
74
Respiration , Excretion , Secretion , Synthesis ,Storage , Growth.
take up O2 from the blood or tissue fluid for use in their metabolic
All animals cells
Respiration:
activities, these produce primarily energy together with CO2 & H2O which are return to the blood.
This process is carried out by means of intracellular oxidizing enzymes
All animal cells get rid of waste products resulting from their own activity
Excretion & Secretion :
by passing them into the blood or tissue fluid
Kidney, Epithelium
..
e.g
Certain cells are modified for removing waste products from the body
*
,Skin , Lunge & Liver.
* Some cells form secretions and in this case secretary granules may be found in them e.g..
1- Pancreatic acini
which have zymogon granules that synthesis & secretion of enzymes.
2- Mast cells:
Store & Release the chemical mediator for the immune response .Its secretion
granules contain Heparin & Histamine.
3- Adipose cell:
Stores fat for providing energy.
4- Hepatocytes
: Store Glucose as Glycogen to re replenish blood in cases of degreased supply
of external glucose.
5- Skin cell
synthesize a variety of products that are released inside or outside the body.
, nails & heal wounds
that renew the surface of skin
protein
keratin,
Synthesize
Epidermis:
-
A
skin.
secret oils & waxes secret that lubricate the
Sebaceous glands
-
B
wastes.
secrete small quantities of urea
Sweat glands
-
C
synthesizes melanin.
Pigment cell
-
D
6- The cells of proximal convoluted tubules of the kidney
transport ion & absorb
metabolites & digest protein.
7- The intestinal epithelium cells
reabsorb metabolites & synthesize digestive enzymes as
disaccharides & peptidases.
GROWTH
* It can be defined as an increase in the mass of living material which can be achieved by:
1- The addition of a new materials to those already present .
2- Cellular division.
3- DNA & protein replication.
75
* Growth is an inherent property of life which is rapid in the embryonic & fetal stages & in early
childhood.
* Cellular activity requires high demand of cellular energy ATP
Ex. Muscular contraction & nerve impulse.
* Most cellular activities are controlled by
a negative feedback:
which is a Mechanism of
output is counter to & cancel the input .
which the
response in
homeostatic
* In animals such as ourselves, the internal environment of our bodies must have certain
conditions within tolerable limits to continue the healthy functioning of us .
* In negative feedback, various receptors & effectors bring about a reaction to ensure that
such conditions remain favorable.
& endocrine & circulatory system work together to regulate body
mammals nervous
In
*
.
temperature
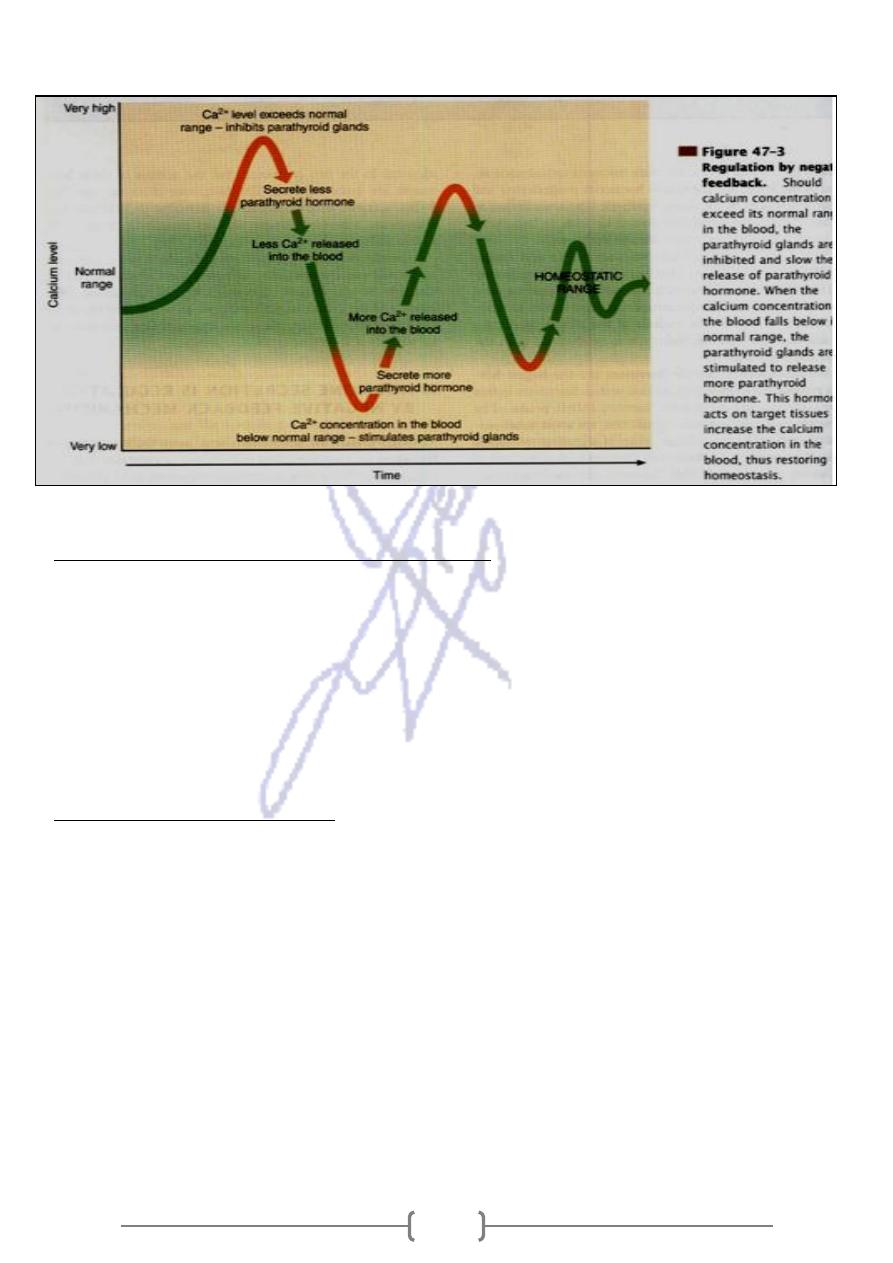
* Regulation of blood sugar & hormone secretion is typically regulated by Negative feedback
mechanism ,in which a hormone is released in response to some change in a steady state &
triggers a response .
* So the principle of negative feedback control is illustrated by the diagram below .
Effectors
message
—
receptor
factor increase corrective responses
.Factor normal
-
no change in factor
-----
Factor normal
factor decrease- corrective responses
----
Effectors
message
–
receptor
--
76
Requirements of Negative feedback control
* Because mammals are worm blooded, the enzymes that are part of their make up as a warm
blooded animal require a certain temperature to operate optimally.
* Also the water concentration of a cell & its chemical concentration must remain at a certain
level to allow normal cellular processes to occur.
* In light of this the feedback mechanism in such warm blooded animals is essential in regards
to allowing the body to work in optimal conditions, so any change in from the normal in
temperature is corrected by the feedback mechanism .
Advantages of homeostasis .
* Homeostasis has survival value because it means an animal can adapted to changing
environment.
* It can deal with the temperature differences you face when you step our your front door .
