
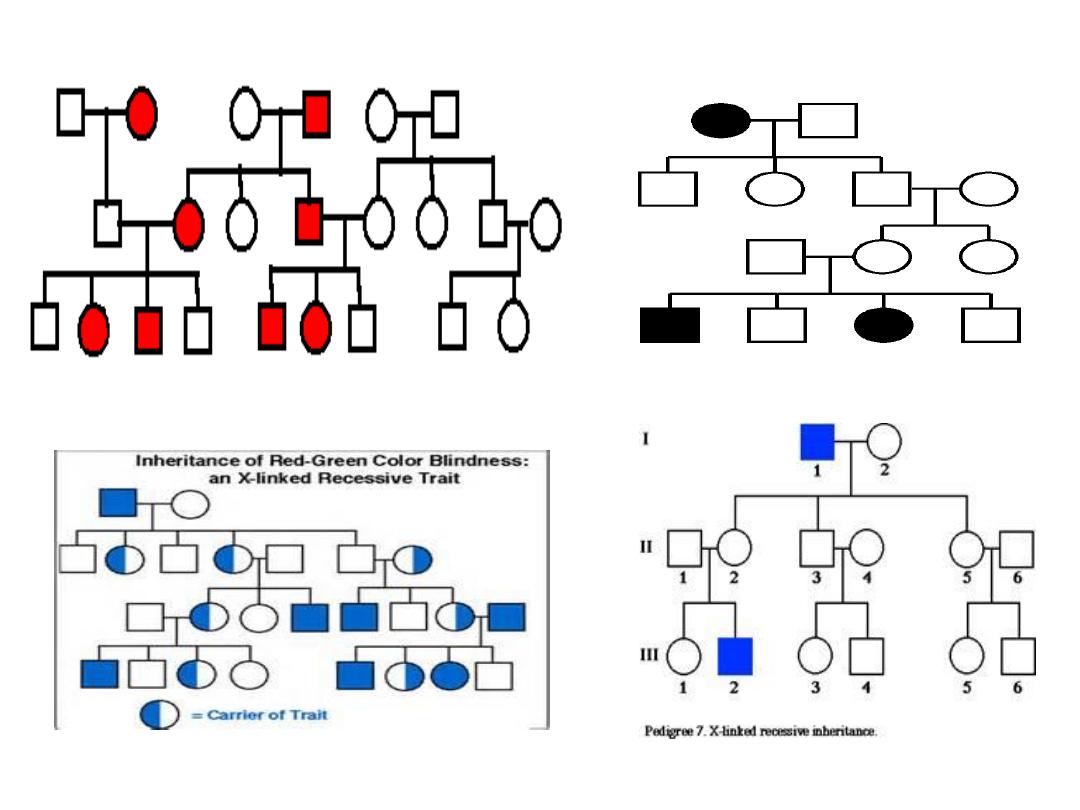
Genetic disorders
Dec. 9 . 2015

Genetic disorders
Objectives
• SNP & CNV
• Types of genetic disorders
• Genes encoding structural pr.
Marfan Syndrome “MFS”
Ehlers- Danlos Syndrome “EDSs”
• Genes encoding receptor proteins’ or channels.
Familial hypercholestremia.

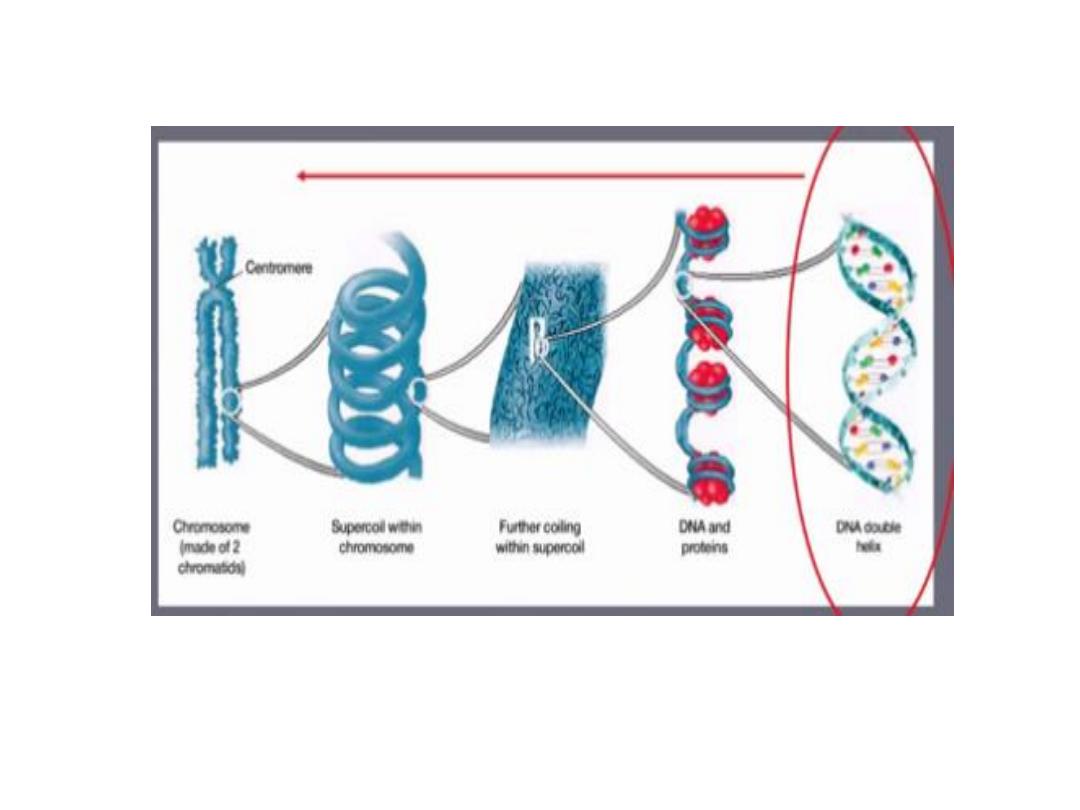
The DNA encodes 30,000 genes

CNV
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism
Copy Number Variation
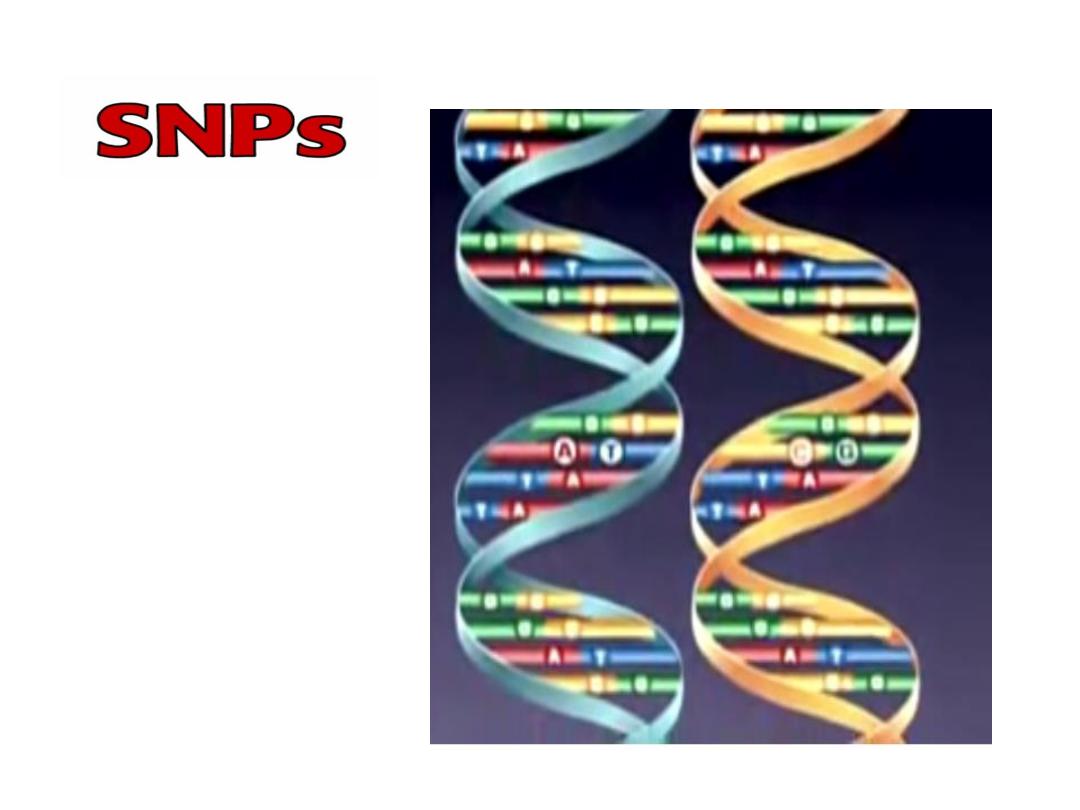
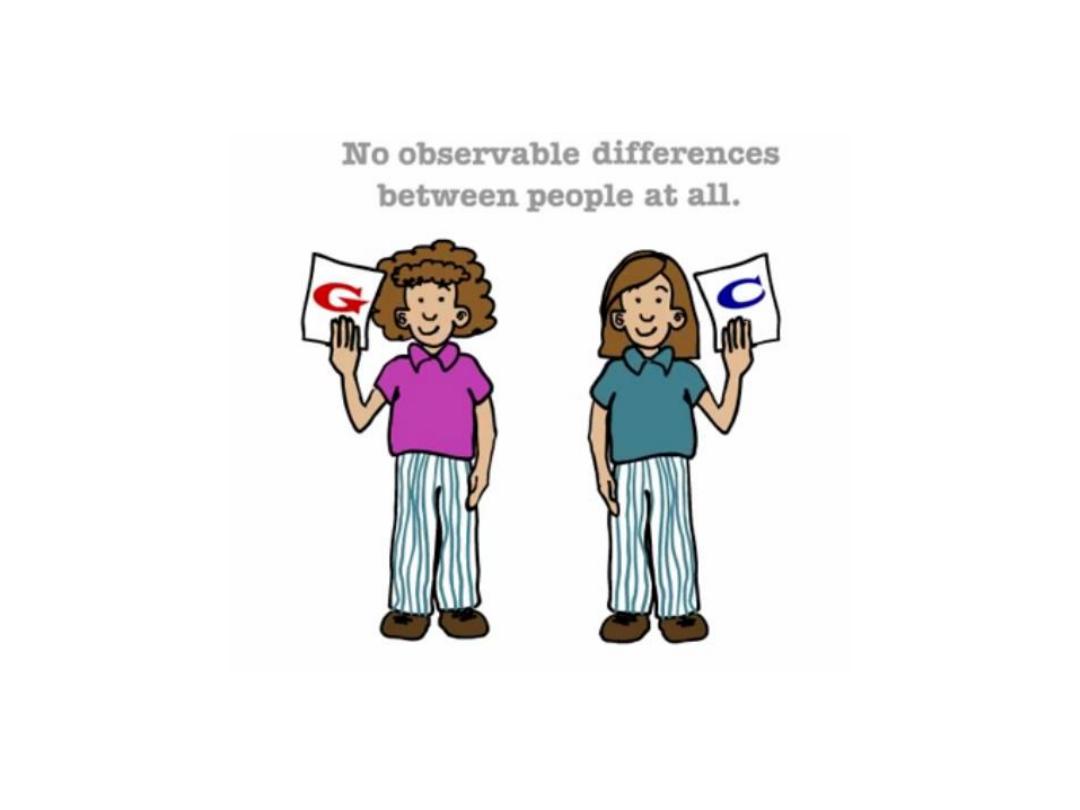


