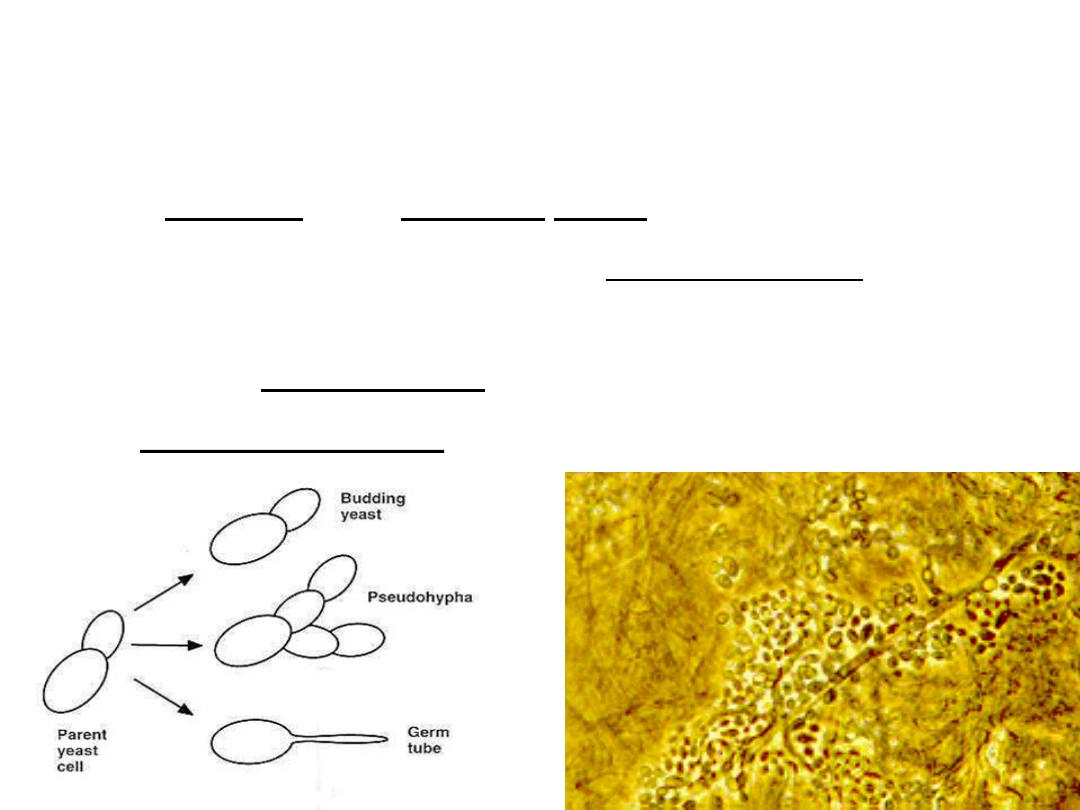
Gram positive, oval budding yeast cells.
If buds fail to detach, they form pseudohyphae.
Pseudohyphae are differentiated from true hyphae by the
presence of constrictions at septations between the cells.
But, Candida glabrata does not form pseudohyphae.

Diseases
In normal host, candida may cause:
1) Oral thrush or moniliasis (patches of creamy white
exudate that cover the mucous membrane of the
mouth).
2) Vulvovaginal moniliasis: itching and cheese appearing
vaginal discharge.
3) Rash in the skin folds of obese persons.
4) Diaper rash.
5) Paronychia of the nails (thickening and loss of the nails).
