
Chapter 1
Old and New Frontiers and
an Introduction to
Molecular Regulation and
Signaling

LIST OF CONTENTS
•
Definitions
•
Gene expression
•
Levels of Regulation of gene expression
•
Gene transcription
•
Chromatin, nucleosomes, gene
•
Transcription factor
•
Alternative splicing
•
Post translational modifications
•
Induction & organ formation
•
Epithelial-mesenchymal interaction
•
Cell signalling: paracrine signalling
•
Paracrine factors
•
Juxtacrine factors
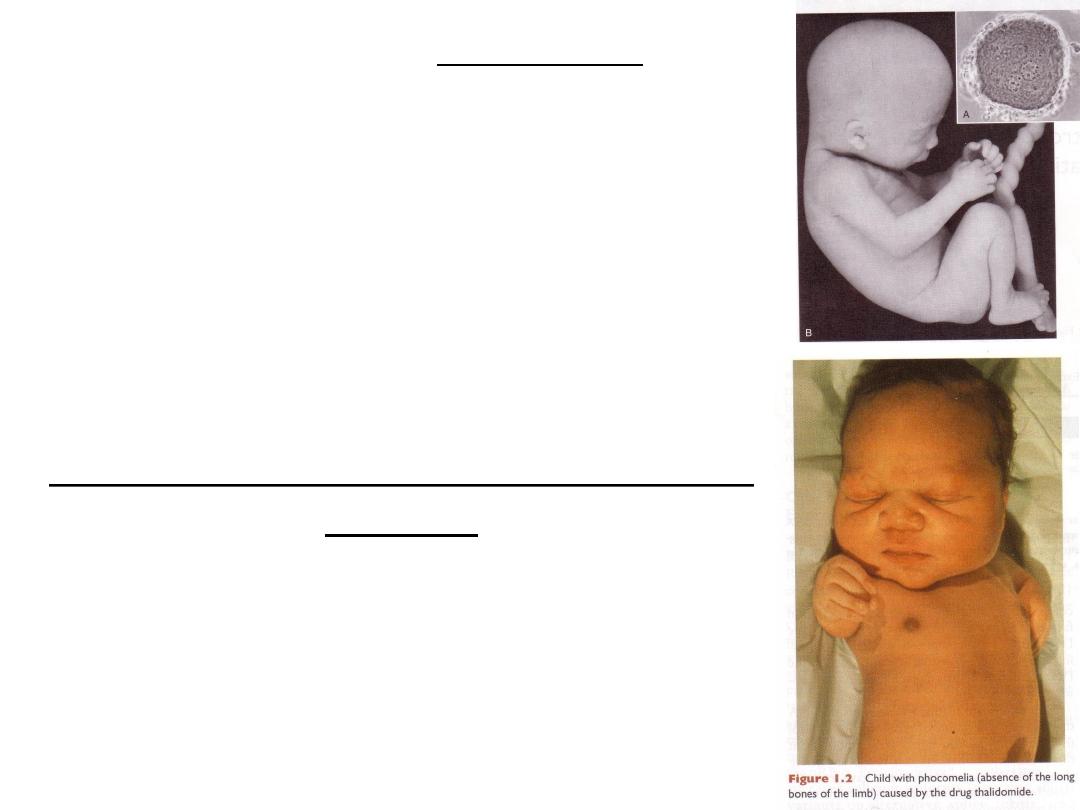
Embryology
• Definition: study of the complex
phenomena and their integration during the
developmental process from a single cell to
a baby.
• It also includes investigations of molecular,
cellular and structural factors that
contribute to the formation of the
organism.
• OBSERVATIONS + INVESTIGATIONS
Better understanding of embryology will
result in:
– New techniques of prenatal
diagnosis & treatment
– Therapeutic procedures to
infertility problems
– Mechanisms to prevent birth
defects
Embyogenesis, fetal period, teratology
• EMBYOGENESIS (EMBRYONIC PERIOD, ORGANOGENESIS) the first 8 wks of
human development: The process f progressing from a single cell through the
period of establishing organ primordia.
• FETAL PERIOD: from 9wks until birth. Process of differentiation.
• TERATOLOGY: the study of embryological origins and causes of birth defects.