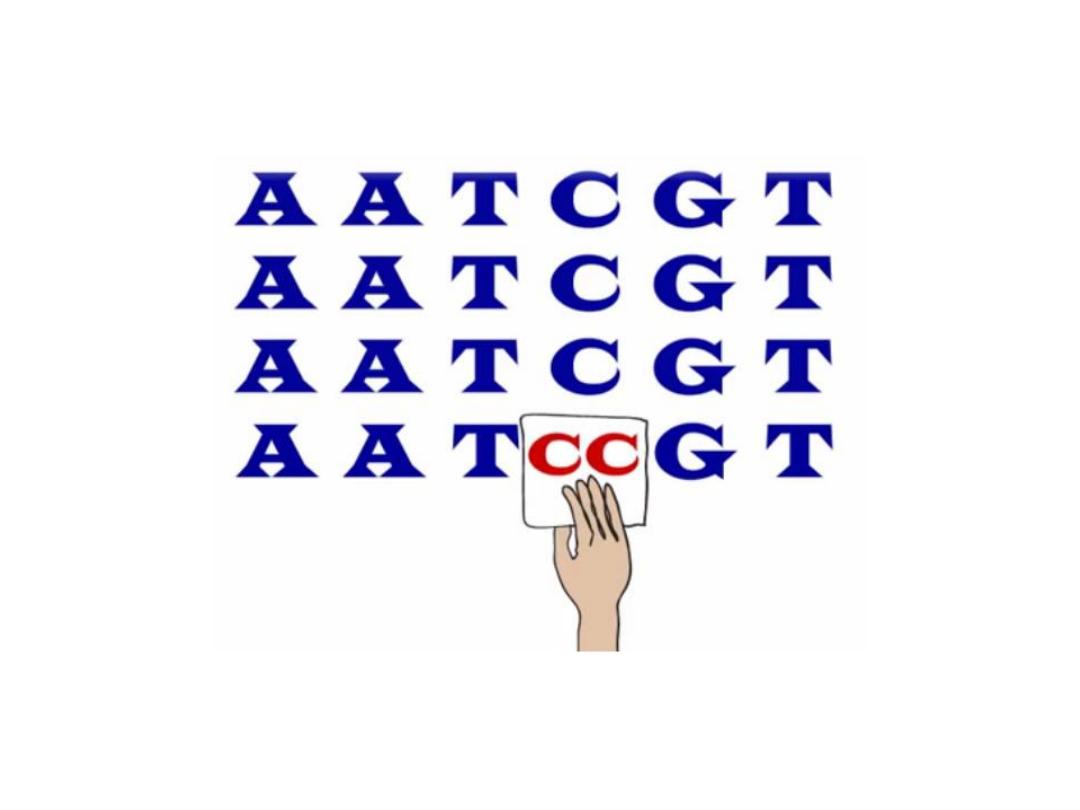
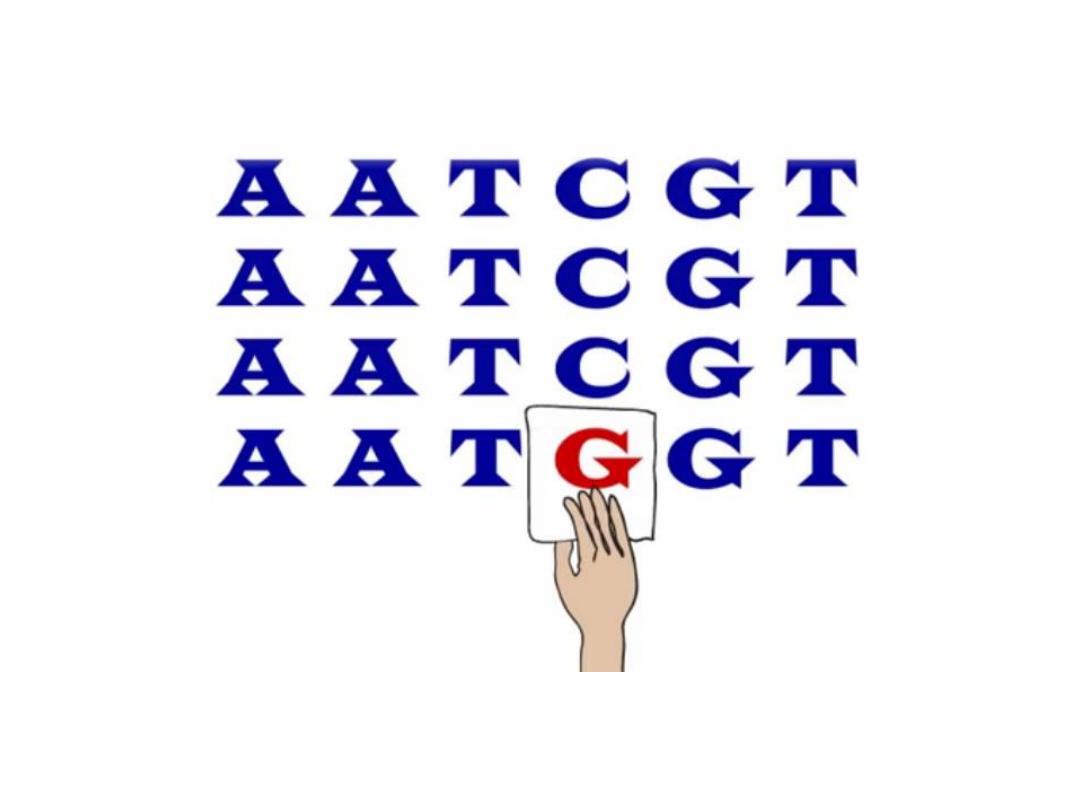



