71
* Cells are the basic units of organisms, but sometimes a single cell is the organism.
* A unicellular organism does everything that a living thing does; it grows, responds to the
environment, transforms energy and reproduces.
Unicellular organisms can be either prokaryotes or eukaryotes
Prokaryotes live almost everywhere .Many eukaryotes are single celled organisms .Some
Algae & yeast are euk. Some protests & some algaes are colonial they live with other cells of
their own kind and are attached to one another, but have very few specialized structures.
* Multicultural organisms are all made up of many Eukaryotic cells , which cannot live on their
own, but are dependent upon one another to perform function that keep all the cells alive.
So the cells in multicellular organisms are specialized to perform specific functions for the
organism .This is called CELL SPECIALIZATION.
* Each cell or type of cell has a separate role or job to do,some cells might be specials to
produce movement, others to produce enzymes needed to break down foods during digestion
* The human body has many different type of specialized cells each one has different functions
, and so they would have different of certain organelles. Example:
1- Pancreas's cells, must produce enzyme for digestion, so they contain hug amount of R.E.R,
Golgi bodies & vacuoles filled with protein.
2-Parotid gland -: Accumulation protein is synthesized, segregated & accumulated in the apex
of the cell; exported of the cell in response to specific stimuli.
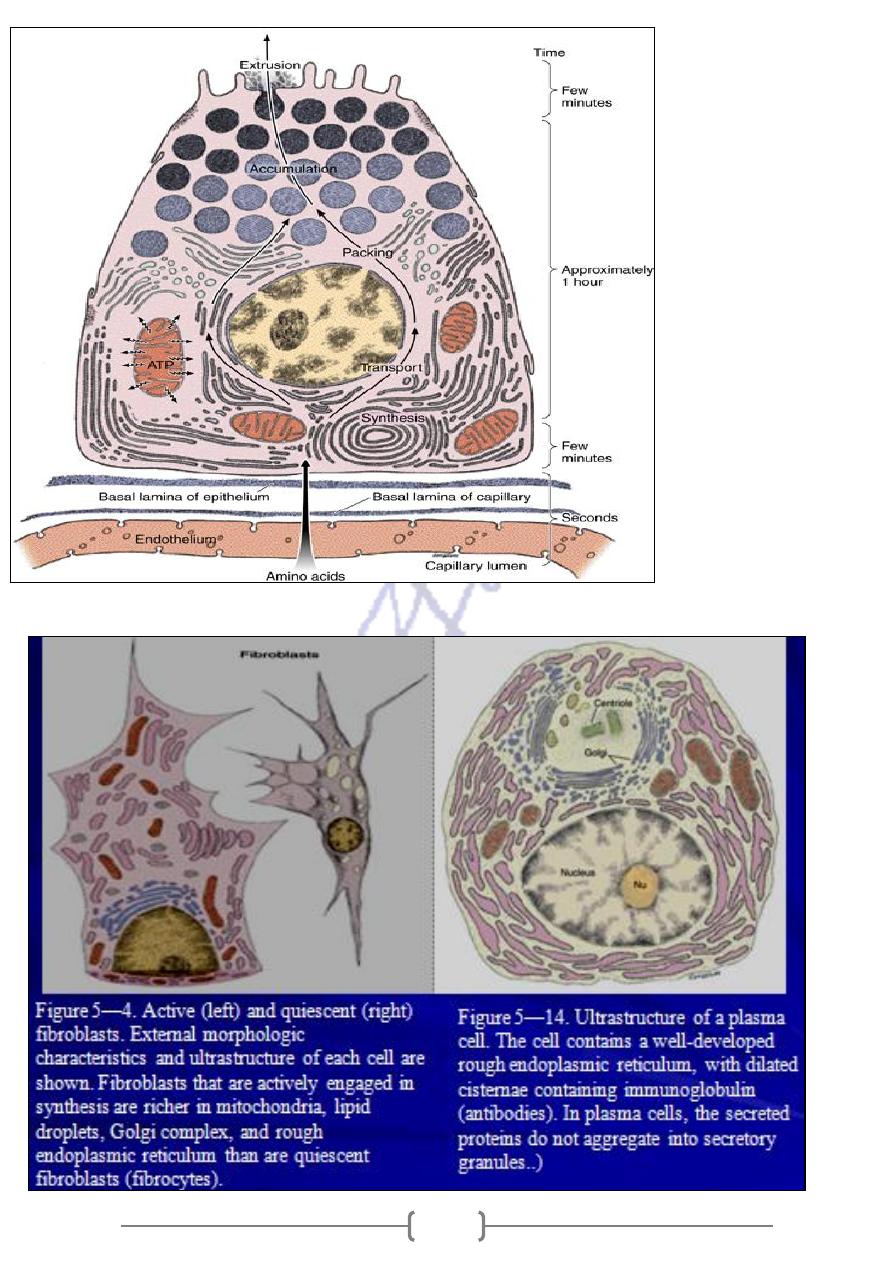
3-Fibroblast & plasma cells ,within these cells ,proteins are synthesized on membrane- bound
polyribosome& the newly synthesized polypeptides are injected directly into cisternia of the
R.E.R.-----Golgi app., small vesicle bud from Golgi app. Migrate to cell surface -Exocytosis.
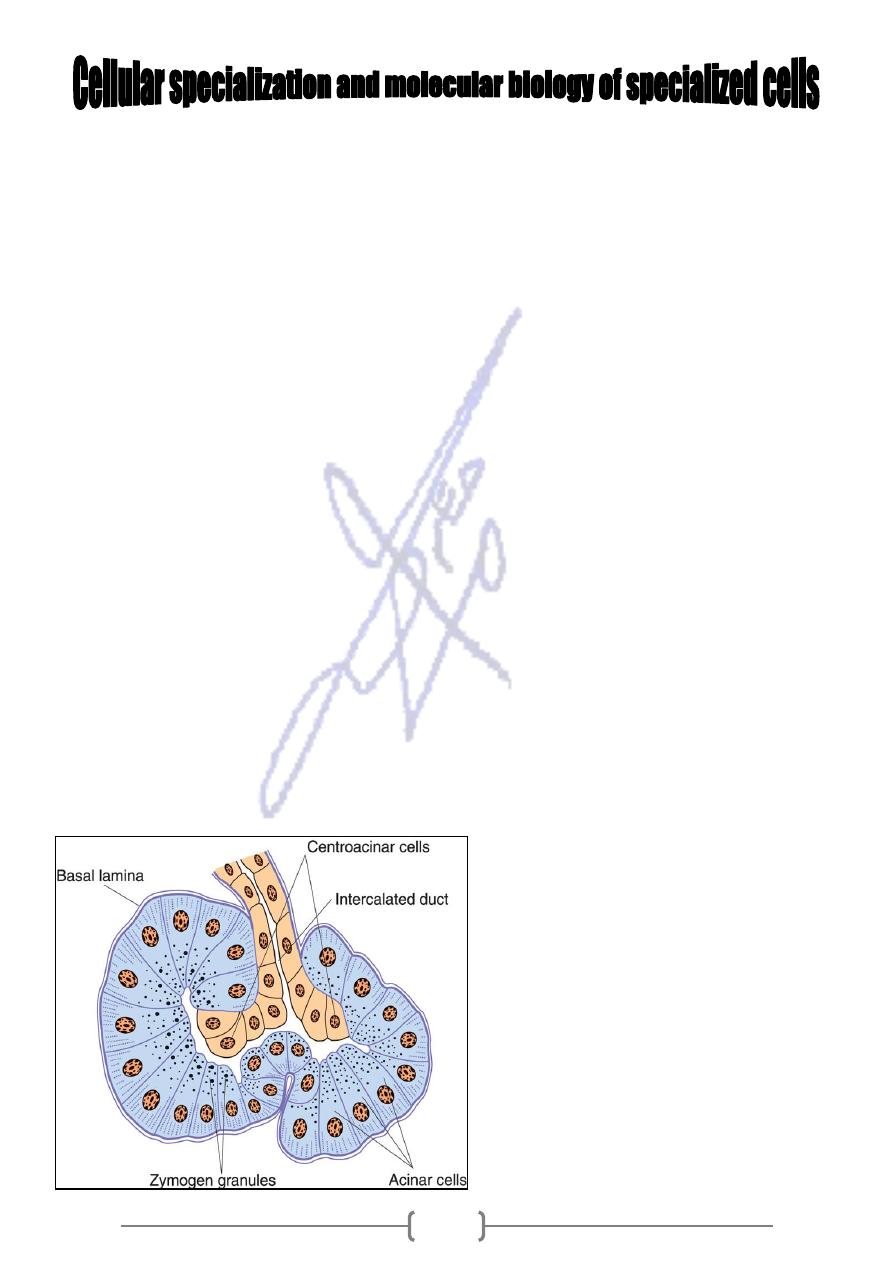
Figure 16—6. Schematic drawing of the
structure of pancreatic acini. Acinar cells
are pyramidal, with granules at their
apex and rough endoplasmic reticulum at
their base. The intercalated duct partly
penetrates the acini. These duct cells are
known as centroacinar cells. Note the
absence of myoepithelial cells.
71
Figure 4—27.
Diagram of a serous
(pancreatic acinar)
cell. Note its evident
polarity, with
abundant rough
endoplasmic
reticulum in the
basal region and the
Golgi complex and
zymogen granules
are in the apical
region. To the right
is a scale indicating
the approximate
time necessary for
each step of
synthesis and
secretion.
