
Chapter 18
Central
Nervous
System
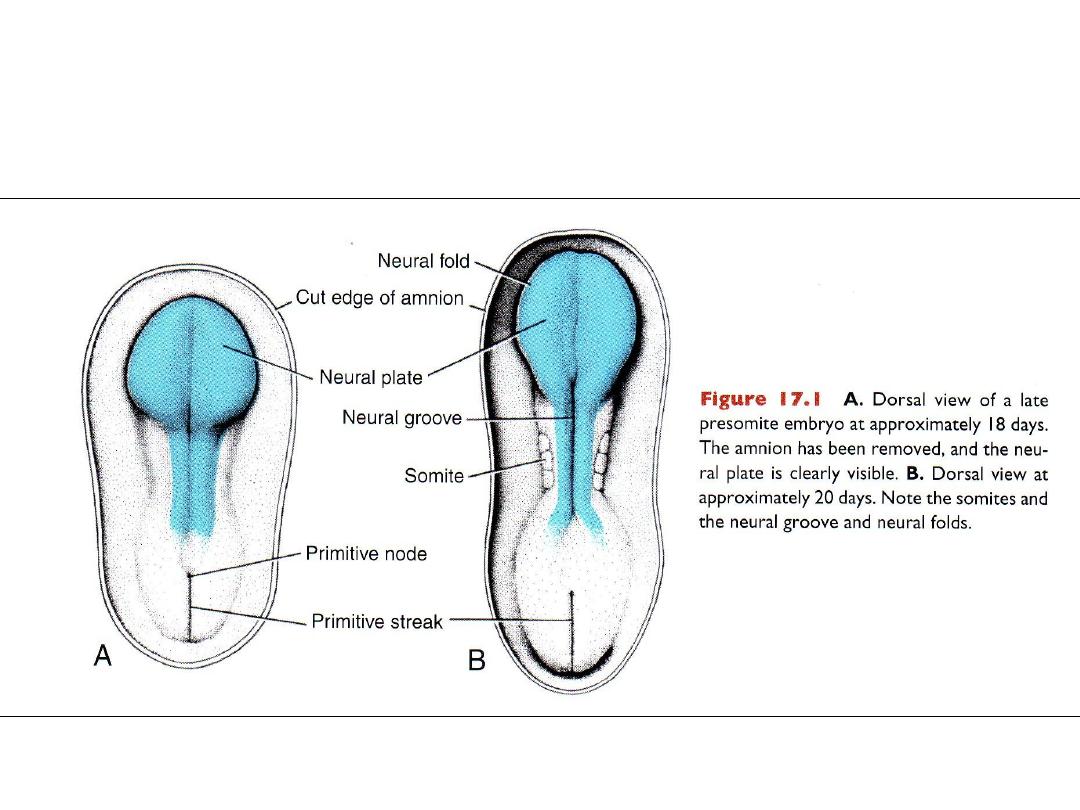
Beginning of 3
rd
week
Neural tube
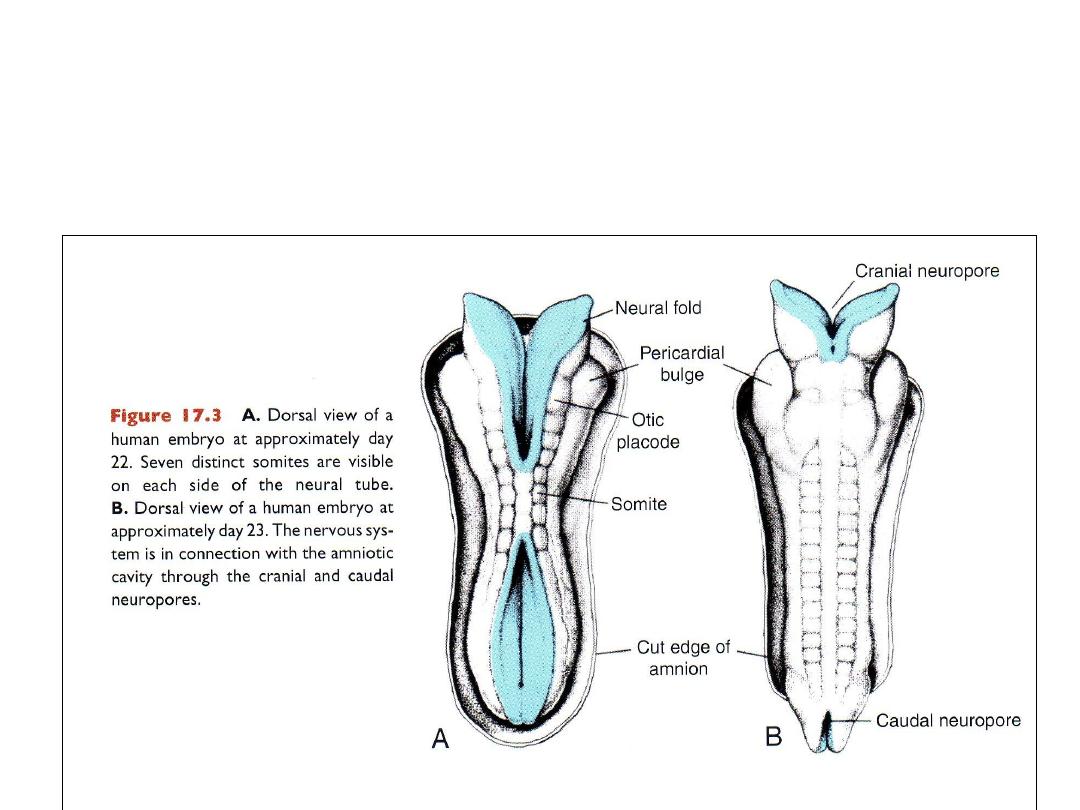
Fusion begins in cervical region
cranial & caudal neuropores
closure of cranial neuropore: day 25
closure of caudal neuropore: day 28
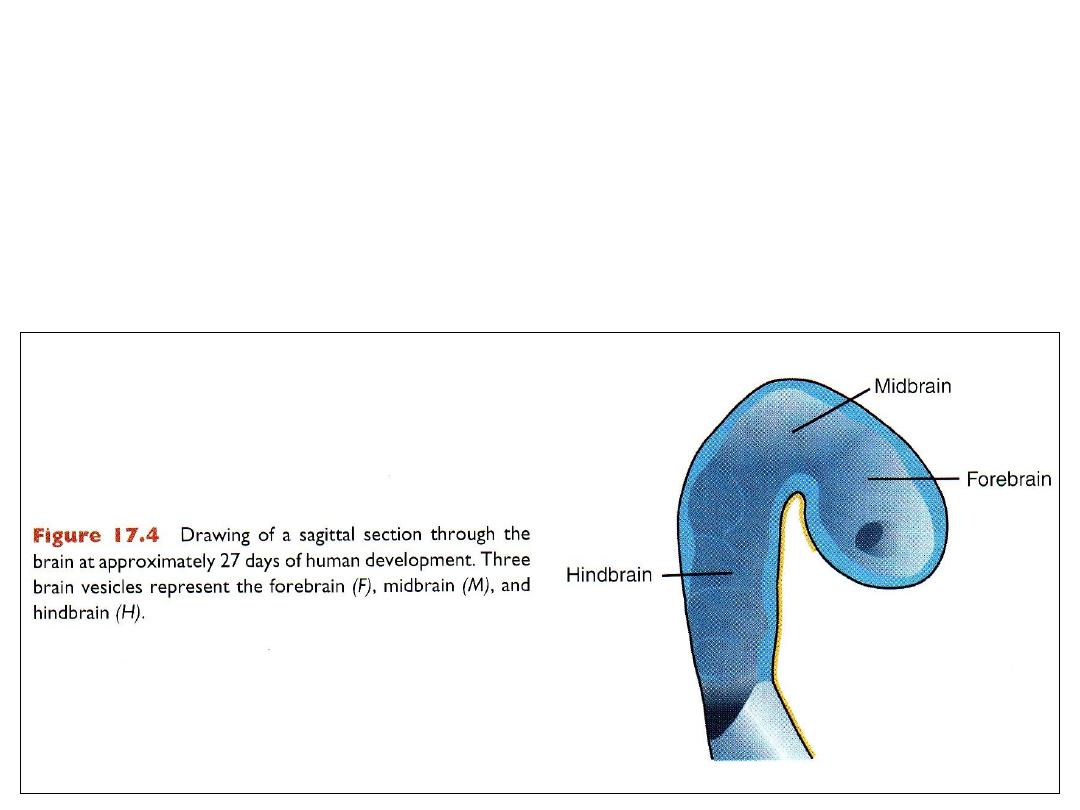
The cephalic end of neural tube
Primary brain vesicles (day 25)
1.