Gene expression
• In human genome, number of genes ≈ 35000
• Number of proteins = 3 X number of genes
• NOT TRUE: One gene One protein
• TRUE: One gene many proteins
Levels of regulation of gene expression
1.
Different genes may be transcribed
2.
Selective processing of DNA transcription from a gene
Transcription factors, Enhancers
Nuclear RNA (nRNA), alternative splicing, splicing isoforms
3.
Selective translation of mRNA
4.
Posttranslational modifications

GENE TRANSCRIPTION
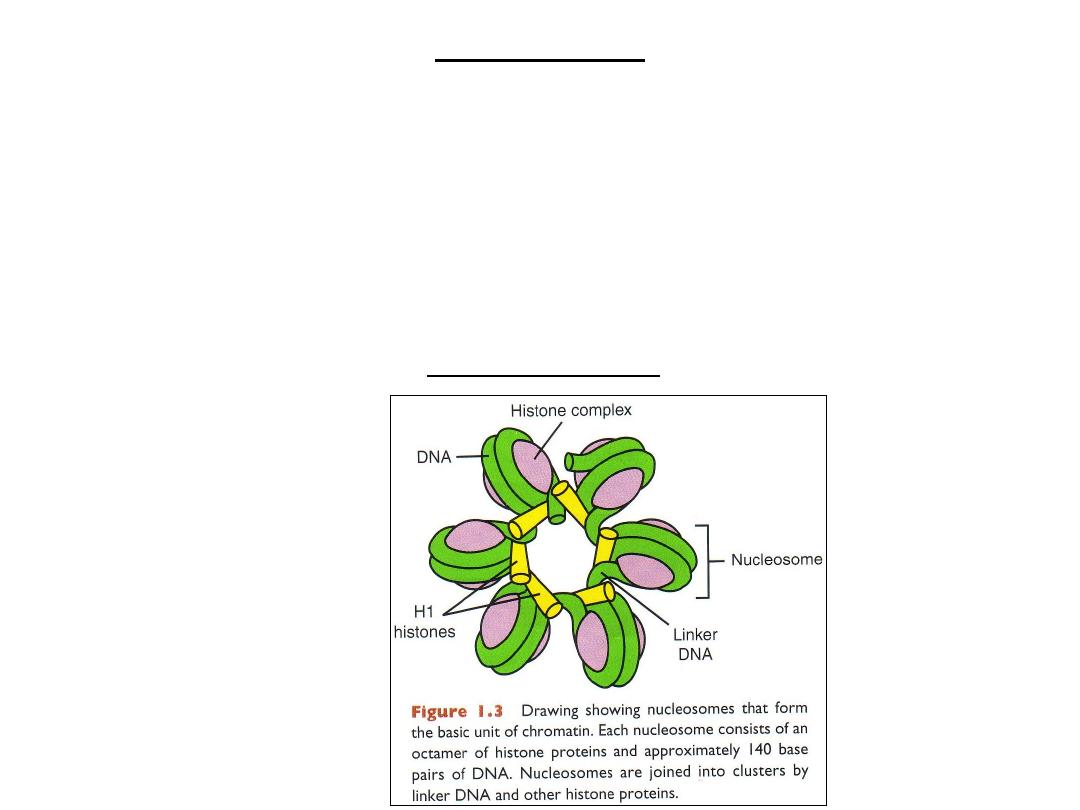
Chromatin
• Chromatin: DNA + histone proteins
