14
2
Part
–
Nucleotide metabolism
Lec. 5
Synthesis of pyrimidine ribonucleotides
shorter pathway than for purines
base is made first, then attached to ribose-P (unlike
purine biosynthesis)
only 2 precursors (aspartate and glutamine, plus
HCO
3
-
) contribute to the 6-membered ring
requires 6 steps (instead of 11 for purine)
the product is UMP (uridine monophosphate)
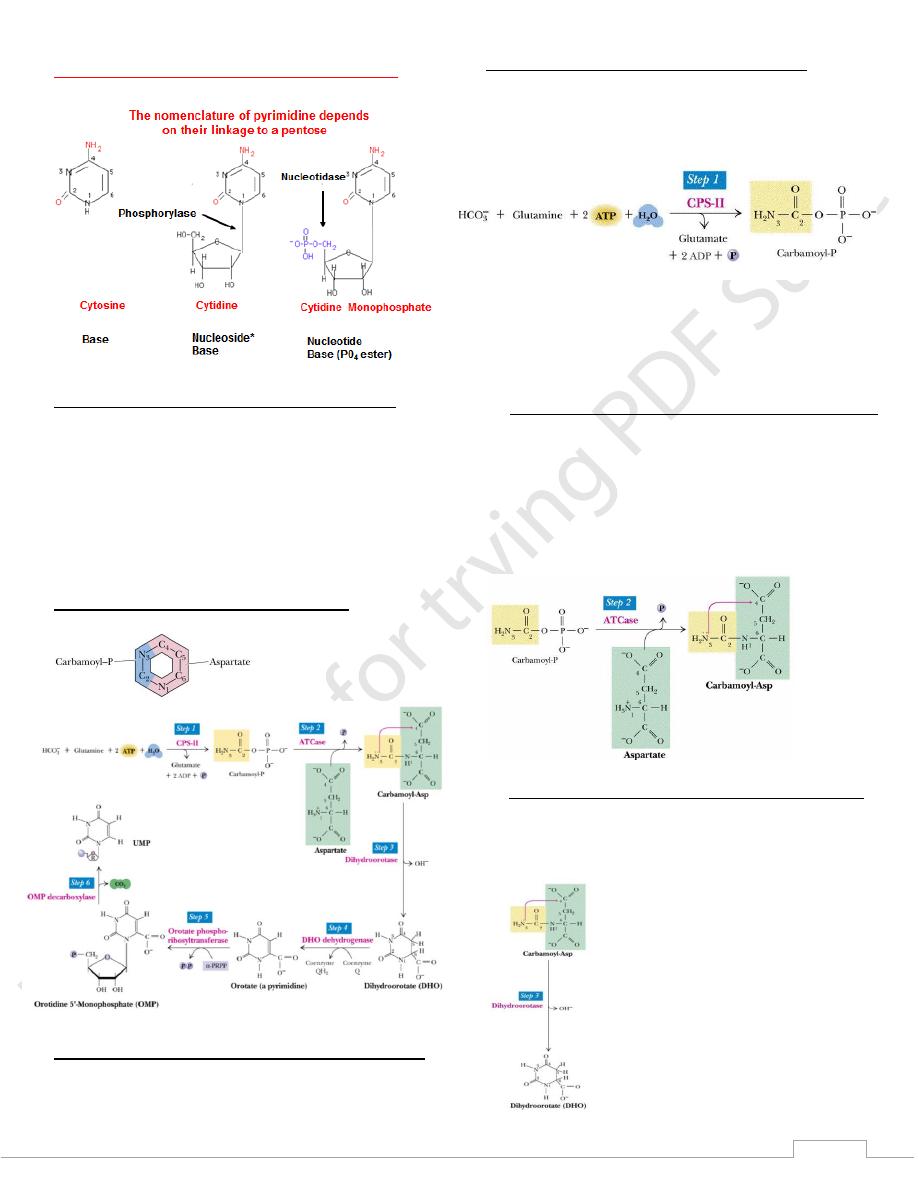
Origin of atoms in pyrimidine ring
Step 1: synthesis of carbamoyl phosphate
Condensation of glutamine, bicarbonate in the presence of
ATP
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase exists in 2 types:
CPS-I which is a mitochondrial enzyme and is dedicated to
the urea cycle and arginine biosynthesis)
CPS-II, a cytosolic enzyme used here
CPS-II is the major site of regulation in animals: UDP and
UTP inhibit the enzyme and ATP and PRPP activate it
It is the committed step in animals
Step 2: synthesis of carbamoyl aspartate
• enzyme is aspartate transcarbamoylase (ATCase)
• catalyzes the condensation of carbamoyl phosphate with
aspartate with the release of Pi
• ATCase is the major site of regulation in bacteria; it is
activated by ATP and inhibited by CTP
• carbamoyl phosphate is an “activated” compound, so no
energy input is needed at this step
Step 3: ring closure to form dihydroorotate
enzyme: dihydroorotase
forms a pyrimidine from carbamoyl aspartate
water is released in this process
15
In E. coli, the first 3 enzymatic reactions are
catalyzed by 3 separate proteins/enzymes
In animals, all 3 steps are found in a multifunctional
enzyme (210 kD).