Prosencephalon or forebrain
2.
Mesencephalon or midbrain
3.
Rhombencephalion or hindbrain
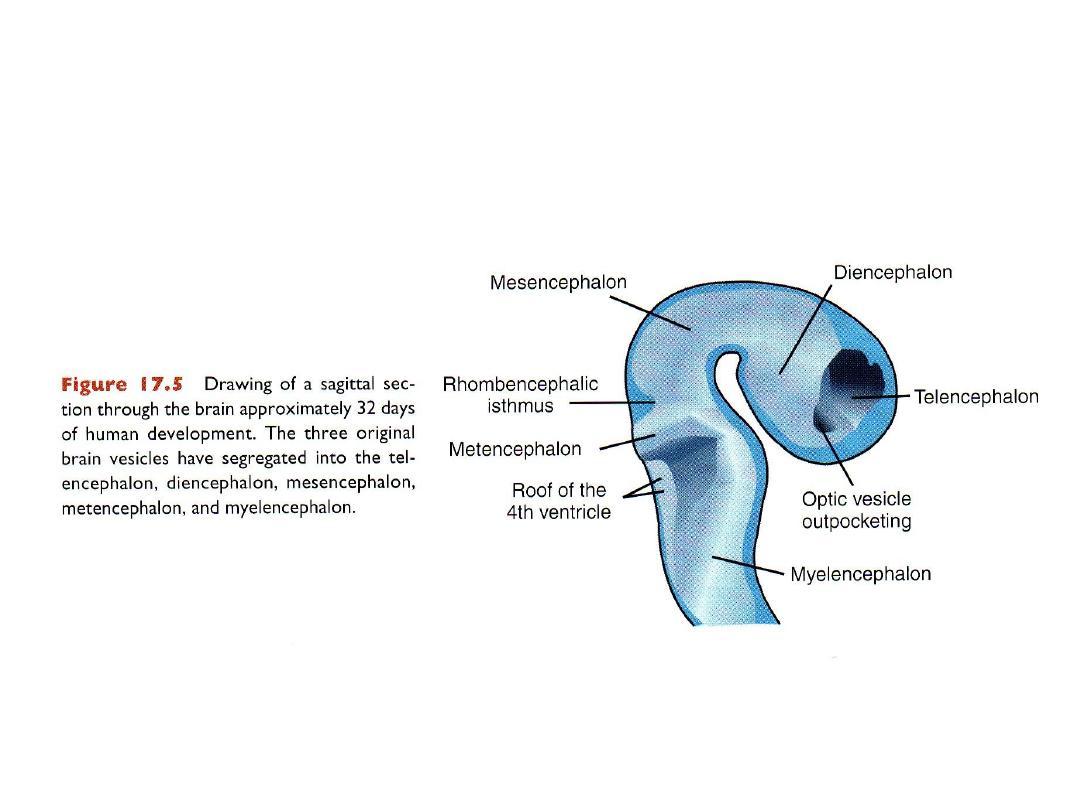
Brain at day 32
SPINAL CORD
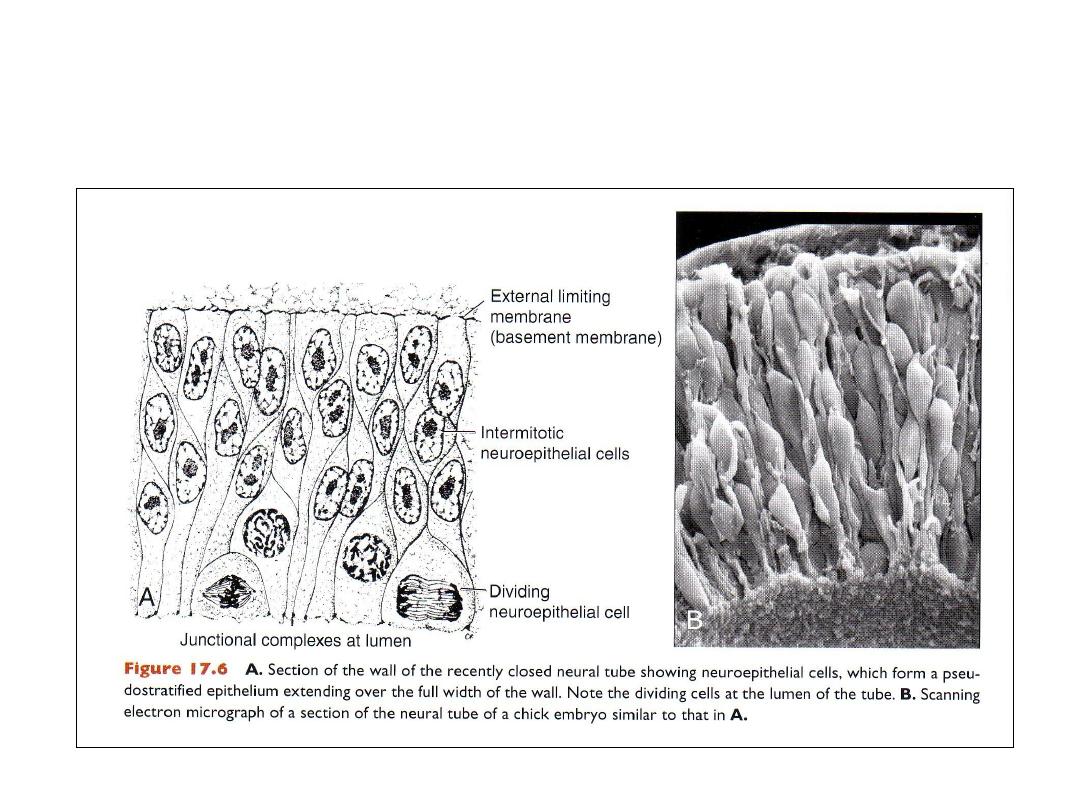
Neuroepithelium
• Before closure, the wall of the neural tube consists of
neuroepithelial cells
.
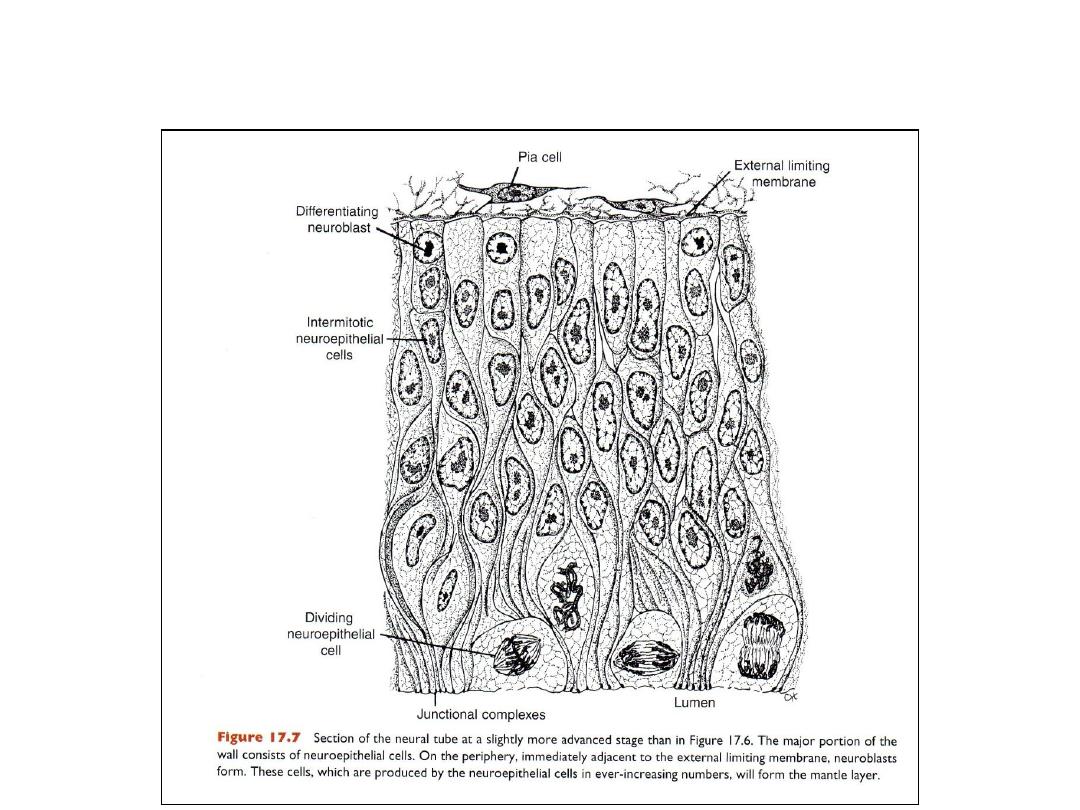
• After closure, neuroblasts appear.
