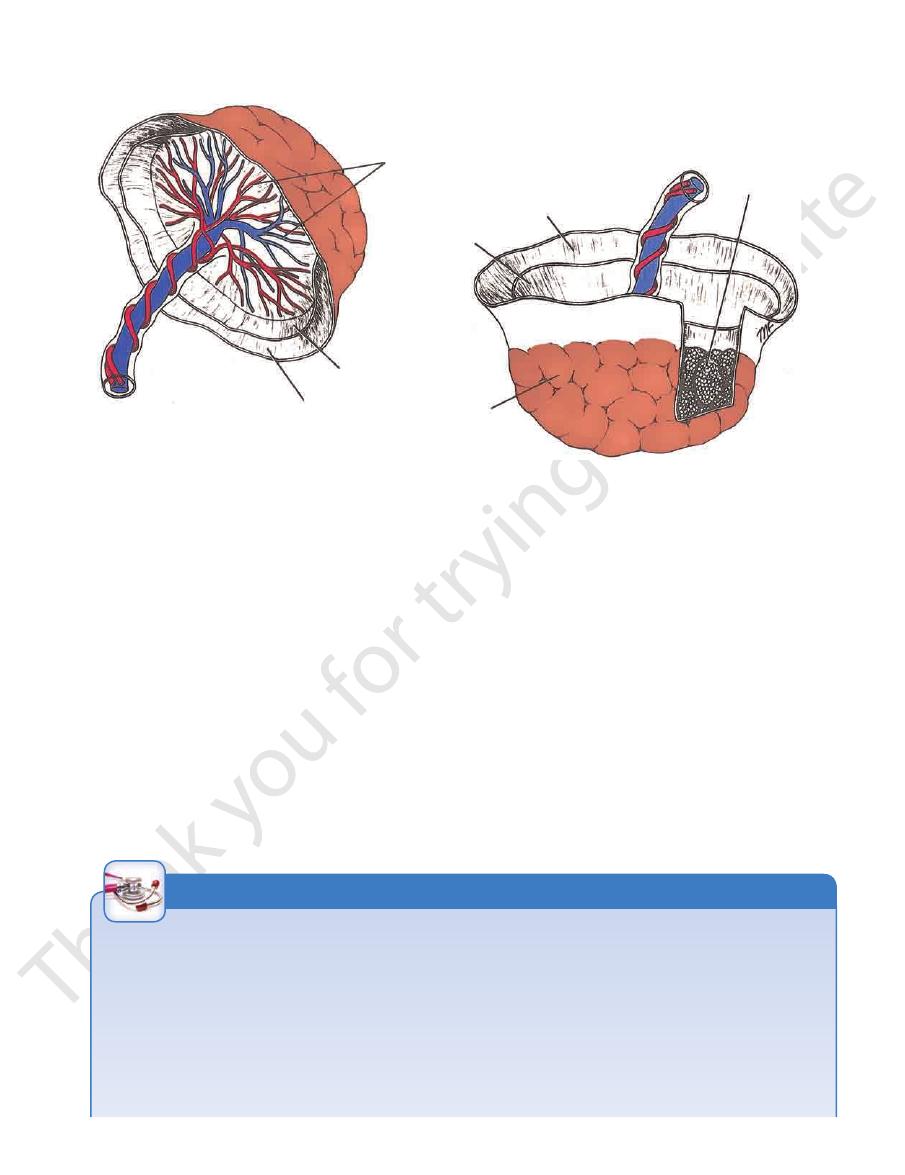
Basic Anatomy
295
branches of umbilical
arteries and umbilical
vein seen through
amnion
amnion
chorion
umbilical cord
(20" long)
cotyledon
amnion
chorion
decidua basalis
removed to show
underlying chorionic
villi and placental septa
A
B
FIGURE 7.36
The mature placenta as seen from the fetal surface
wall, is supported by the perineal body (see Fig. 7.5).
The lower part of the vagina, especially the posterior
genital diaphragm (see Chapter 8).
The middle part of the vagina is supported by the uro
the vaginal wall by pelvic fascia (see Figs. 7.28 and 7.29).
sacrocervical ligaments. These structures are attached to
ani muscles and the transverse cervical, pubocervical, and
The upper part of the vagina is supported by the levatores
Supports of the Vagina
The inferior hypogastric plexuses.
Nerve Supply
inguinal nodes.
nal iliac nodes, and the lower third drains to the superficial
internal iliac nodes, the middle third drains to the inter
The upper third of the vagina drains to the external and
Lymph Drainage
drains into the internal iliac vein.
The vaginal veins form a plexus around the vagina that
Veins
vagina.
and the vaginal branch of the uterine artery supply the
The vaginal artery, a branch of the internal iliac artery,
Arteries
forms part of the birth canal.
serves as the excretory duct for the menstrual flow and
The vagina not only is the female genital canal, but it also
Function
diaphragm (see Chapter 8) and the bulb of the vestibule.