The acronym CAD is used as a name for the
multienzyme: carbamoyl phosphate synthetase,
aspartate transcarbamoylase and dihydroorotase
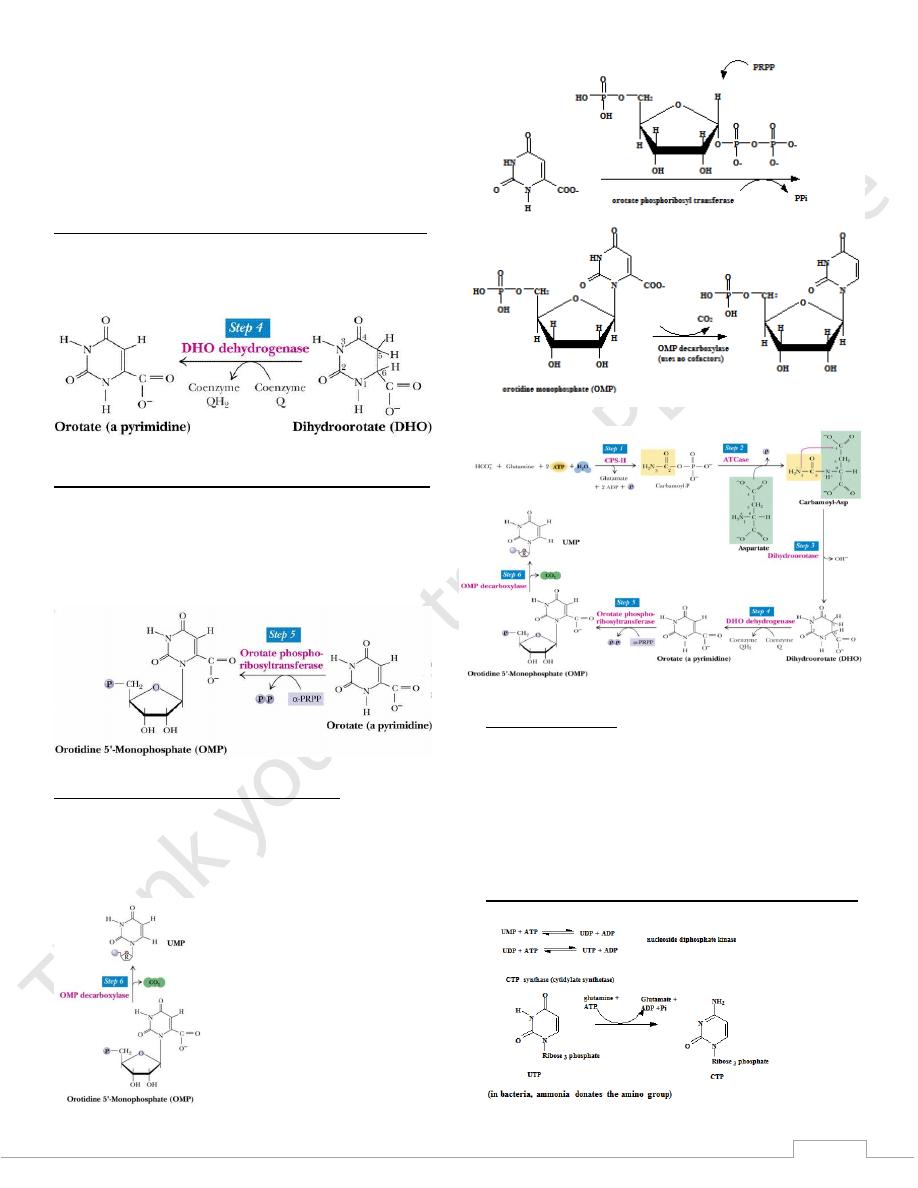
dihydroorotate to orotate
4: oxidation of
Step
An irreversible reaction
Enzyme: dihydroorotate dehydrogenase
Oxidizing power is derived from quinones (thru coenzyme Q)
Step 5: acquisition of ribose phosphate moiety
Enzyme: orotate phosphoribosyl transferase
Ribose phosphate originates from PRPP
product is orotidine-5’-monophosphate (OMP)
orotate phosphoribosyl transferase is also used in salvage
of uracil and cytosine to their corresponding nucleotide
Step 6: decarboxylation of OMP
enzyme: OMP decarboxylase
product: uridine monophosphate (UMP)