• Neuroblasts form the mantle layer (a zone around the neuroepithelial
layer).
• The mantle layer later forms the gray matter of the spinal cord.
• The marginal layer (outermost layer of spinal cord) contains nerve fibers
of neuroblasts in mantle layer.
• Myelination cause the marginal layer to become white: the white matter
of the spinal cord.
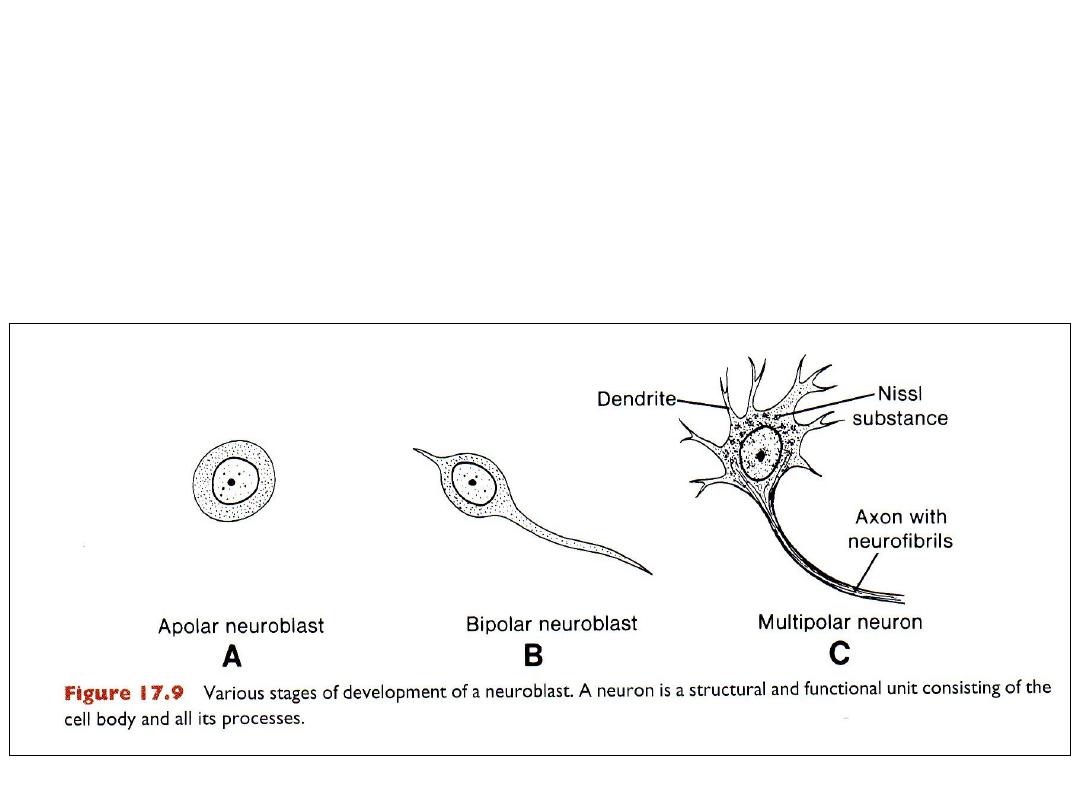
HISTOLOGICAL DIFFERENTIATION
Nerve cells
• Neuroblasts arise by division of neuroepithelial cells.
• They differentiate: apolar, bipolar then multipolar neuroblasts.
• Neuroblasts lose their ability to divide after differentiation
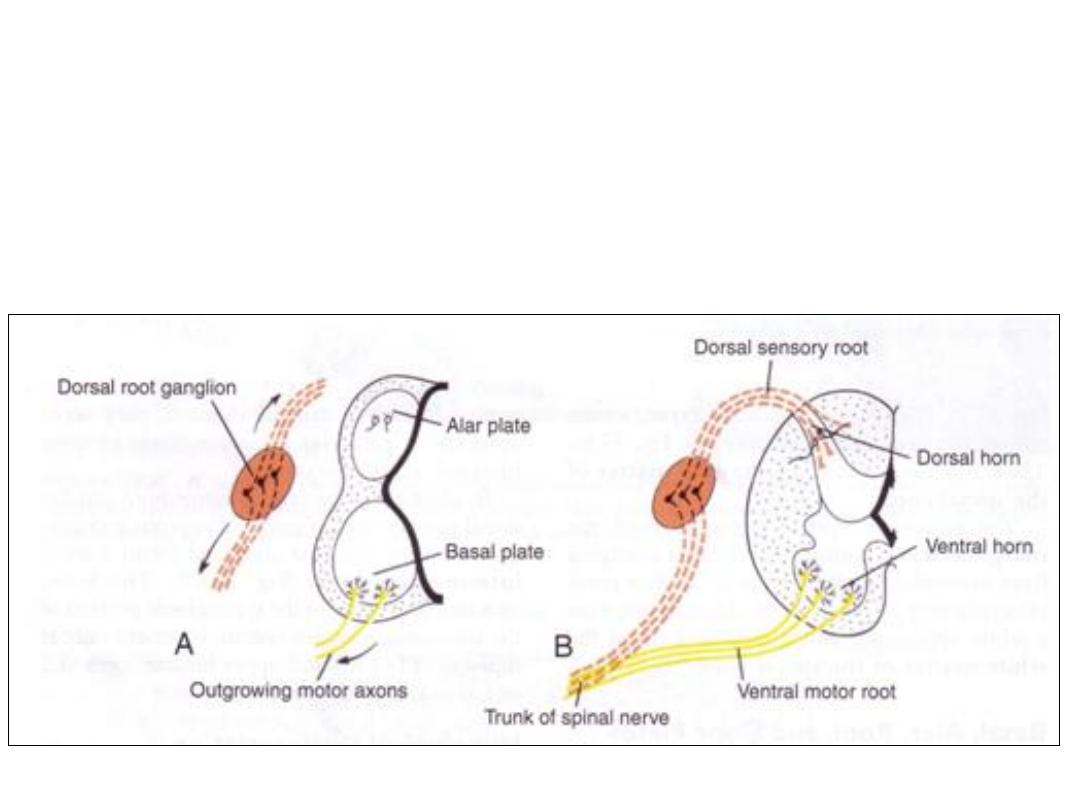
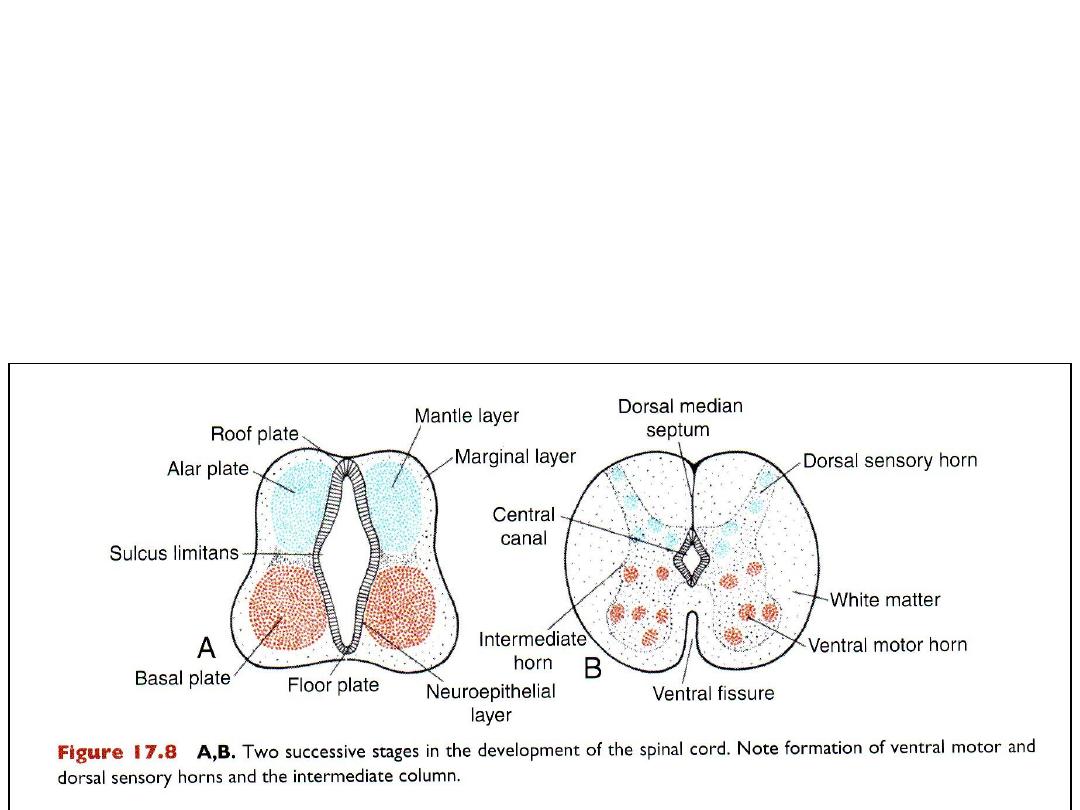
• Axons of neurons in the basal plate form the ventral root of the spinal
cord, they conduct motor impulses to muscles.
