
Chapter 14
RESPIRATORY
SYSTEM
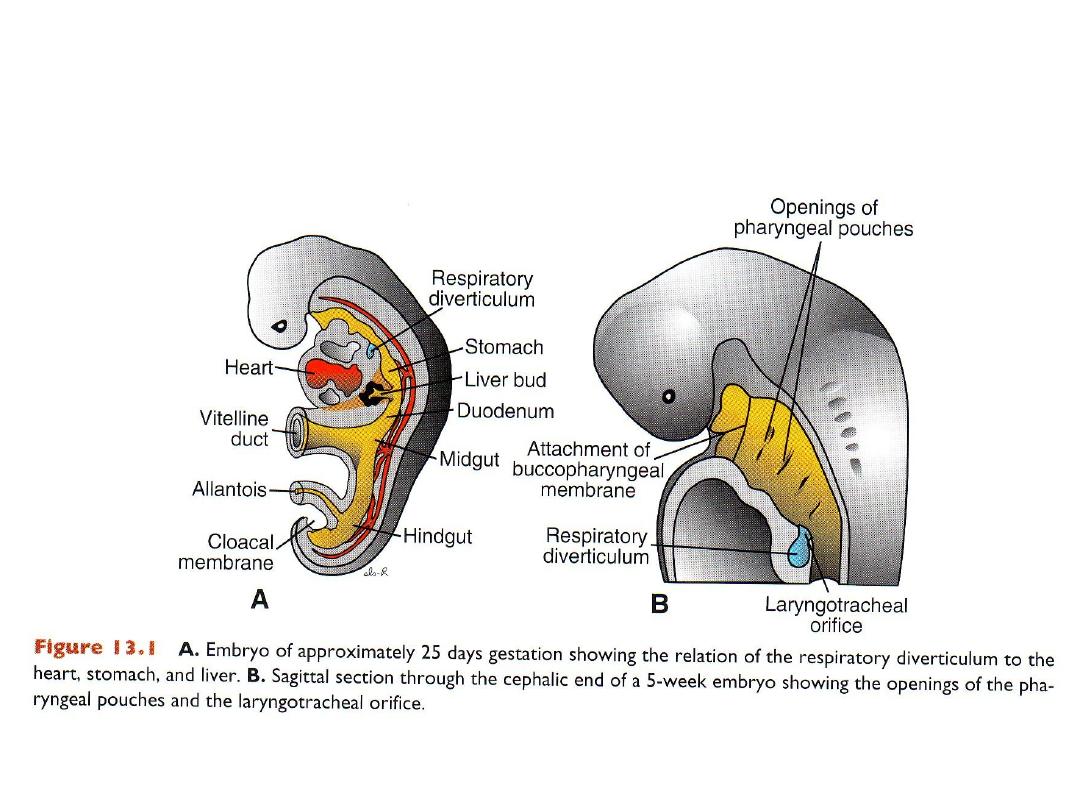
Formation of the lung buds
Embryo: 4wks old
Origin of tissues
• Epithelial lining of larynx, trachea, bronchi & lung (alveoli): endoderm
• Cartilage, muscles & C.T: splanchnic mesoderm around foregut