• Nucleosome= DNA (140 BP) + histones
• Nucleosomes linked by H1 histone (linker DNA)
• Nucleosomes = coiled DNA= HETEROCHROMATIN : NO TRANSCRIPTION
• EUCHROMATIN = uncoiled DNA: transcription
Nucleosomes
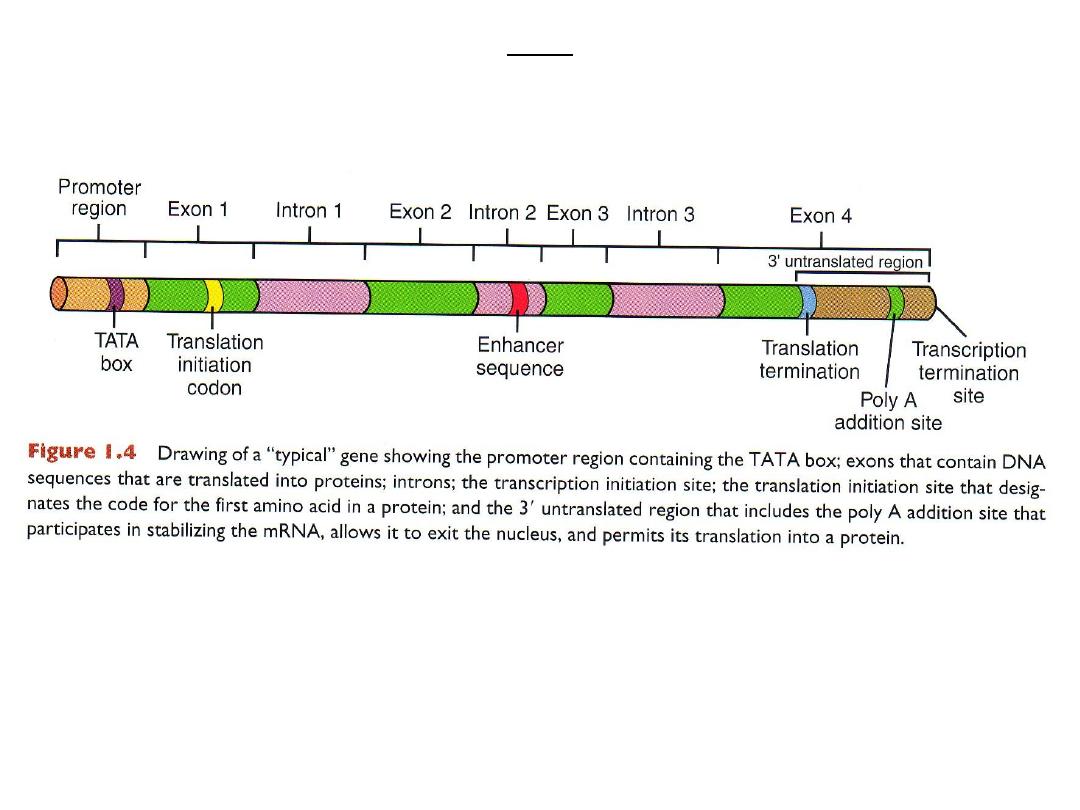
Gene
exons, introns, promoter region, transcription initiation site, translation
initiation site, translation termination codon, transcription factors,enhancers
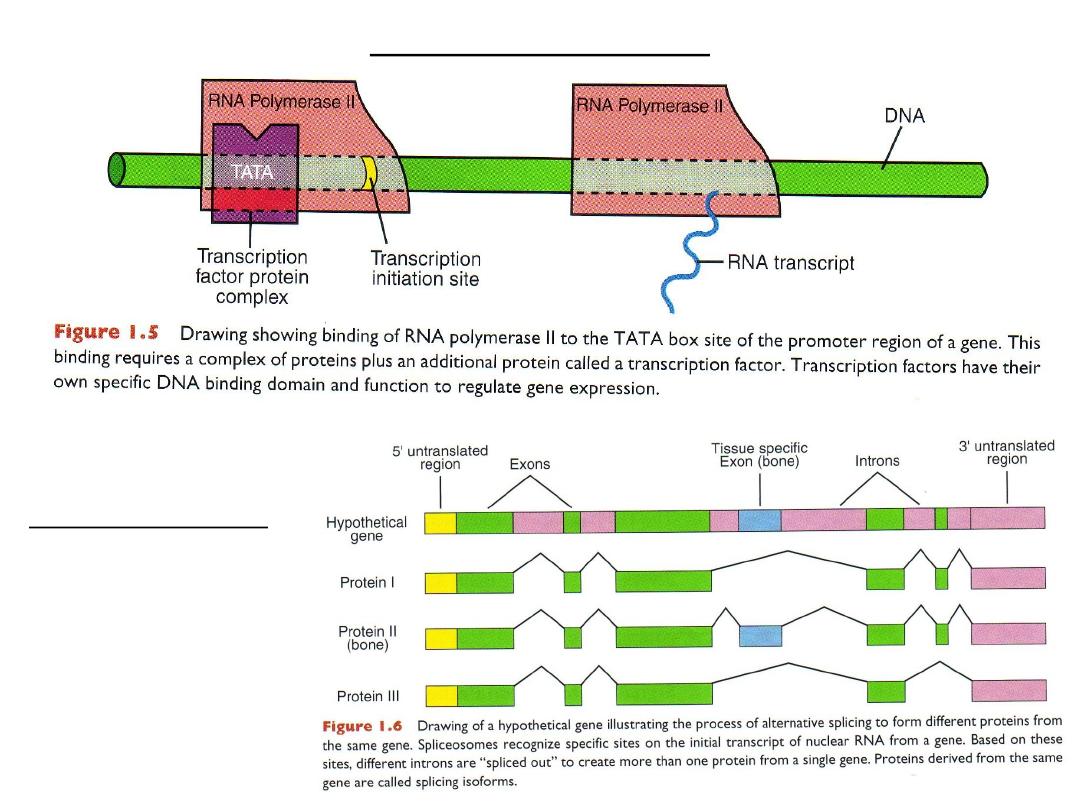
Transcription factor
Alternative splicing
nuclear RNA (nRNA):
longer than mRNA
splicing isoforms:
different proteins
from the same gene