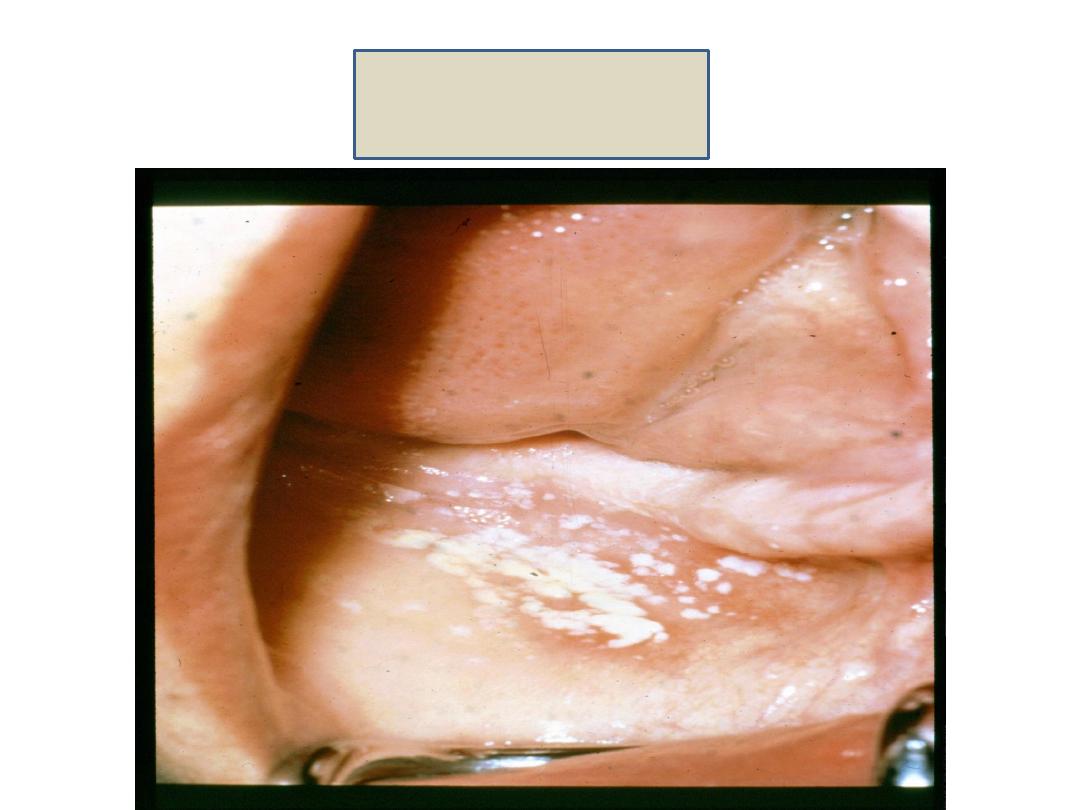
Oral thrush
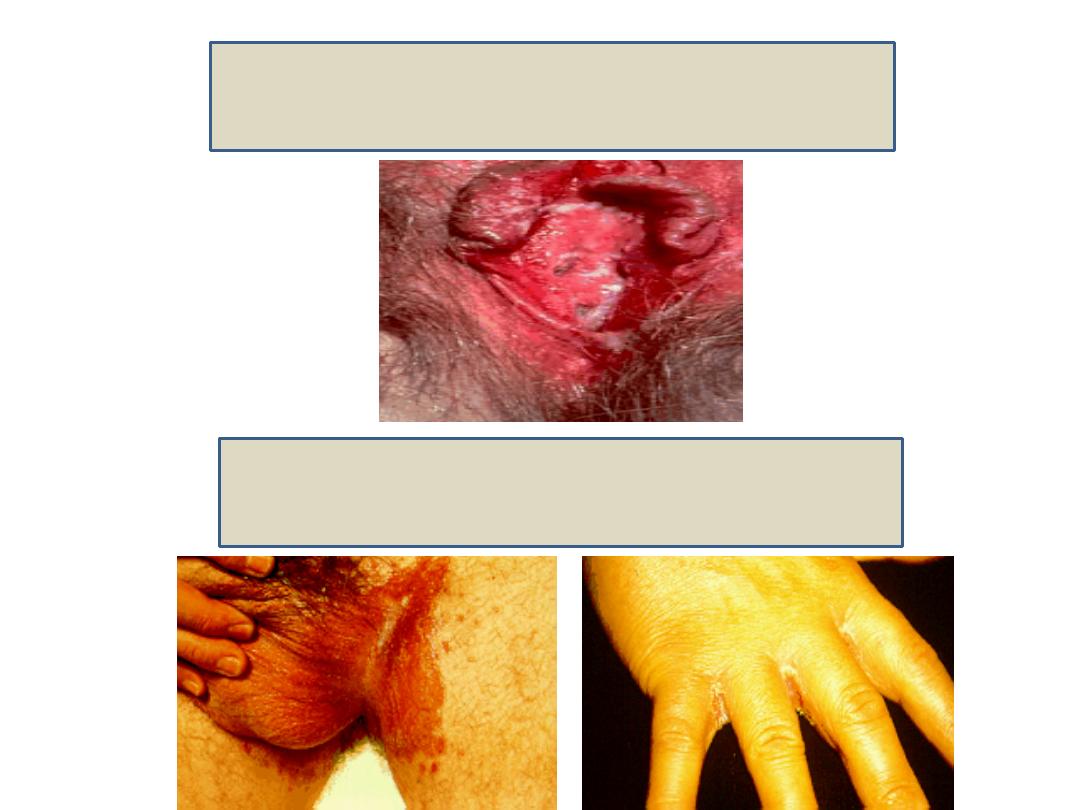
Vulvovaginal moniliasis
Rash in the skin folds
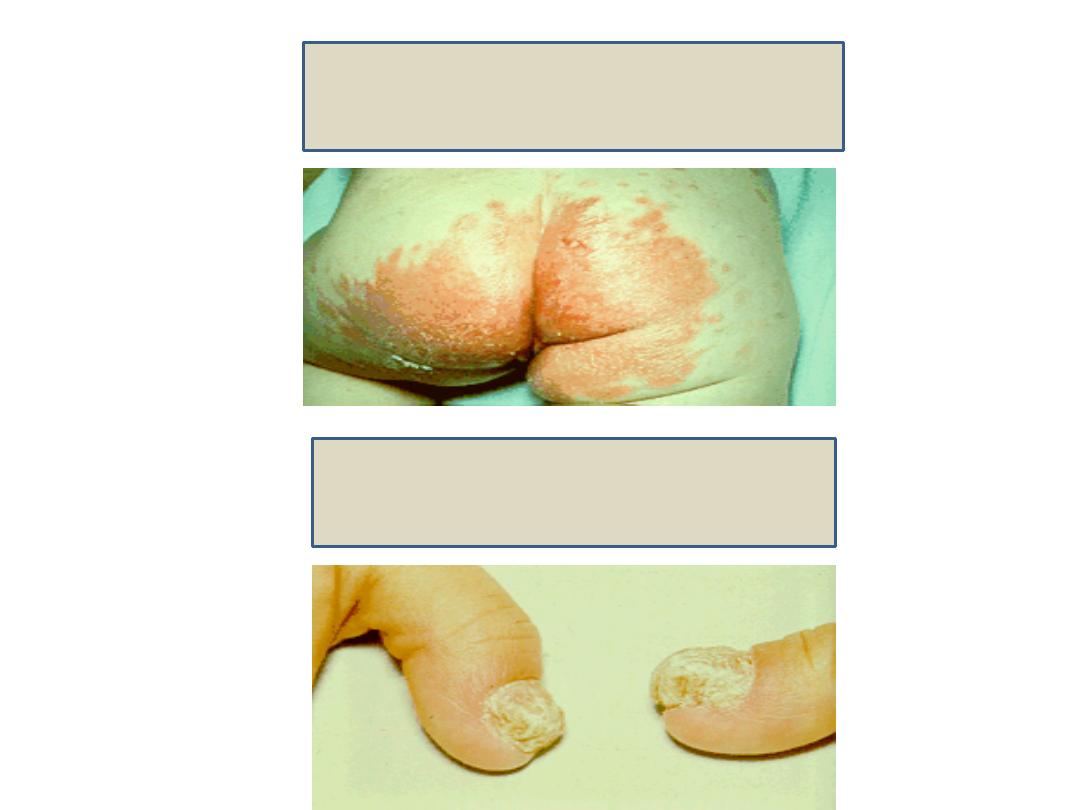
Diaper rash
Paronychia

In immunocompromised individuals such as:
1) Esophageal thrush.
2) Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis.
3) Systemic or disseminated candidiasis (even to the eye).
AIDS
Diabetes
mellitus
Malignancy
Defect in cell mediated immunity
Corticosteroids
Catheters
Laboratory diagnosis
Specimen:
according to the site of the lesion.
