2
Lec.1+2 Biosynthesis of fatty acids lipogenesis
• Excess amounts of ingested carbohydrate & protein can be
converted to fatty acids & stored as triglycerols.
• Fatty acid synthesis occurs primarily in liver, and adipose
tissue(cytosol)
• Many cells can use glucose or fatty acids as source of energy
(heart, skeletal muscle prefers fatty acids but brain &
erythrocytes can't use fatty acids as a source of fuel; it's use
glucose or ketone bodies . why
The Biosynthesis (lipogenesis) of fatty acids can be considered
as a two-stage process:
Stage 1: in mitochondria.
Stage 2 : in cytosol.
Stage 1: transfer of acetyl CoA from
mitochondria to the cytosol
• Source of acetyl-coA :
1) Oxidation of pyruvate.
2) Degradation of fatty acids.
3) Degradation of Ketone bodies.
• Involve transfer of acetate units from
acetyl CoA in mitochondrial matrix
to the cytosol, to form cytosolic
acetyl CoA. why?
Because:
The coenzyme A portion of acetyl
CoA cannot cross the
mitochondrial membrane, & only the
acetyl portion is transported to the
Cytosol in the form of citrate ,which
produced in mitochondrial matrix
through condensation
of oxaloacetate & acetyl CoA by citrate synthase.
Stage 2 in cytosol
• Step 1: citrate cleaved by ATP- citrate lyase to produce
cytosolic acetyl CoA & oxaloacetate
• Step 2: Carboxylation of acetyl CoA to form malonyl CoA.
The energy for the carbon - carbon condensations in F.A
synthesis is supplied by the process of carboxylation and then
decarboxylation of acetyl groups in the cytosol.
• Step 3 : This step involves 7 steps: elongation of the F.A
chain (in 2-carbon increments) by fatty acid synthase.
Carboxylation of acetyl CoA to form malonyl CoA.
Acetyl CoA carboxylation via Acetyl CoA carboxylase which
requires: biotin, ATP & bicarbonate (HCO3 -) as a source
of CO2.
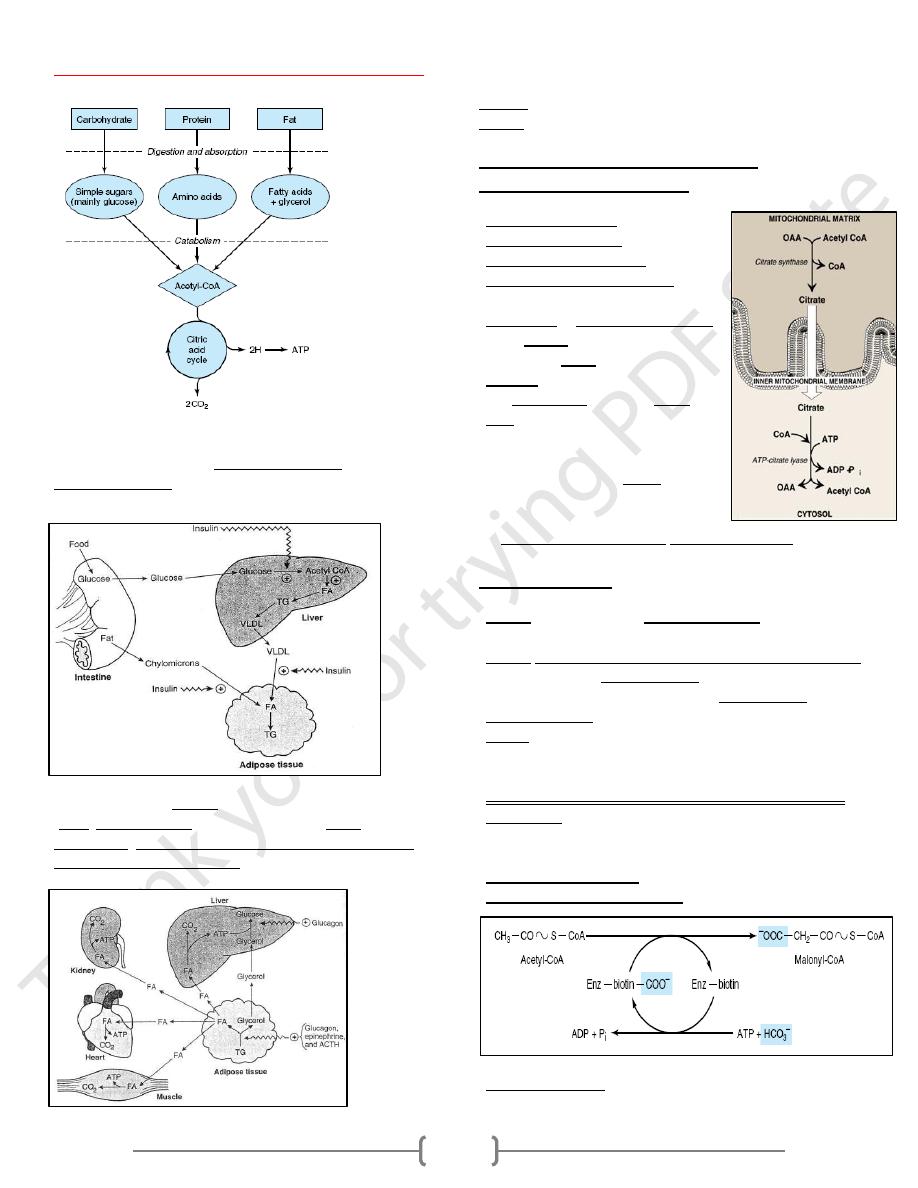
Acetyl CoA carboxylase is a multi-enzyme protein; consist of
3 identical functional subunits:
1) Biotin carboxylase, Which activates CO2 by attaching it to a
nitrogen in the biotin ring in an ATP-dependent reaction.