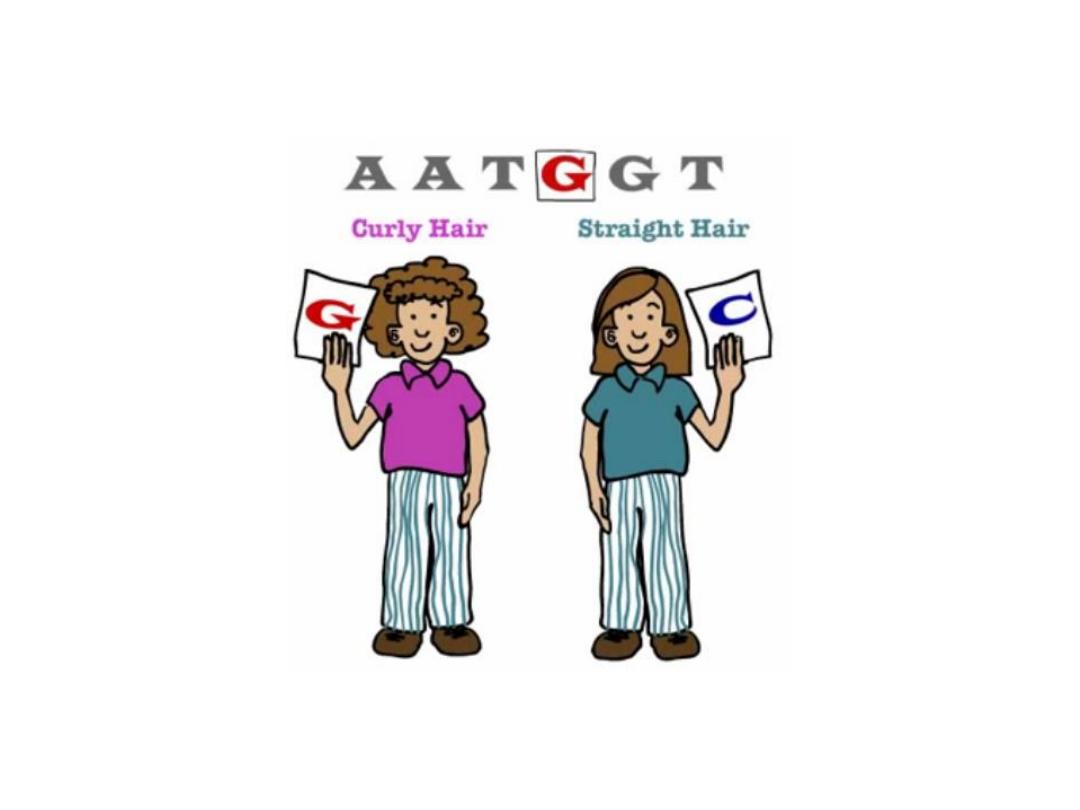
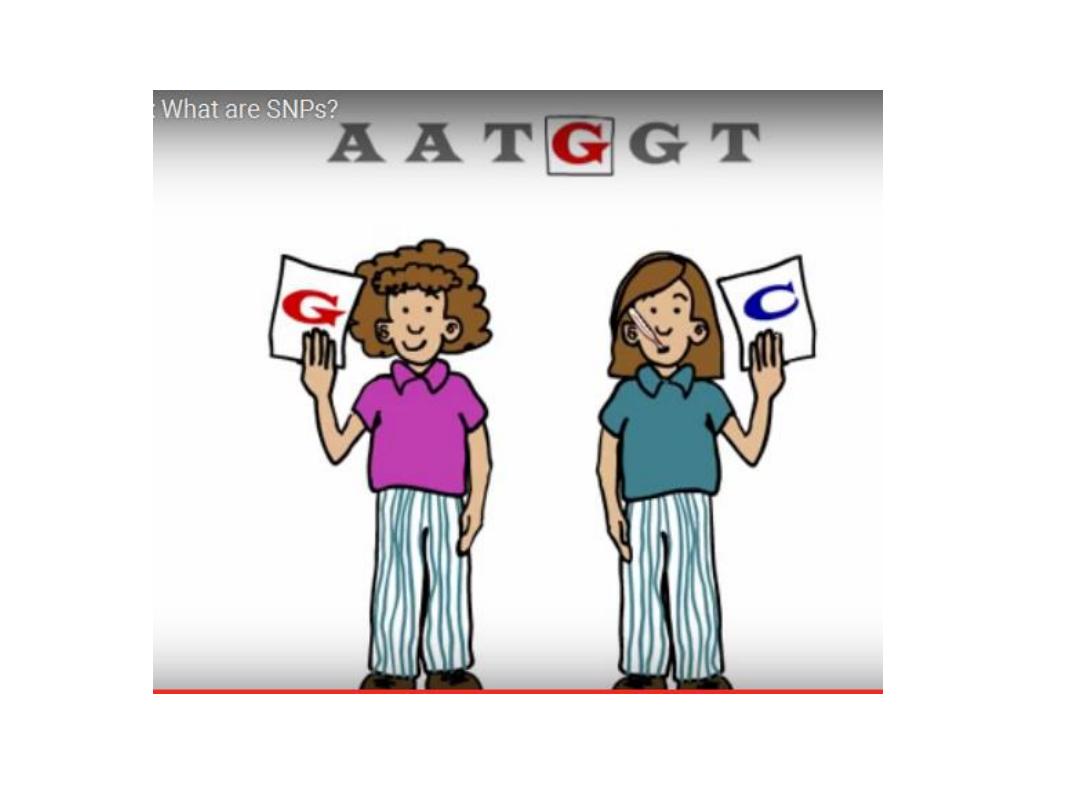
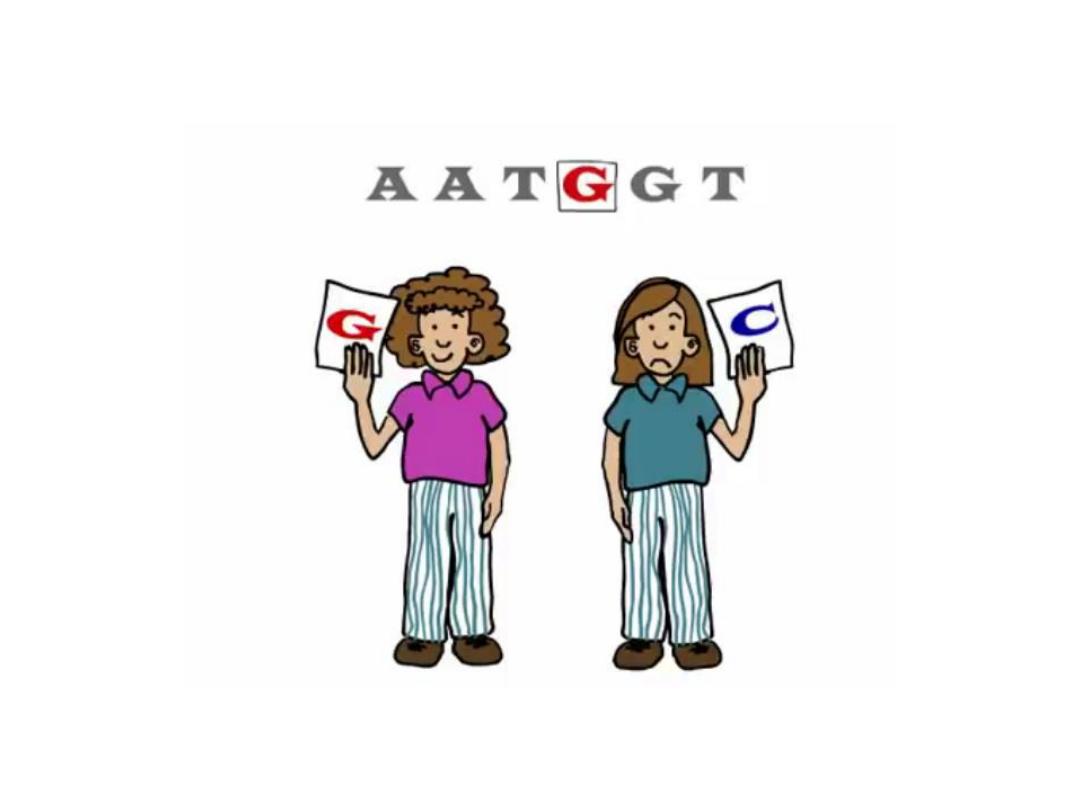

