SUBCUTANEOUS MYCOSES
By
Dr. Mohammed H. Mushrif
Lecturer of Medical Mycology

Fungi that cause subcutaneous mycoses
normally reside in the soil.
They enter subcutaneous tissues by traumatic
inoculation with contaminated material.
Subcutaneous mycoses is usually confined to
subcutaneous tissues but in rare occasions
may become systemic.
1) Sporotrichosis
2) Chromoblastomycosis
3) Mycetoma
4) Phaehyphomycoses

Sporotrichosis

Causative fungus
Sporotrichosis is caused by Sporothrix
schenkii.
This fungus is a dimorphic fungus. At room
temperature, it grows as a mold producing
branching septate hyphae + conidia & in
tissues or at 37 degree, it grows as small
budding yeast cells.
This fungus lives on plants, grass, trees and
rose thorns.
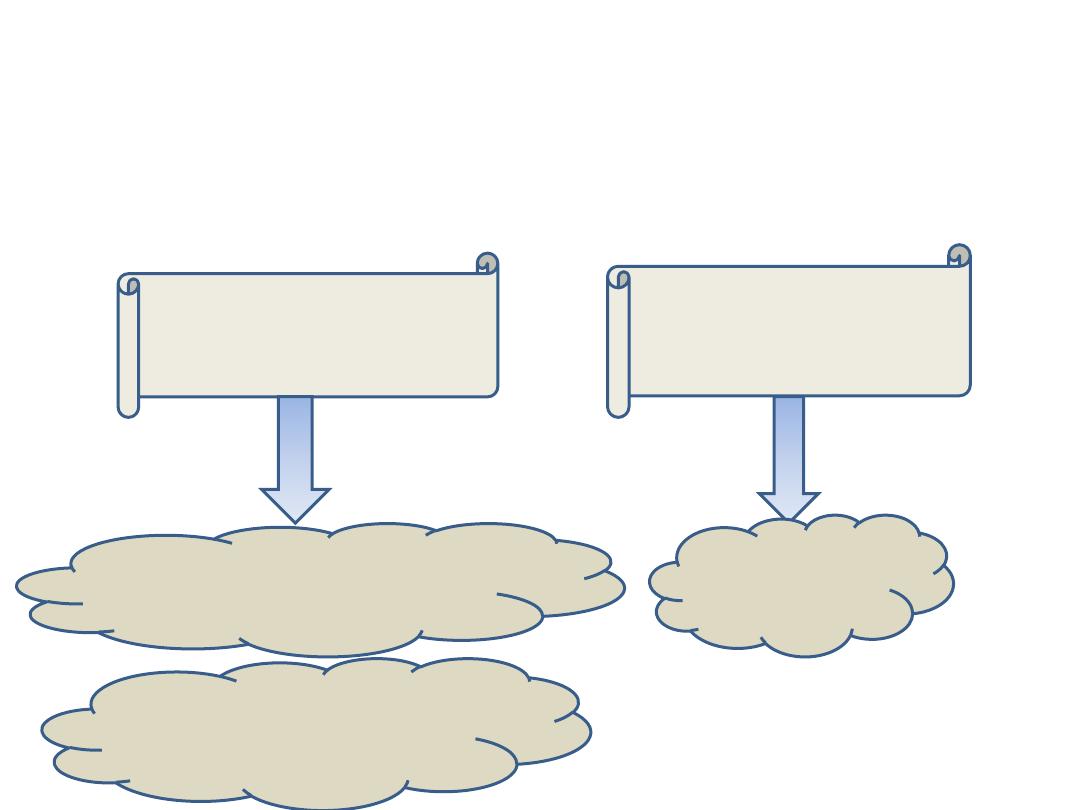
Portals of entry
Sporothrix schenkii infects the body by two
routes either by:
Traumatic
inoculation
Rarely,
inhalation
Lymphocutaneous
sporotrichosis
Pulmonary
lesion
Fixed cutaneous
sporotrichosis

Pathogenesis
The conidia or hyphal fragments are introduced into
the skin by traumatic inoculation usually by rose
thorns.
So, this disease is an occupational risk to gardeners
and agricultural workers.