3
2) Biotin carrier protein: Has the long, flexible biotin arm
carries the activated CO
2
from the biotin carboxylase site to
the transcarboxylase active site.
3) Biotin transcarboxylase Which transfers activated CO2 from
biotin to acetyl-CoA, producing malonyl-CoA
This carboxylation is both the rate-limiting and the regulated
step in fatty acid synthesis.
Regulation of acetyl CoA carboxylase
1)
Short term regulation
:
a) Citrate:
Lead to allosteric
activation of the enzyme
which causes dimers to
polymerize. This
stimulatory effect under
conditions of high citrate
concentration (energy
storage is desirable i.e.
increase synthesis of FA).
b) Palmitoyl-CoA
(The end product of the
pathway): lead to allosteric
inactivation of the enzyme
(feedback inhibition).
c) Malonyl-CoA:
Lead to allosteric
inactivation of the enzyme.
d) Reversible
phosphorylation:
Covalent regulation of by
cAMP dependent protein
kinase:
Epinephrine & glucagon :
Lead to phosphorylation of
the enzyme & thereby,
inactivate it
Insulin:
Lead to dephosphorylation of
the enzyme and activate it.
2) Long term regulation:
1- Prolonged consumption of a diet containing excess calories
(high-calorie, high-carbohydrate diets) causes an increase in
acetyl CoA carboxylase synthesis, thus increasing fatty acid
synthesis.
2- Low-calorie diet or fasting state causes a decrease in acetyl
CoA carboxylase synthesis, thus decreasing in fatty acid
synthesis.
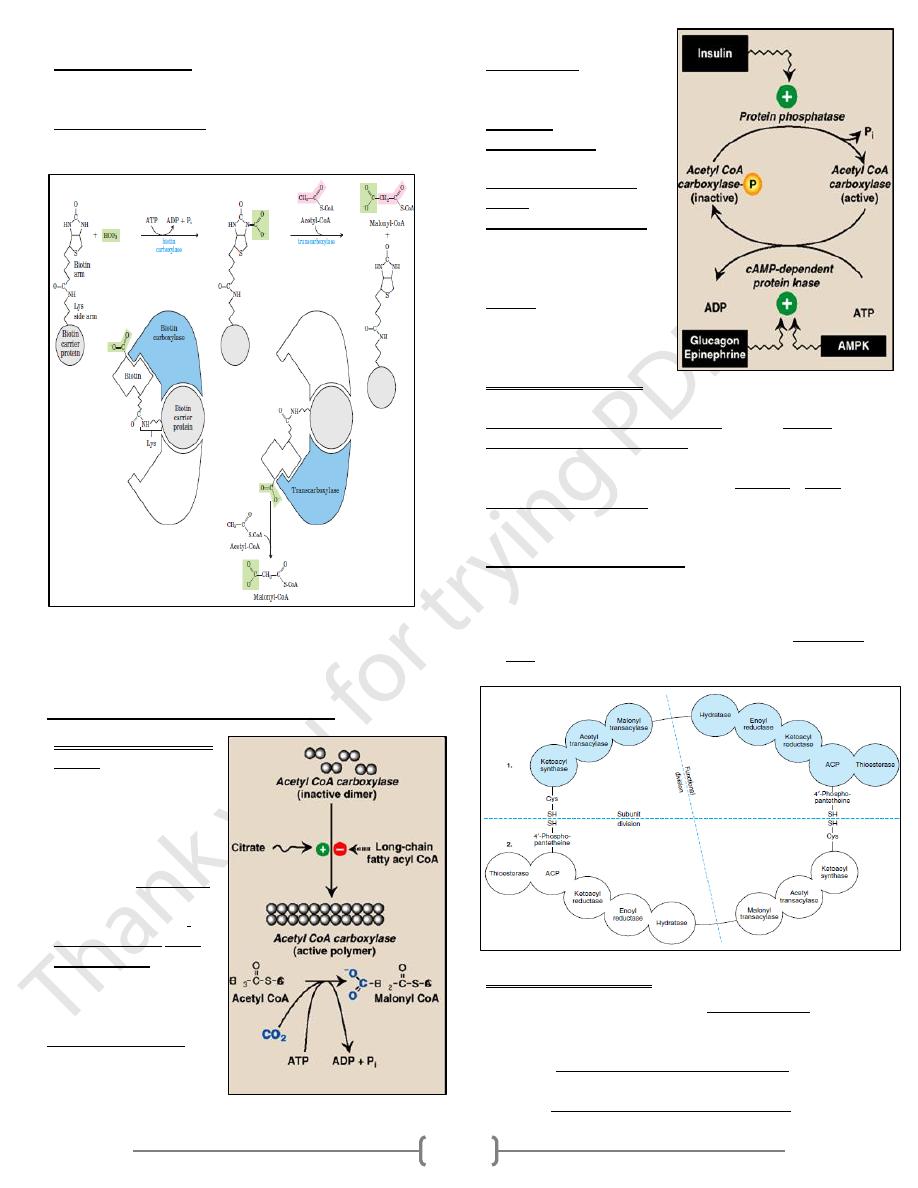
Fatty acid synthase (FAS)
Dimer enzyme each monomer composed of:
1) 7 different enzymatic activities.
2) Acyl carrier protein (ACP), covalently binds to Pantothenic
acid, it carries acetyl and acyl units on its terminal thiol (-
SH) gp.
Biosynthesis of fatty acids
• acetyl CoA + CO2 → Malonyl CoA (1 ATP utilized)
• Intermediates covalently linked to FAS
1) Condensation ( acetyl CoA + Malonyl CoA ) = 4c
2) Reduction (require the reduced cofactor NADPH ).