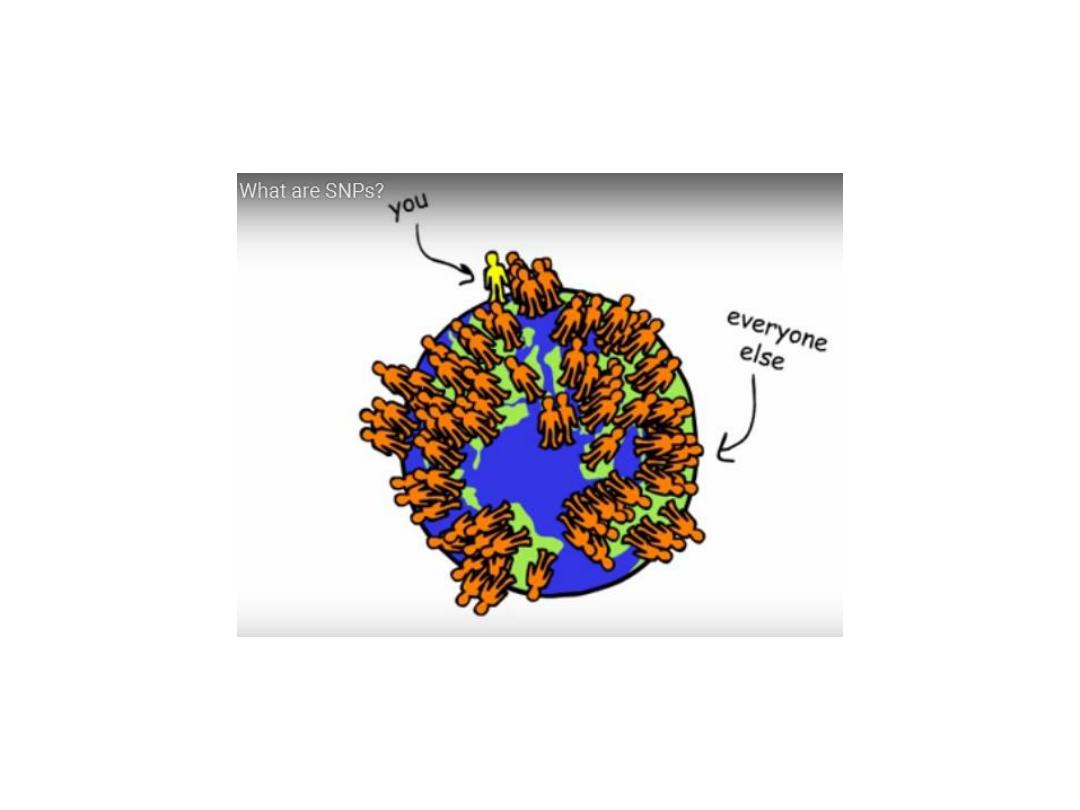

SNPs are used as genetic markers
to identify genes responsible for
disease susceptibility
or a
particular trait.
SNPs as gene mapping markers

Point mutations
Not all single base pair differences are
SNPs
They can be a mutation if least
abundant allele has
a frequency < 1% in
a population

Causes of gene mutations

Mutation
Gene directly leads to
disorder
Mendelian pattern of
inheritance
Rar
e
Polymorphism
Gene confers an increased
risk, but does not directly
cause disorder
No clear inheritance pattern
Common in population
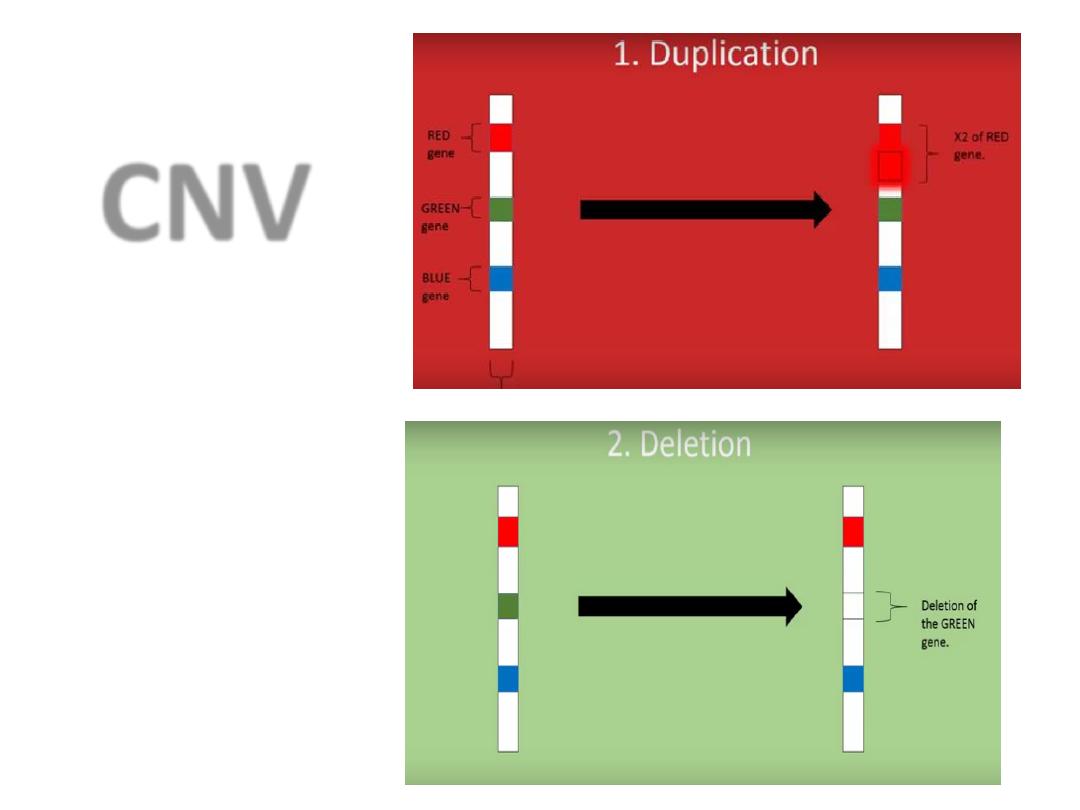
CNV
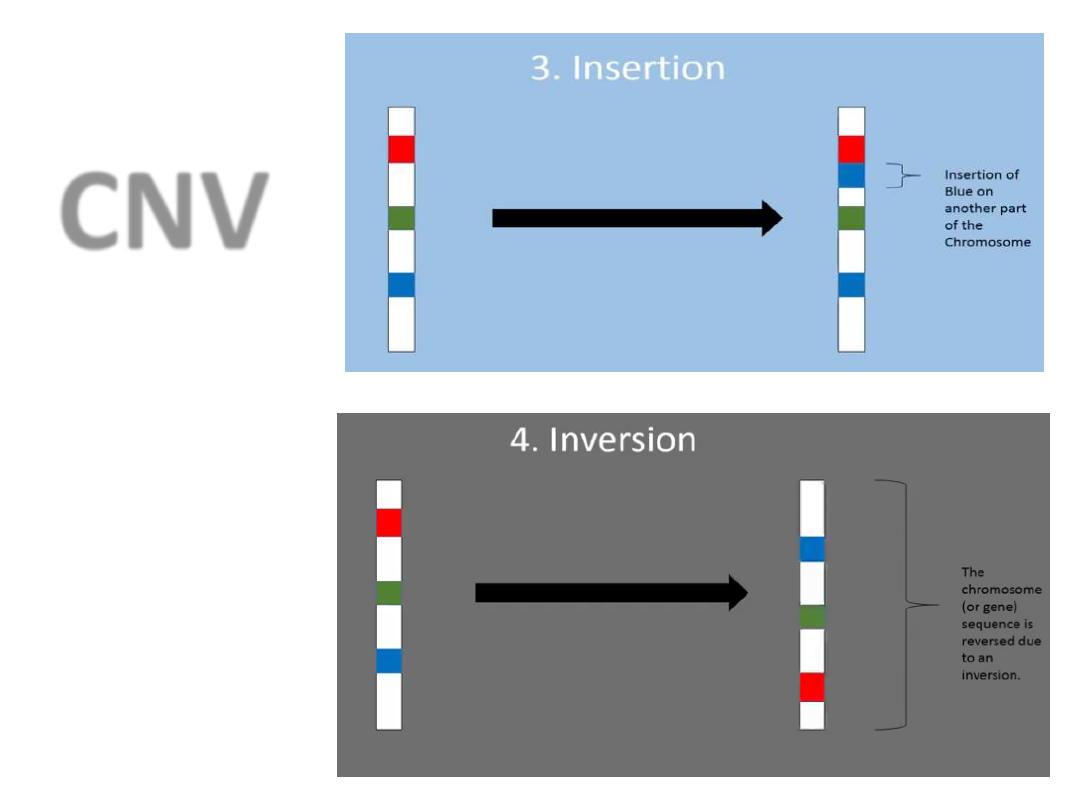
CNV

CNV
• It was generally thought that genes were almost
always present in
two copies
in a genome.
• However, recent discoveries have revealed that
large segments of DNA ranging in size from
thousands to millions of DNA bases, can vary in
copy-number.
• CNV; affecting a greater fraction of the genome
than single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs).