Axons of neurons in the dorsal sensory horn (alar plate) penetrate
into the marginal layer of the cord where they ascend to higher or
lower levels to form association neurons.
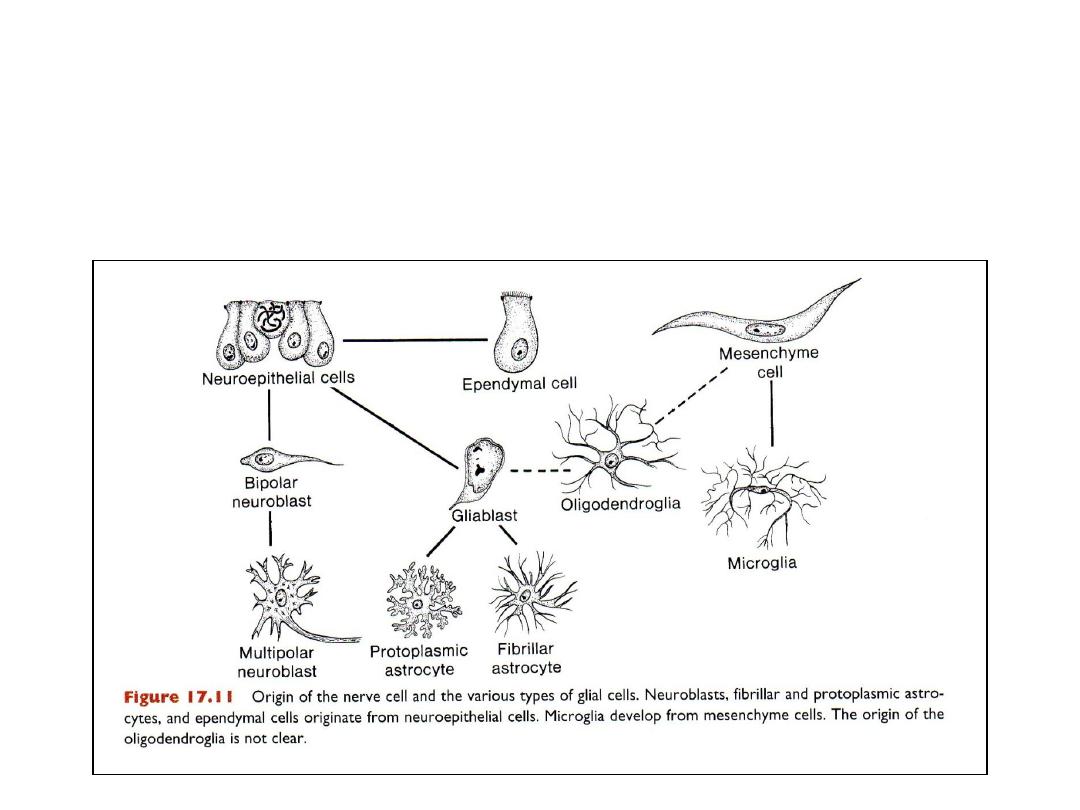
GLIAL CELLS
• Majority of glioblasts are formed from neuroepithelial cells after