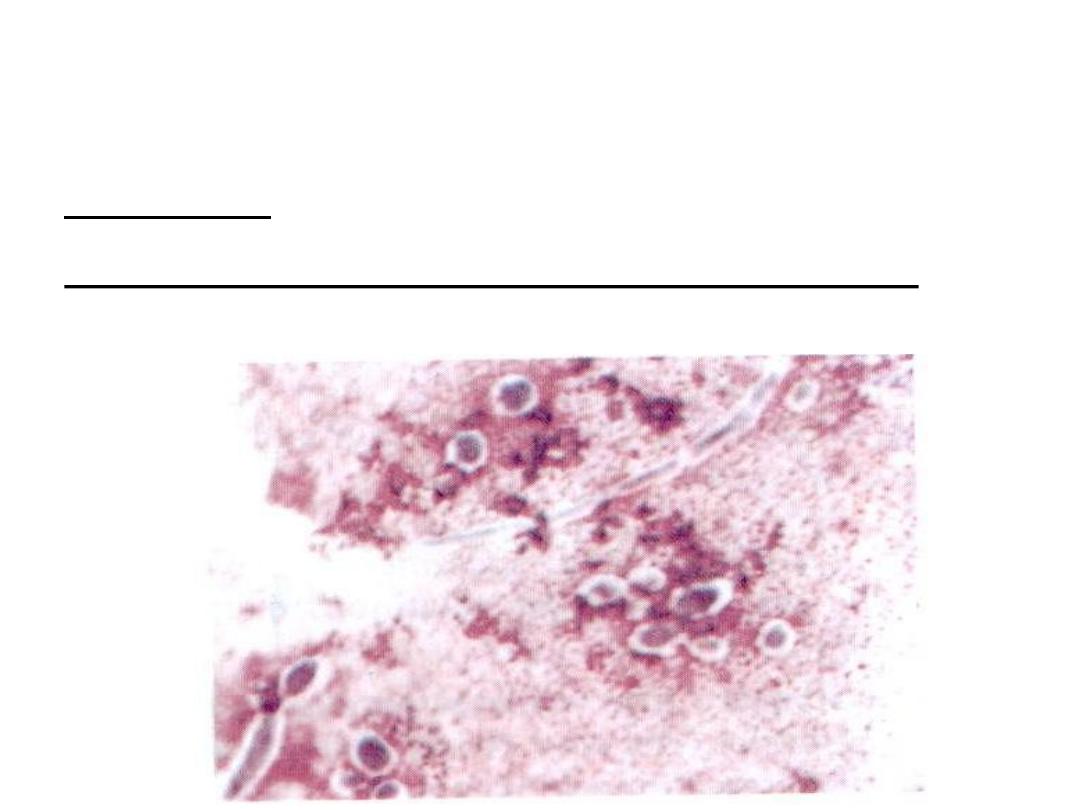
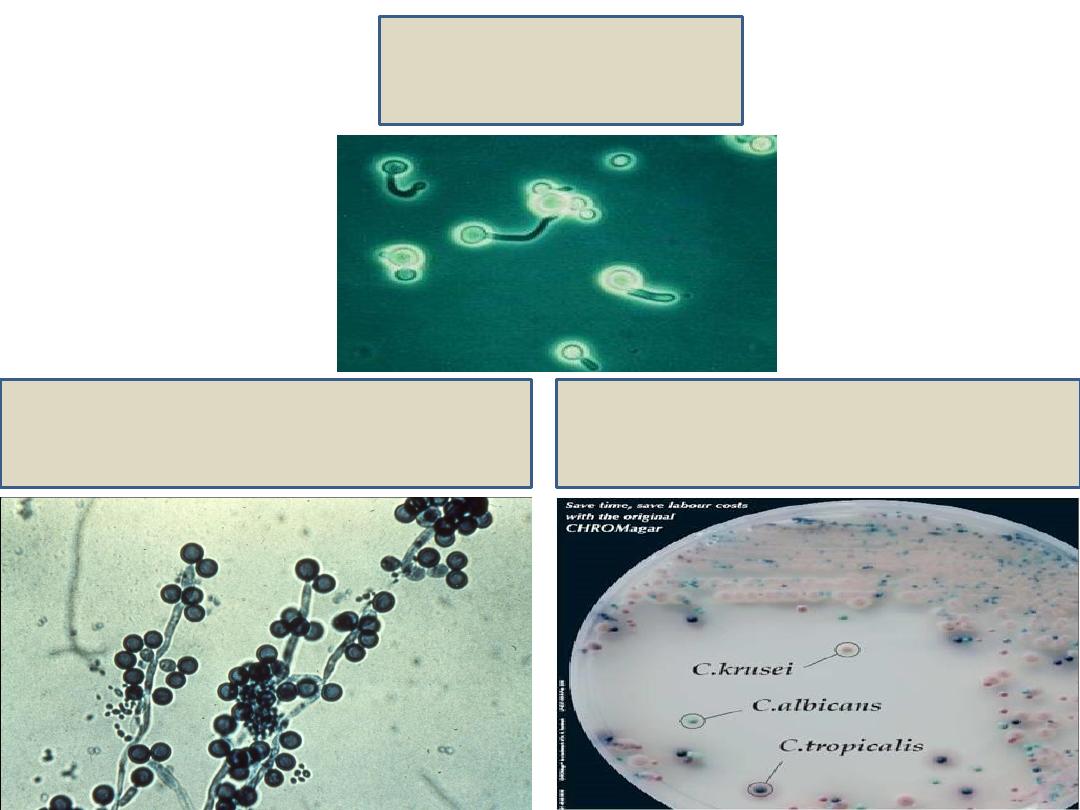
Direct examination of Gram stained smear:
Gram
positive oval budding yeast cells + pseudohyphae.