Copy Number Variation (CNV)
• CNV
; is when the number of copies of a
particular gene varies from one individual to
the next.
• The genome experiences
gains and losses
of
genetic material.
• The extent to which CNV contributes to
human disease is not yet known.
• Some
cancers
are associated with elevated
CNs of particular genes.
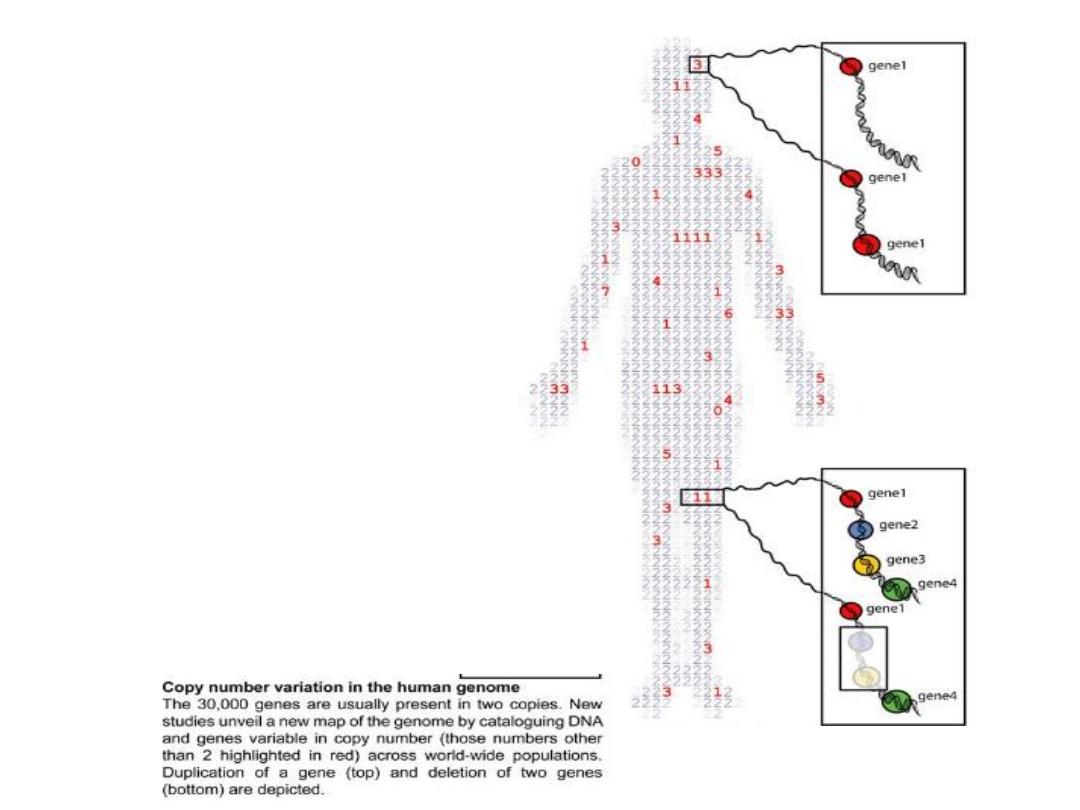
Genes are found to be CNV
are;
Genes that are involved in the
immune system
and in
brain
development and activity
–
two functions that have
evolved rapidly in humans
–
tend to be enriched in CNVs.
While, genes that play a role in
early development and cell
division
– both critical to
fundamental biology
– tend to
be spared
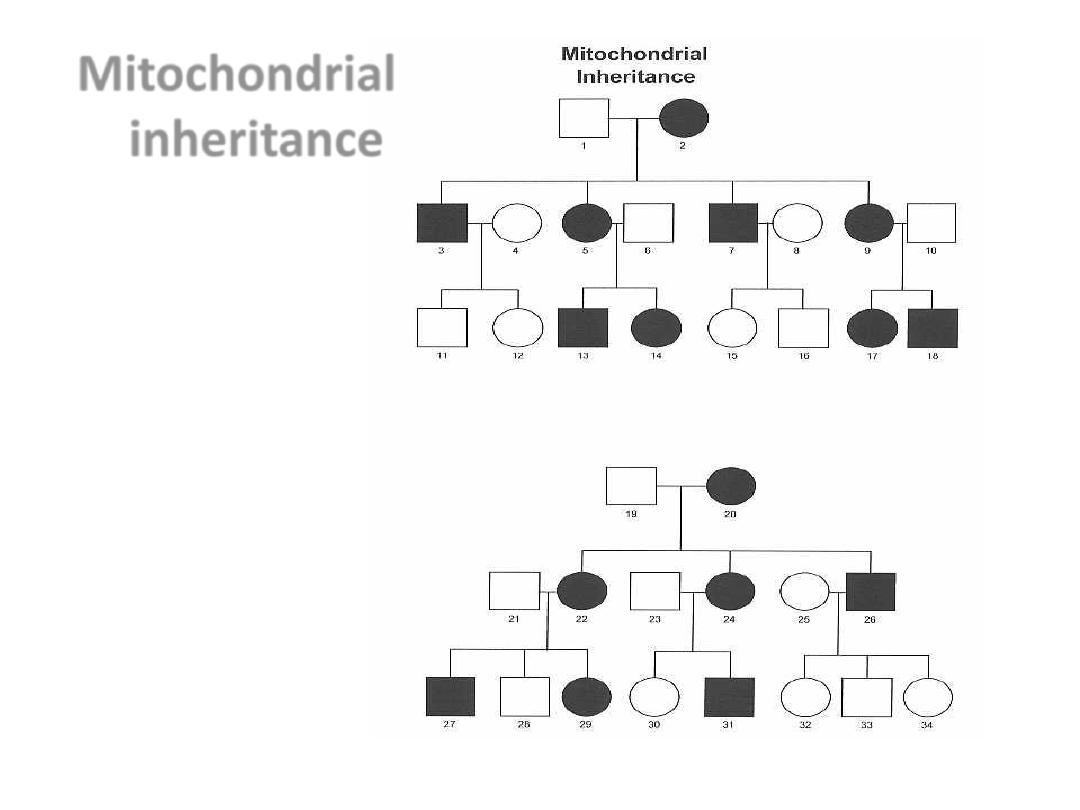
Mitochondrial
inheritance

SINGLE GENE DISORDERS
• STRUCTURAL PROTEIN DEFECT
(Marfan, Ehl-Dan)
– Structure
– Function
– Quantity
• RECEPTOR/TRANSPORT PROTEIN DEFECT
(Familial
Hypercholesterolemia)
• ENZYME DEFECT
(Most of them, e.g., PKU)
– Accumulation of substrate
– Lack of product
– Failure to inactivate a protein which causes damage
• ENZYME DEFECT WHICH INCREASES DRUG
SUSCEPTIBILITY:
G6PDPrimaquine

STRUCTURAL PROTEIN DEFECTS
• Marfan Syndrome
– Fibrillin-1 defect.
– Tall, dislocated lens, aortic arch aneurysms, etc.
– Abraham Lincoln?
• Ehlers-Danlos Syndromes (AD, AR)
– Multiple (30?) different types
– Classical, Hypermob., Vasc., KyphoSc., Joints., Derm
– Various collagen defects
– Hyperelastic skin, hyperextensible joints
•
surrounding the amorphous
.