In its lower part, the vagina is related to the urogenital
levator ani compresses the walls of the vagina together.
(see Figs. 7.19 and 7.28). Contraction of the fibers of
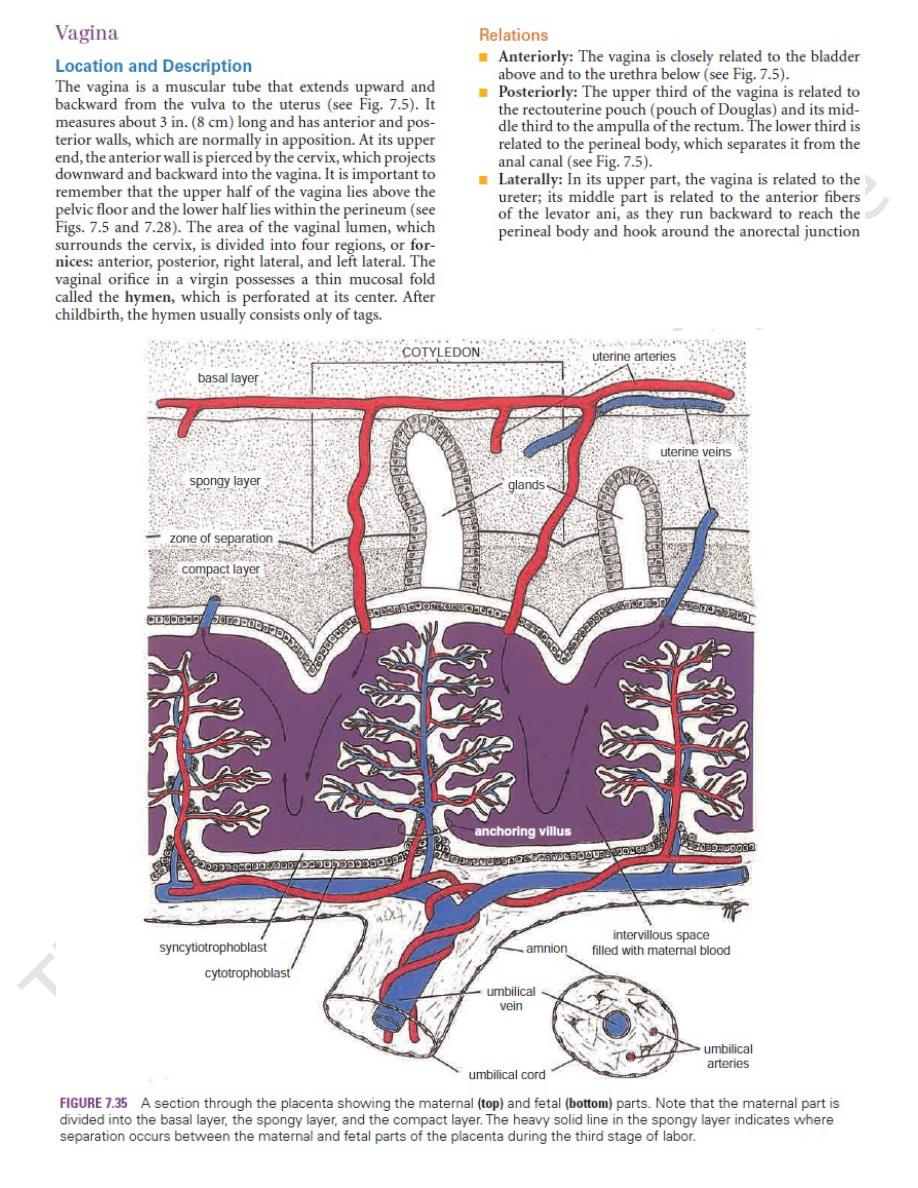
and from the maternal surface
(A)
(B).
Blood Supply
-
-
Vaginal Examination
The anatomic relations of the vagina are of great clinical impor-
tance. Many pathologic conditions occurring in the female pelvis
may be diagnosed using a simple vaginal examination.
or anterior rectal wall are damaged in childbirth, prolapse
nal walls. However, if the supports of the bladder, urethra,
The vaginal vault is supported by the same structures that
The ureters, the pelvic fascia and the anterior
The following structures can be palpated through the vaginal
walls from above downward:
■
■
Anteriorly: The bladder and the urethra
■
■
Posteriorly: Loops of ileum and the sigmoid colon in the rec-
touterine peritoneal pouch (pouch of Douglas), the rectal am-
pulla, and the perineal body
■
■
Laterally:
fibers of the levatores ani muscles, and the urogenital dia-
phragm
Prolapse of the Vagina
support the uterine cervix. Prolapse of the uterus is neces-
sarily associated with some degree of sagging of the vagi-
C L I N I C A L N O T E S
(continued)
