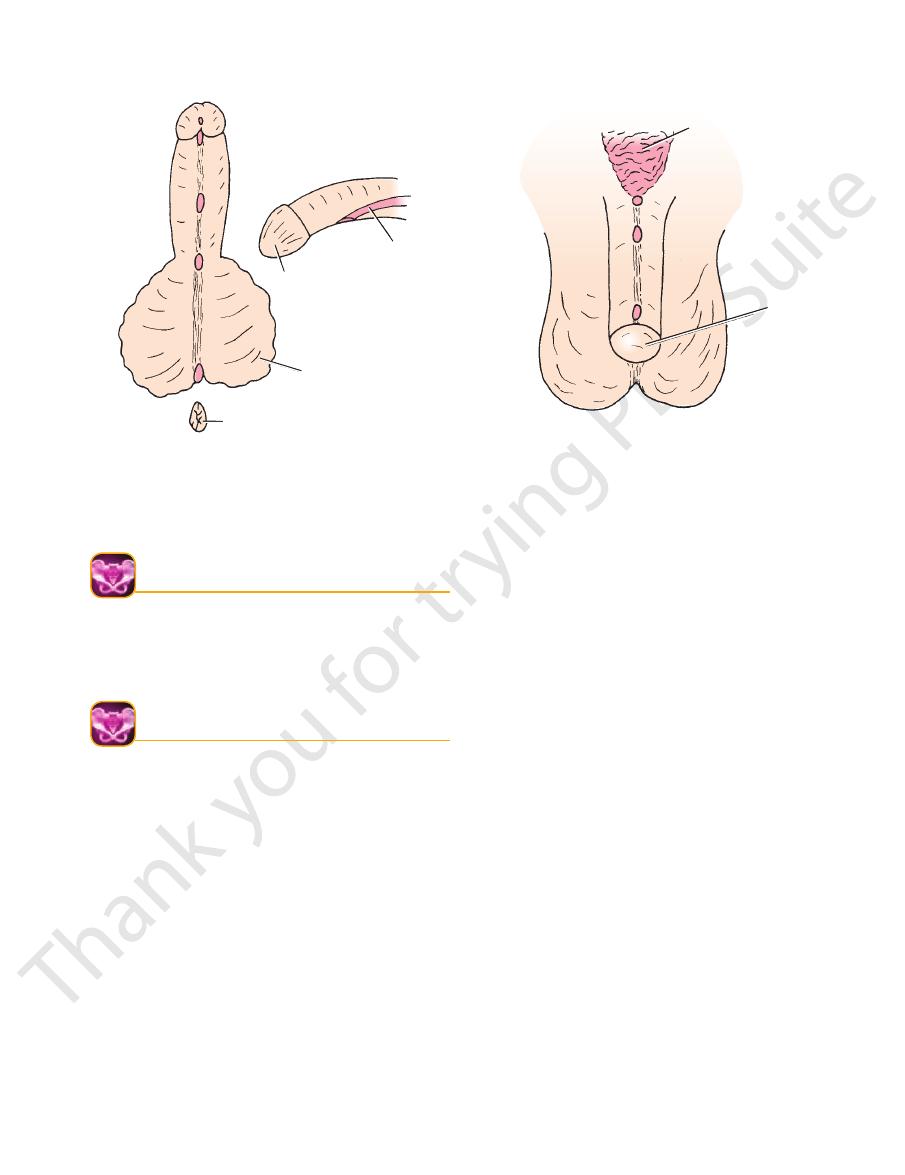
Surface Anatomy
329
penile
urethra
glans
scrotum
anus
1
2
3
4
5
FIGURE 8.23
Types of hypospadias: (
(chordee) of the penis also is present.
) perineal. Ventral flexion
) penoscrotal, and (
) glandular, (
1
2) coronal,
(3) penile, (4
5
extrophy of bladder
glans
FIGURE 8.24
Types of epispadias.
natomy
aphic
adiog
R
R
a
The radiographic anatomy of the bones forming the
in Figures 8.25 and 8.26.
and 7.43. A cystourethrogram of the male urethra is shown
boundaries of the perineum is shown in Figures 7.39, 7.41,
natomy
face
s
uR
a
The perineum when seen from below with the thighs
the anterior triangle, which
anal triangle;
anus, is called the
(see Fig. 8.2). The posterior triangle, which contains the
by joining the ischial tuberosities with an imaginary line
It is customary to divide the perineum into two triangles
weight of the body.
