
The Upper Limb Joints #1
Lab Session 7
Dr. Hayder Jalil Al-Assam
MBChB (Iraq), MRes Anatomy (UK)
: dr_hayder_anatomy@yahoo.com
Upper Limb Joints
• The sternoslvicular joint
• The acromioclavicular joint
• The shoulder joint
• The elbow joint
• The wrist joint
• The inter-carpal joints
• The carpo-metacarpal joints
• The metacarpophalangeal joints
• The interphalageal joints
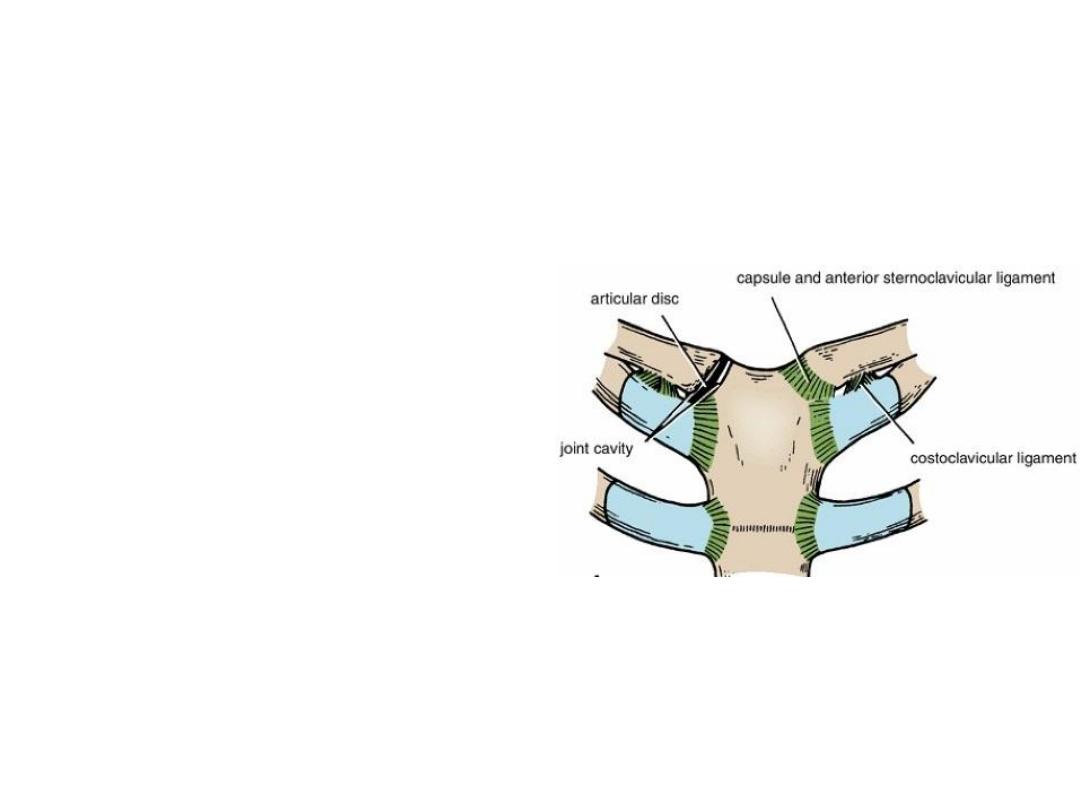
Sterno-clavicular Joint
• The only joint connecting UL with
the axial skeleton
• Synovial Double plane joint
• Ligaments:
Anterior & posterior sterno-clavicular
ligaments, Costo-clavicular
ligament
• Articular disc (fibrocartilage)
divides the joints interior into
medical & Lateral compartments
• Supraclavicular nerve & nerve to
subclavius supply the joint.