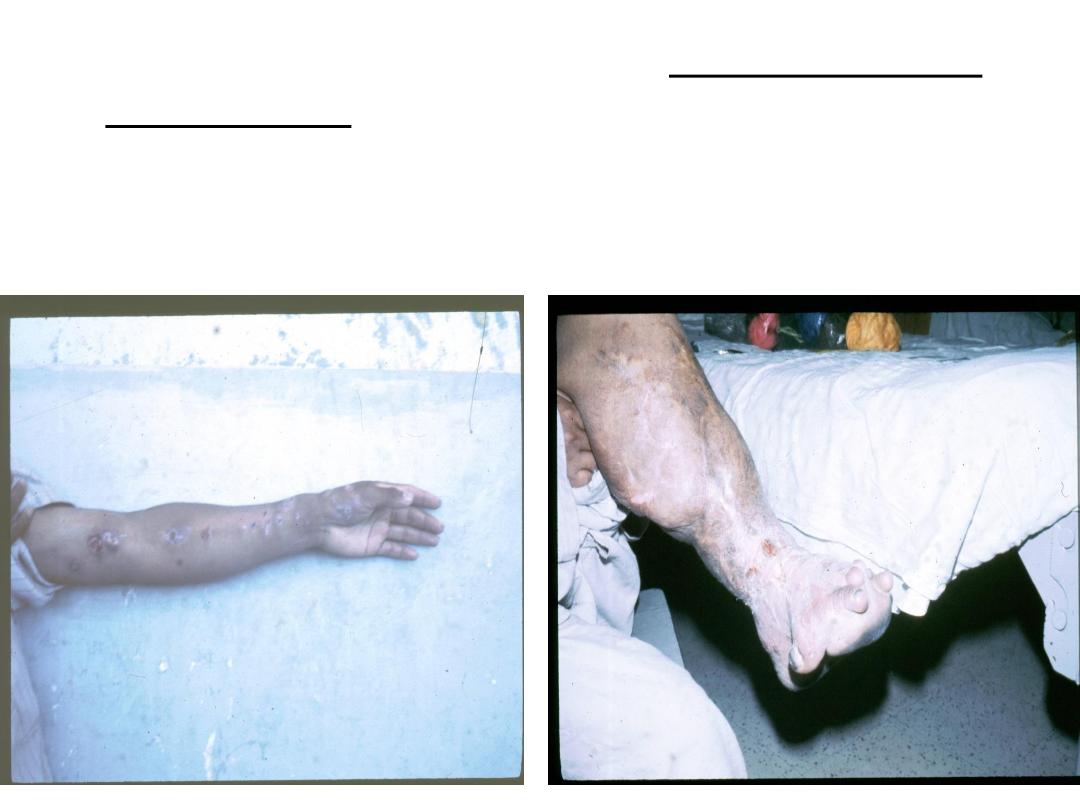
About 75% of the cases develop lymphocutaneous
sporotrichosis. The initial lesion is a granulomatous
nodule that will ulcerate and become necrotic.
Multiple subcutaneous nodules occur along the
lymphatic vessels.
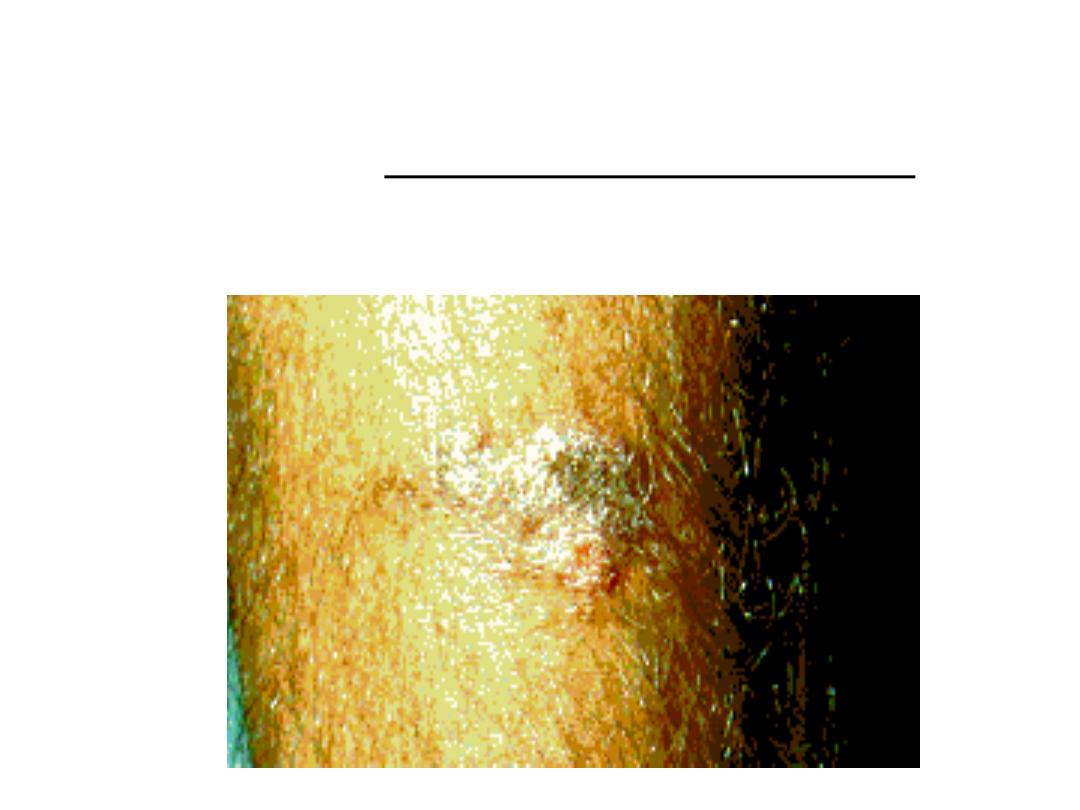
In endemic areas such as Mexico, South Africa and
Japan, population has some immunity to sporothrix
so they develop fixed cutaneous sporotrichosis in
which the patient has only single non lymphatic
nodule which is limited and non progressive.