the lower border of the gluteus maximus and supports the
ting position, the ischial tuberosity emerges from beneath
tuberosity is covered by the gluteus maximus. In the sit
of the buttock (see Fig. 8.3). In the standing position, the
The ischial tuberosity can be palpated in the lower part
Ischial Tuberosity
the anus (see Fig. 8.3).
the cleft between the buttocks about 1 in. (2.5 cm) behind
The inferior surface and tip of the coccyx can be palpated in
midline at the lower extremity of the anterior abdominal wall.
and 8.28). It is felt as a solid structure beneath the skin in the
midline between the bodies of the pubic bones (Figs. 8.3, 8.27,
The symphysis pubis is the cartilaginous joint that lies in the
ischial tuberosities.
and laterally by the
coccyx,
posteriorly by the tip of
symphysis pubis,
anteriorly by the
abducted (see Fig. 8.2) is diamond shaped and is bounded
the
Symphysis Pubis
Coccyx
-
contains the urogenital orifices, is called the
scrotum.
The male urogenital triangle contains the penis and the
Male Urogenital Triangle
(Fig. 8.29).
Around the anal margin are coarse hairs
anal sphincter.
external
brown and is puckered by the contraction of the
in the midline. In the living, the anal margin is reddish
The anus is the lower opening of the anal canal and lies
Anal Triangle
triangle.
urogenital
Anus
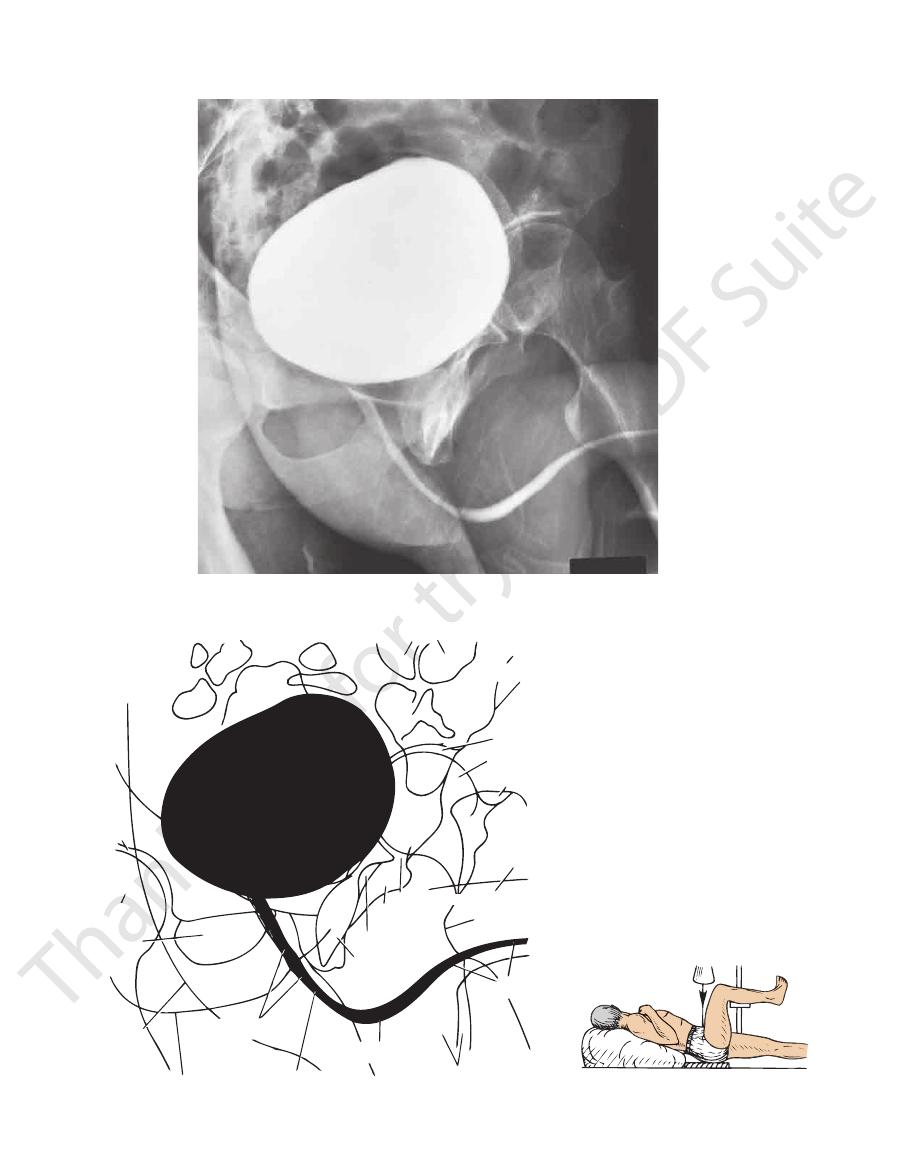
330
CHAPTER 8
The Perineum
FIGURE 8.25
Cystourethrogram after intravenous injection of contrast medium (28-year-old man).
