Ions in living
system &
their
importance

• Ions ( Cations & Anions) in the fluids of living systems are distributed
between cells, called (Extracellular fluid ) and within cells, called (
Intracellular Fluid) and also within the blood vessels called ( Plasma
Fluid).
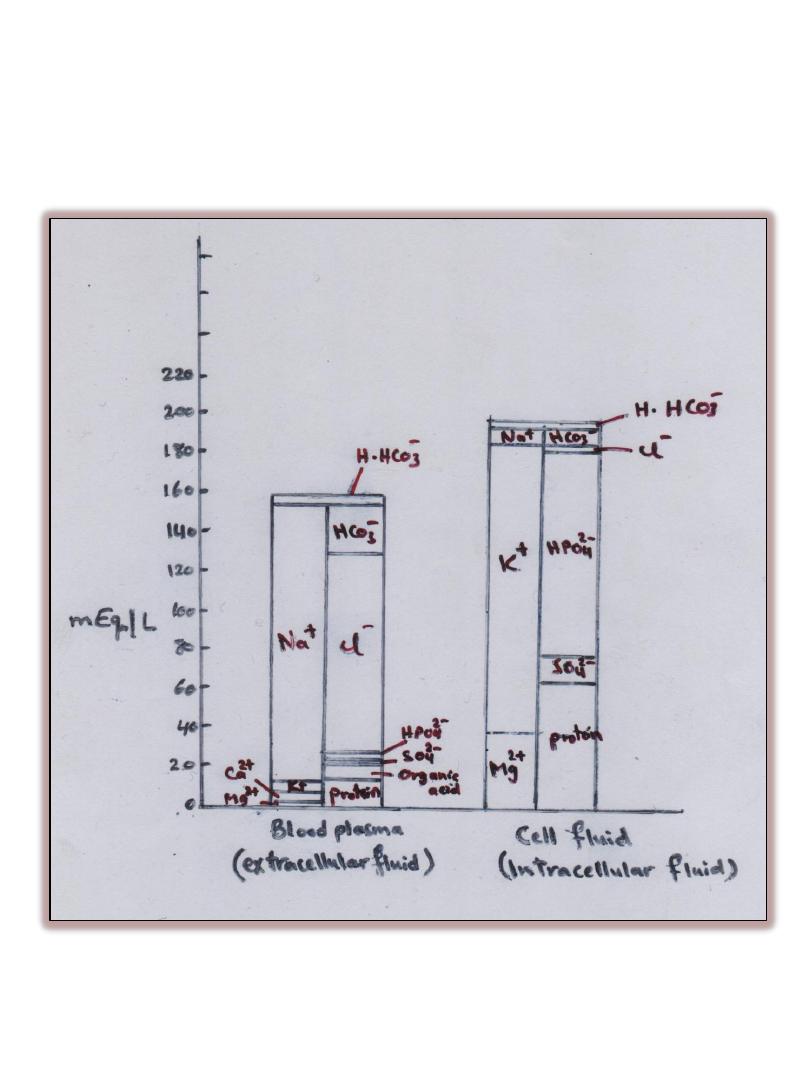
• The most common cations are Na
+
, K
+
, Mg
+2
, Ca
+2
while , the anions
are Cl
-
, HCO3
-
.
• K
+
& Mg
+2
are found mostly in intracellular fluids where as Na
+
& Mg
+2
are found in intercellular fluids.
• Although most body Ca
+2
(1200 g/70 kg) are found in the bones and
teeth, a small amount (
≈ 1%) is present in blood serum Ca
+2
is
necessary for proper blood clotting , contraction of muscle , transmission
of signals within the nervous system, and good cardiac function.
• Most Mg
+2
ions are in bone and within cells .
• Mg
+2
functions in muscle and nerve action and is also part of many
biological catalysts.
• Proper nerve transmission, in nerve cells, depends on the correct Na
+
ion
conc. outside the cell & K
+
ion conc. Inside the cell.
• The role of Cl
-
is to maintain electrical neutrality as other ions move
across membranes. It plays a part in acid – base balance in blood, which is
regulated in part by HCO3
-
shifts a cross membranes.

• Very small quantities, called trace amount, of many metallic cations are
also needed to maintain life.
• Fe
+2
in Hemoglobin play an important role in the transport of O
2
& CO
2
• Cu
+2
, Zn
+2
, Co
+2
and Mn
+2
ions assist enzymes in their biological roles.
• Trace amount of the metallic ions usually exist as ( Complex ions) , which
is made up of one or more cations surrounded by other ions or molecules.
These ions and molecules contain N, O, S atoms that form bond
Cu
+
2
+ 4 NH
3
Cu (NH
3
)
4
+2
• Some times the reaction of metallic cation and large molecules is
poisonous to the living system such as Hg
+2
& Pb
+2
.
• Pb
+2
ions have a toxic effect on the kidneys and cause nerve damage .
Hg
+2
ions cause extensive damage to the brain and nervous system.

• The major ions occur primarily as free, the trace metals occur
primarily in combination with proteins.
• The dietary requirements for ions (electrolytes) vary widely most need
to be consumed only in small amounts or at rare intervals. Some like
Ca, P are continuously excreted and must be ingested regularly in
order to prevent deficiency (700 mg Ca/day) bone enter & leave.
• There are almost no metabolic process that are not dependent on or
affected by ions.
• Among Functions
Maintenance of osmotic pressure and water distribution in the various
body fluid compartments.
Maintenance of the proper PH.
Regulation of the proper function of the heart and other muscles.
Involvement in oxidation – reduction reactions.
Participation in catalysis as cofactors for enzymes.
Abnormal levels of ions may be either the cause or the consequences
of variety of disorders . ( excess or deficiency )