Marfan Syndrome
• AD
• Mutation affect fibrillin (Glycopr. In microfibrils
in ECM)
• Aorta, Ligaments, Cilliary zonules (lenses)
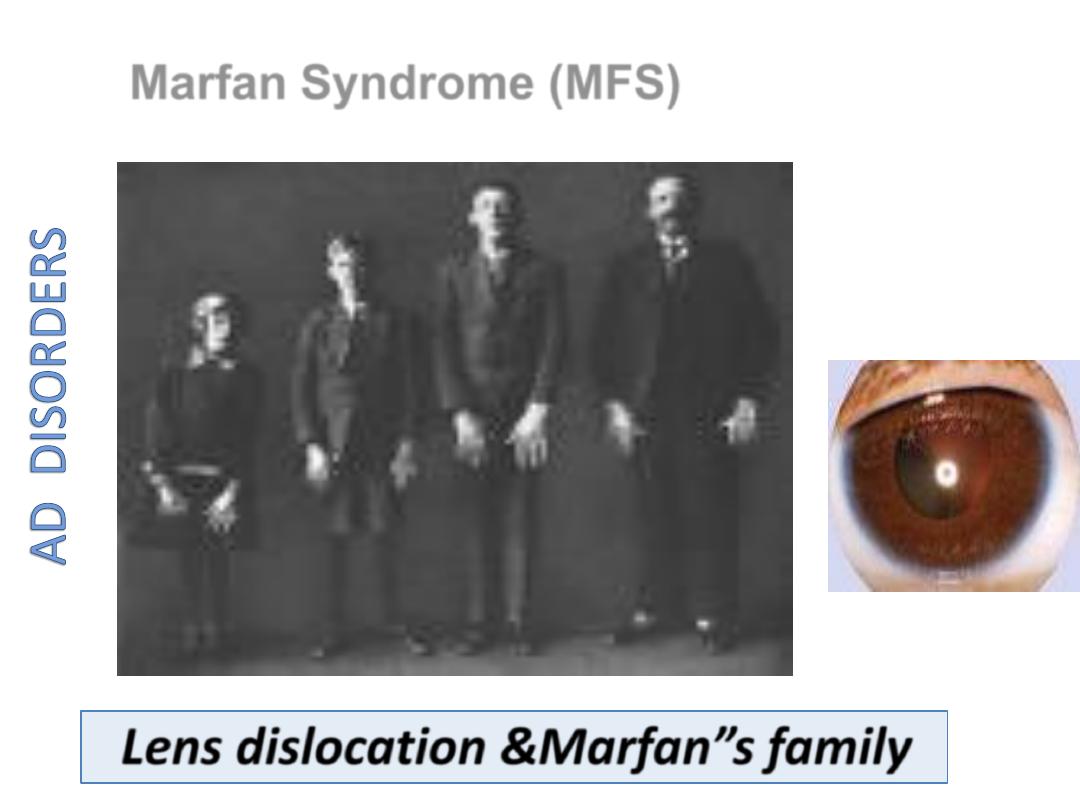
Lens dislocation &Marfan”s family
Marfan Syndrome (MFS)
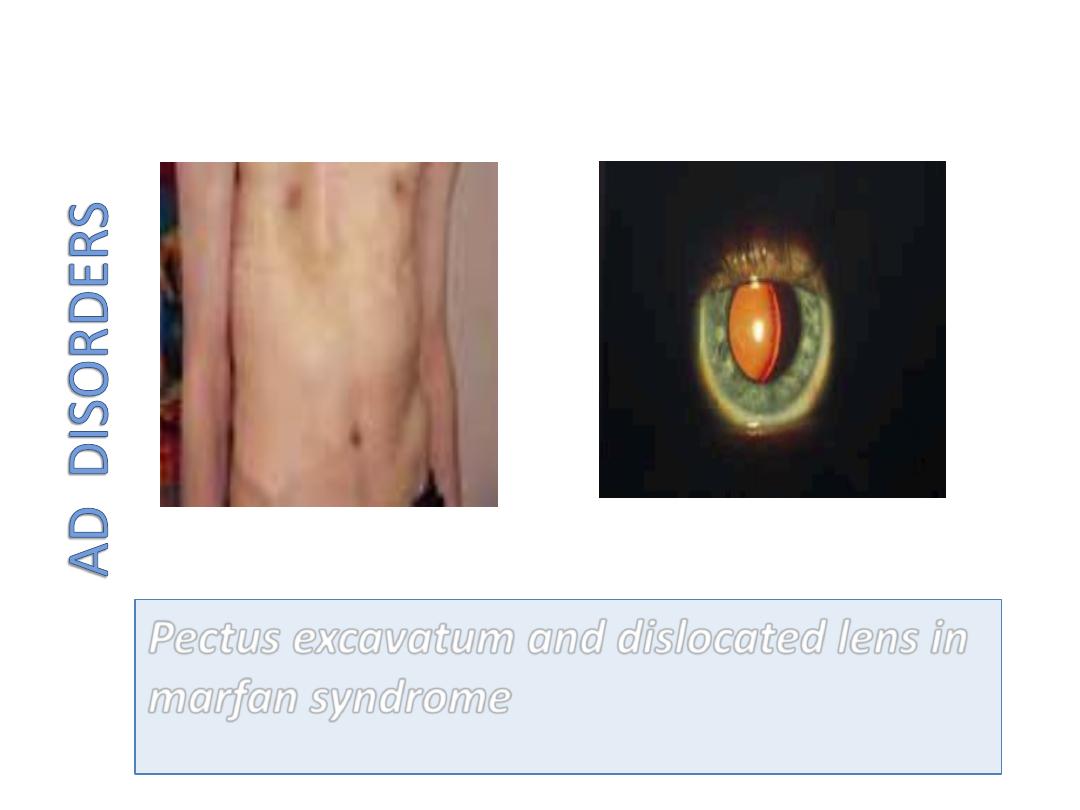
Pectus excavatum and dislocated lens in
marfan syndrome
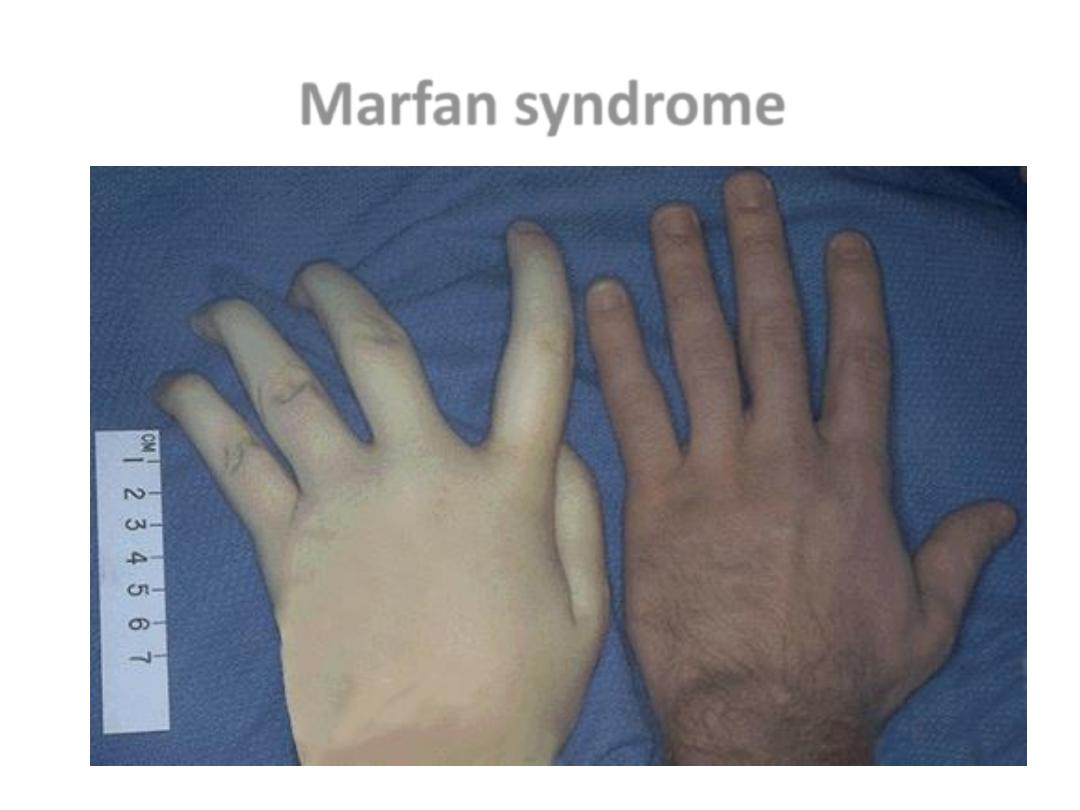
Marfan syndrome
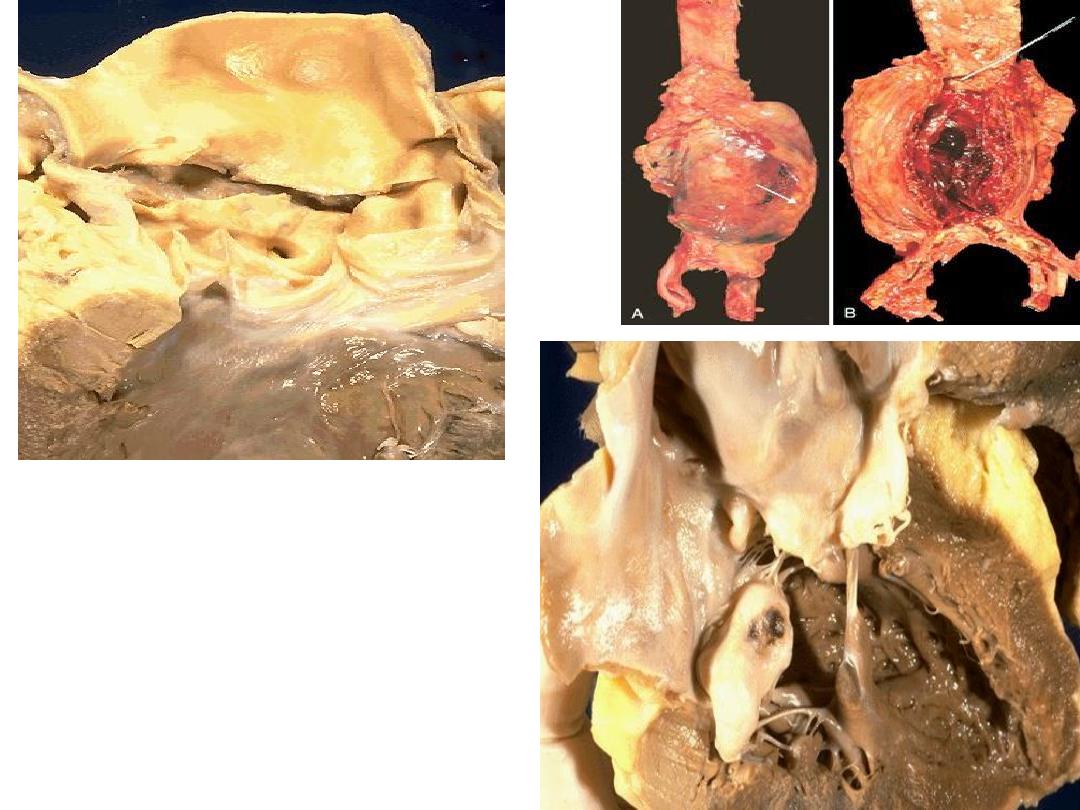
Aorta Media fragmentation & aneurysm
Valve Incompetence
Mitral Floppy valve, prolaps