72
Steroid –Secreting cells:
They found in testes, ovaries & adrenals .They are endocrine cells
specialized for synthesizing and secreting steroids with hormonal activity.
The cytoplasm of steroid –secreting cells contains an exceptionally rich S.E.R., which contains
the enzymes necessary to synthesize Cholesterol from acetate & other substrates.
the site of
Mitochondria contain tubular rather than lamellar cristae .In addition to being
energy product ,these organelles have the necessary enzymatic equipment to participate in
.
subsequent reaction that result in steroid hormones
So this process results from collaboration between SER & Mitochondria, which represents the
cooperation between intracellular organelles.
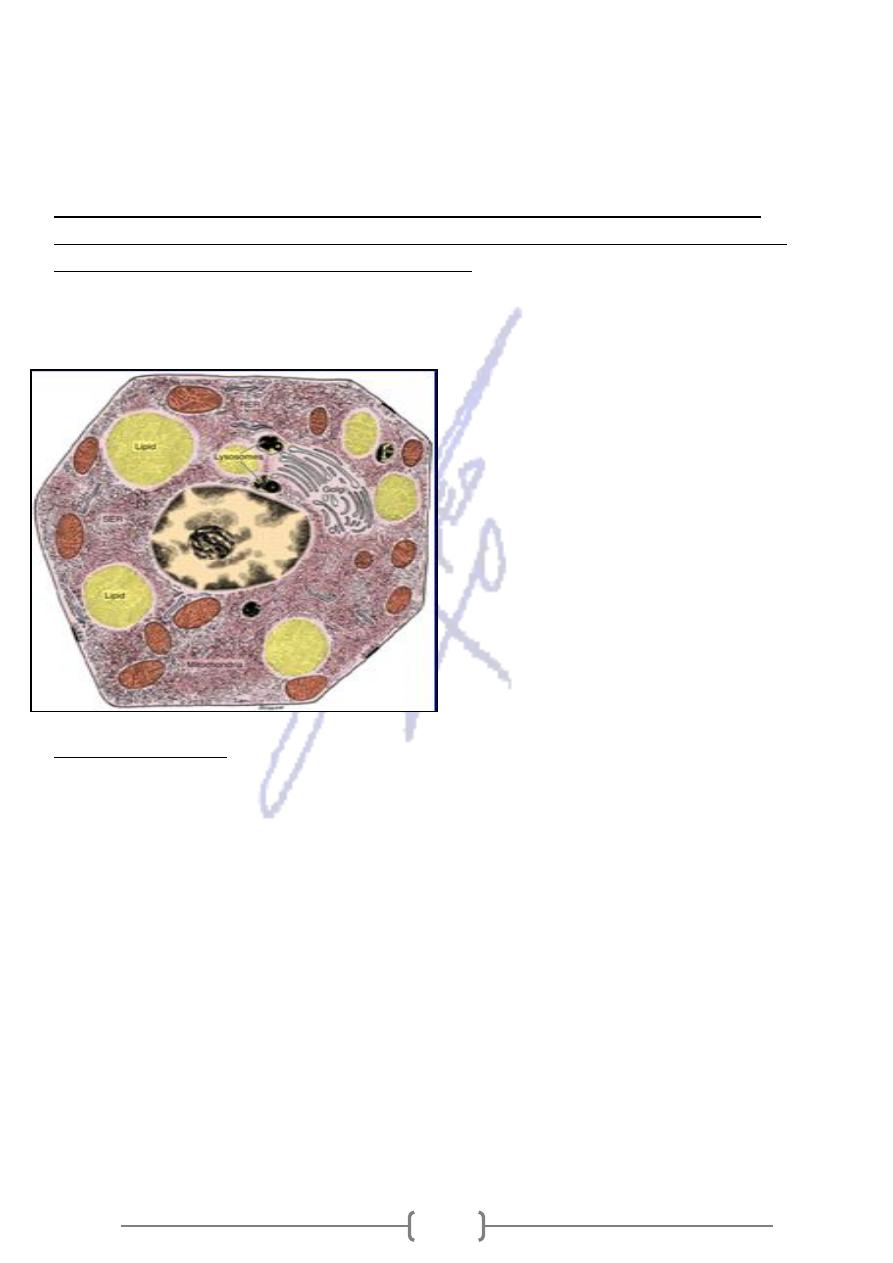
Figure 4—36. Diagram of the ultrastructure
of a hypothetical steroid-secreting cell. Note
the abundance of the smooth endoplasmic
reticulum (SER), lipid droplets, Golgi complex,
and lysosomes. The numerous mitochondria
have mainly tubular cristae. They not only
produce the energy necessary for the activity
of the cell but are also involved in steroid
hormone synthesis. Rough endoplasmic
reticulum (RER) is also shown.
:
examples are
Others
Muscles
help us to move which result from over developed cytoskeleton . Skeletal muscle cells
are packed with fibers that arrange in a highly ordered fation.
The fibers are actin filaments & myosin. When they contract, muscle cells use chemical energy
to pull these fibers past on other, generating the force.
Light – Sensitive cells:
Composed of two different parts
1- lower part, packed with mitochondria about 4-5 times the amount in other types of cells.
2- Upper part, contains small flattened membranes called disks, they contain:
A- a pigment called Rhodopsin, which absorbs light & signals the rest of cells that light has
stuck the disk.
B- Messages are then sent to other cells and results in the sensation (VISION)
Street sweepers :
*Cell make and release mucus ,a sticky substance that is made of water ,salt
& carbohydrates , particles of dust and dirt that are inhaled are trapped in the mucus & cannot
travel further into the respiratory tract .Underneath the mucus layer , there is another layer of
73
cell that have cilia ,which move ,creating a sweeping motion & keeps the passages clean &
open for business .
Red blood cells :
*Specialized to transport oxygen contain a protein that binds O2 lungs &
transports the oxygen throughout the body where it is let go ,this protein is hemoglobin and it
contain iron .