production of neuroblasts ceses.
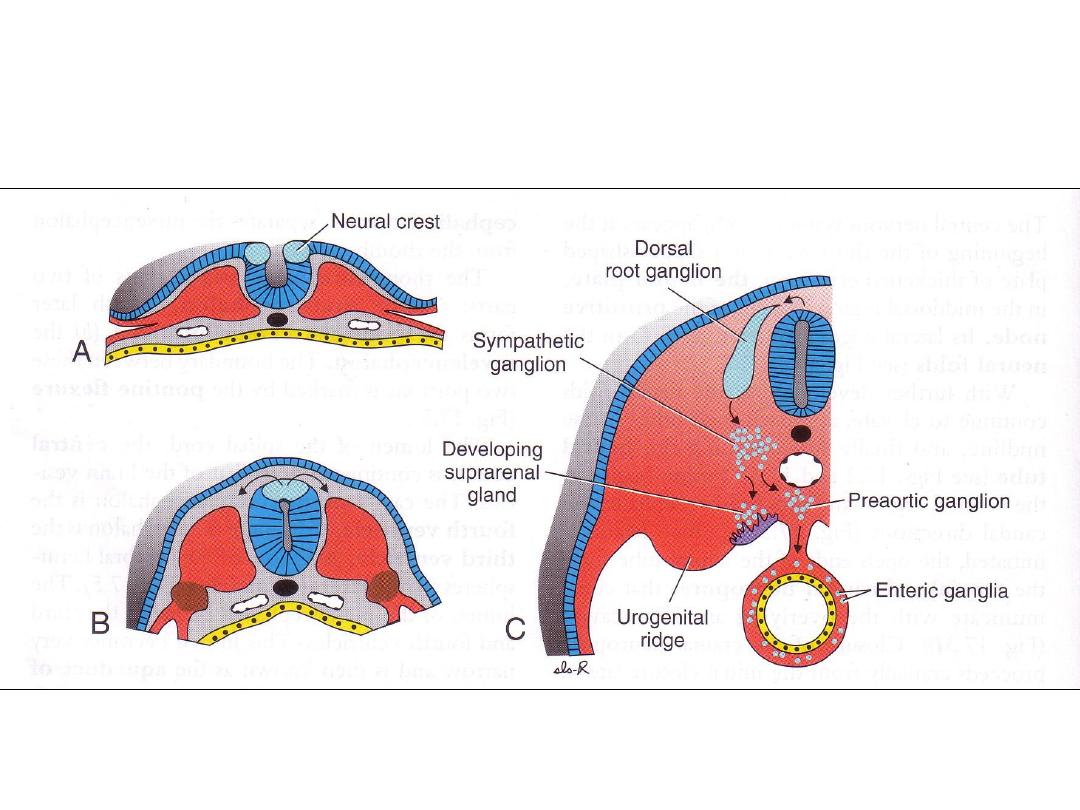
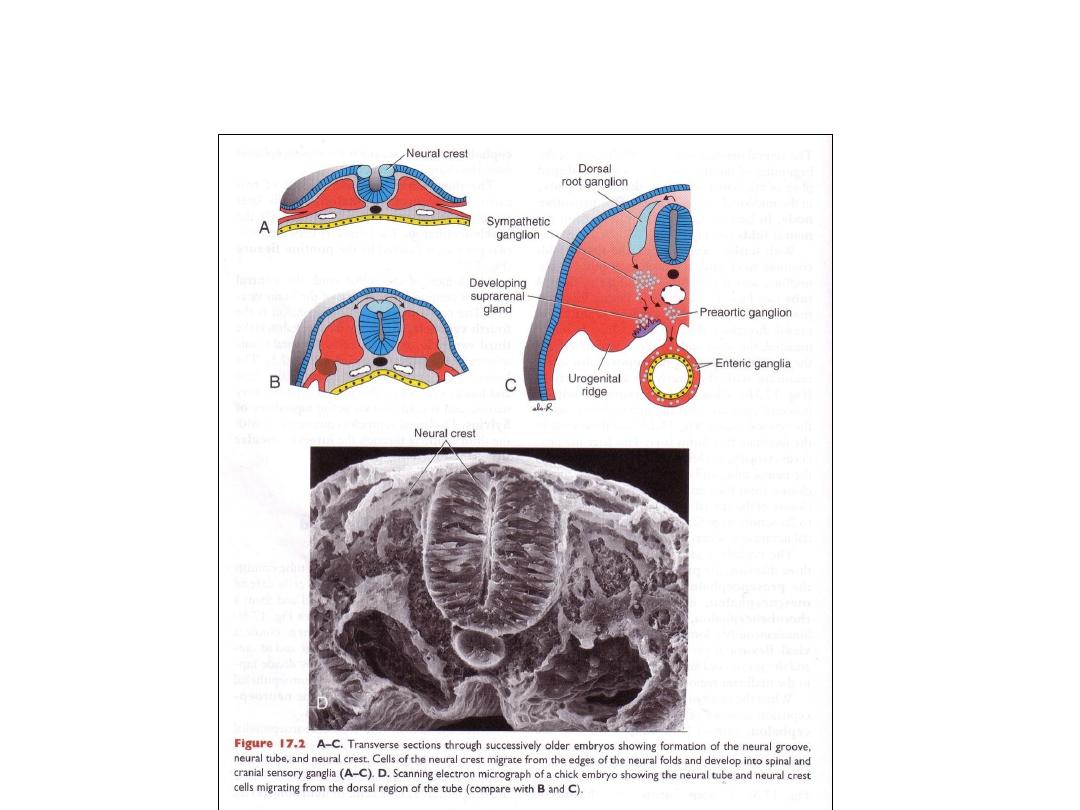
NEURAL CREST CELLS
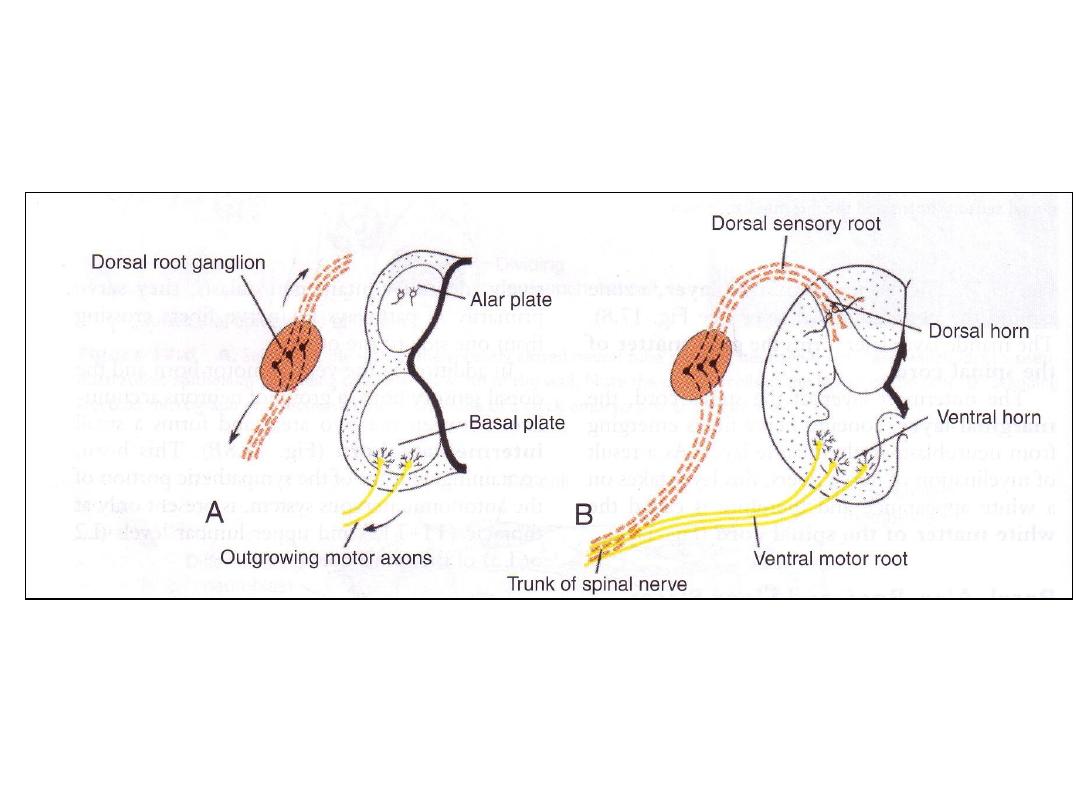
• Sensory ganglia neuroblasts (from neural crest cells): form dorsal root
neurons