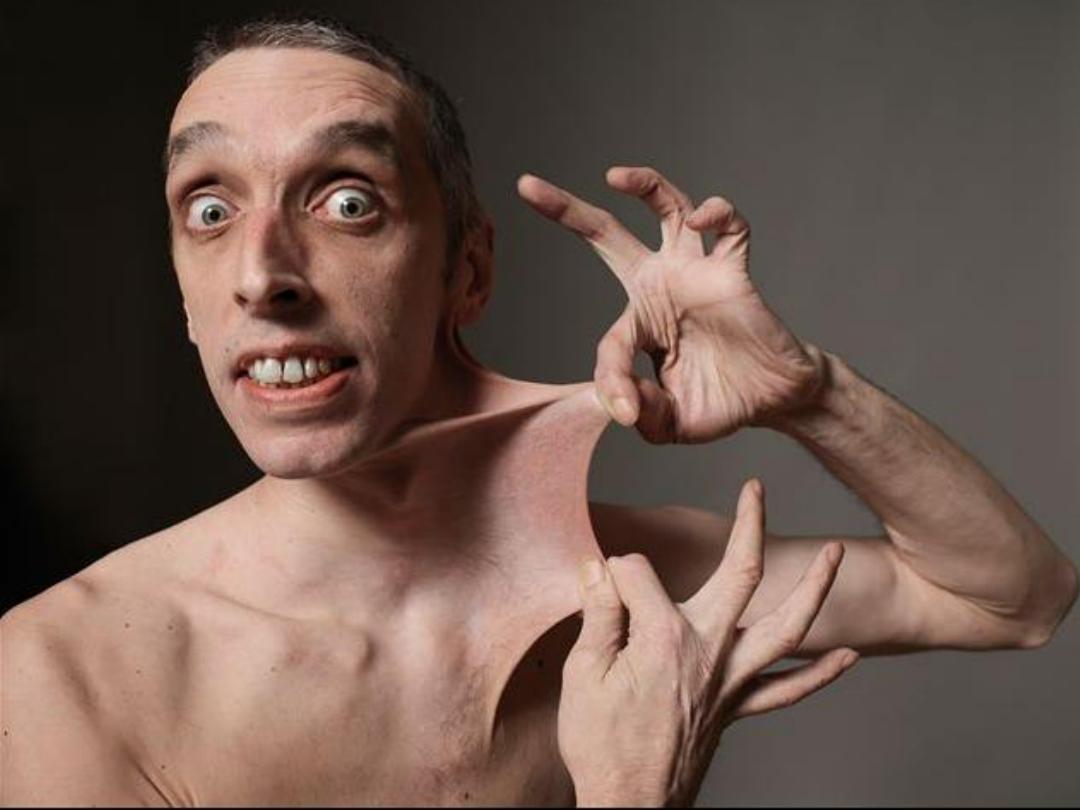
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDSs)
(Cutis Laxa)
• Group of dis. (more than 30).
• Single gene diorders (
AD or AR
)
• caused by defect in collagen synthesis or
structure weakness in tissue rich in
collagen.
• considerable increase in skin, joints &
ligament extensibility

Ehlers-Danlos
syndrome

Ehlers-Danlos
syndrome
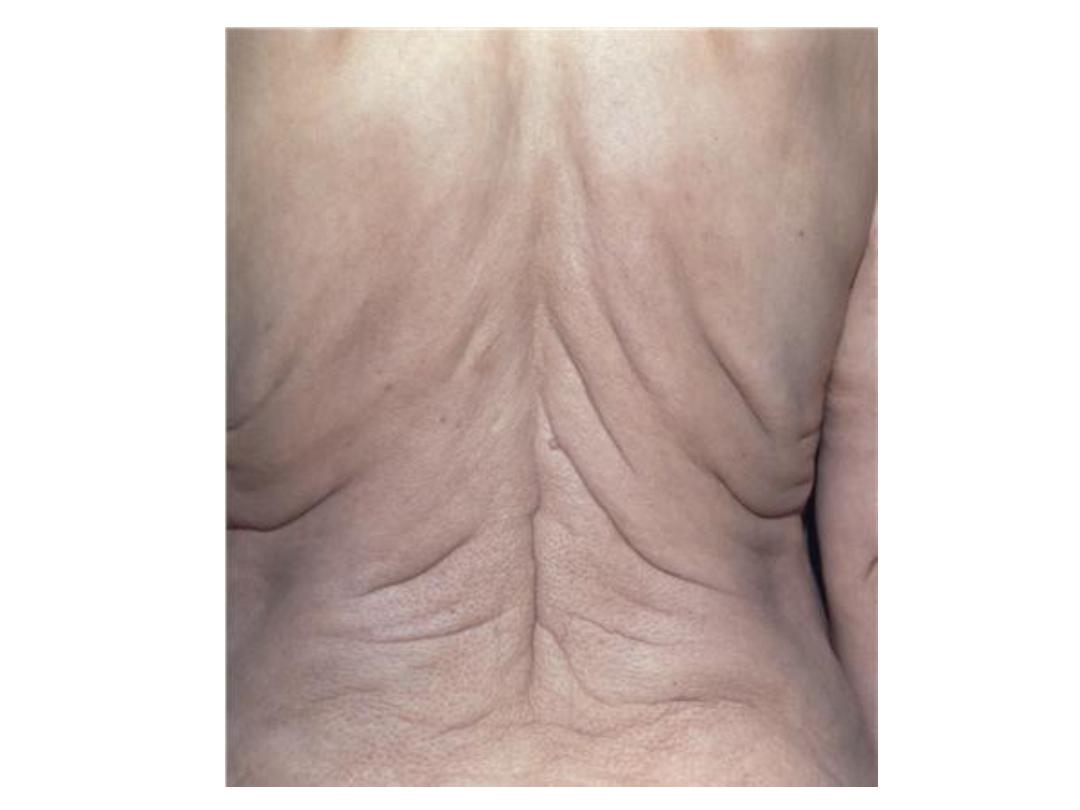
Cutis
Laxa

RECEPTOR PROTEIN DEFECTS
• FAMILIAL HYPERCHOLESTEROLEMIA
– LDL RECEPTOR defect
– Cholesterol TRANSPORT across liver cell impaired
– CHOLESTEROL BUILDUP IN BLOOD
• “Scavenger System” for CHOL,
• MACROPHAGES are “FOAMY”