Post translational modifications
• Phosphorelation
• Cleavage
• Glycosylation
• Combination with other proteins
Induction & organ formation
• Induction
• Inducer
• Responder
• Competence: capacity to respond
• Competence factor
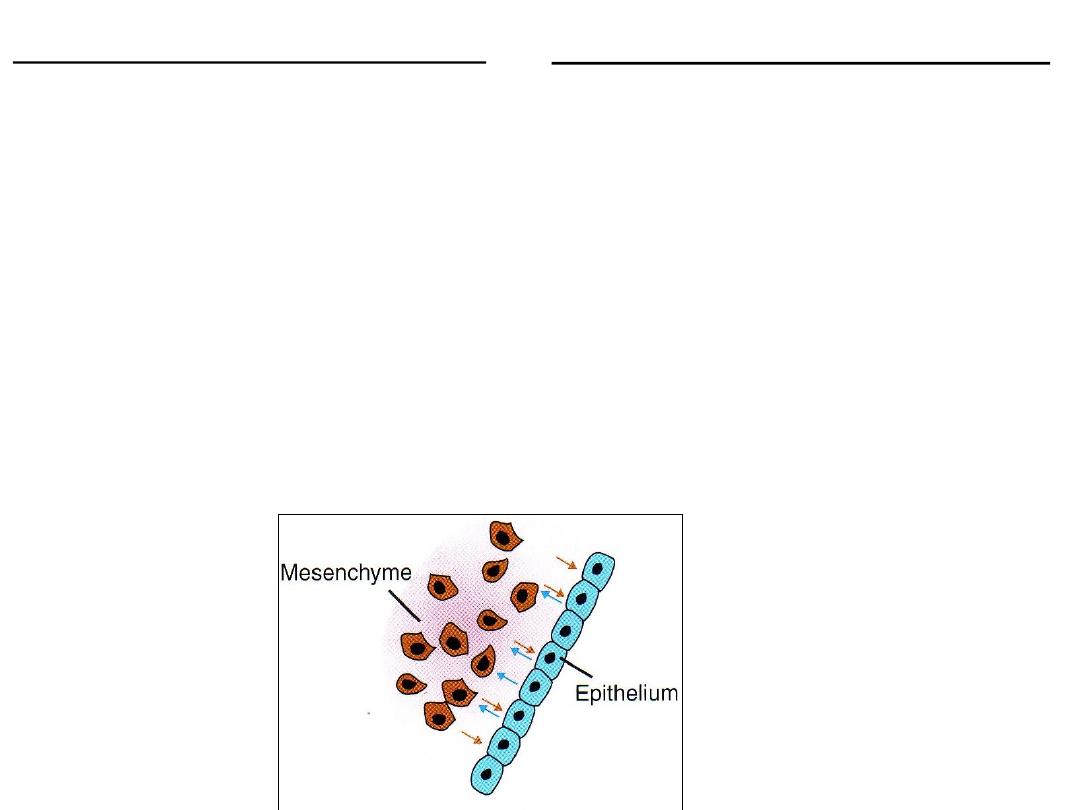
Epithelial-mesenchymal interaction:
gut endodermmesenchyme=liver & pancreas
limb ectoderm (epithelium) mesenchyme=limb differentiation
cross talk

Cell signaling:
• Paracrine interactions: paracrine factors
• Juxtacrine interactions
Paracrine Signaling
• Paracrine factors act by signal transduction pathways.