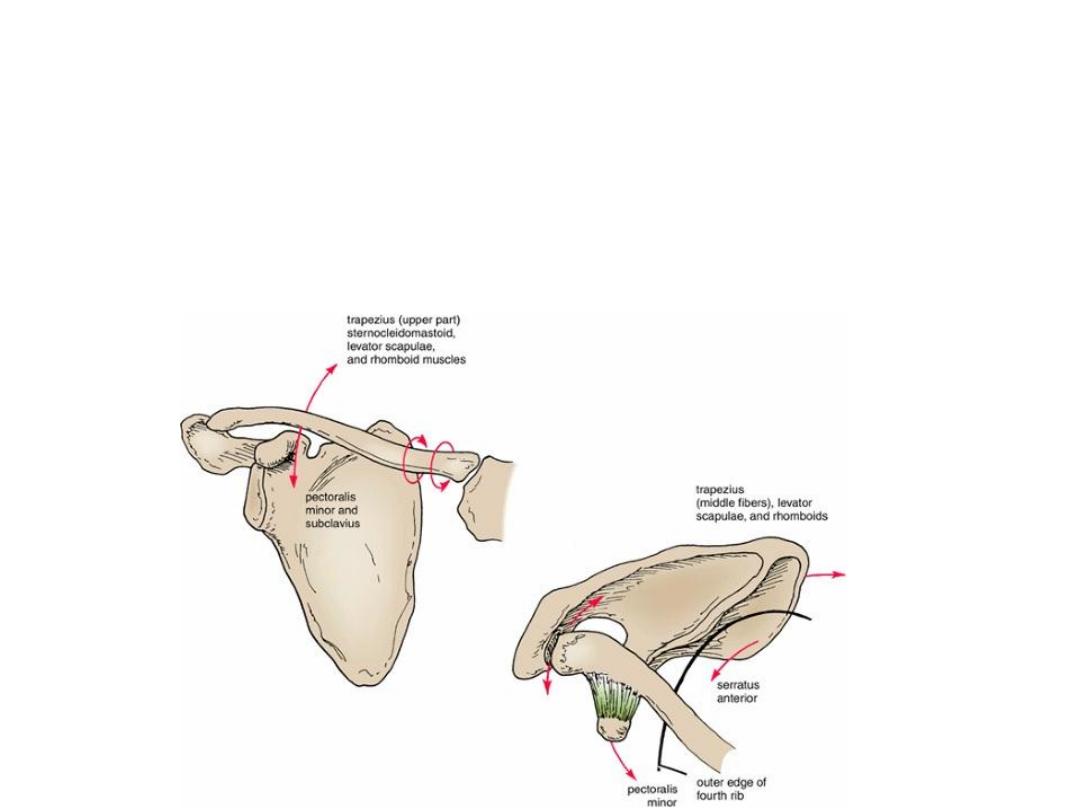
Movements of the sterno clavicular
joint
• Forward and backward movement of the clavicle takes place
in the medial compartment. Elevation and depression of the
clavicle take place in the lateral compartment.
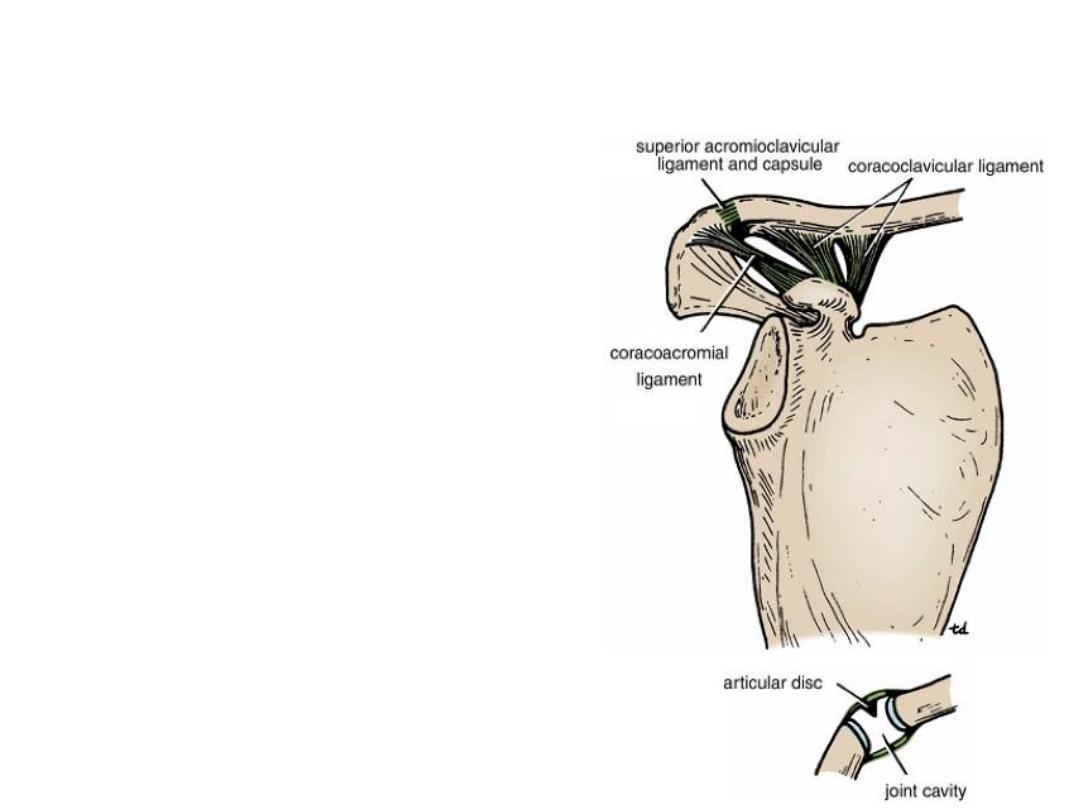
Acromioclavicular Joint
• Synovial plane joint
• Ligaments:
Superior & inferior acromioclavicular
ligament reinforces the capsule
The very strong coracoclavicular ligament.