In animals, steps 5 and 6 are catalyzed by a single
polypeptide with 2 active sites
Orotic aciduria
An inherited human disease caused by a deficiency in the
multifunctional enzyme that catalyzes the last 2 steps in the
pyrimidine synthesis
large amounts of orotic acid in urine
retarded growth and severe anemia
treat by administration (injection) of uridine and/or cytidine
Synthesis of uridine and cytidine triphosphate
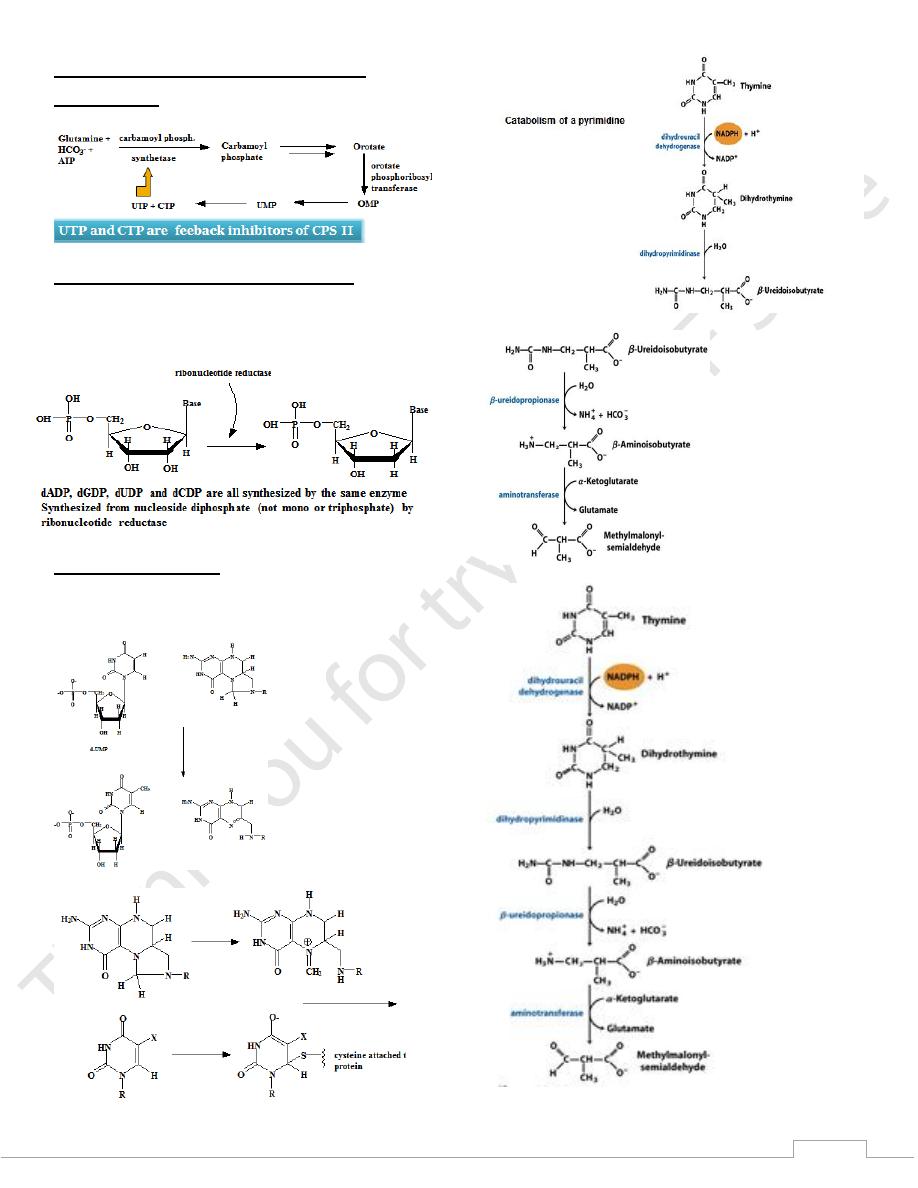
16
Regulation of pyrimidine nucleotide
biosynthesis
Formation of deoxyribonucleotides
All pathways shown previously led to synthesis of
ribonucleotides
Synthesis of dTMP
Methylation of d-UMP via N
5
,N
10
-methylene THF
Reaction inhibited by 5-fluorouracil (Efudex)