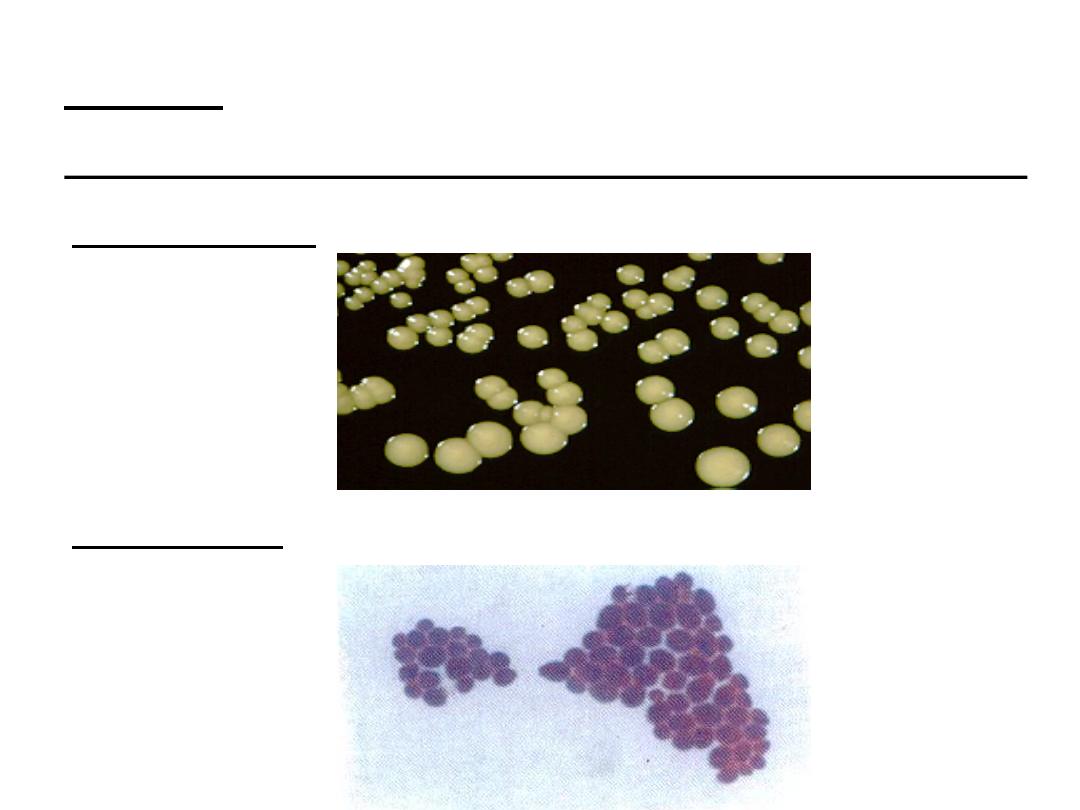
Culture:
on SDA at 37 degree.
Identification of candida on the plate is done by:
1. Morphology:
soft cream colored colonies with yeasty
odor.
2. Gram film:
Gram positive oval budding yeast cells.

3. Biochemical reactions:
to differentiate between
Candida albicans and other species.
o Germ tube test:
Candida albicans forms germ tube when
incubated in serum for 1 – 2 hour at 37 degree.
o Chlamydospore formation:
Candida albicans forms
chlamydospores on corn meal agar incubated at 30 degree.
o Sugar fermentation:
Candida albicans ferment glucose and
maltose with acid and gas production.
o Inoculation of the yeast on chromogenic agar:
each
candida species produces a different color on this medium.
Germ tube
Chlamydospores
CHROMagar
Treatment
• Oral thrush: fluconazole
• Cutaneous lesions: nystatin and clotrimazole
ointments.
• Mucocutaneous candidiasis: ketoconazole
• Disseminated candidiasis: amphotericin B