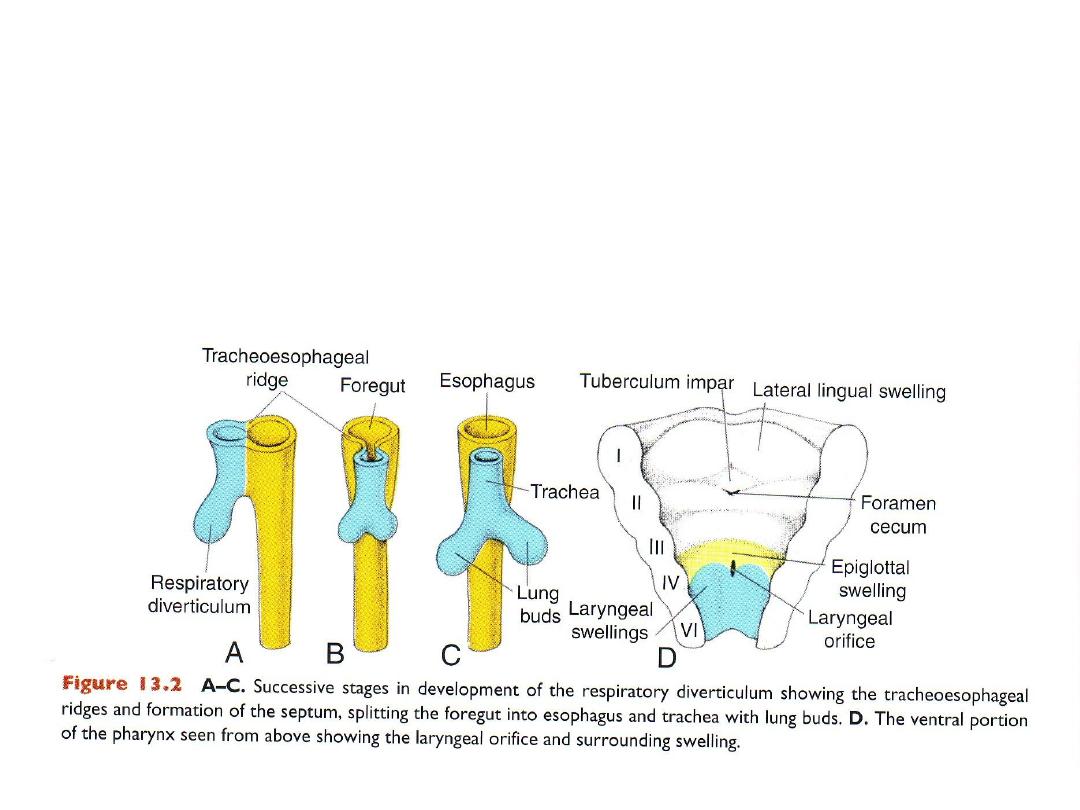
Formation of tracheo-esophageal ridges & septum
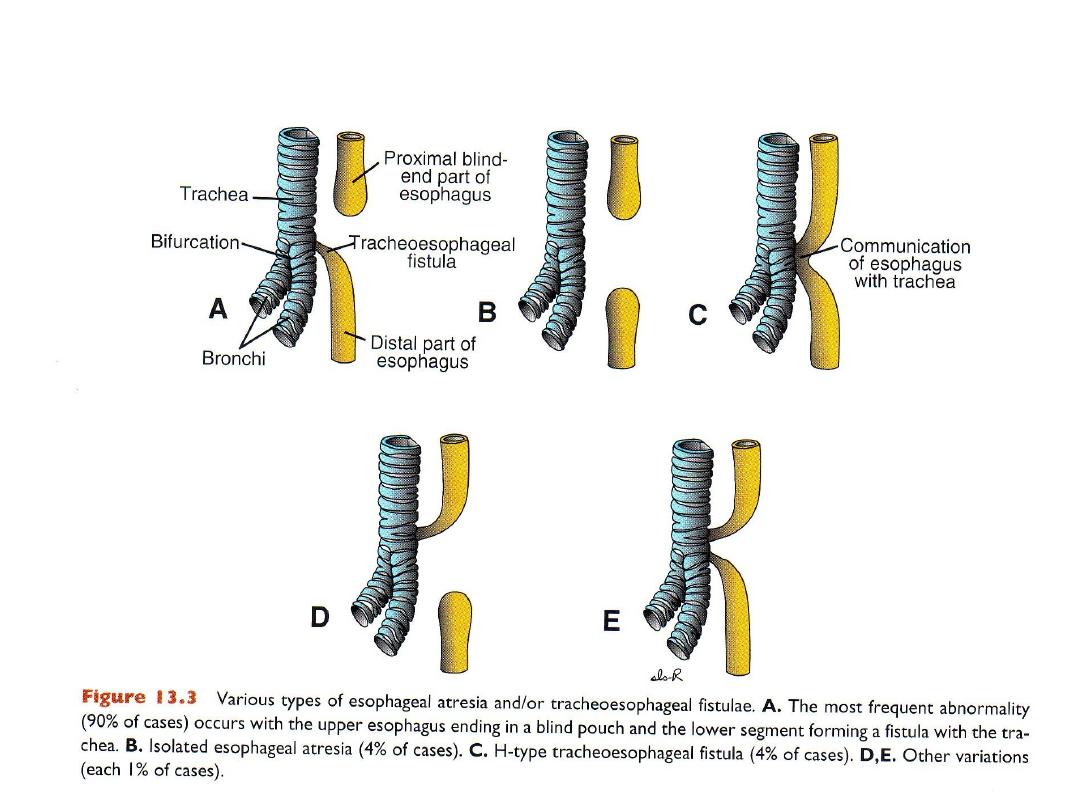
Abnormalities in partitioning: Esopgageal atresia &/or tracheoesophgeal fistula
VACTERL association
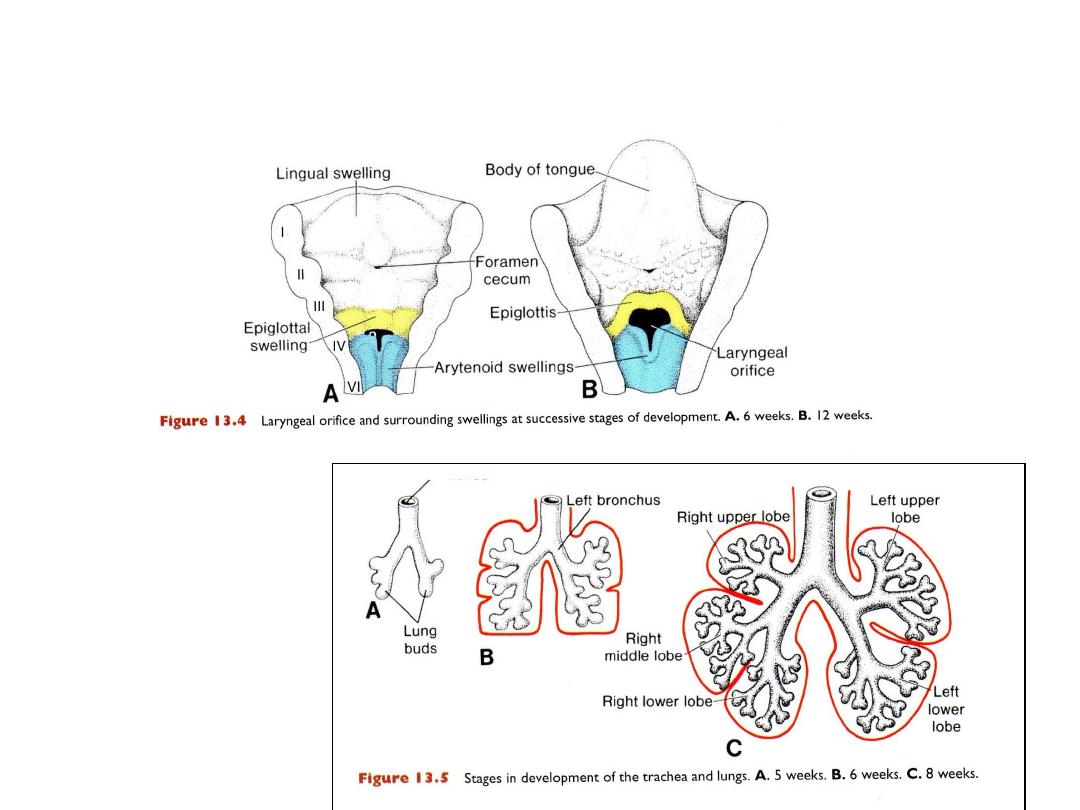