3) Dehydration (loss of H2o)
4) Reduction (require the reduced cofactor NADPH ).

4
This cycle of reactions is repeated 6 times, each time
incorporating a 2 carbon unit (derived from malonyl CoA) into
the growing fatty acid chain at the carboxyl end.
When the fatty acid reaches a length of 16 carbons, the
synthetic process is terminated with palmitate.
8-acetyl-coA +7ATP+14NADPH+14H+ → palmitate +8 CoA+
7ADP + 7Pi+14NADP+6H2O
Regulation of Fatty Acid Synthase
1) In liver:
Insulin: stimulates FAS gene expression, thus excess
glucose is stored as fat.
Polyunsaturated fatty acids: diminish FAS gene
expression in liver cells.
2) In fat cells:
Leptin: produced by fat cells in response to excess fat
storage, inhibit FAS expression has a role in regulating
food intake and fat storage.
Leptin: regulates body weight by decreasing food intake,
increasing energy expenditure, and inhibiting fatty acid
synthesis.
Summary
• Write a balanced equation for synthesis of palmitate from
acetyl-CoA, listing net inputs and outputs:
8 acetyl-CoA + 14 NADPH + 7 ATP
palmitate + 14 NADP
+
+ 8 CoA + 7 ADP + 7 P
i
• Summary based on malonate as an input:
Acetyl-CoA + 7 malonyl-CoA + 14 NADPH
palmitate + 7 CO
2
+ 14 NADP
+
+ 8 CoA
• Fatty acid synthesis occurs in the cytosol. Acetyl-CoA
generated in mitochondria is transported to the cytosol via a
shuttle mechanism involving citrate.
• Elongation beyond the 16-C length of the palmitate product
of Fatty Acid Synthase is mainly catalyzed by enzymes
associated with the endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
• ER enzymes lengthen fatty acids produced by Fatty Acyl
Synthase as well as dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids.
• Fatty acids esterified to coenzyme A serve as substrates.
• Malonyl-CoA is the donor of 2-carbon units in a reaction
sequence similar to that of Fatty Acid Synthase except that
individual steps are catalyzed by separate proteins.