Dorsal sensory root of spinal nerve
Peripheral fibers participate in formation of spinal nerves
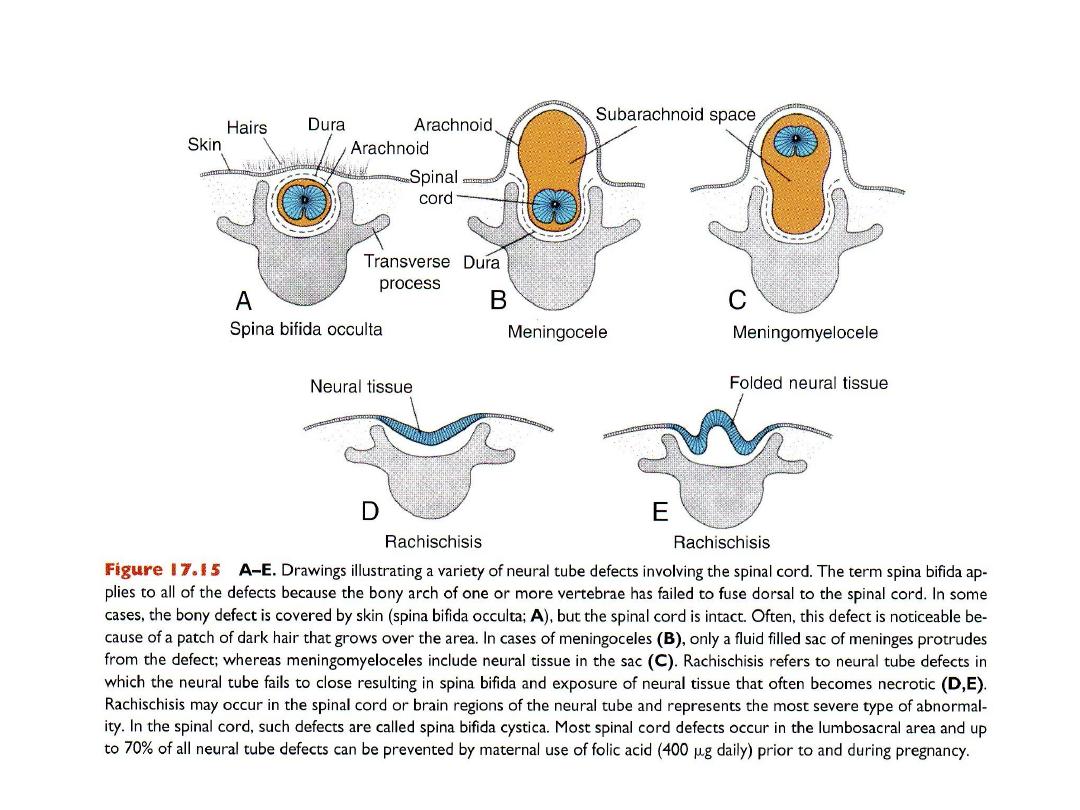
NEURAL TUBE DEFECTS

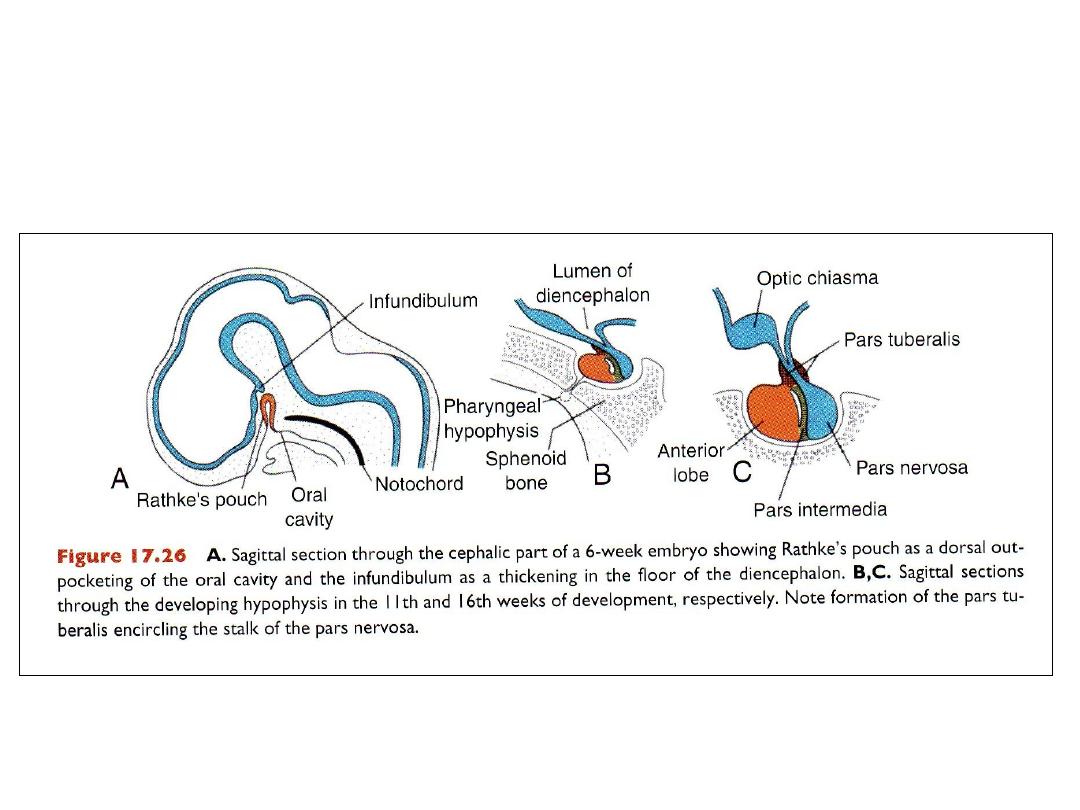
HYPOPHYSIS
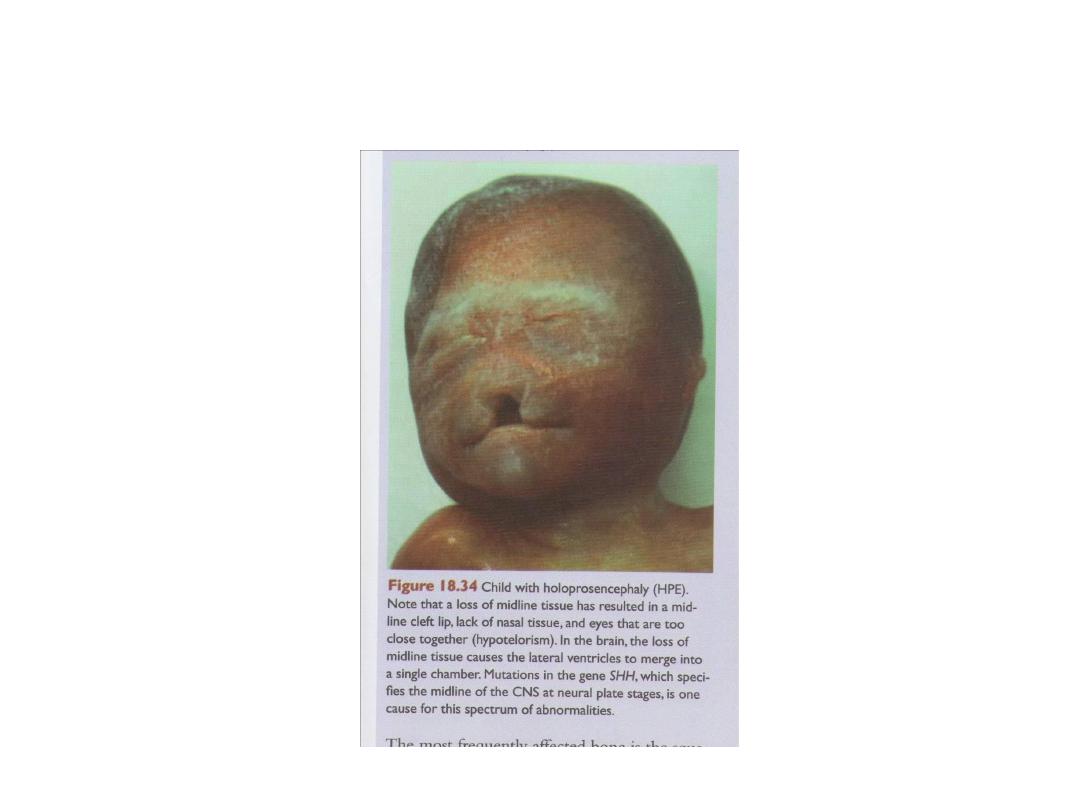
Holoprosencephaly