hip joint
head of femur
obturator
foramen
skin fold
ramus of ischium
membranous part of urethra
prostatic part
of urethra
bulbous part
of urethra
ischial
tuberosity
obturator foramen
lesser trochanter
inferior ramus
of pubis
body of penis
greater trochanter
head of femur
hip joint
anterior inferior
iliac spine
gas in bowel
cassette
scrotum
penile part of urethra
u
b lb
urinary bladder filled with
radiopaque material
body of pubis
FIGURE 8.26
The main features seen in the cystourethrogram shown in Figure 8.25.
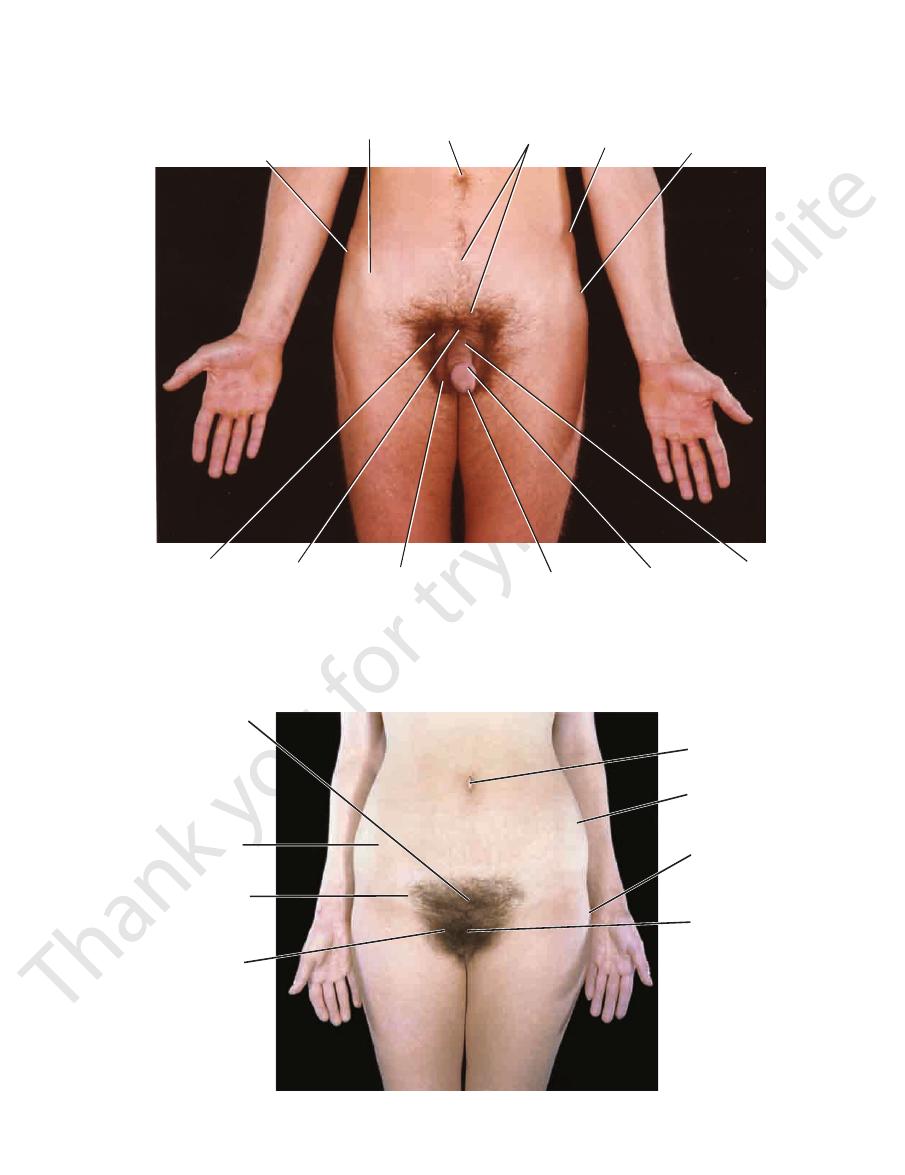
Surface Anatomy
331
tuber cle
tuber cle
of iliac crest
anterior superior
iliac spine
umbilicus
male
distribution
of pubic hair
iliac
crest
greater trochanter
of femur
pubic
symphysis
pubis
scrotum
external
urethral orifice
glans penis
body
of penis
FIGURE 8.27
Anterior view of the pelvis of a 27-year-old man.