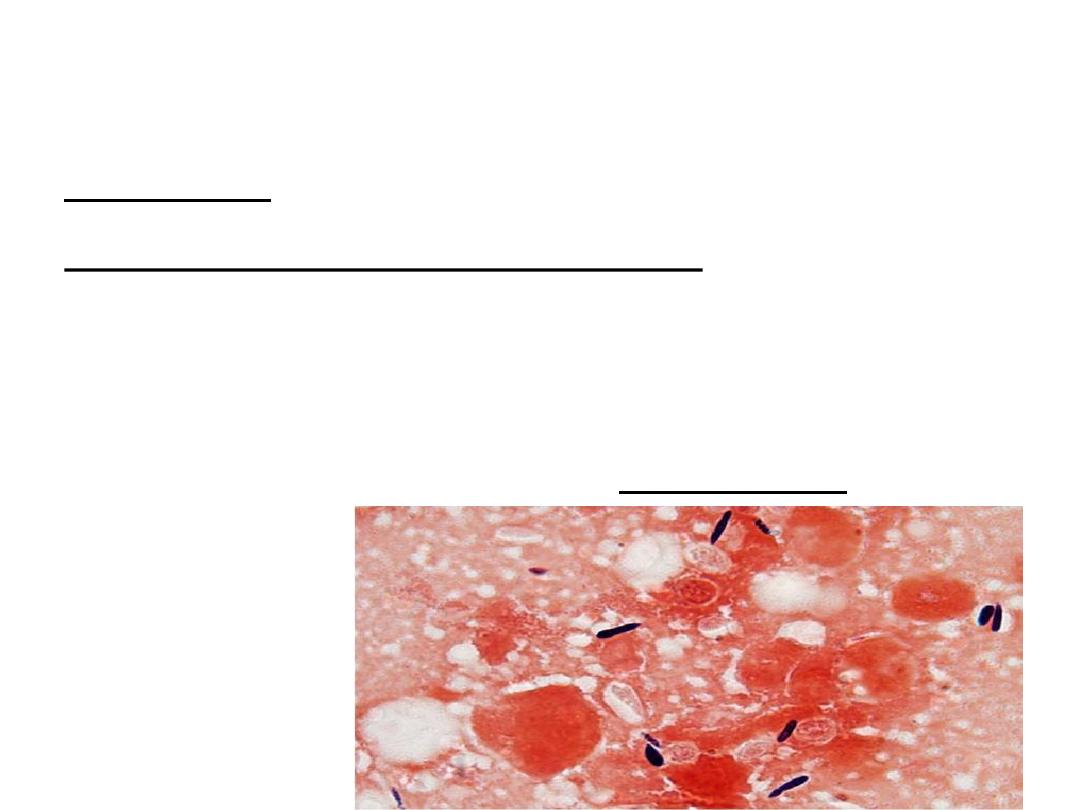
Laboratory diagnosis
Specimen:
biopsy or exudate from the lesion.
Direct microscopic examination:
Yeasts are seen in tissue sections stained with Gomori
methenamine silver which stain cells black or periodic acid
Schiff which stain cells red.
Yeast cells are round, fusiform or cigar shaped (1-3 X 3-10
µm).