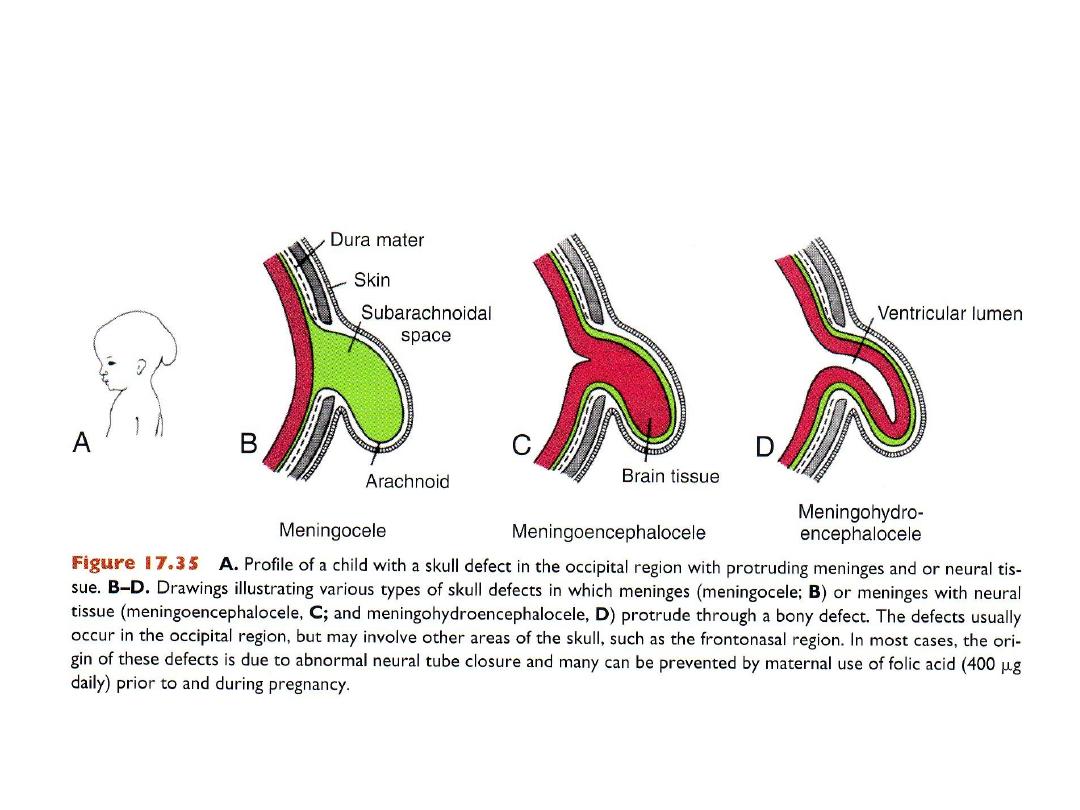
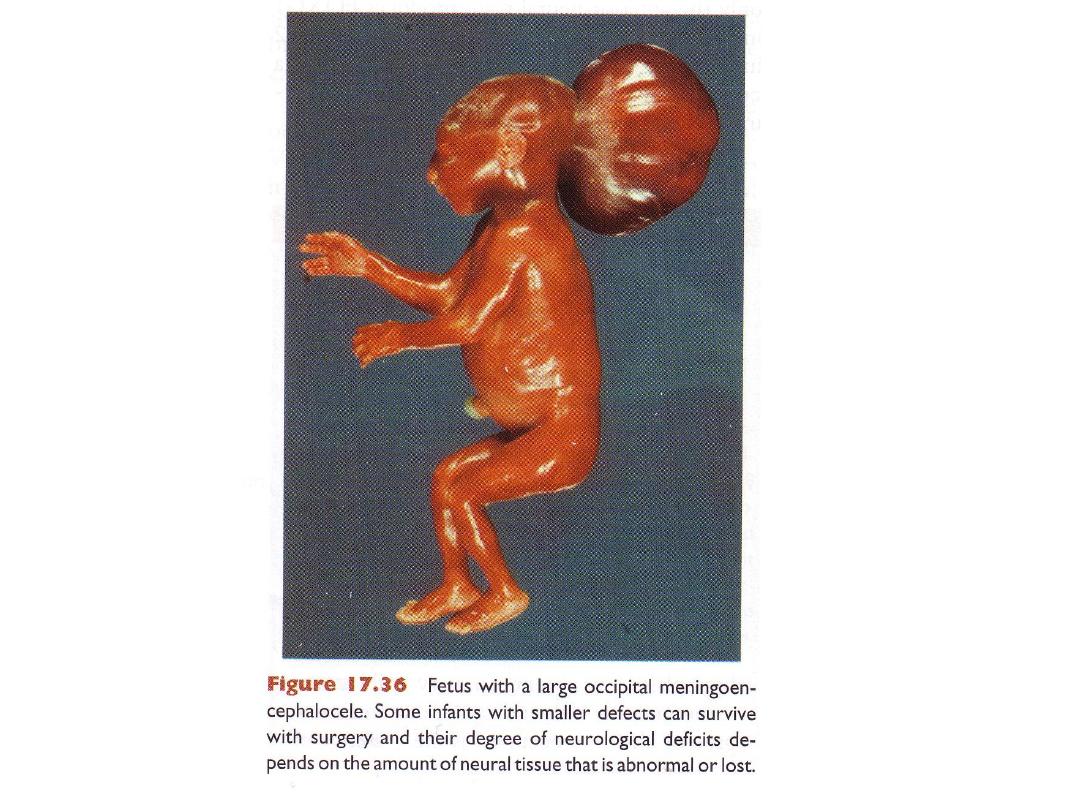
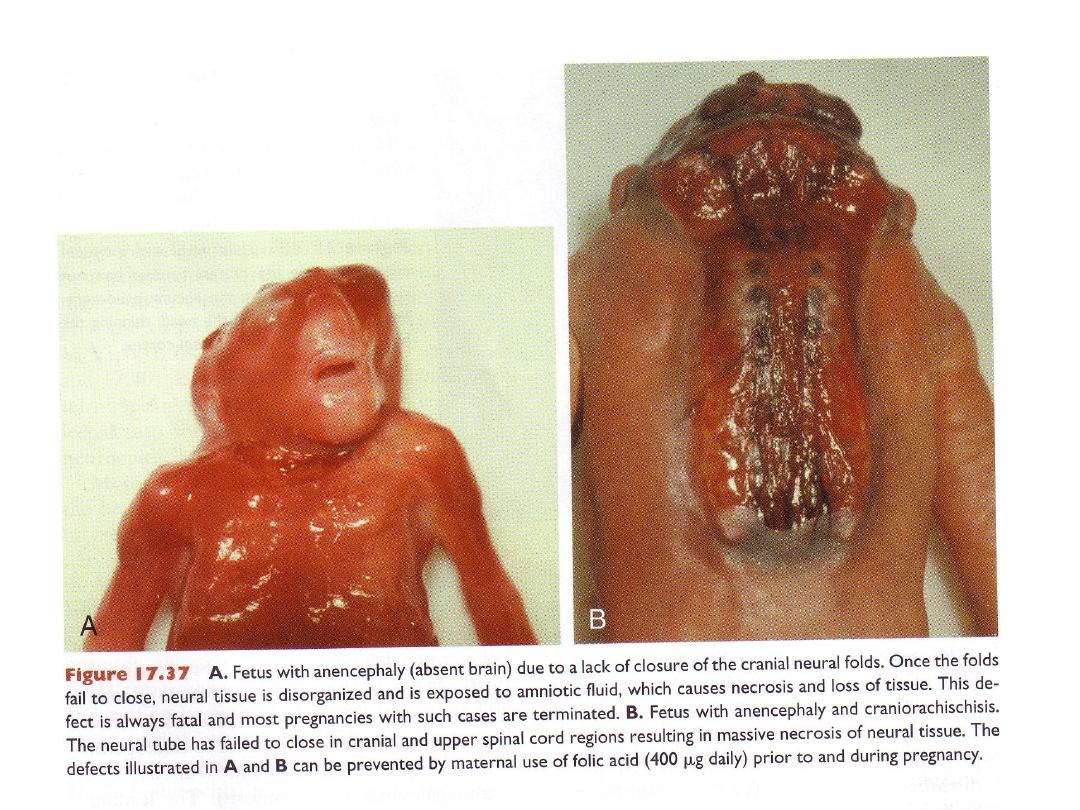
Neural tube defects in skull region
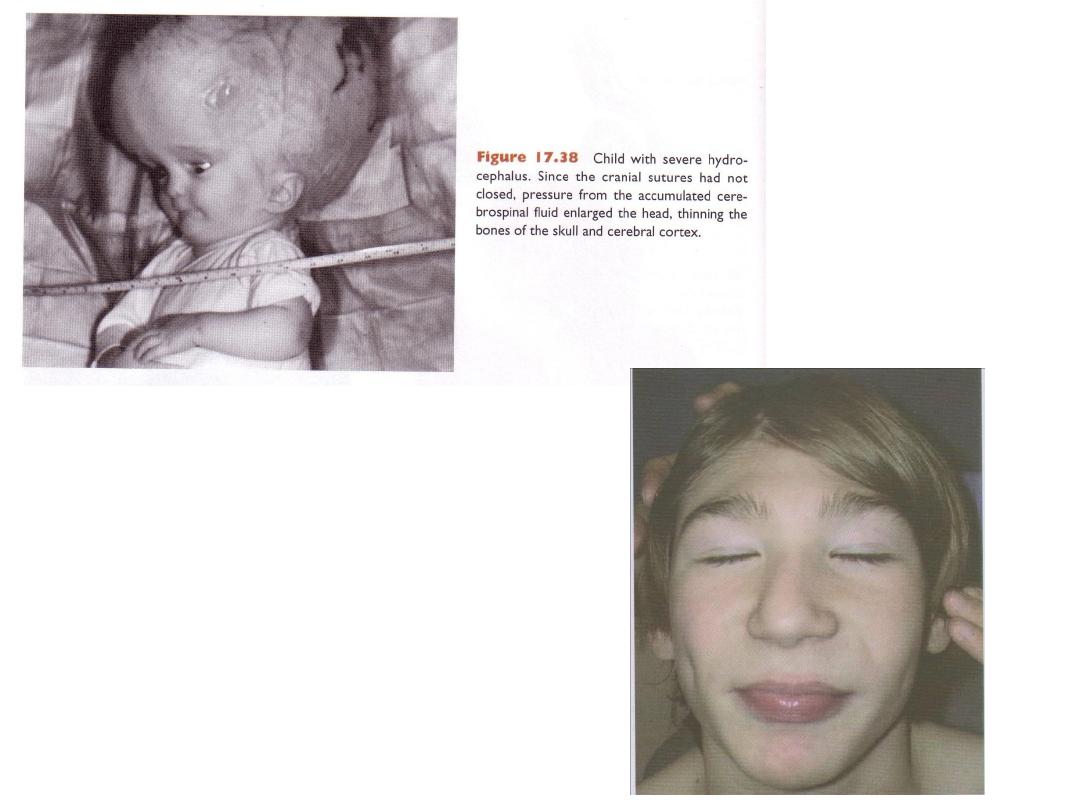
Microcephaly
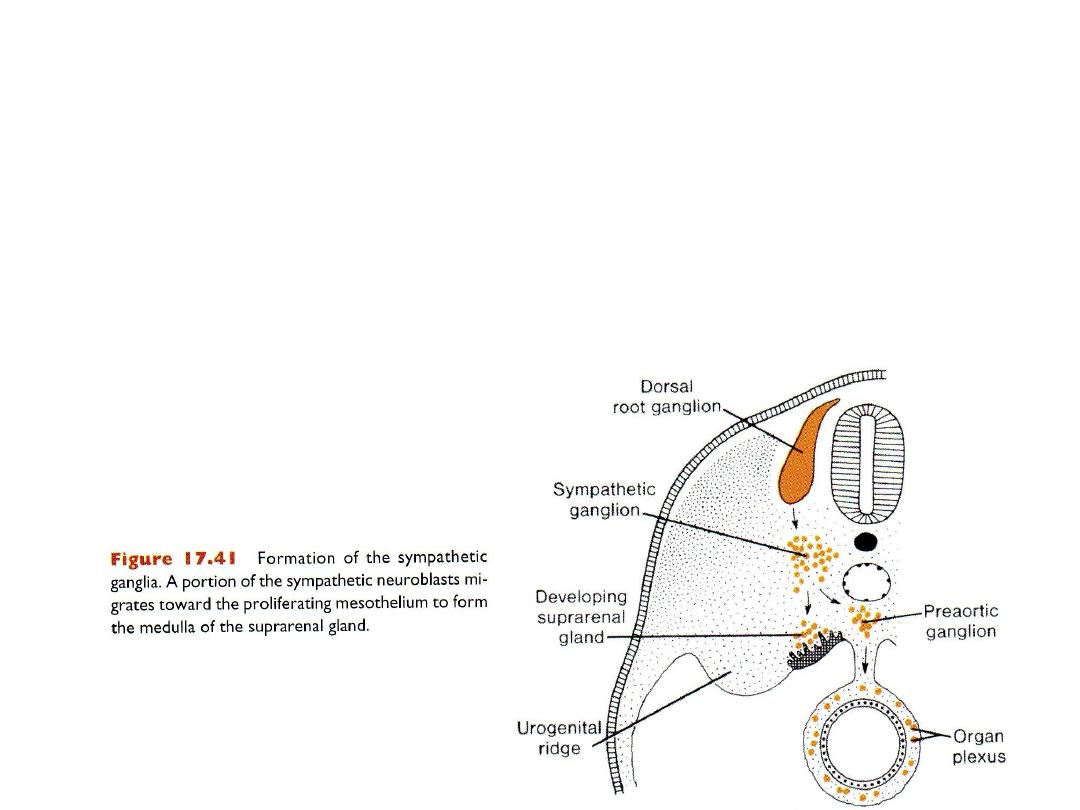
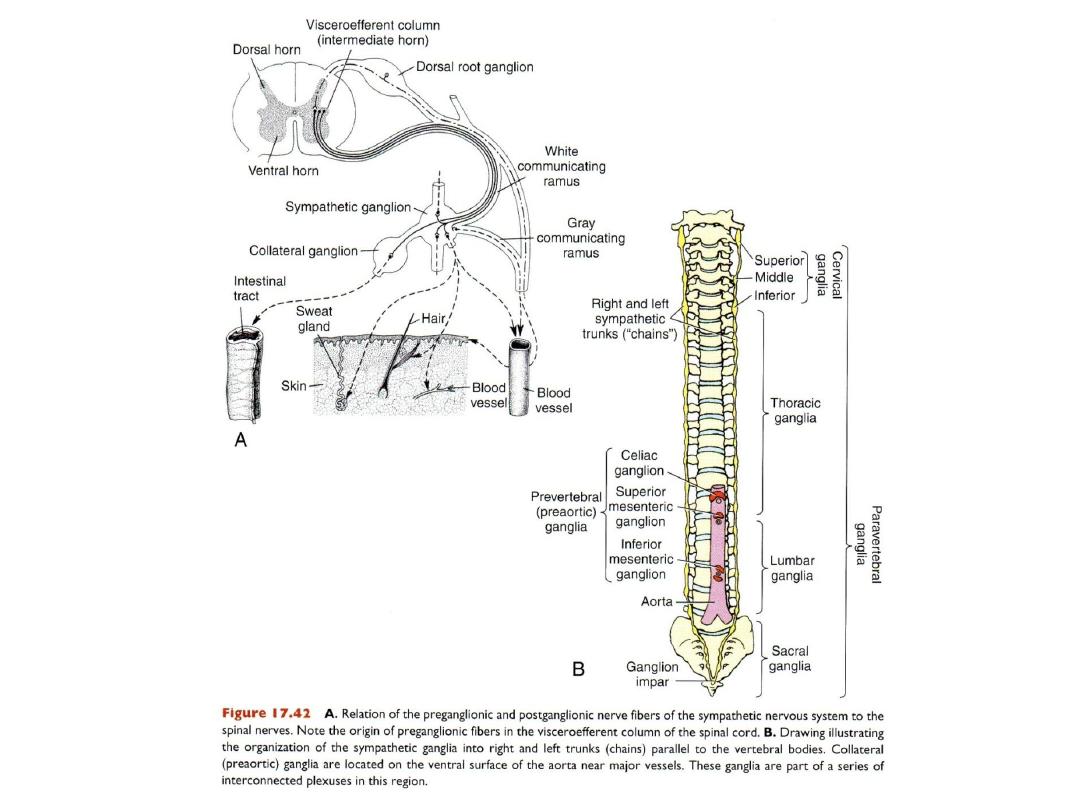