mons pubis showing
female distribution
of pubic hair
anterior superior
iliac spine
site of inguinal
ligament
pubic tubercle
umbilicus
iliac crest
greater trochanter
of femur
symphysis pubis
FIGURE 8.28
Anterior view of the pelvis of a 29-year-old woman.
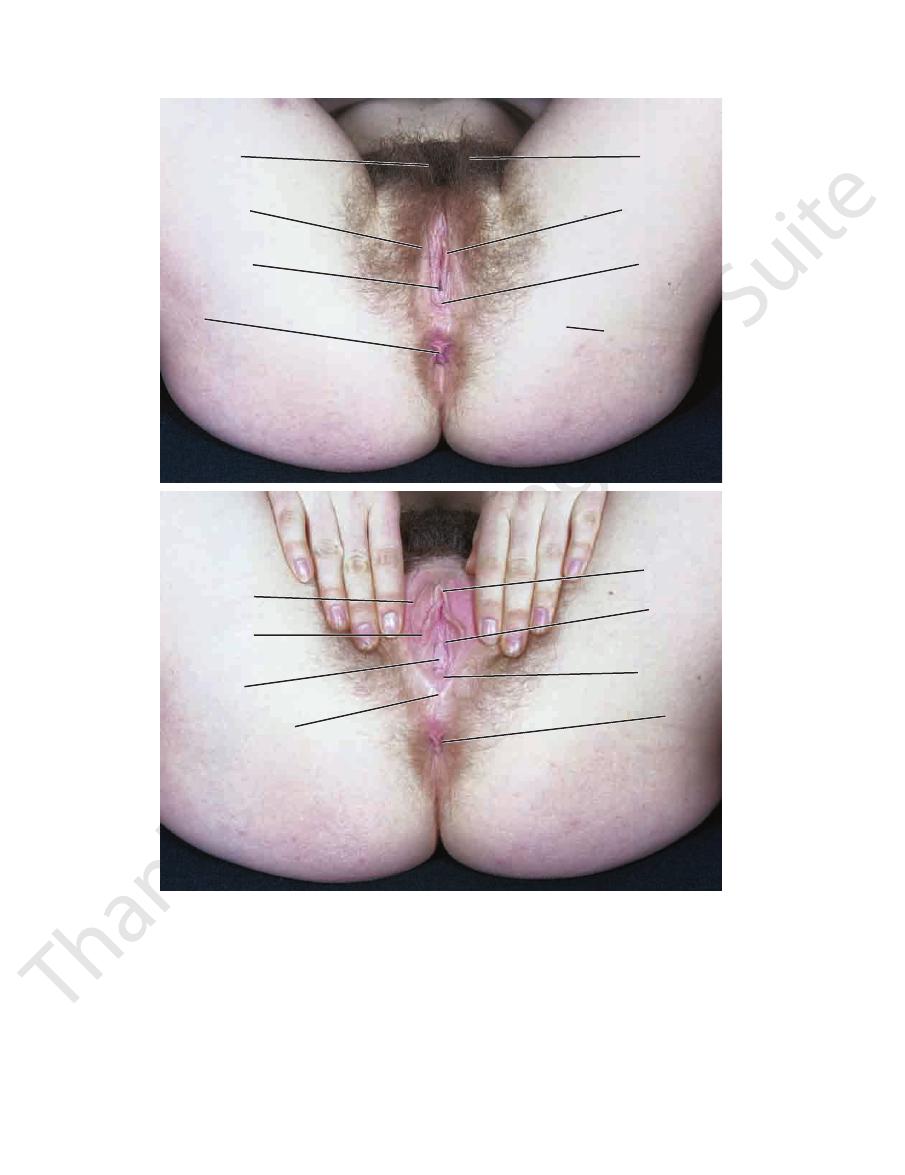
332
CHAPTER 8
The Perineum
mons pubis
labium majus
vaginal orifice
anus
pubic hair
labium minus
fourchette
site of
ischial tuberosity
labium majus
labium minus
anterior
vaginal wall
union of labia majora
prepuce
of clitoris
external
urethral
meatus
fourchette
anus
A
B
FIGURE 8.29
The perineum in a 25-year-old woman, inferior view.