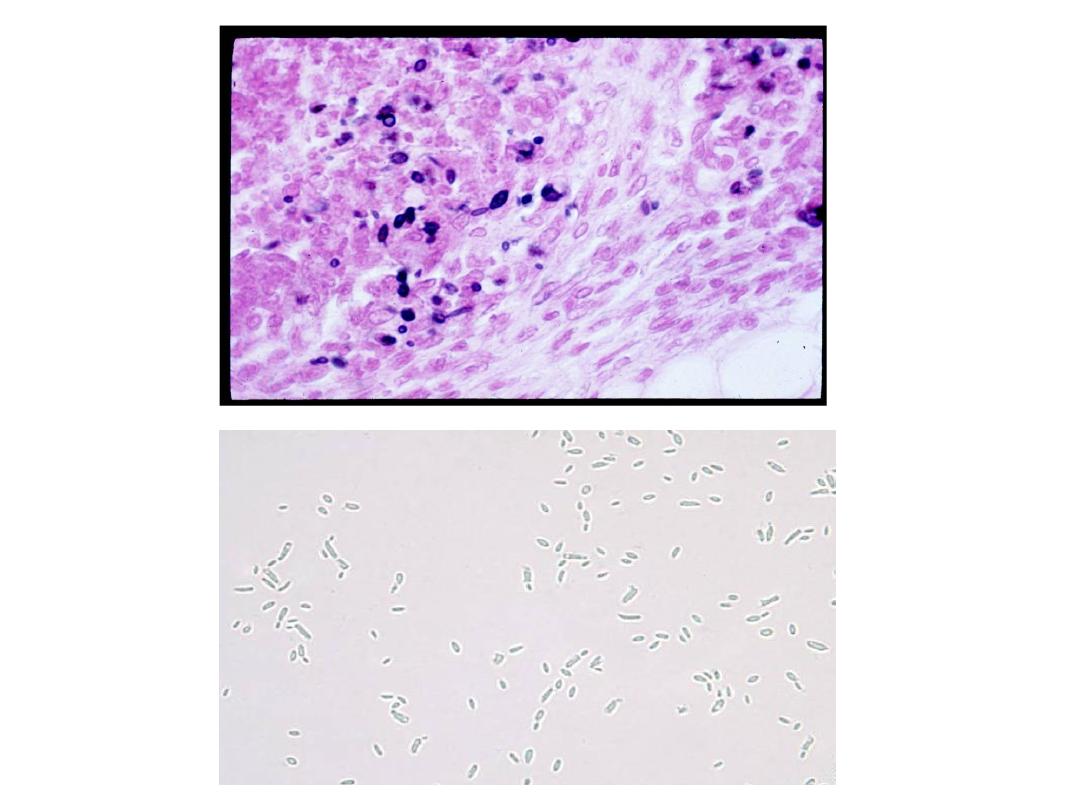

Culture:
It is the most reliable method of diagnosis of
sporotrichosis.
Culture is done on SDA with antibiotics at 25 degree
(colonies are black and shiny then become wrinkled and
fuzzy with age).
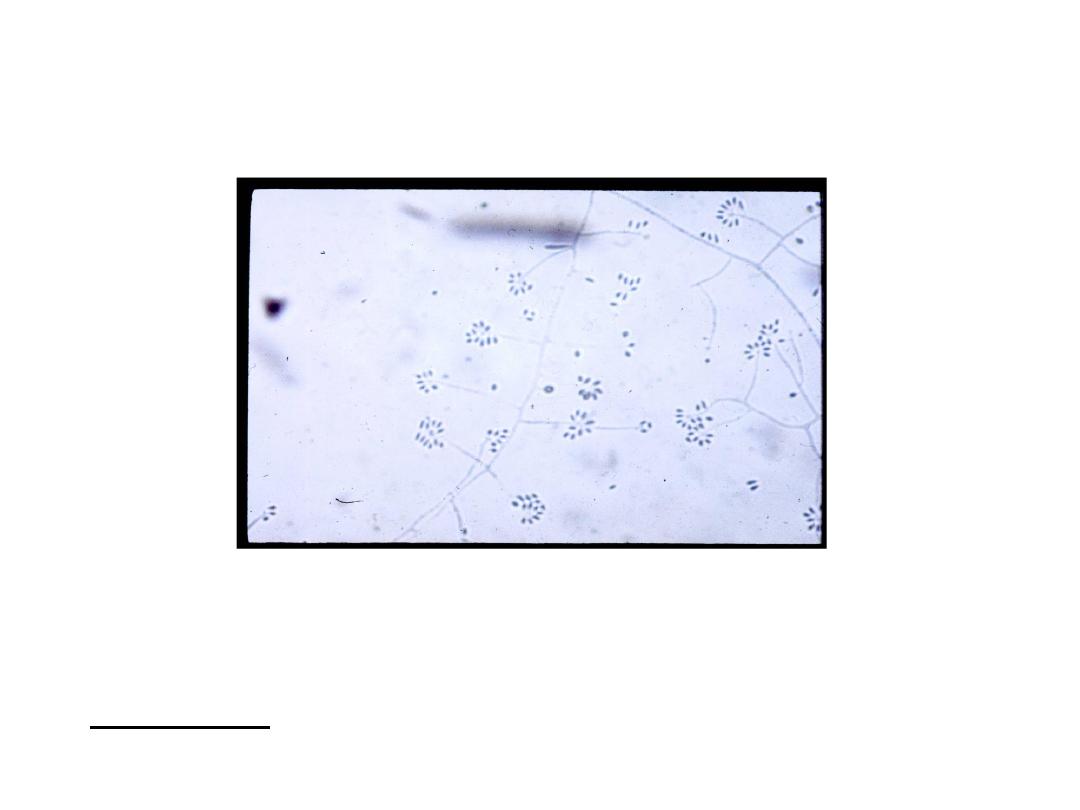
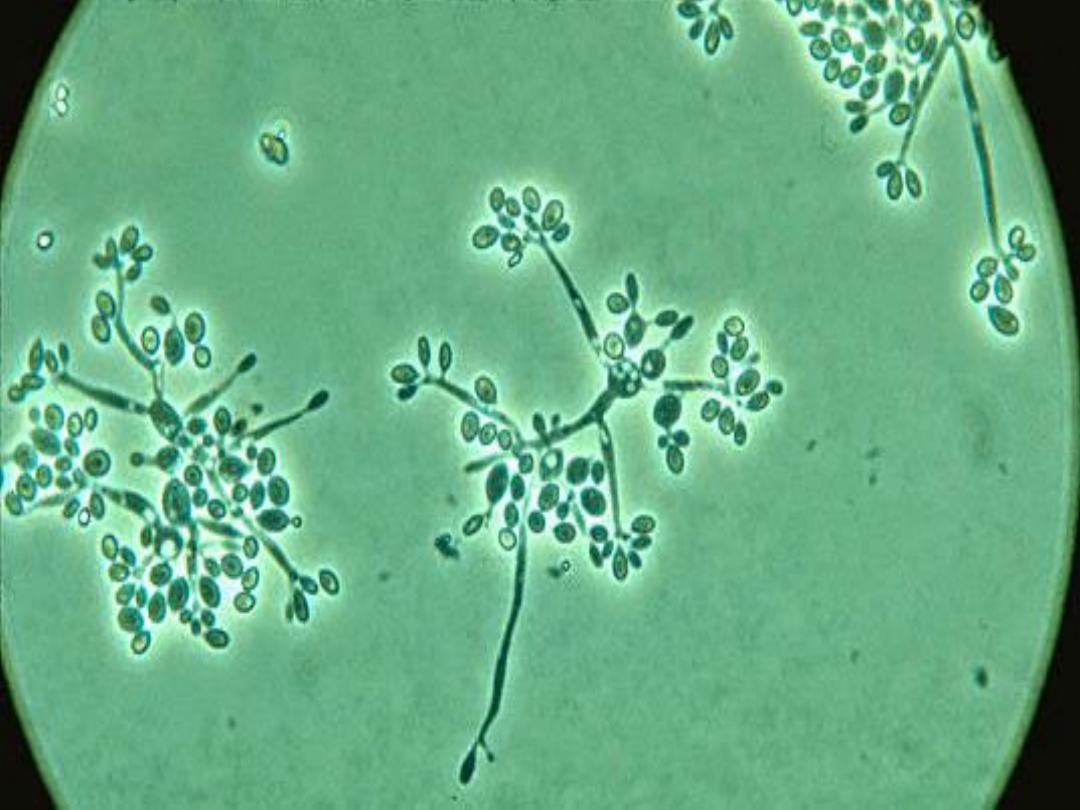
Under the microscope: hyphae are seen bearing
clusters of oval conidia (2 – 4 µm) at the tip of slender
conidiophore resembling daisy.
If the plate is incubated at 37 degree, it will convert to
a yeast culture.
Serology:
latex agglutination test.

Treatment
• Oral potassium iodide in milk.
• Or itraconazole.
• Amphotericin B in systemic infections.