• Genes encoding receptors pr. or channels.
– LDL RECEPTOR defect
– Cholesterol TRANSPORT across liver cell impaired
– CHOLESTEROL BUILDUP IN BLOOD
• “Scavenger System” for CHOL,
• MACROPHAGES are “FOAMY”
Xanthoma of familial hypercholesterolemia
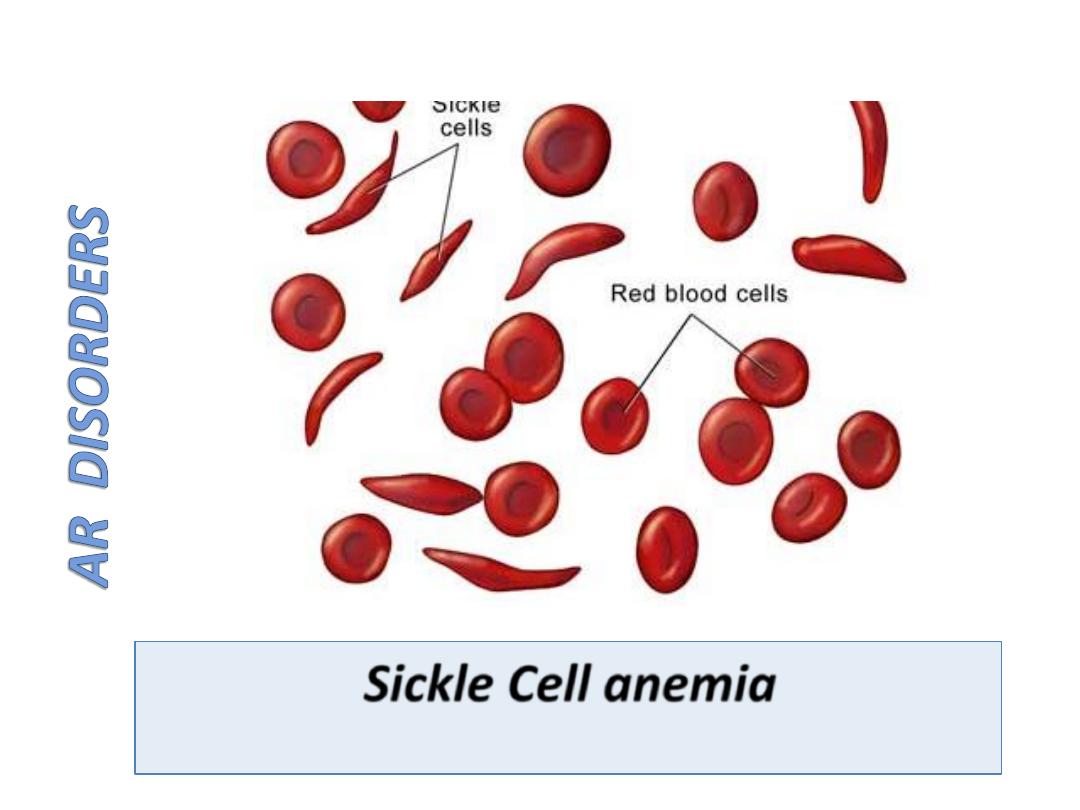
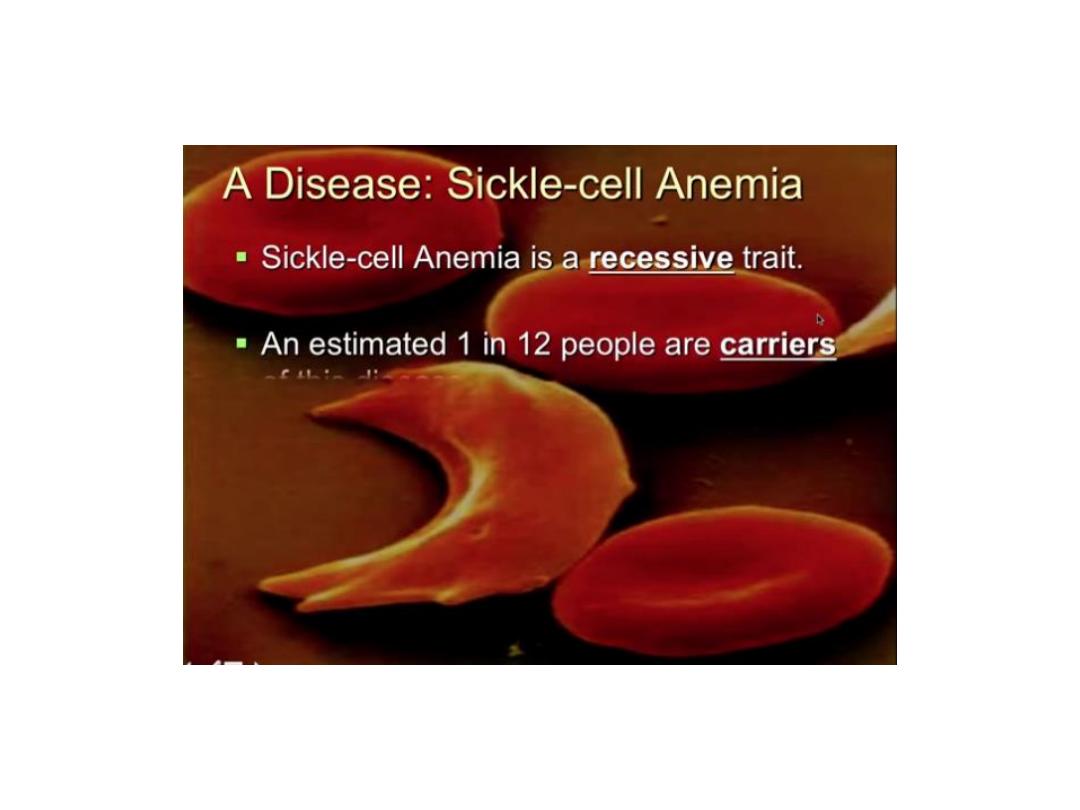
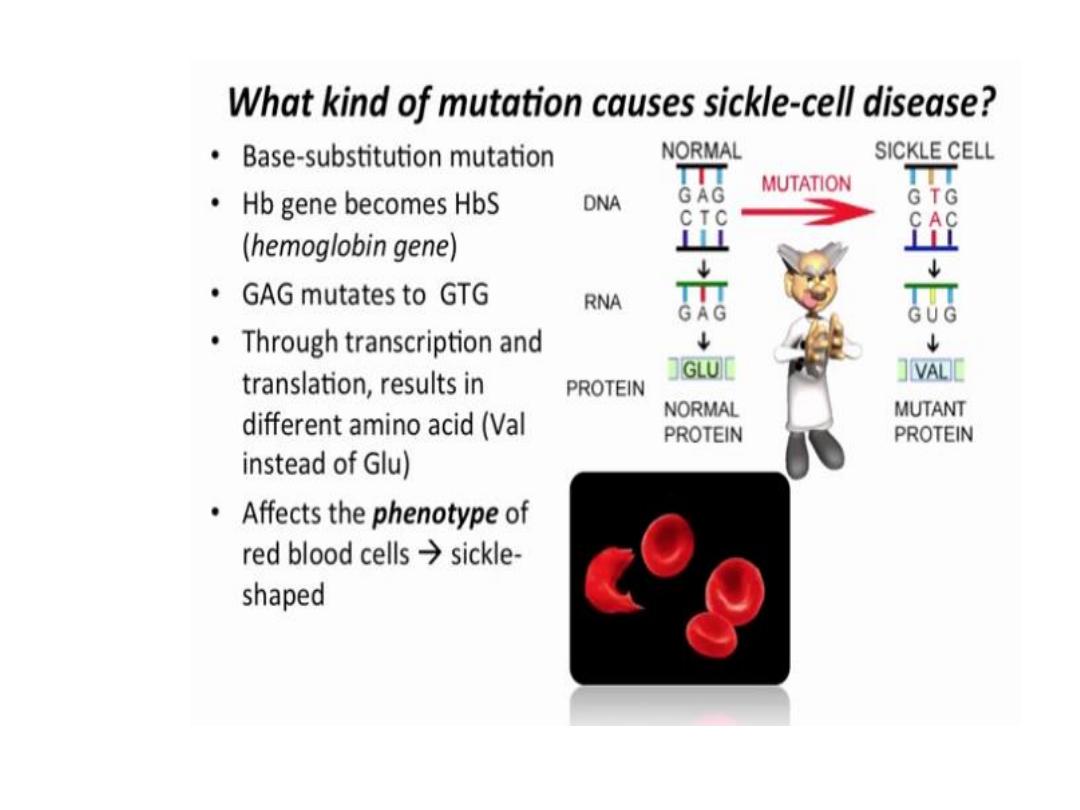
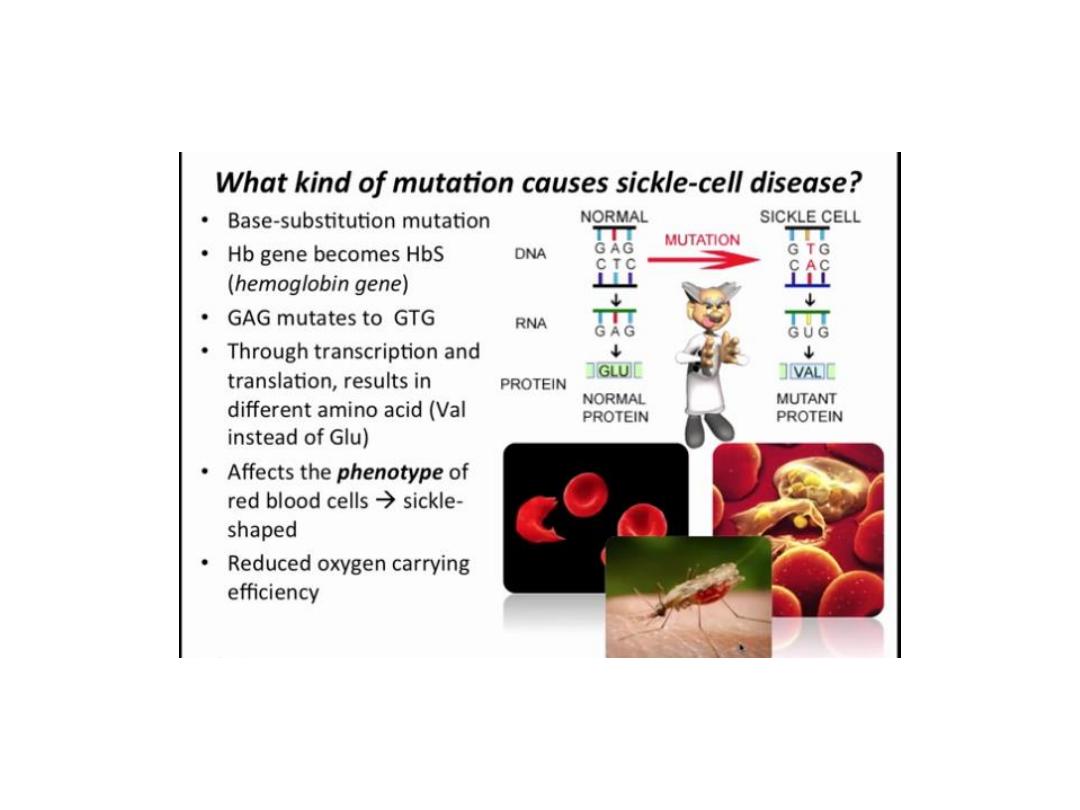
Sickle Cell anemia

NEXT LECTURE
Diseases caused by mutation in protein that
regulate cell growth