Extending from the
external urethral meatus.
glans is the
penis (see Figs. 8.13, 8.16, and 8.27). At the summit of the
forms the extremity of the body of the
glans penis
The
(see Fig. 8.13).
in the midline
superficial dorsal vein
usually possesses a
the dorsal surface (anterior surface of the flaccid organ)
which is suspended from the symphysis pubis. Note that
is the free portion of the penis,
body of the penis
The
the scrotum.
deep palpation in the midline of the perineum, posterior to
The bulb can be felt on
left crura of the penis.
right
bulb of the penis
masses of erectile tissue called the
consists of three
root of the penis
8.13, 8.16, and 8.27). The
The penis consists of a root, a body, and a glans (see Figs.
With labia separated.
With labia together.
A.
B.
Penis
and the
and

Surface Anatomy
The bilateral origin of the scrotum is indicated by the
of the scrotum is rugose and is covered with sparse hairs.
8.27) containing the testes and the epididymides. The skin
The scrotum is a sac of skin and fascia (see Figs. 8.12 and
extent, and it should be possible to retract it over the glans.
neck of the penis. The prepuce covers the glans for a variable
is formed by a fold of skin attached to the
foreskin
or
puce
pre
(see Fig. 8.16). The
corona
base of the glans is called the
The edge of the
frenulum.
glans to the prepuce called the
lower margin of the external meatus is a fold connecting the
333
-
Scrotum
presence of a dark line in the midline, called the
(see Fig. 8.29).
prepuce
is partly hidden by the
glans of the clitoris
Fig. 8.19). The
This is situated at the apex of the vestibule anteriorly (see
Clitoris
minus (see Fig. 8.19).
between the hymen and the posterior part of the labium
Small orifices, one on each side, are found in the groove
Vestibular Glands
tags of the hymen remain (see Fig. 8.19).
teriorly or posterolaterally, and after childbirth only a few
Fig. 8.19). At the first coitus, the hymen tears, usually pos
which is perforated at its center (see
hymen,
fold called the
The vaginal orifice is protected in virgins by a thin mucosal
Vaginal Orifice
fourchette at its base (see Figs. 8.19 and 8.29).
by the labia minora, with the clitoris at its apex and the
The vestibule is a smooth triangular area bounded laterally
Vestibule
(see Figs. 8.19
frenulum
and a posterior
prepuce
anterior
Anteriorly, they split to enclose the clitoris, forming an
fourchette.
terior ends are united to form a sharp fold, the
that lie between the labia majora (see Fig. 8.19). Their pos
The labia minora are two smaller, hairless folds of soft skin
Labia Minora
riorly in the midline (see Figs. 8.19 and 8.29).
extending posteriorly from the mons pubis to unite poste
The labia majora are prominent, hair-bearing folds of skin
Labia Majora
umbilicus.
rior margin, whereas in the male it extends upward to the
The pubic hair in the female has an abrupt horizontal supe
skin found anterior to the pubis (see Figs. 8.19 and 8.28).
The mons pubis is the rounded, hair-bearing elevation of
(see Figs. 8.19, 8.28, and 8.29).
“Vulva” is the term applied to the female external genitalia
Vulva
Female Urogenital Triangle
to enter the spermatic cord at the upper end of the scrotum.
emerges from the tail and ascends medial to the epididymis
vas deferens
inferiorly (see Fig. 4.21). The cordlike
and a pointed
body,
head,
having an expanded upper end or
of the testis. The epididymis is a long, narrow, firm structure
Each epididymis can be palpated on the posterolateral surface
ous tissue or skin.
nalis (see Fig. 4.21) and are not tethered to the subcutane
have a firm consistency. They lie free within the tunica vagi
The testes should be palpated. They are oval shaped and
Testes
along the line of fusion.
raphe,
scrotal
-
-
Epididymides
a
tail
Mons Pubis
-
-
-
and 8.29).
-
Orifices of the Ducts of the Greater
www.thePoint.lww.com/Snell9e.
Clinical Cases
and
Review Questions
are available online at