Autonomic nervous system
• Sympathetic NS
• Parasympathetic NS
• 2 neuron systems
• Preganglionic neurons: in brain & spinal cord
• Post ganglionic neurons (in autonomic ganglia) origin from neural crest
cells.
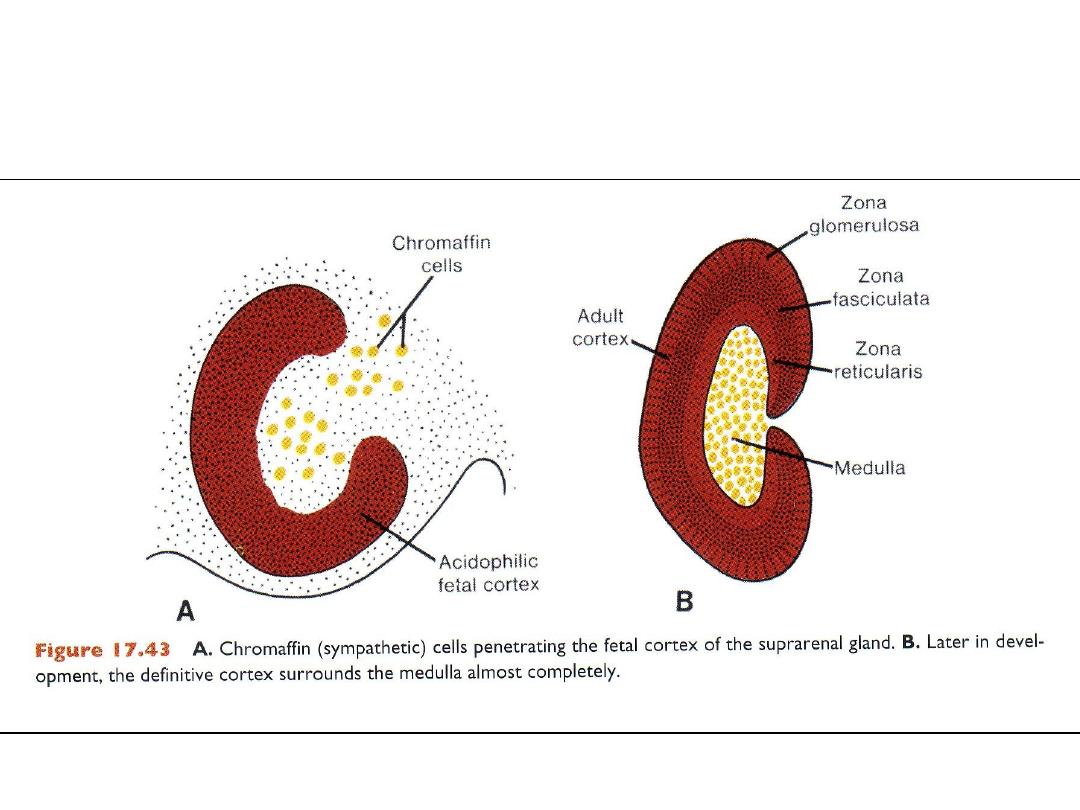
SUPRARENAL GLAND