• Nerve supply: The suprascapular nerve
• a wedge-shaped fibrocartilaginous disc
within the joint.

Shoulder Joint
•
Synovial ball-and-socket joint
•
Capsule attachment: medially to the margin of the glenoid cavity, laterally to the
anatomic neck of the humerus.
•
Ligaments:
The glenohumeral ligaments are three weak bands of fibrous tissue.
The transverse humeral ligament strengthens the capsule and bridges the gap
between the two tuberosities.
The coracohumeral ligament strengthens the capsule above and stretches from the
root of the coracoid process to the greater tuberosity.
The coracoacromial ligament extends between the coracoid process and the
acromion.
Synovial membrane forms a tubular sheath around the tendon of the long head of the
biceps brachii. It extends through the anterior wall of the capsule to form the
subscapularis bursa beneath the subscapularis muscle (Fig. 9-34).
•
Nerve supply: The axillary and suprascapular nerves.
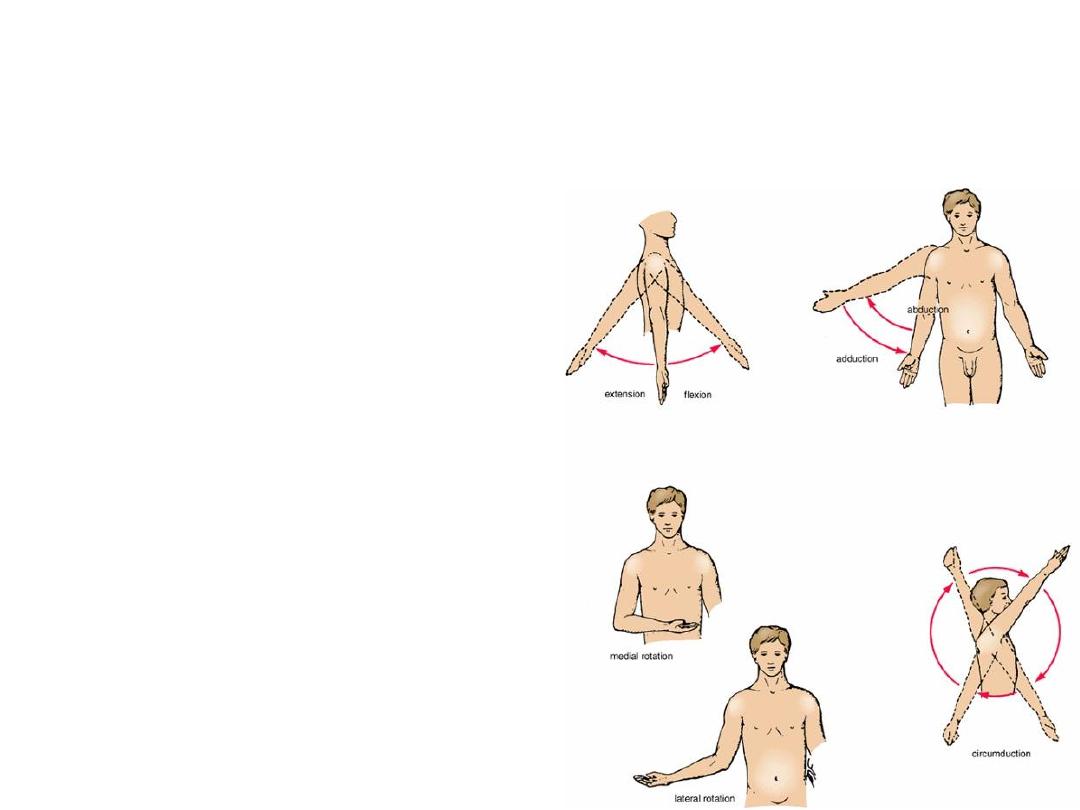
Movements of the Shoulder Joint
• The shoulder joint has a wide
range of movement.