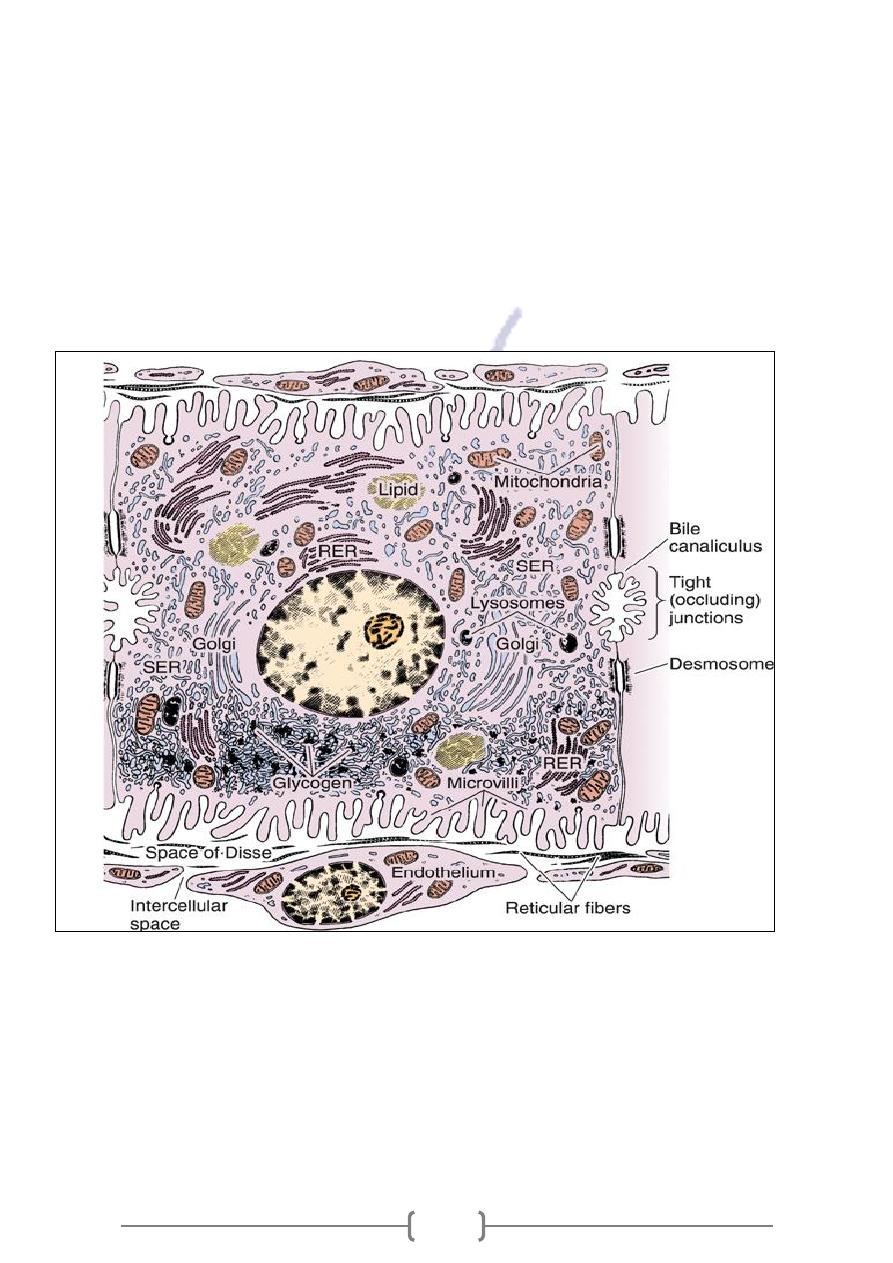
Hepatocytes (liver cells):
They take substances (glucose & cholesterol) from blood and releases (blood protein & urea) in
to it .They have huge number of mitochondria & some of SER .They store glucose as glycogens
& replenish blood when glucose is needed
Figure 16—17. Ultrastructure of a hepatocyte. RER, rough endoplasmic reticulum; SER, smooth
endoplasmic reticulum. x10,000.