LARYNX
Cartilage & muscle from mesenchyme of: 4
th
& 6
th
pharyng. Arches
Innervation of laryngeal muscles: vagus nerve
Trachea,
bronchi &
lungs
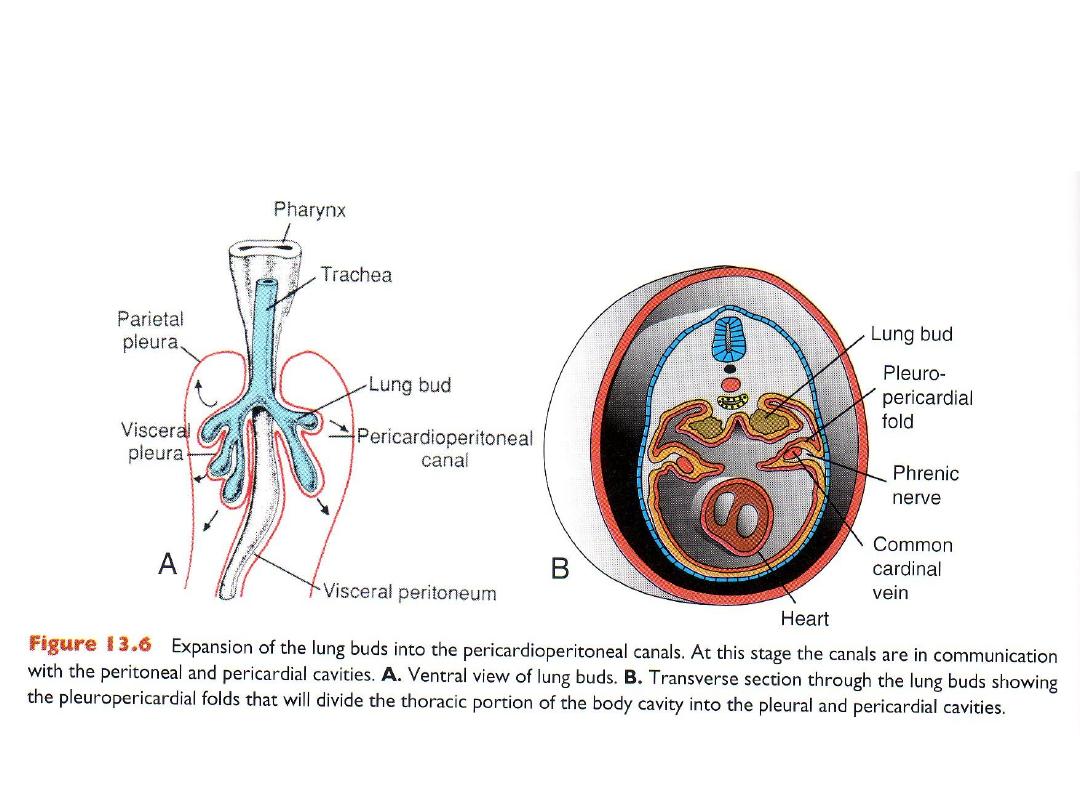
Formation of membranes
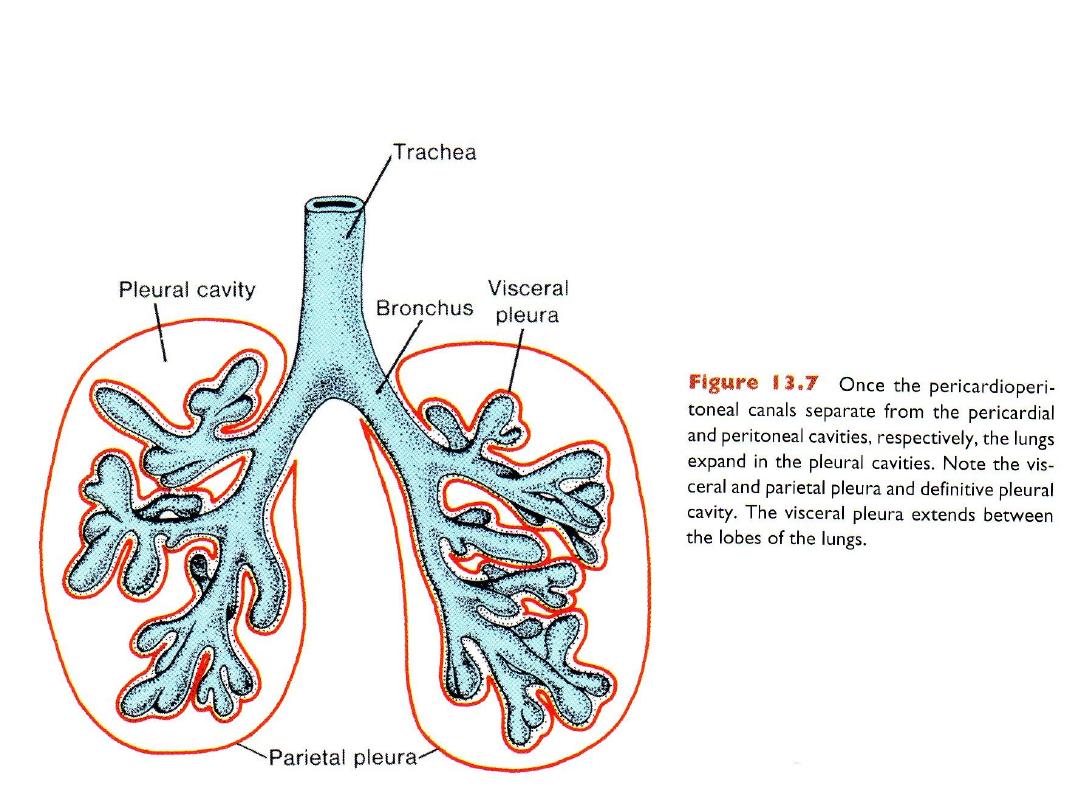
Formation of pleura