• Rotator cuff muscles that cross
in front, above, and behind the
joint namely, the subscapularis,
supraspinatus, infraspinatus,
and teres minor.
• The weakest part of the
shoulder joint is the inferior
surface. Little support from the
tendon of long head of the
triceps.
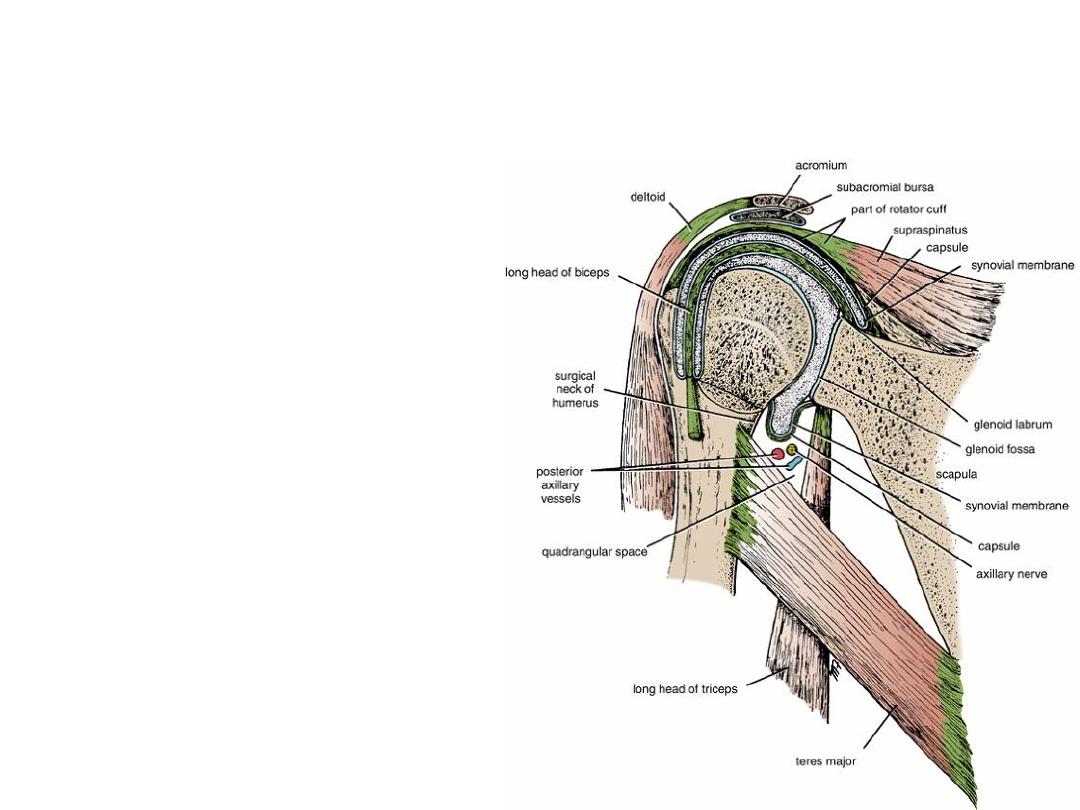
Quadrangular Space
• The quadrangular space is an
intermuscular space, located
immediately below the shoulder
joint. It is bounded above by the
subscapularis and capsule of the
shoulder joint and below by the
teres major muscle. It is bounded
medially by the long head of the
triceps and laterally by the surgical
neck of the humerus.
• The axillary nerve and the
posterior circumflex humeral
vessels pass backward through this
space.

The End