• Signal transduction pathway includes a signaling molecule (the ligand) and
a receptor.
• The receptor spans the cell membrane and has an extracellular domain
(the ligand-binding region), a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic
domain.
• Binding of ligandActivation of the receptoractivation of intracellular
proteins activation of a transcription factor.
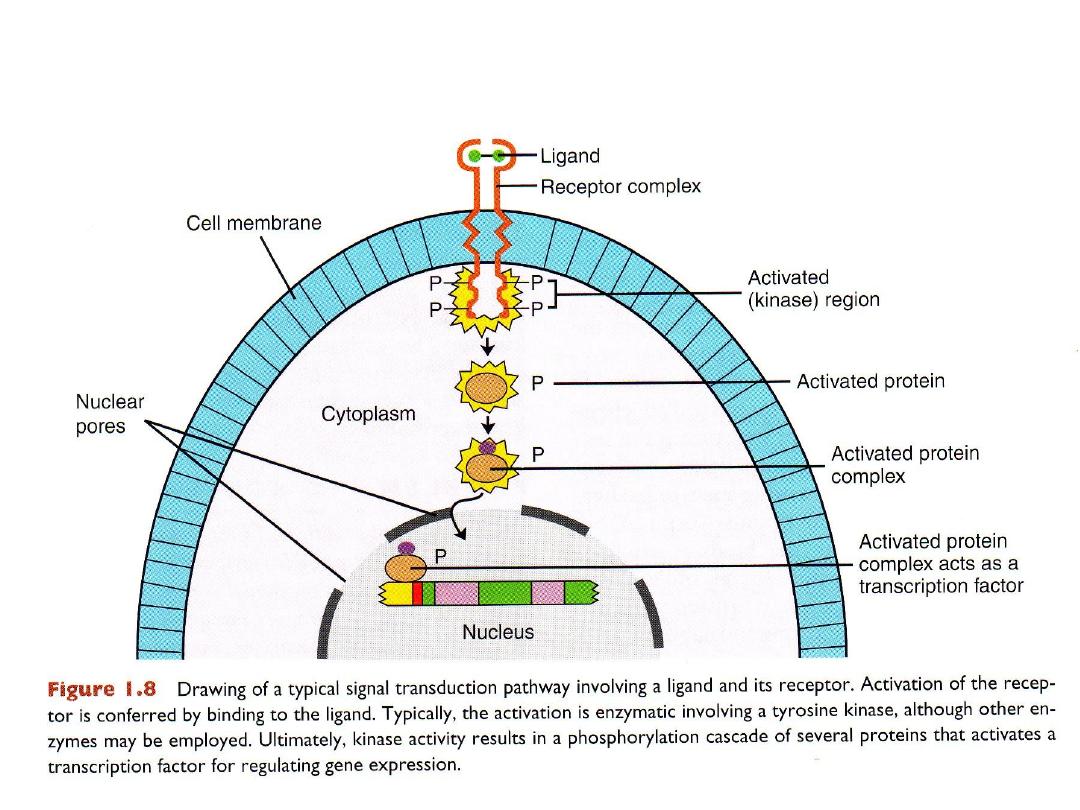
Signal transduction pathways
Paracrine factors
Growth & Differentiation factors (GDFs)
1.
Fibroblast Growth Factors (FGF)
2.
WNT proteins
3.
Hedgehog proteins
4.
Transforming growth factor β families (TGF β superfamily)
Juxtacrine factors
• Juxtacrine signaling is mediated through signal transduction pathways as
well but does not involve diffusable factors.
• Ways of juxtacrine signaling:
1. Ligands bound to cell surface
2. Extracellular matrix
3. Direct cell-to-cell communication: through gap junctions