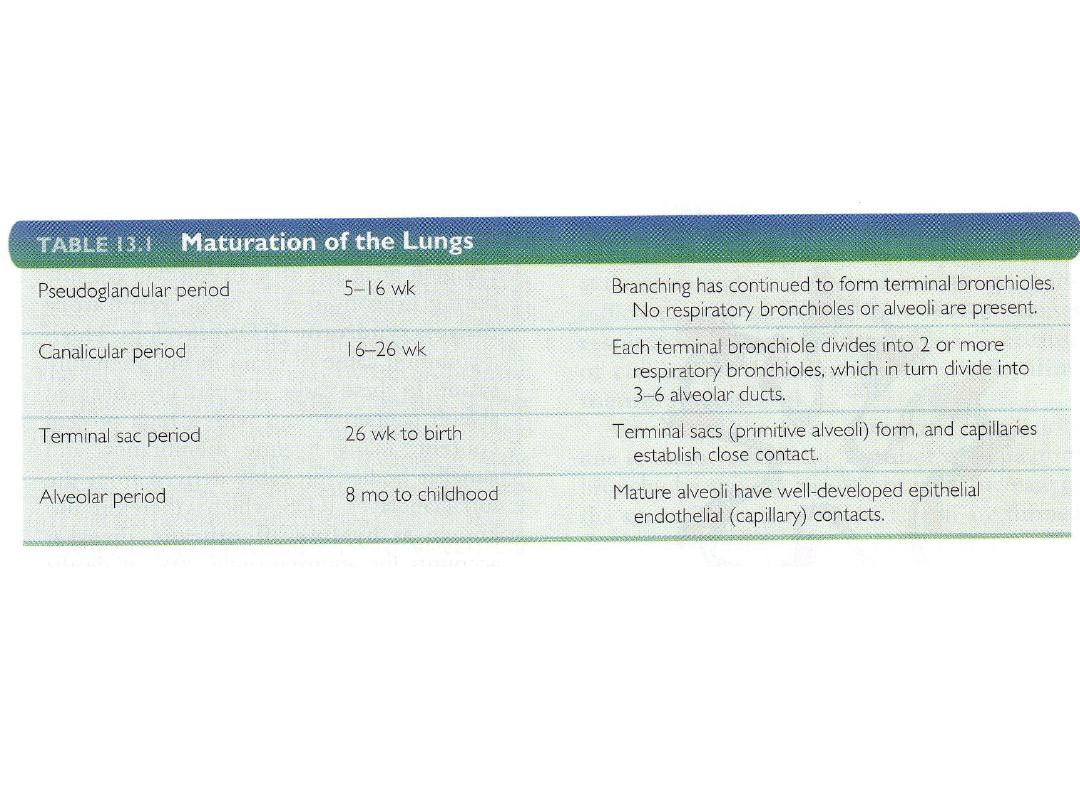
MATURATION OF THE LUNGS
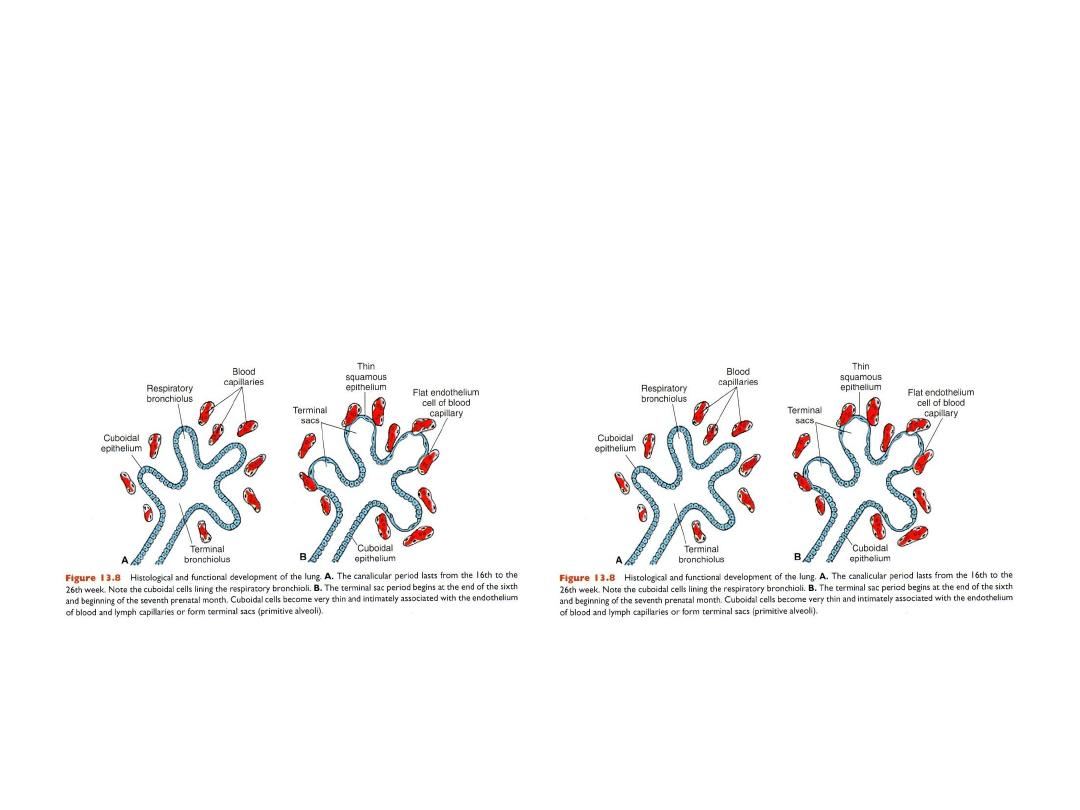
Maturation of the lungs
CANALICULAR PERIOD
16-26 wks
Terminal sac period, begins at
beginning of 7
th
month
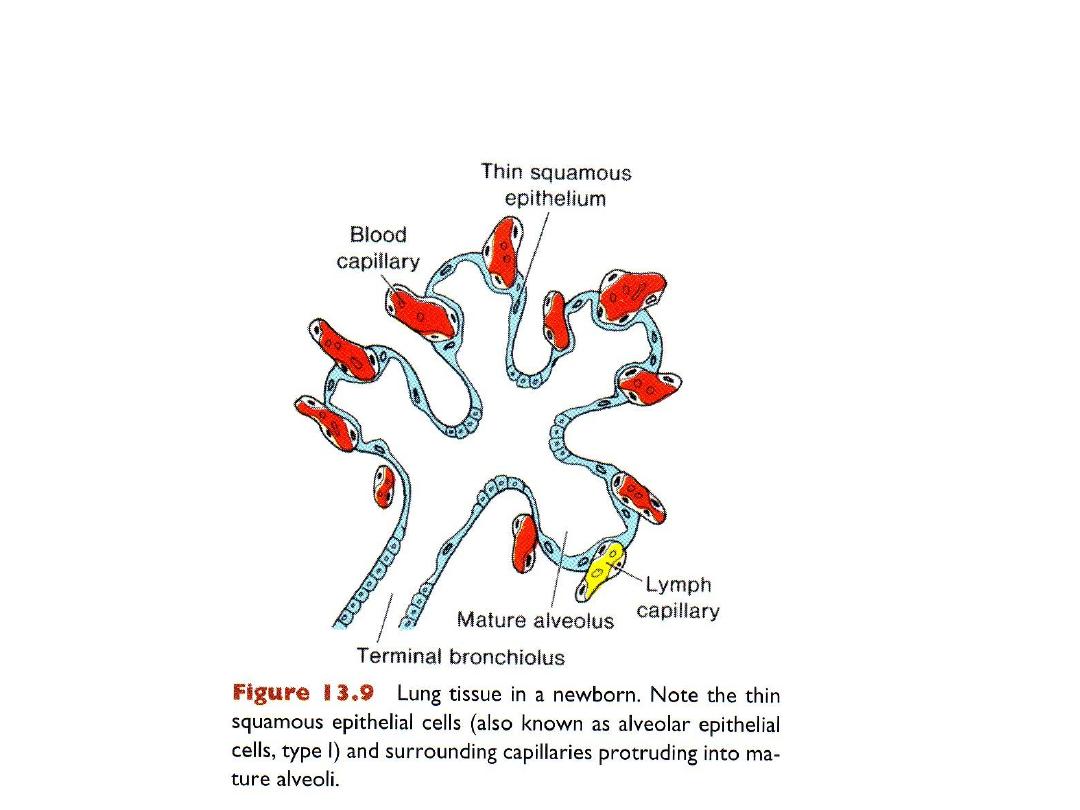
Alveolar period, 8
th
month to childhood
Alveolar I, blood-air barrier, alveolar II: surfactant)

Type II alveolar epithelial cells
• Type II alveolar epithelial cells develop at end of 6
th
month
• Produce surfactant (phospholipid-rich fluid) to lower surface tension at the air-
alveolar surface.
• Mature alveoli are not present before birth
• New alveoli are formed during the first 10 years of postnatal life
• Growth of lungs after birth: increase in number of respiratory bronchioles & alveoli
– not increase in size of alveoli
RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME
(Hyaline membrane disease)
• Absent or insufficient surfactant in premature infants (before 7
th
month)
• Collapse of primitive alveoli
• Treatment:
– artificial surfactant
– Glucocorticoids to stimulate surfactant production
